Jawetz Chapter 3-4- Classification
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Differentiate identification from classification.
Identification
Practical use of a classification scheme
Isolate and distinguish from the complex flora
Verify authenticity and special properties in clinical setting
Isolate causative disease agent
2.Classification
Categorization into taxonomic groups
Which are the most useful taxonomic ranks in microbiology?
Family, genus, species
____________ is used to discriminate characteristics below the species level
Subtyping
Give examples of selective media.
Sodium azide, bile salts, colistin, nalidixic acid
What is the limitation of using and applying numerical taxonomy in classifying bacteria?
It’s a static system that does not consider evolution, only general traits
The ________________ is a system that uses numerical taxonomy based on unweighted biochemical characteristics to identify a wide range of medically important microorganisms.
Analytical Profile Index (API)
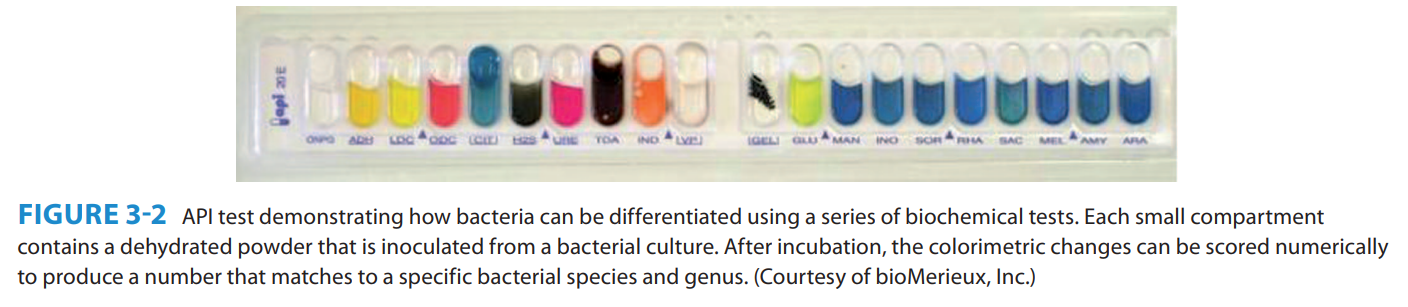
Give examples of nucleic-acid based taxonomy methods.
Plasmid Analysis
Restriction Endonuclease Analysis
Genomic Analysis
Repetitive Sequence Analysis
Ribosomal RNA Sequencing
Ribotyping
What are plasmids?
Extrachromosomal genetic elements found in bacteria.
Which laboratory technique is commonly used to determine the number and size of plasmids?
Agarose gel electrophoresis.
In what kind of outbreak is plasmid analysis most useful and why might plasmid analysis be more effective in a localized hospital outbreak than in a widespread epidemic?
Outbreaks restricted in time and place, such as in a hospital.
Because localized outbreaks are more likely to involve closely related bacterial strains with similar plasmid profiles, making it easier to trace and link infections.
Can plasmids be isolated from an individual bacterium?
Yes.
Suppose a hospital is experiencing a bacterial outbreak. How might plasmid analysis help determine whether the infections stem from a single source?
By comparing plasmid number and size among isolates, identical or highly similar plasmid patterns suggest a common origin.
What do restriction endonucleases recognize in DNA?
Short DNA sequences called restriction sequences.
What type of DNA is typically several megabases in size and analyzed using PFGE?
Genomic DNA.
What is the size range of DNA fragments produced in PFGE?
Approximately 10 to 800 kilobases.
Why would two bacterial isolates producing the same restriction fragment pattern suggest a common source in an outbreak?
Because identical patterns indicate similar or identical DNA, implying they came from the same strain.
the presence of a common fragment may confirm that a specific bacterial isolate was identical to other isolates associated with an outbreak.
How does using restriction enzymes with long recognition sequences benefit genomic analysis?
They cut less frequently, creating fewer, larger fragments that are easier to analyze for unique patterns.
Why is PFGE more suitable than standard gel electrophoresis for analyzing whole bacterial genomes?
PFGE can separate very large DNA fragments that cannot be resolved by standard electrophoresis.
Why is the classical definition of species not applicable to bacteria?
Because bacteria reproduce vegetatively and rarely undergo recombination of large genome portions.
What type of bacterial genes evolve slowly and are used to compare distantly related groups?
Housekeeping genes (e.g., those encoding cytochromes).
What method allows for precise comparison of DNA sequences in bacteria?
DNA genome sequencing.
What type of genes are useful for comparing closely related bacteria?
Rapidly diverging genes (e.g., those encoding surface antigens).
What does a similar G + C content between two bacteria suggest?
Taxonomic relatedness.
How can DNA sequencing resolve taxonomic classification issues in bacteria?
By revealing the degree of genetic similarity or divergence between organisms, regardless of reproduction method.
Why might relying solely on rapidly diverging genes misrepresent deep evolutionary relationships among bacteria?
Because these genes change too quickly and may not reflect the stable core genome shared by more distant relatives.
If two bacterial strains have very different housekeeping genes but similar surface antigen genes, what might that suggest?
They may be unrelated overall but have evolved similar surface antigens due to environmental pressures or convergent evolution.
Why is G + C content considered in bacterial taxonomy despite advances in sequencing?
It still provides a quick, general indication of genetic similarity and is useful for preliminary classification.
What are the repetitive DNA sequences used in bacterial subtyping called?
Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs).
What is the size range of repeat units in satellite DNA?
10 to 100 base pairs.
What does MLVA stand for?
Multiple-Locus VNTR Analysis.
What technique is used in MLVA to analyze VNTRs?
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
Name one bacterial species where MLVA is especially useful.
Bacillus anthracis (others: Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis).
Why are VNTRs effective for subtyping monomorphic bacterial species?
Because even genetically similar organisms show diversity in repeat unit sizes and copy numbers at VNTR loci.
How can variation in VNTR loci affect bacterial gene expression?
Since VNTRs may be located in gene regulatory regions, changes in repeat number can influence transcriptional activity.
hat does the diversity at multiple VNTR loci suggest about bacterial evolution or population structure?
It indicates microevolutionary changes and can reflect transmission pathways or clonal relationships in outbreaks.
How has genome sequencing enabled the use of VNTR analysis?
By providing complete DNA sequences, allowing researchers to identify and characterize repetitive elements across species.
What type of RNA is used to determine evolutionary relationships among prokaryotes?
16S ribosomal RNA (16S rRNA).
Why are rRNA genes useful in phylogenetic studies?
because they are highly conserved and diverge slowly over time.
What new kingdom was identified through rRNA sequencing?
Archaebacteria (Archaea).
Why is 16S rRNA sequencing preferred over other genes for constructing phylogenetic trees in prokaryotes?
Because it is universally present, functionally conserved, and accumulates mutations at a slow, steady rate, making it ideal for tracking evolutionary divergence.
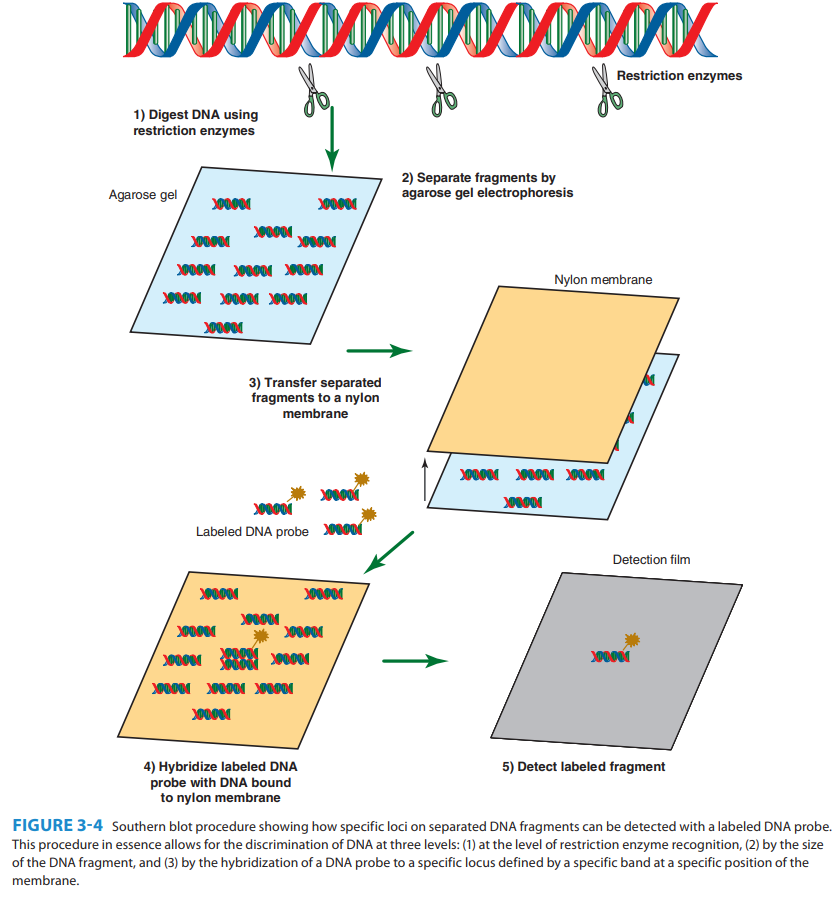
What is the name of the technique used in ribotyping that was named after its inventor?
Southern blot analysis, named after Edwin Mellor Southern
What type of genes does ribotyping analyze to identify bacteria?
Ribosomal RNA genes (16S and 23S rRNA).
What is used as a probe to detect ribosomal gene fragments during ribotyping?
A labeled DNA fragment complementary to rRNA genes.
Why can ribotyping provide good discriminatory power?
Because many organisms have multiple copies (5–7) of rRNA genes, leading to diverse fragment patterns.
Which group of bacteria might ribotyping not be effective for due to having only one rRNA gene copy?
Mycobacteria.
If a probe binds to multiple bands on a Southern blot, what does this suggest about the bacterial genome?
That the organism has multiple copies of rRNA genes with complementary sequences.
Give examples of species that can be detected through biochemical test that determines carbohydrate breakdown.
Escherichia spp.
What does the Voges-Proskauer (VP) test detect?
Acetoin, a product of glucose fermentation via the butylene glycol pathway.
Name at least three VP-positive bacteria.
Enterobacter aerogenes
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Serratia marcescens
Is Escherichia coli VP positive or negative?
VP negative (uses mixed acid fermentation instead).
Which Gram-positive spore-former is VP positive?
Bacillus cereus
Which biotype of Vibrio cholerae is VP positive?
El Tor biotype
How does the Voges-Proskauer test work?
Voges-Proskauer is highly related to glucose fermentation, and the following test has the following steps:
1.You grow the bacteria in a sugar-rich liquid (usually glucose broth).
2.Add special chemicals (α-naphthol and KOH) after incubation.
3.If acetoin is present, the chemicals react and turn the liquid red or pink — that means it's VP positive.
4.If it stays yellow or copper, it's VP negative.
Acetoin, which is also called ___________, is a ___________ (positive/neutral/negative) compound detected in the Voges-Proskauer test.
acetylmethylcarbinol; neutral
What happens during the ONPG test?
ONPG test is highly related to the lactose fermentation pathway. Displayed below are the steps of how it is performed:
1.A small amount of bacteria is added to a tube containing ONPG and sometimes a broth or buffer.
2.The mixture is incubated (usually at 35–37°C) for a few hours (or up to 24 hours).
3.If the bacteria produce β-galactosidase, the ONPG is broken down, and the liquid turns yellow.
The ONPG in ONPG test stands for ______________ which acts like a “fake _______”
ortho-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside, lactose
It is used to differentiate Staphylococcus aureus from other, less pathogenic staphylococci.
Coagulase test
This test is particularly useful in differentiation of staphylococci (positive) from streptococci (negative), but it also has taxonomic application to Gram-negative bacteria
Catalase test
The amino acids usually tested in the decarboxylase test are ________, ___________, and ___________
lysine, ornithine, arginine
Proteinase is the same as __________
protease
Describe the Southern Blot procedure
The enzyme _________ breaks down urea into two molecules of ammonia and one molecule of CO₂, raising the pH of the medium. This increase in pH changes the color of the test medium to _________, indicating a positive result; otherwise, the color is _________ in a negative result. This test can help differentiate P. vulgaris from other enteric rods.
Urease; bright pink (fuchsia); yellow/orange
The oxidase test detects the ____ component of the cytochrome–oxidase complex. A positive reaction causes the reagent to change from clear to _________ when oxidized. This test is useful for distinguishing Pseudomonas aeruginosa (oxidase ____) from E. coli (oxidase ____).
c; purple (or dark blue); +; -
The nitrate reduction test detects a bacterium's ability to reduce ________ to nitrites or nitrogen gas. This test is commonly used in __________ to detect the presence of Gram-negative rods that may be causing _________.
nitrates; urinalysis; urinary tract infections (UTIs)
In the citrate utilization test, bacteria that can use _________ as their sole carbon source will grow on the agar medium. This growth usually causes the medium to turn from green to _________ due to an increase in pH. Bacteria such as _________ are examples of citrate-positive organisms.
sodium citrate; blue; Klebsiella pneumoniae
The ability of some bacteria to produce hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) from amino acids or other sulfur-containing compounds is detected by the formation of a __________ color, due to the reaction of H₂S with heavy metals like iron. This test is useful in distinguishing between ________________.
black; Gram-negative rods
The indole test detects an organism’s ability to break down __________ into indole. A positive result is indicated by a __________ color after the addition of a benzaldehyde reagent, while a negative result shows __________ color change.
tryptophan; red; no
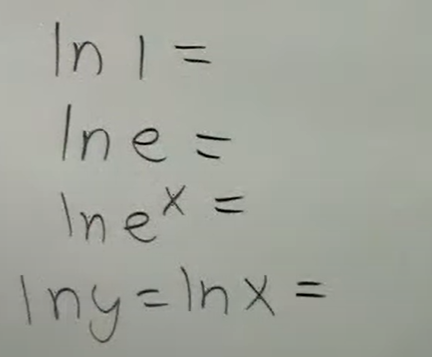
Review the fundamentals of natural logarithms with these basic problems.
Note:
when there’s ln, there is an invisible base e
ln (x) is the same as log base e (x)
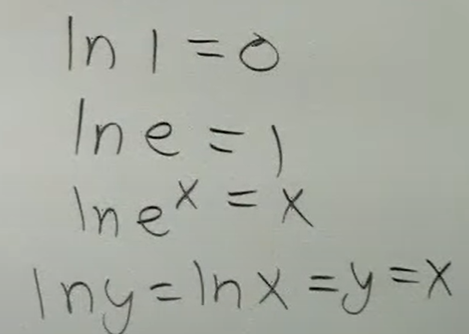
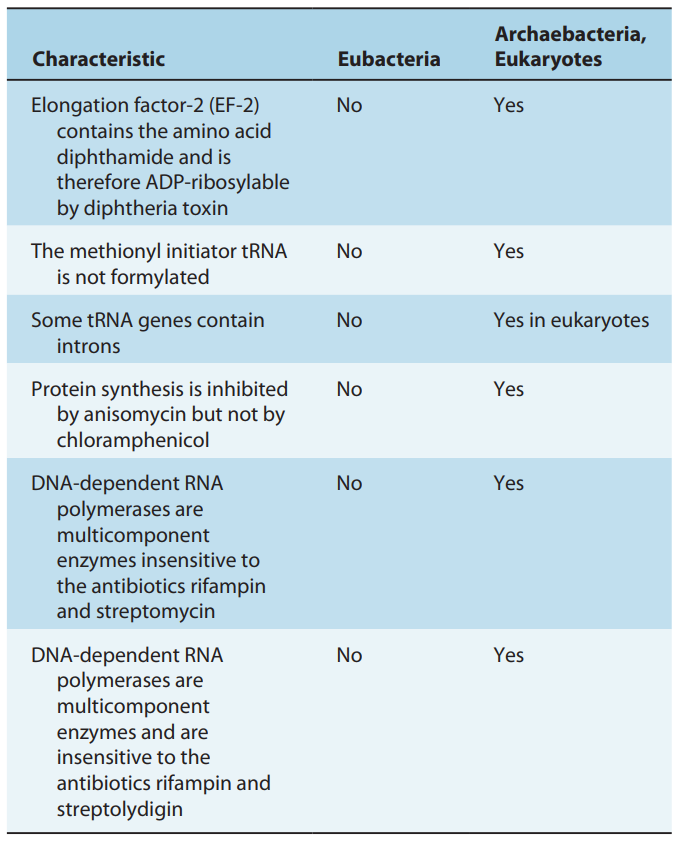
What method involves counting colonies formed by single bacteria on an agar plate?
Viable cell count.
What is the ideal colony range on a plate for accurate viable count data?
30 to 300 colonies.
What does a barely turbid E. coli suspension roughly indicate in terms of cell concentration?
About 10⁷ cells/mL.
What does biomass density measurement often require?
Determining the dry weight of the culture.
Why doesn’t turbidity always reflect cell viability?
Because dead cells still contribute to turbidity.
Why might viable cell count be more reliable than turbidity when assessing live bacterial concentration? In what situation might turbidity overestimate the number of living cells?
Because it excludes dead cells, which can still contribute to turbidity but cannot form colonies
During the death phase, when many cells are dead but still present in the suspension..
What advantage does measuring protein content offer when estimating biomass density?
It provides an indirect but practical estimate of total cell mass without needing to dry and weigh cultures.
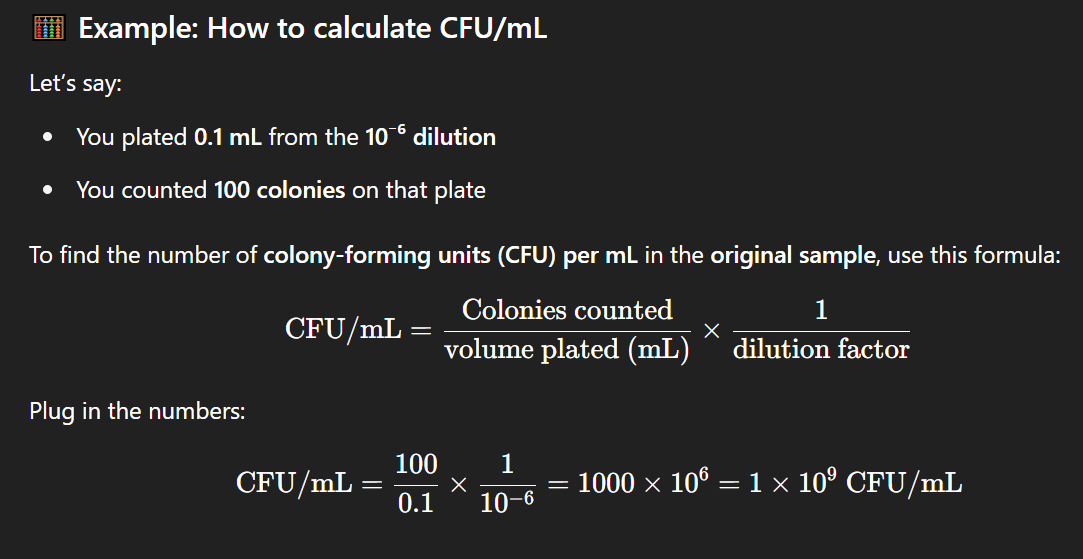
How can you estimate the original CFU/mL from a plate with 100 colonies and a 10⁻⁶ dilution?
Why do we need to study batch cultures despite it being different in the human body?
Even though this test-tube situation is different from the human body — which constantly supplies nutrients — studying batch cultures helps us understand:
How bacteria grow and survive
When they're most active
When they’re vulnerable to antibiotics
Their basic genetics and metabolism
What does the bacterial growth curve represent?
The events in a population of bacterial cells, not individual cells.
What is the term used for a culture that shows the typical bacterial growth curve?
Batch culture.
🧪 This setup is called a batch culture, which means:
You only add bacteria once.
You don’t add more food or remove waste.
It’s a closed system, like a sealed bottle with limited resources.
How might results differ if a growth curve were applied to a continuous culture instead of a batch culture?
A continuous culture maintains cells in a particular growth phase (usually log phase), so the classic phases of the growth curve may not be observed.
What experimental limitation is implied by using a batch culture to study bacterial growth?
Nutrients become depleted and waste accumulates over time, affecting growth phases and not mimicking constant environments.
What characterizes the lag phase?
Cells adapt to a new environment by synthesizing enzymes and intermediates necessary for growth.
What typically limits growth during the exponential phase in aerobic organisms?
Oxygen availability.
What happens during the stationary phase?
Growth ceases due to nutrient depletion or waste accumulation, but cell turnover may maintain a stable viable count.
What does VBNC stand for?
Viable But Not Culturable.
What triggers the VBNC state in bacteria?
Starvation or stress during the stationary phase.
Why might a long lag phase occur when transferring bacteria to a new medium?
Because only a few cells may be genetically capable of growing in the new environment, requiring time to multiply.
Why does the exponential phase end even when nutrients are present?
Due to the accumulation of toxic metabolic products or insufficient oxygen diffusion at high cell densities.
How does cell turnover maintain a constant viable count during the stationary phase?
New cells are formed as old ones die and lyse, releasing nutrients.
What could explain the persistence of a few bacterial cells for years during the death phase?
A very slow death rate and possible nutrient recycling from lysed cells.
How is the VBNC state similar to sporulation in some bacteria?
Both are survival mechanisms that involve dormancy and can resume growth under favorable conditions.
A complex multicellular microbial community that forms on surfaces.
biofilm
What type of growth do bacteria in biofilms exhibit?
Sessile, not planktonic (free-floating) growth.
What structure surrounds and protects a biofilm community?
A glycocalyx.
A communication process in which bacteria use small signaling molecules to coordinate gene expression based on population density.
quorum sensing
Name a signaling molecule used in quorum sensing.
Homoserine lactone.
Why are bacteria in biofilms often more resistant to antibiotics and immune responses?
Inner biofilm layers are shielded by outer layers and glycocalyx, and bacteria may express different genes due to quorum sensing.
How does biofilm formation benefit bacterial survival in nutrient-limited environments?
It enables metabolic diversity, with outer cells accessing nutrients and inner cells being protected.