Ch 23 - Why do countries trade?
International trade: exchange of goods and services between countries
Benefits of international trade:
- Lower prices, consumers can buy at a lower price than domestic
- Producers can buy less expensive raw materials and semi manufactured goods
- Prices may be lower in some countries because they have access to natural resources, quality of labour, quality in capital, different tech levels
- Greater choice: consumers have access to domestic and international products
- Increased competition
Economies of scale:
- Size of market increases
- Demand increases
- Production decreases
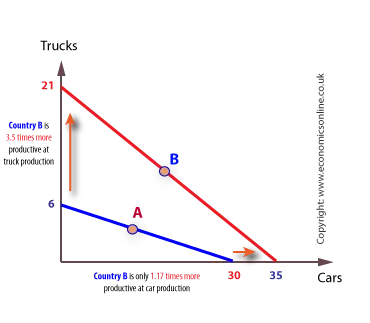
Absolute advantage: ability of an individual, company, region, or country to produce a greater quantity of a good or service with the same quantity of inputs per unit of time
Comparative advantage: which goods should a country produce for export and which should it import
- A trade can be positive for both countries when one country has an absolute advantage in producing all goods
Limitations to production:
- based on a number of assumptions
- theories can limit the application of theory in real life
- no transport costs
- two economies producing goods
- costs do not change and returns to scale are constant
- goods being traded are identical
Factors of production remain in the country
- factors of production move rather than the goods
- developed goods may invest capital in LDCs to produce goods
- labour may migrate from low wage to high wage countries
Despite the limitations, comparative advantage is at the core of international theory
Dumping
- International trade may subject a country to dumping. Dumping occurs when imports are sold at prices below their marginal costs. This is often done with the help of foreign government subsidies.
Specialisation
- is the second fundamental principle associated with trade, and results from the division of labour.
- Given that each worker, or each producer, is given a specialist role, they are likely to become efficient contributors to the overall process of production, and to the finished product. Hence, specialisation can generate further benefits in terms of efficiency and productivity
Absolute Advantage vs. Comparative Advantage
- Absolute Advantage
- A country has this in the production of a good if it can produce it using fewer resources than another country
- Shows which country specializes in what kind of product compared to another country for the same product
- Comparative Advantage
- A country has this in the production of a good if it can produce the good at a lower opportunity cost than another country
- Country with the higher opportunity cost should specialize in the product compared to another country for the same product
- Trade protectionism:
- Trade protectionism: policies aimed at restricting the flow of imports into a country and creating an artificial advantage to exporting firms.
- Tariff: tax on imports aimed at increase the costs of production for foreign firms. These raise the domestic price and domestic production, so that less in imported and consumed.