3.4. Inheritance
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:34 AM on 1/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Gregor Mendel
Considered the father of genetics due to his research with pea plants to study inheritance
2
New cards
Monohybrid cross
The crossing of two individuals that only differ in one trait
3
New cards
Mendel’s experiment
Performed monohybrid crosses between pea plants
* Transferred the pollen from one variety to the reproductive parts of another variety
* Experimented seven different pairs of characteristics, leading to very reliable results
* Each crossing was repeated with many pea plants
* Transferred the pollen from one variety to the reproductive parts of another variety
* Experimented seven different pairs of characteristics, leading to very reliable results
* Each crossing was repeated with many pea plants
4
New cards
What were the traits tested by Mendel?
Flower color, plant height, seed color, seed shape, pod color, pod shape and flower position
5
New cards
What did Mendel observe in each crossing?
* All plants in the F1 generation had the same characteristic as one of the parent plant
* Pea plants in F2 generation had characteristics of both parent plants in a 3:1 ratio
* Pea plants in F2 generation had characteristics of both parent plants in a 3:1 ratio
6
New cards
Mendel’s discoveries
* Traits do not disappear between generations, but are rather not expressed
* Each trait is coded by alleles, which can be dominant or recessive
* Each trait is coded by alleles, which can be dominant or recessive
7
New cards
Segregation
The separation of two alleles of a diploid nucleus into two haploid nuclei
8
New cards
Law of segregation
The allele expressed by the offspring is determined by whether they inherited the dominant or recessive form of allele
9
New cards
Genotype
The combination of alleles that determine any given trait
10
New cards
Phenotype
The observable characteristics of an organism
11
New cards
Dominant allele
Only one needs to be inherited for the characteristics to be expressed
12
New cards
Recessive allele
Two need to be inherited for the characteristic to be expressed
13
New cards
What happens when there is only one recessive allele?
It will remain hidden and the dominant characteristic will be expressed
14
New cards
Homozygous
An individual with two identical alleles
15
New cards
Types of homozygous
Homozygous dominant: two copies of dominant allele
Homozygous recessive: two copies of recessive allele
Homozygous recessive: two copies of recessive allele
16
New cards
Heterozygous
An individual with two different alleles
17
New cards
Punnett grid
* Illustrates the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring resulting from a genetic cross
* Predicts the probability of offspring displaying a certain genotype or phenotype
* Predicts the probability of offspring displaying a certain genotype or phenotype
18
New cards
Co-dominance
When both alleles for a trait are equally expressed in a heterozygote
* Both alleles are considered dominant
* Both alleles are considered dominant
19
New cards
Examples of co-dominance
Mirabilis jalapa
* Allele Cw → white flower
* Allele CR → red flower
* Offspring will be CRCW; some parts are red and some are white
Palomino horse
* Allele HB → chestnut horse
* Allele HW → white horse
* Offspring will be HBHW; some hairs will be chestnut and some white
* Allele Cw → white flower
* Allele CR → red flower
* Offspring will be CRCW; some parts are red and some are white
Palomino horse
* Allele HB → chestnut horse
* Allele HW → white horse
* Offspring will be HBHW; some hairs will be chestnut and some white
20
New cards
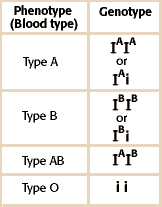
ABO blood group (genotypes and phenotypes)
Gene for blood type is I, and has three common alleles: I^A, I^B and i
21
New cards
Why are I^A and I^B dominant?
All three alleles cause the production of a glycoprotein in the membrane of red blood cells
* I^A alters this glycoprotein by addition of acetyl galactosamine. Since this altered glycoprotein is absent in people lacking I^A (type B and O), if exposed to it, they will make anti-A antibodies
* I^B alters this glycoprotein by addition of galactose. Since this altered glycoprotein is absent in people lacking I^B (type A and O), if exposed to it, they will make anti-B antibodies
* Allele i is recessive because it does not alter the glycoprotein. Thus, heterozygous and homozygous dominant give the same phenotype
* I^A alters this glycoprotein by addition of acetyl galactosamine. Since this altered glycoprotein is absent in people lacking I^A (type B and O), if exposed to it, they will make anti-A antibodies
* I^B alters this glycoprotein by addition of galactose. Since this altered glycoprotein is absent in people lacking I^B (type A and O), if exposed to it, they will make anti-B antibodies
* Allele i is recessive because it does not alter the glycoprotein. Thus, heterozygous and homozygous dominant give the same phenotype
22
New cards
Why are I^A and I^B co-dominant?
The genotype IAIB causes the glycoprotein to be altered by addition of acetyl-galactosamine and galactose. As a consequence, neither anti-A nor anti-B bodies are produced. This genotype therefore gives a different phenotype to IAIA and IBIB so the alleles IA and IB are co-dominant
23
New cards
Incomplete dominance (+ example)
When neither allele is fully expressed and rather an intermediate expression of a trait is seen (e.g. snapdragon)