Proteins: Structure, Function, and Amino Acids Overview
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are made up of amino acids attached linearly.
What is the basic structure of an amino acid?
An amino acid consists of a carboxyl group, an amino group, and an R group.
How many different types of amino acids are there?
There are 20 different types of amino acids, each with a unique R group.
What distinguishes essential amino acids from non-essential amino acids?
Essential amino acids must be acquired through diet, while non-essential amino acids can be synthesized in the body.
List the eight essential amino acids.
Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Methionine, Threonine, and Lysine.
What is a peptide bond?
A peptide bond is formed by attaching a NH2 group to a COOH group via Dehydration Synthesis.
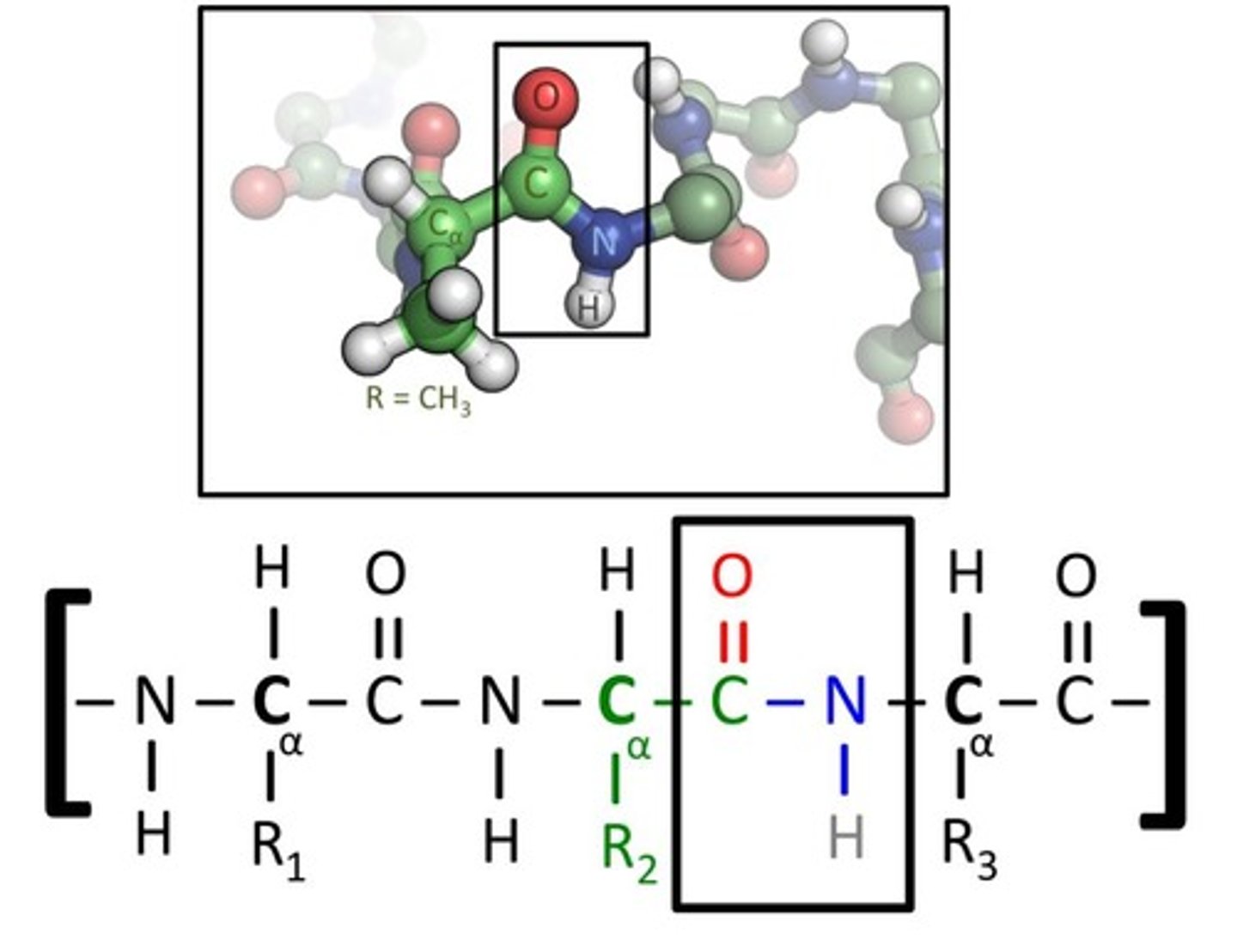
What is the difference between a peptide and a polypeptide?
A peptide is a chain of amino acids, while a polypeptide is a peptide with more than 50 amino acids.
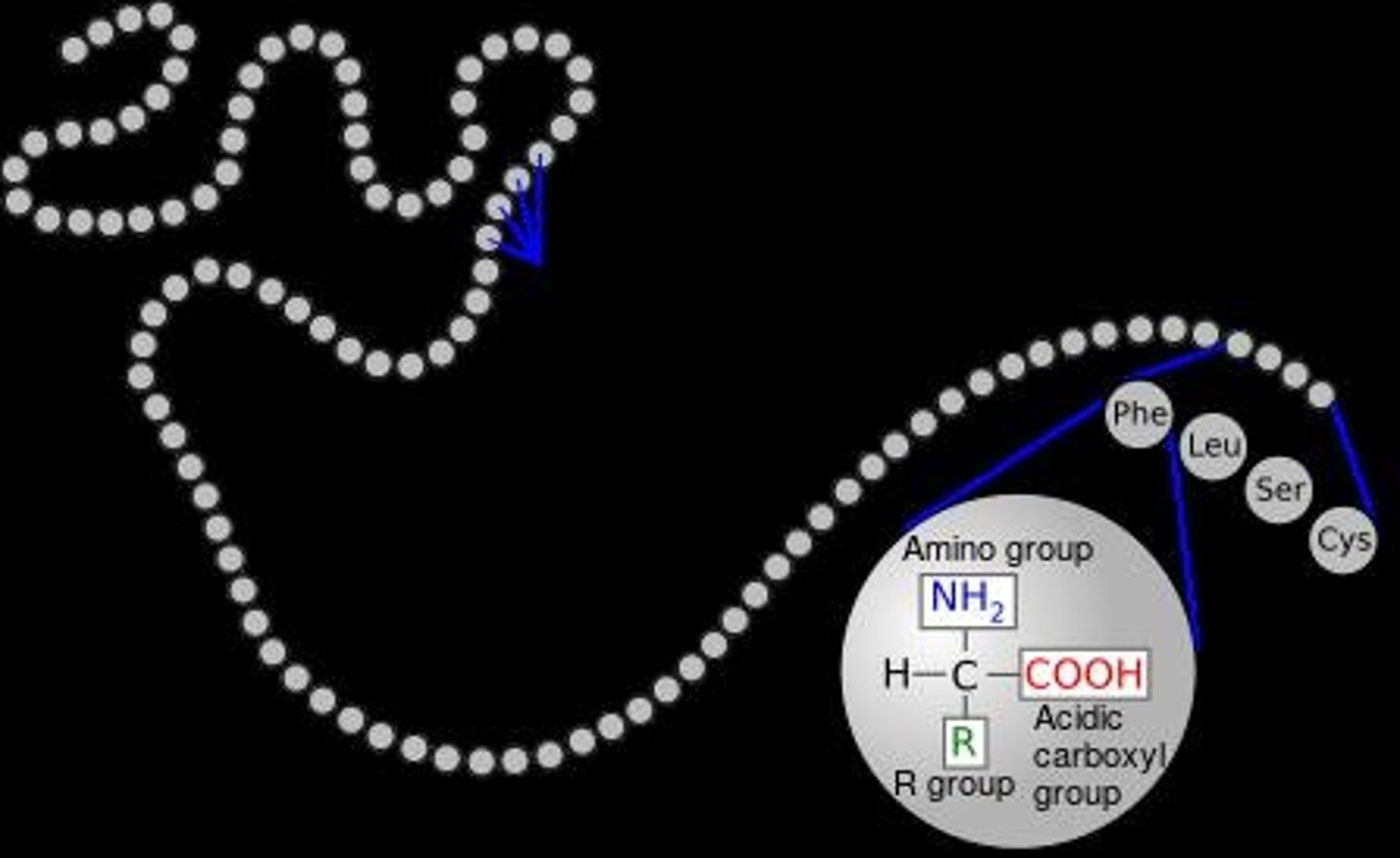
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary structures.
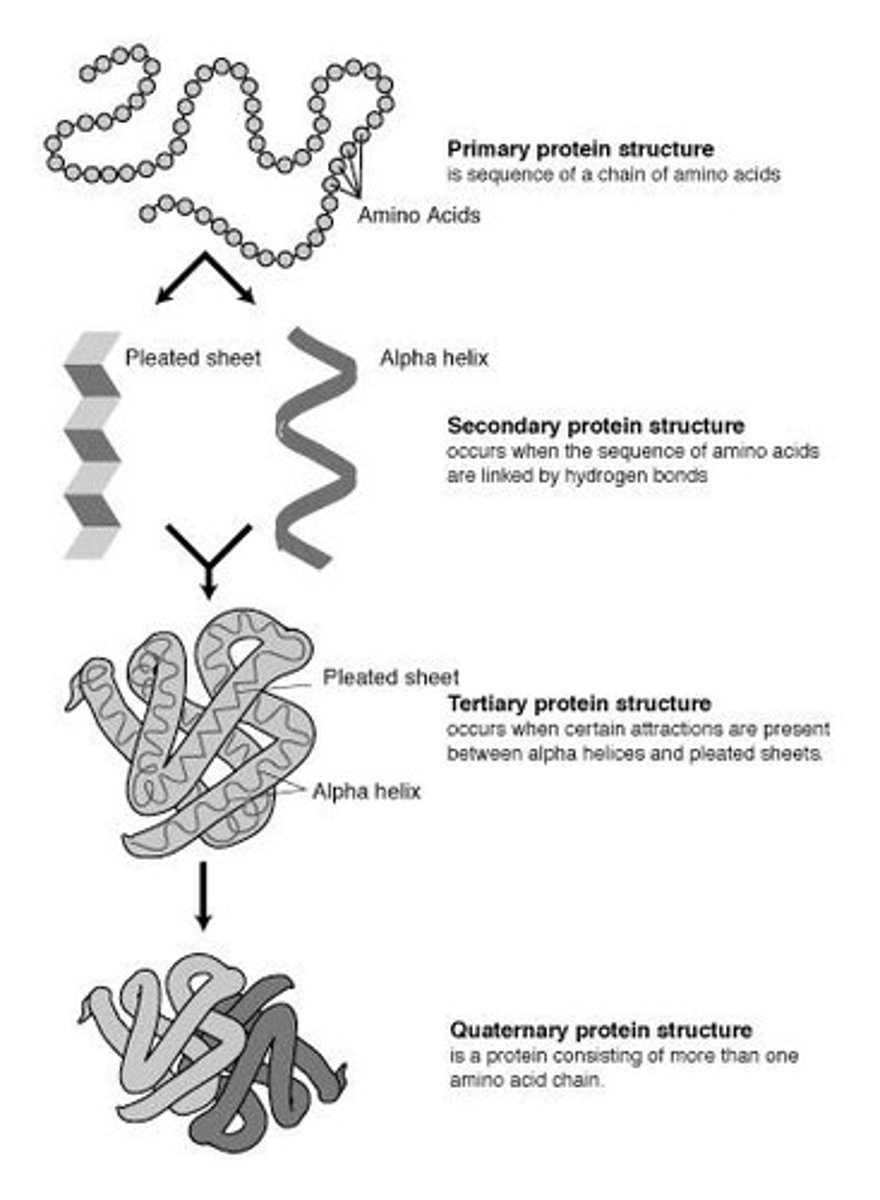
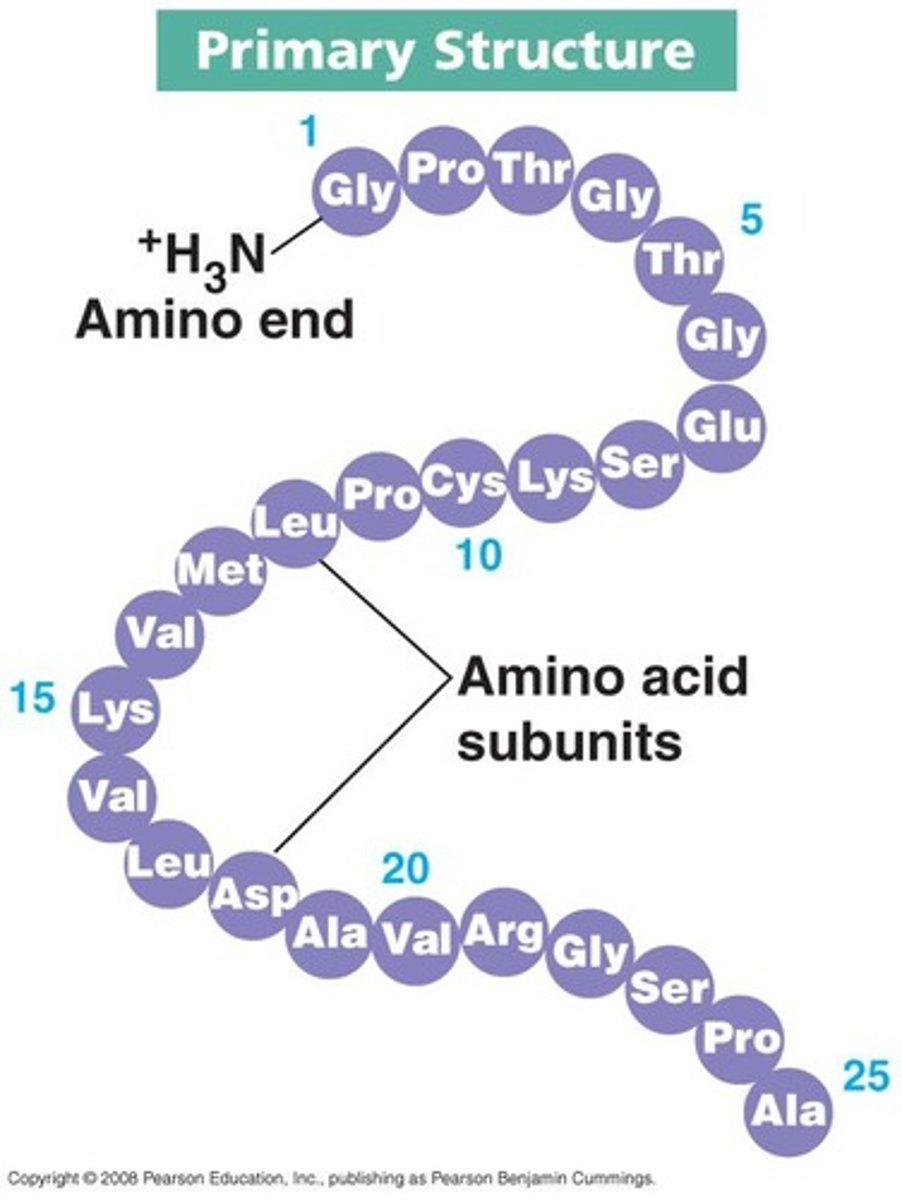
What characterizes the primary structure of a protein?
The primary structure is a linear chain of amino acids.
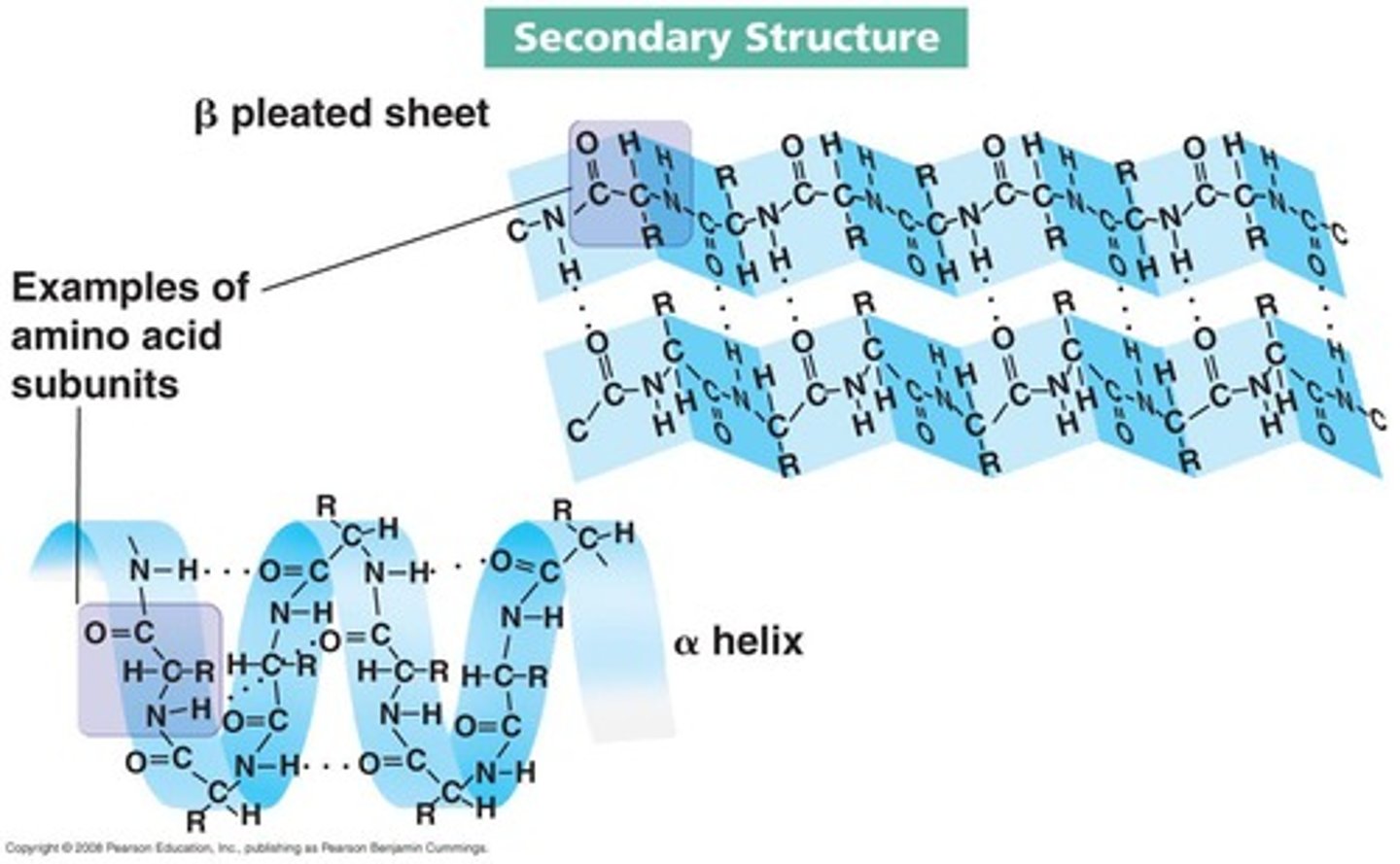
What types of patterns are formed in the secondary structure of proteins?
The secondary structure includes Alpha Helix (spiral pattern) and Beta Pleated Sheets (zig-zag pattern).
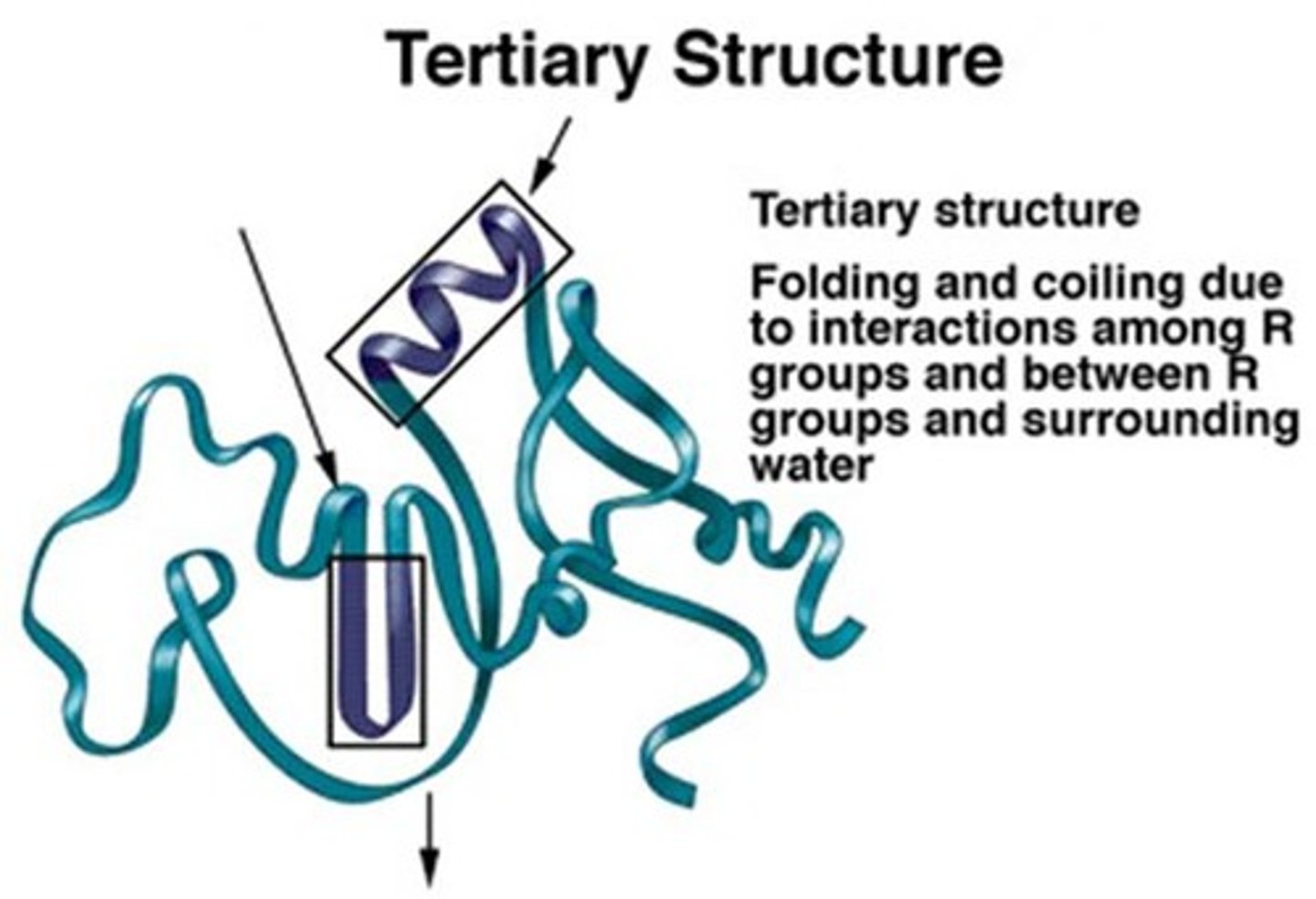
What causes the tertiary structure of a protein?
The tertiary structure is caused by R-group interactions, such as disulfide bridges.
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The quaternary structure involves the linking of several separate polypeptide chains.
How does the shape of a protein relate to its function?
The shape of a protein determines its specific function.
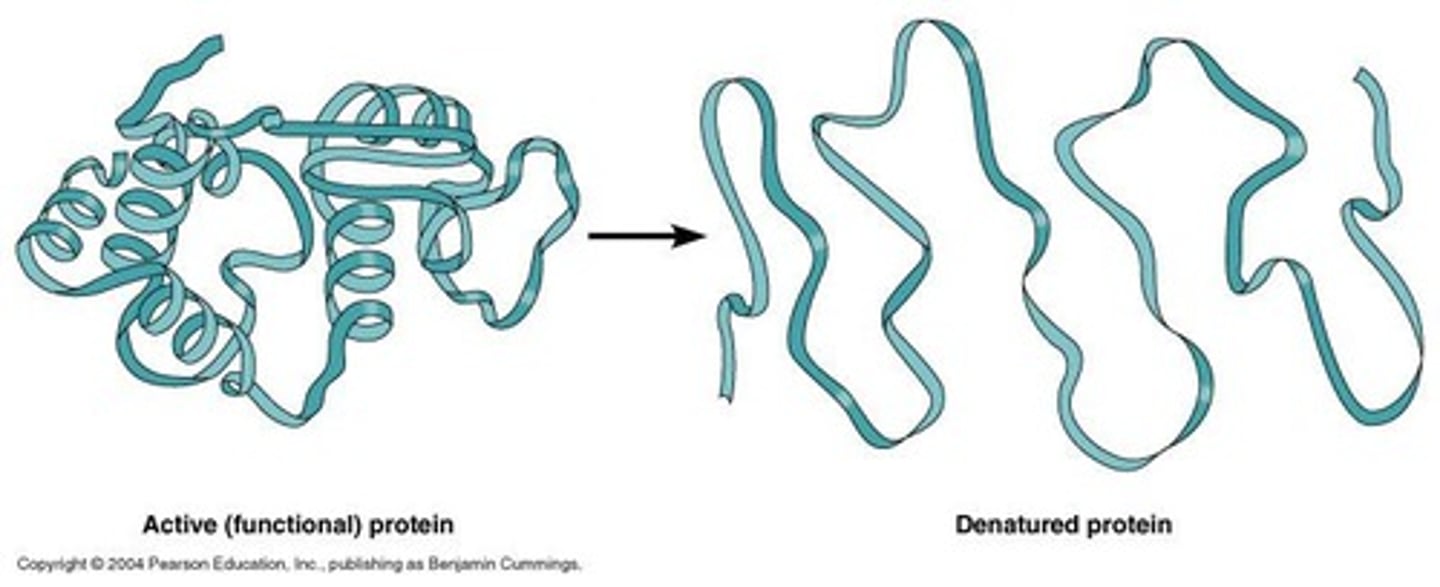
What is denaturation in proteins?
Denaturation is the loss of both the structure and function of a protein due to changes in pH or temperature.
What are protein prosthetic groups?
Protein prosthetic groups are non-protein structures that bond with proteins to assist in their function.
What role do heme groups play in hemoglobin?
Heme groups, which contain iron, help hemoglobin carry oxygen.
What is the significance of R group properties in amino acids?
The properties of R groups dictate the physical characteristics of amino acids and influence protein folding.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology related to proteins?
The central dogma is DNA → RNA → Protein.
Why are proteins considered macromolecules?
Proteins are considered macromolecules because they are large molecules made up of long chains of amino acids.
What vital roles do proteins play in living systems?
Proteins carry out structural and functional roles, such as in spider webs, human hair, muscle tissue, and egg whites.