History Unit 4 Vocabulary
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
Berlin Conference (1884-1885)
A conference between 14 western nations that discussed the partitioning of Africa, establishing rules to amicably divide resources among them at the expense of the people of Africa.

2
New cards
Manifest Destiny (phrase coined in 1845)
The idea that the US is destined (by God) to expand its dominion and spread democracy and capitalism across the entire North American continent.

3
New cards
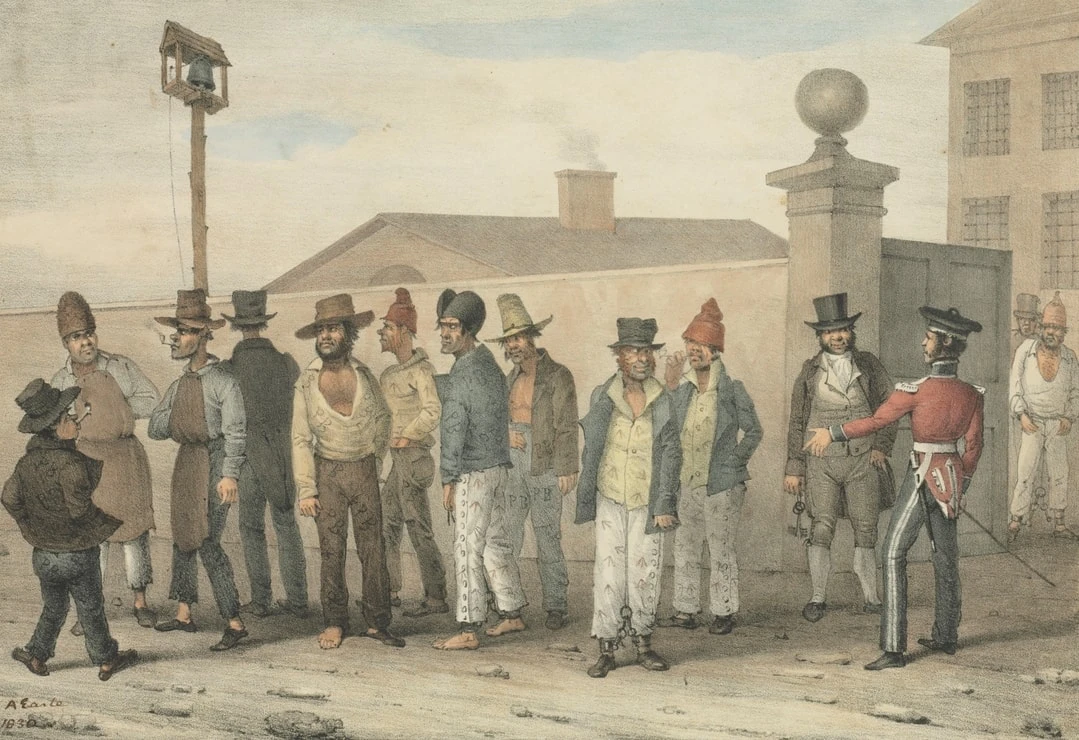
Penal Colony
A settlement used to exile prisoners and separated them from the general population; exile colony

4
New cards
Boer Wars (1899-1902)
A conflict between the British Empire and the Boer Republics over the Empire’s influence in Southern Africa.

5
New cards
Taiping Rebellion (1850-1864)
A revolt against the Qing dynasty in China, fought with religious conviction over regional economic conditions.

6
New cards
Boxer Rebellion
An uprising began by peasants against foreigners in China that later on was supported by the government.

7
New cards
Corvee labor
A form of unpaid, unfree labor which is intermittent in nature for limited periods of time.

8
New cards
Spheres of influence
The claim by a state to exclusive or predominant control over a foreign area or territory.

9
New cards
Trail of Tears (1837-1839)
The forced westward migration of American Indian tribes from the South and Southeast.

10
New cards
Quinine
A tree bark/ drug used to treat malaria.
11
New cards
Ghost Dance
A North American Indian religious cult of the second half of the 19th century, based on the performance of a ritual dance that was believed to drive away white people and restore the traditional way of life.

12
New cards
Treaty of Paris (1783)
A treaty signed between the American colonies and GB; ended the American Revolution and formally recognized the United States as an independent nation.

13
New cards
Killing of Cattle Xhosa (April 1856- May 1857)
For 13 months, 85% of all Xhosa adult men killed their cattle and destroyed their corn in obedience to Nongqawuse’s prophecies.
\
An estimate of 400,000 cattle were slaughtered and 40,000 Xhosa died due to starvation.
\
An estimate of 400,000 cattle were slaughtered and 40,000 Xhosa died due to starvation.

14
New cards
Sepoy
An Indian soldier serving under British/ European orders.

15
New cards
Cash Crops
A crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower.

16
New cards
Monocultures
The cultivation of a single crop in a given area.

17
New cards
Export economies
Specialized production of one or a few natural resources which are exported to other countries.

18
New cards
Apartheid
Racial segregation; a policy of segregation and political, social, and economic discrimination against the nonwhite majority in the Republic of South Africa.

19
New cards
Telegraph
A device for rapid, long-distance transmission of information over an electric wire laid between stations.

20
New cards
Steamships
A ship that used steam instead of sails; enabled fast trade and communications.
\
It greatly reduced both the time and expense of shipping goods to distant markets.
\
It greatly reduced both the time and expense of shipping goods to distant markets.

21
New cards
Railroads
A track or set of tracks made of steel rails along which passenger and freight trains run.
\
The development of railroads (+ steamships) allowed European powers to efficiently transport goods, raw materials, and troops to their colonies.
\
The development of railroads (+ steamships) allowed European powers to efficiently transport goods, raw materials, and troops to their colonies.

22
New cards
Banana republics
Series of laws/ governments made in order to make western businessmen more wealthy.
\
Significance: Highlights the legacy in the region.
\
Significance: Highlights the legacy in the region.

23
New cards
Culture systems
The interaction of different elements in culture
24
New cards
Diaspora
The movement/ migration/ scattering of a people away from an established or ancestral homeland.

25
New cards
Emigrate
To leave one’s place of residence or country to live elsewhere.

26
New cards
Pogrom
A violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews.

27
New cards
Enclave
A distinct territorial, cultural, or social unit enclosed within or as if within a foreign territory.