chp 2 micro chemical principles (copy)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space ( made of atoms)
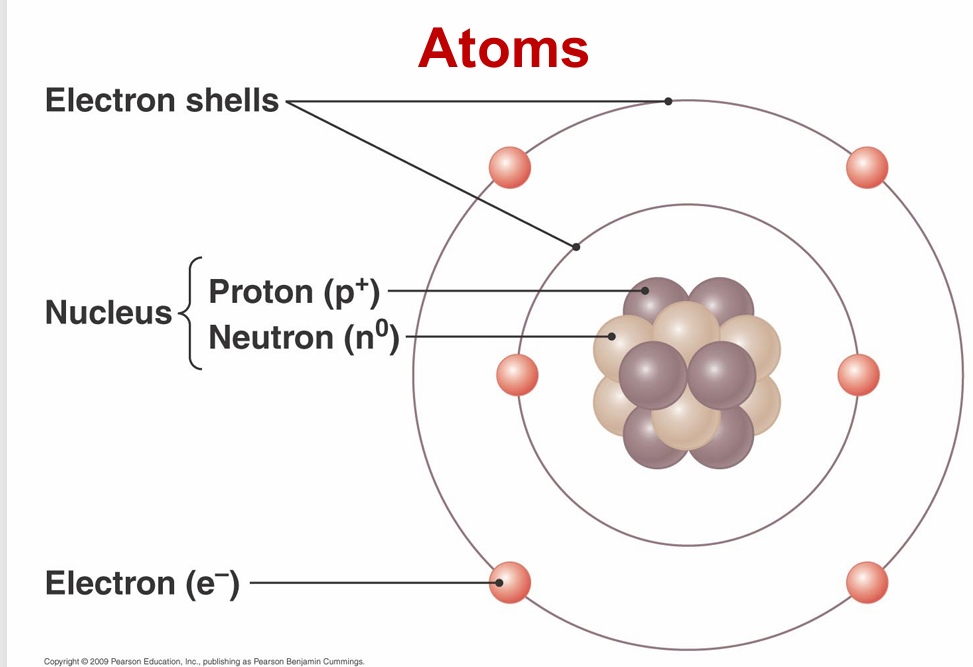
atoms
the smallest chemical units of matter
has No net charge
electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles circling a nucleus
nucleus
structure containing neutrons and protons
neutrons
uncharged particles (neutral)
protons
positively charged particles
atoms
element
composed of a single type of atom
atomic number
equal to the number of protons in the nucleus (determines the identity of an atom)
atomic mass (atomic weight)
sum of masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons
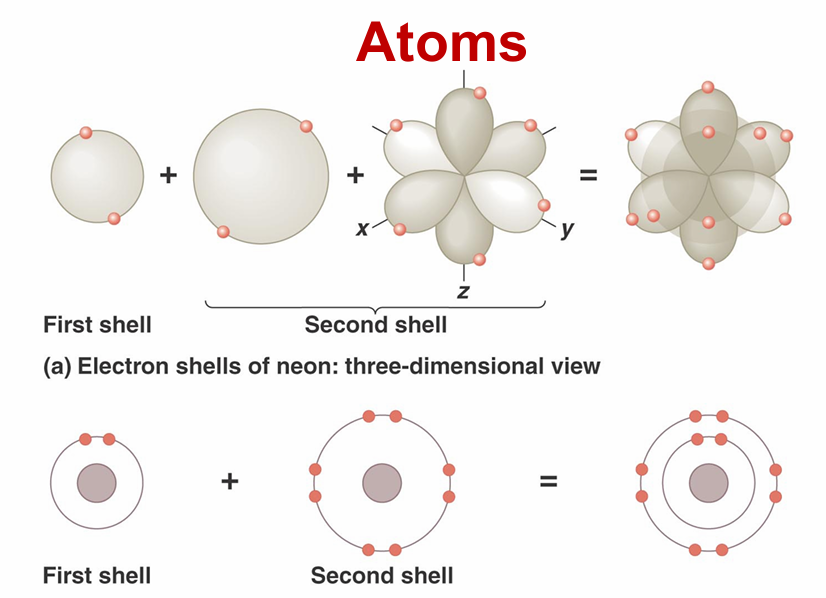
electron configurations
Only the electrons of atoms interact, so they determine atom’s chemical behavior
Electrons occupy electron shells
Valence electrons – electrons in outermost shell that interact with other atoms
atoms
first shell- can hold two electrons
second shell can hold up to 8 electrons
valence
combining capacity of an atom (number of extra or missing electrons in outermost shell)
• Atoms are stable when outer electron shells contain eight electrons
chemical bonds
attachment of atoms combined by sharing or transferring valence electrons
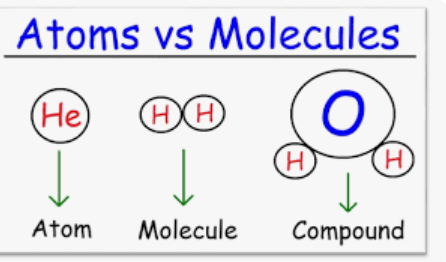
molecule
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
ex: O2 oxygen gas, N2,
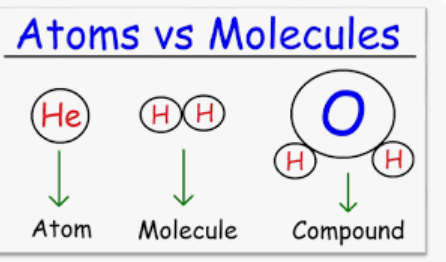
compound
-molecule made up of two or more different types of atoms. Ex: h2o, NaCl,
CO2 (molecule/compound),
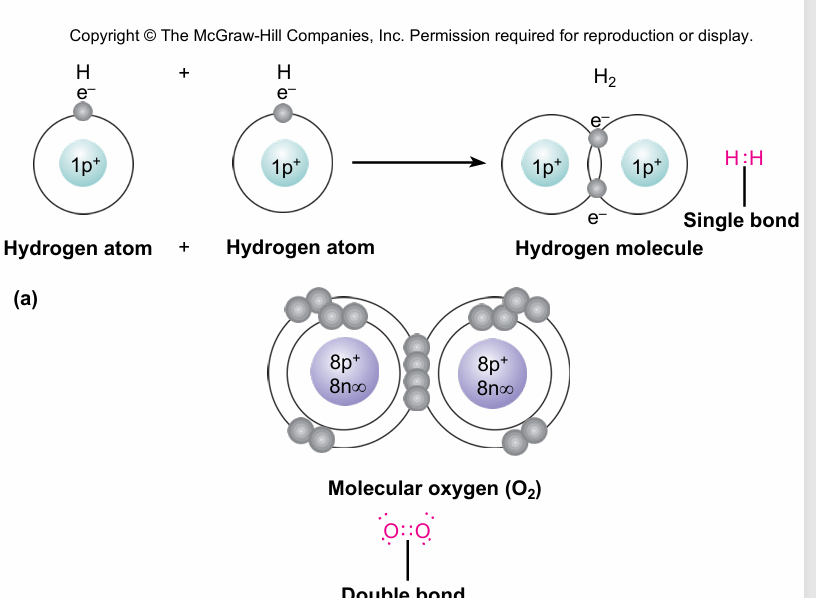
covalent bond
sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms
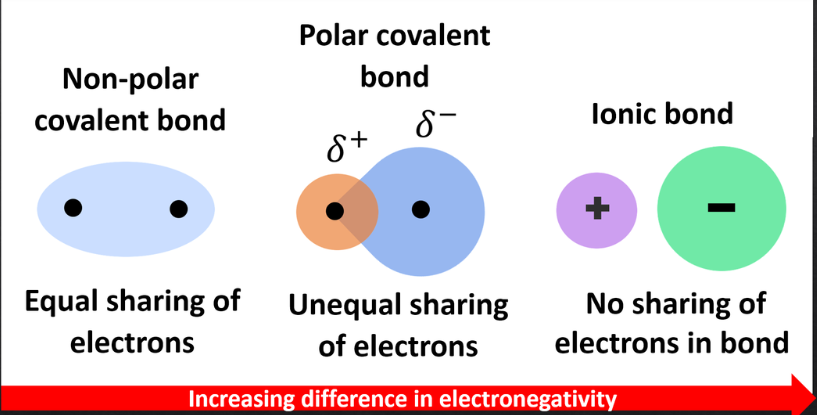
electronegativity
attraction of atom for electrons; the more electronegativity an atom, the greater the pull its nucleus exerts on electrons
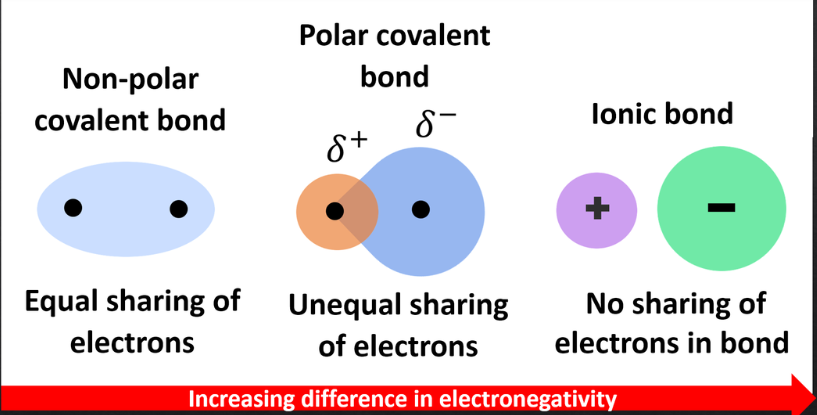
nonpolar covalents bonds
– Shared electrons spend equal amounts of time around each nucleus
– Atoms with similar electronegativities
– No poles exist
– Carbon atoms critical to life; form four nonpolar covalent bonds with other atoms
• Organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen atoms
non polar covalents bonds
Strongest covalent bonds in solution
• The most common bonds in living cells
• Form between C, H, O, N, P, S
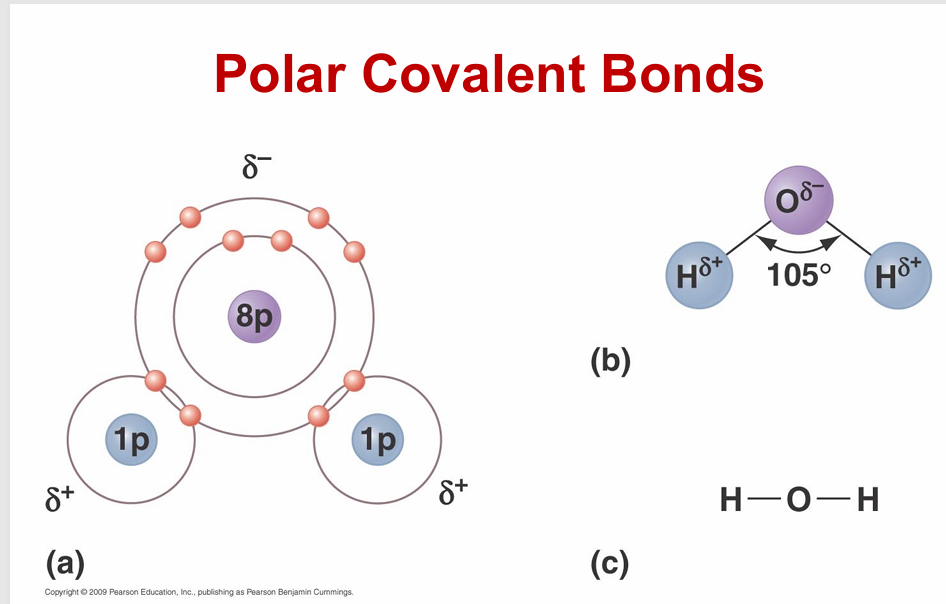
polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing of electrons due to high significantly different electronegativities
Most important polar covalent bonds involve hydrogen
- Allows for hydrogen bonding
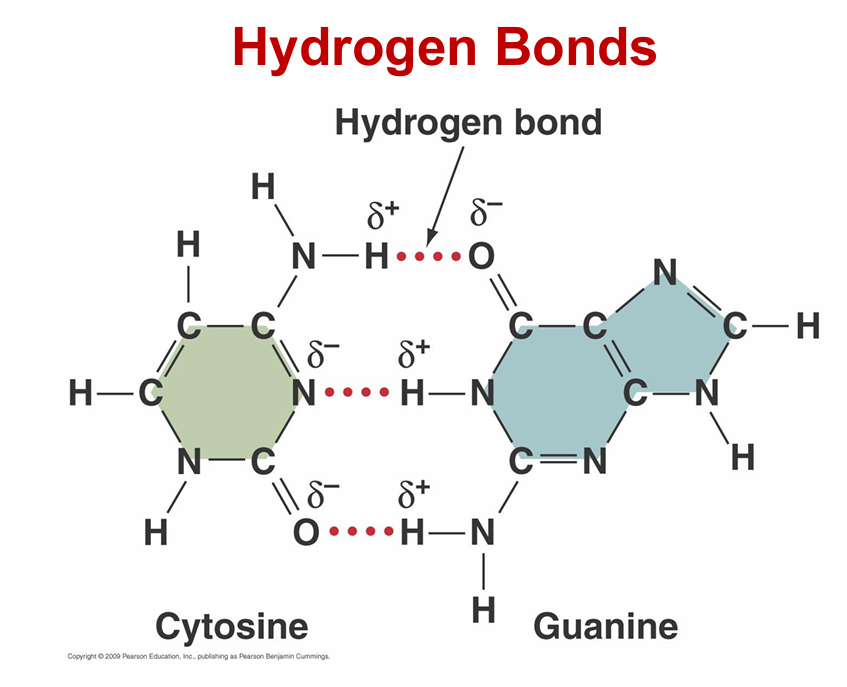
hydrogen bonds
– Not a true bond! Actually an Intermolecular force
– Weak forces that combine with polar covalent bonds
– Electrical attraction between partially charged H+ and full or partial negative charge on different region of same molecule or another molecule
– Weaker than covalent bonds but essential for life
• Many help to stabilize 3-D shapes of large molecules
**anytime you see H+ bind to N, O, F, they can potentially create a hydrogen bond
VERY WEAK!!!
EX: PROTEINS, DNA
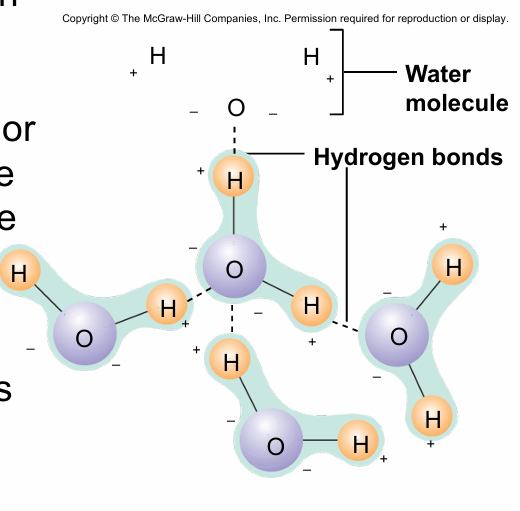
hydrogen bonds
-Weak bond between a H covalently bonded to one molecule and an O or N atom on the same or different molecule + H
- Important in many biological molecules
when H+ binds w/ N,O, F you have the capacity to regenerate a super polar covalent bond. And that H+ has the capacity for a special intermolecular force (hydrogen bond)
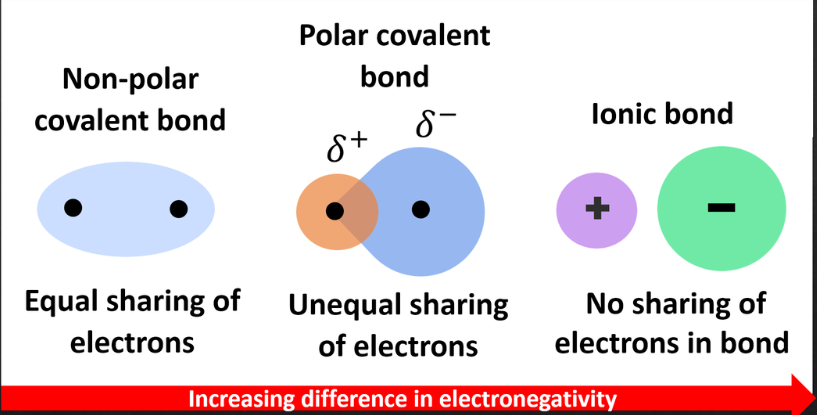
ionic bonds
– Occur when two atoms with vastly different electronegativities come together
– Atoms have either positive (cation) or negative (anion) charges
– Cations and anions attract each other and form ionic bonds (no electrons shared)
– Typically form crystalline ionic compounds known as salts (NaCl)
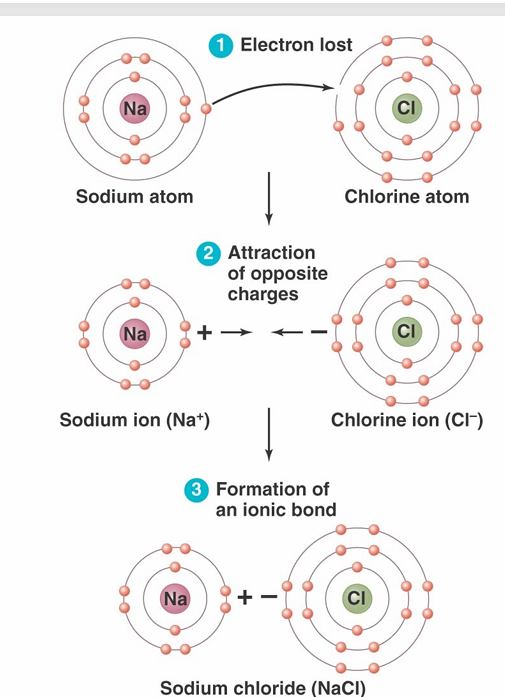
ionic bonds

hydrophilic
“water-loving” molecules attract water to their surface (polar)
hydrophobic
“water-hating” molecules repel water (nonpolar)
amphipathic
“feeling both” molecules have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties (polar and nonpolar parts)
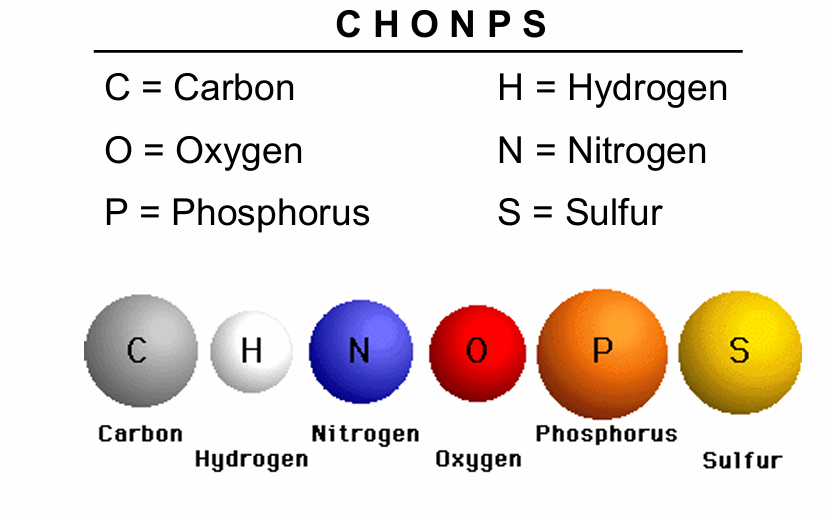
Common Elements in Living Organisms
CHONPS
pH scale
• Measures the acid concentrations of solutions
• Ranges from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic); 7 is neutral
• pH = -log[H+]
H+ is made of single proton/electron
H+ is a proton
PH high=basic (lots of protons)
PH low= acidic (very low protons)
![<p>• Measures the acid concentrations of solutions</p><p>• Ranges from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic); 7 is neutral</p><p>• pH = -log[H+]</p><p>H+ is made of single proton/electron</p><p>H+ is a proton</p><p>PH high=basic (lots of protons)</p><p>PH low= acidic (very low protons)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/06173352-aec4-4ca1-b315-bbce5d0a0779.png)
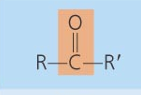
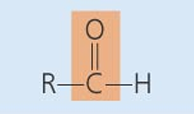
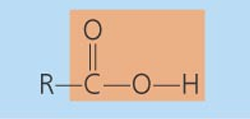
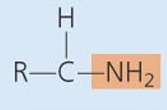
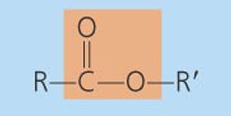
Functional Groups of Organic Molecules
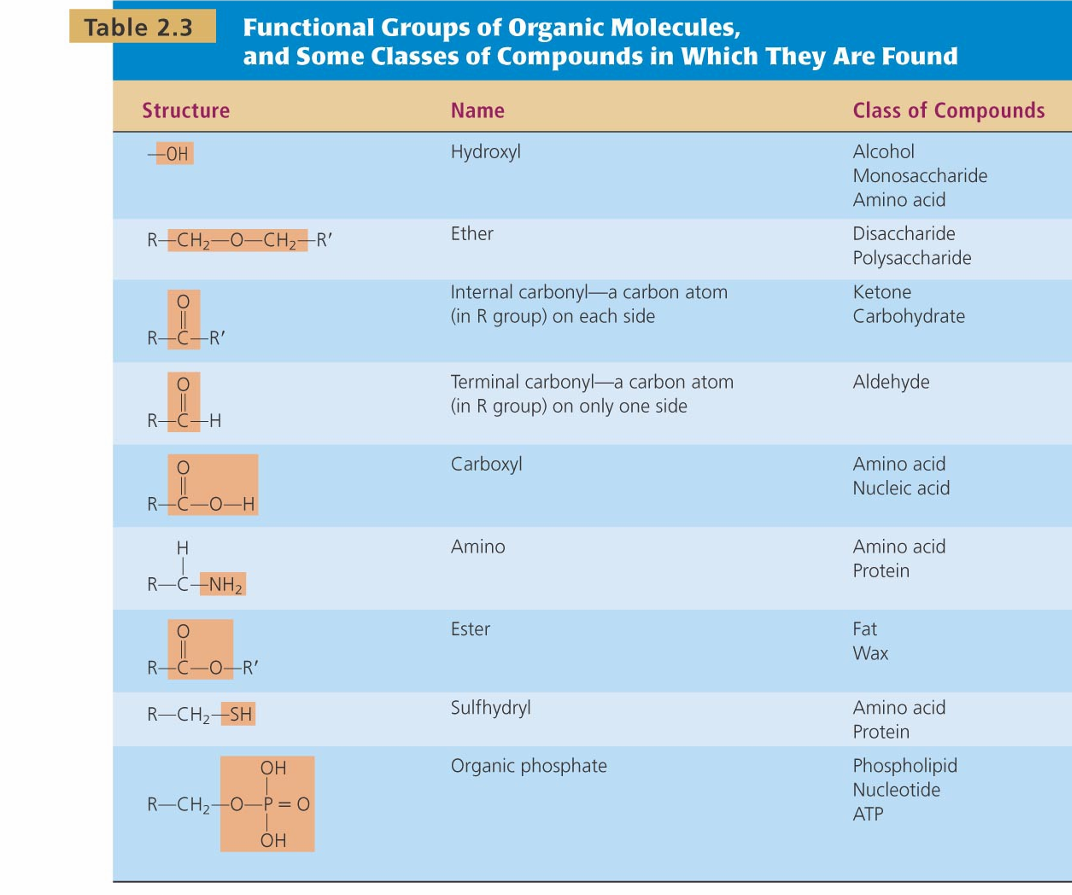
-OH
Hydroxyl
-class of compounds: alcohol, monossacharide, aa
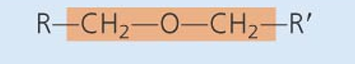
Ether
-class of compounds: Disaccharide ,polysaccharide







chemical reactions
• The making or breaking of chemical bonds
• Involve reactants and products
• Biochemistry involves chemical reactions of living things
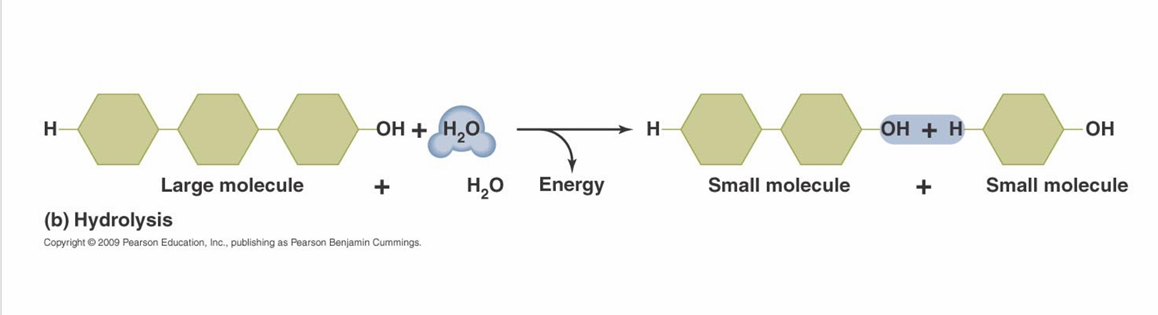
Many biological molecules are composed of
Monomer Units
Monomer units are joined by
Dehydration synthesis reactions (also called condensation reactions)
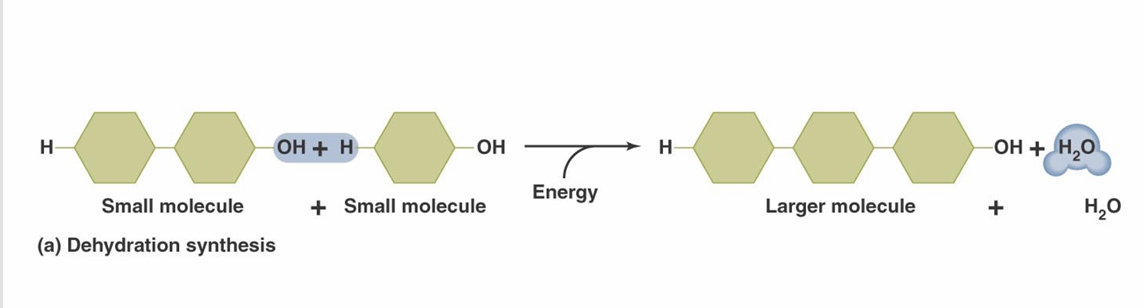
Polymers are broken down by
Hydrolysis reactions
organic molecules
1. Carbohydrates
2. Proteins
3. Nucleic Acids
4. Lipids
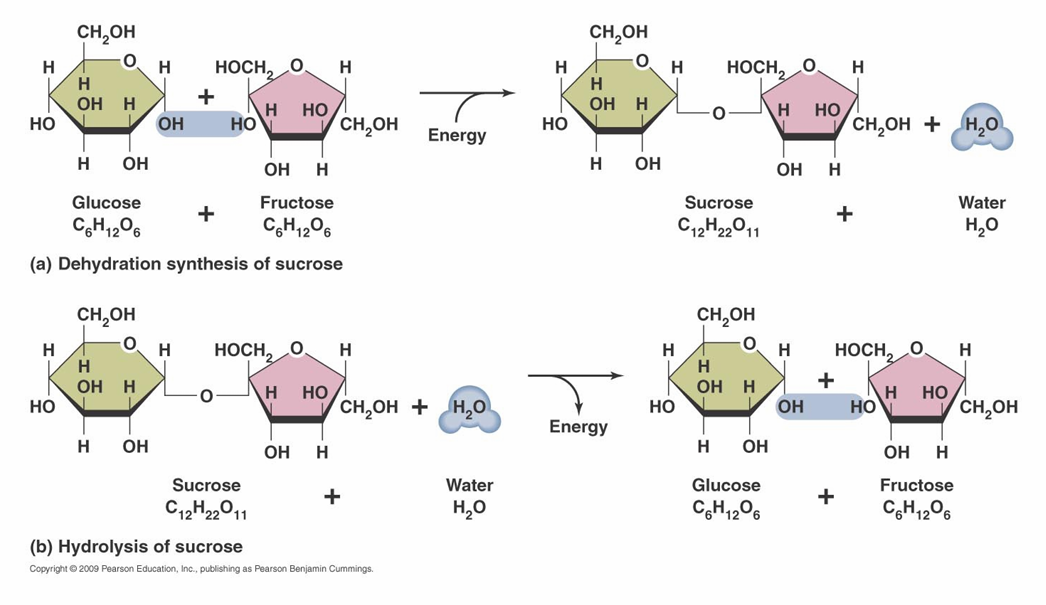
Carbohydrates
– Organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CH2O)n
– Functions
• Medium or Long-term storage of chemical energy
• Ready energy source
• Part of backbones of nucleic acids
• Converted to amino acids
• Form cell wall
• Involved in intracellular interactions between animal cells
– Types
• Monosaccharides: single Ex: fructose
• Disaccharides: double. Ex: sucrose
• Polysaccharides. Ex: starch, cellulose

Carbohydrate synthesis/Hydrolysis
proteins
– Mostly composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur
– Functions
• Structure of cells
• Enzymatic catalysis- speeds up chemical reactions but not consumed in the process
• Regulation
• Transportation
• Defense and offense (immune protein-antibody)
catalyst
speeds up chemical reaction but is not consumed in the process (meaning not a reactant or product)
enzyme
is a protein catalysts
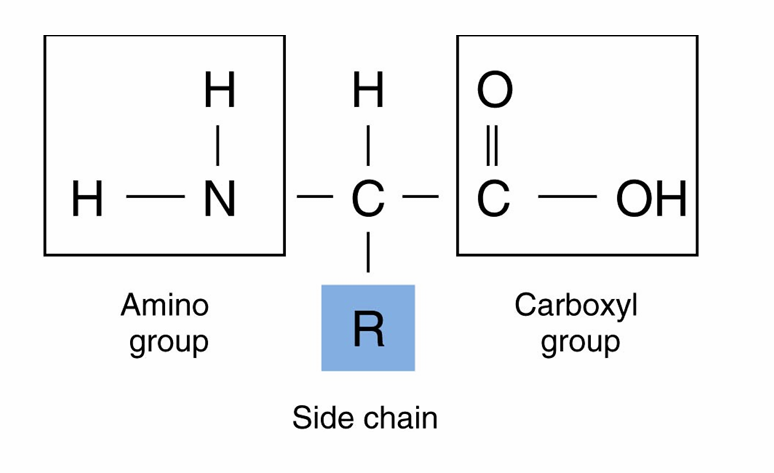
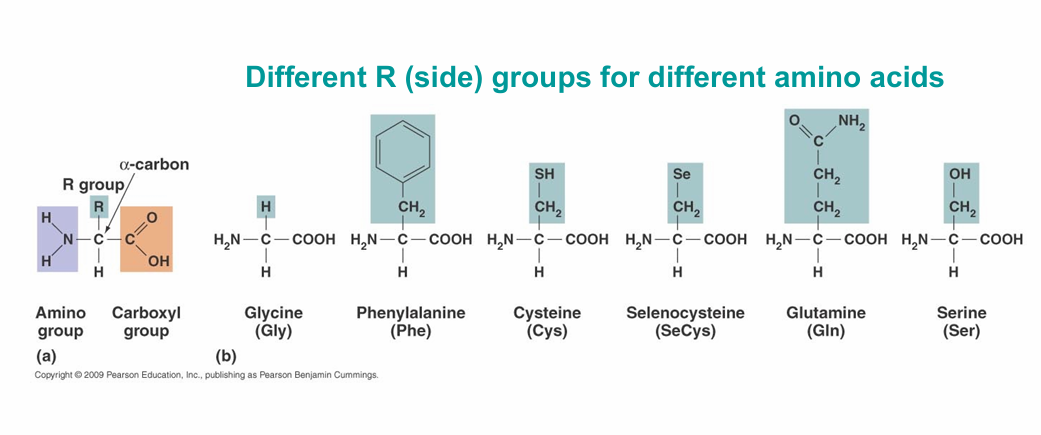
Amino Acids
– The monomers that make up proteins
– Most organisms use only 21 amino acids in the synthesis of proteins
– Side groups affect how amino acids interact with one another and how a protein interacts with other molecules
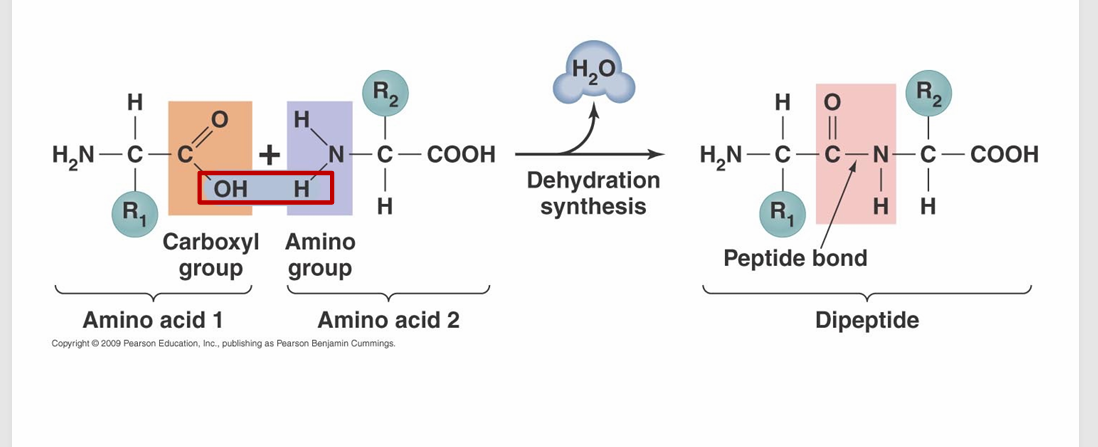
– A covalent bond ( is formed between amino acids by dehydration synthesis reaction
***** (OH) hydroxyl can run dehydration synthesis******
amino acids
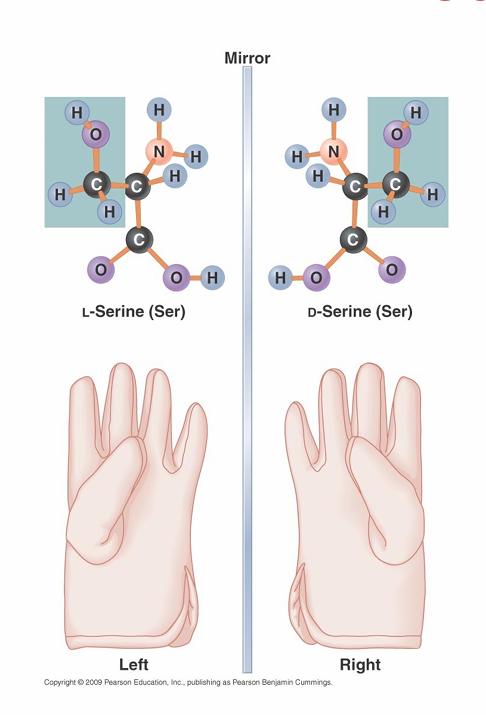
Isomers
• Stereoisomers
– are mirror images of one another
– D-isomers bend light to the the right (clockwise)
– L-isomers bend light to the left (counterclockwise)
Amino Acid Dehydration Rxn.
Protein structure
KNOW WHERE TO FIND A PEPTIDE BOND!
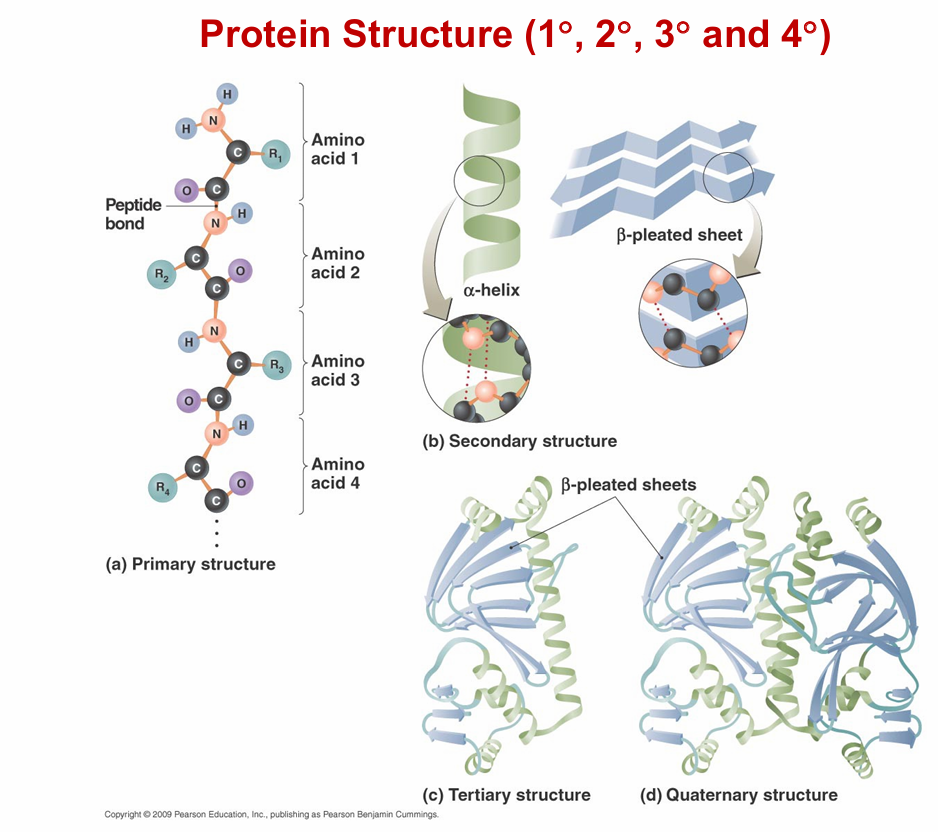
Primary structure
is the order of amino acids
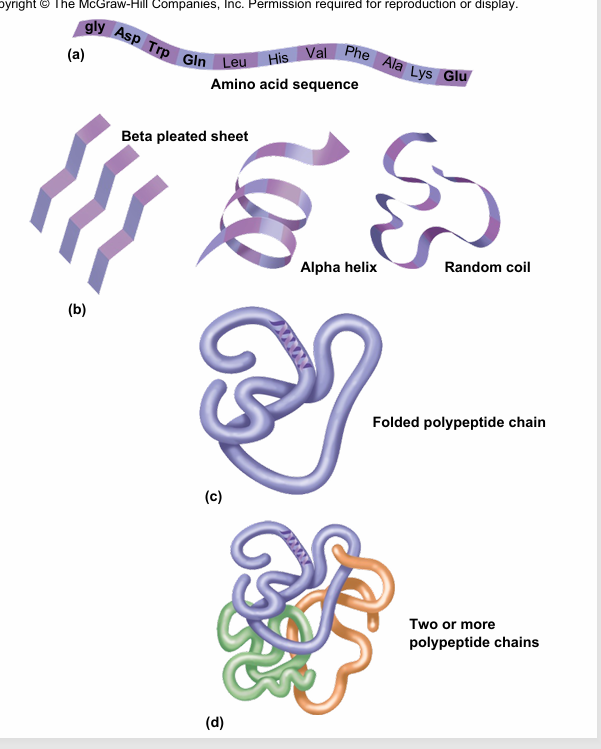
secondary structure
is localized modular structure
-determined by the primary structure is a localized 3 dimensional structure that is determined by hydrogen bonding along the peptide backbone
ex: alpha helix, beta sheet
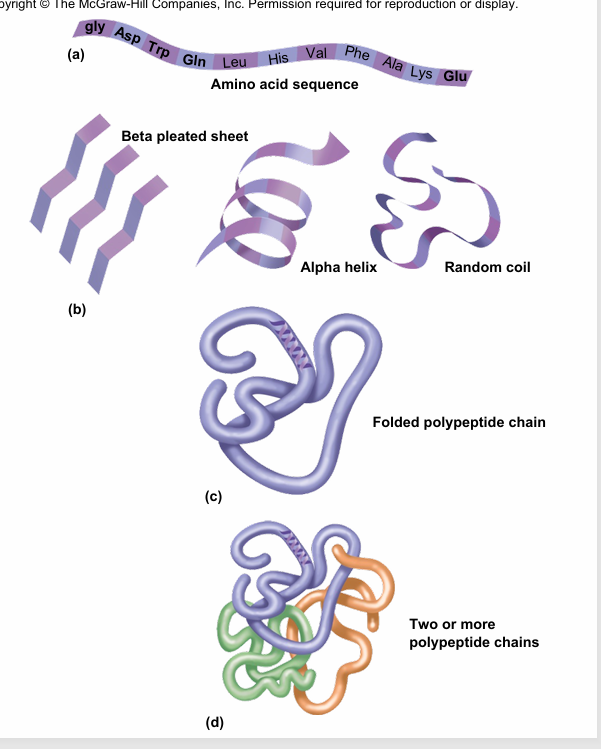
Tertiary Structure
is the global three-dimensional shape of the polypeptide (chain of AA)
-what determines tertiary structure?: interaction of the R groups
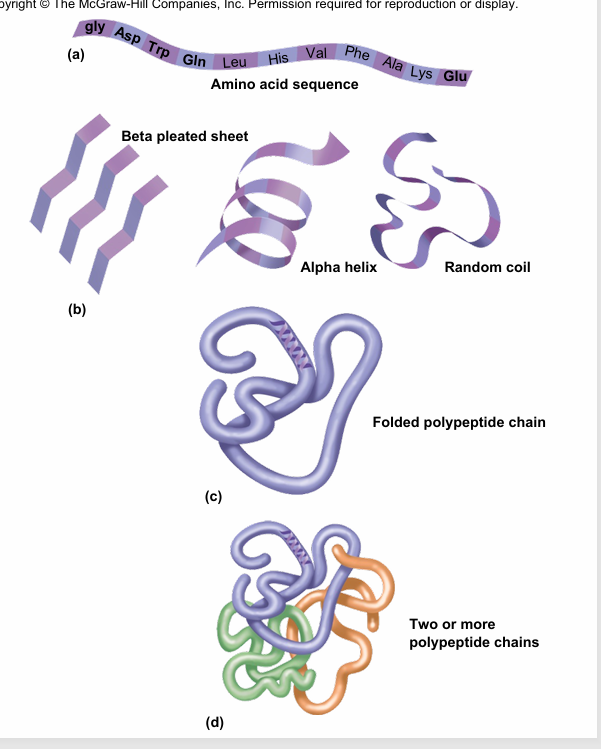
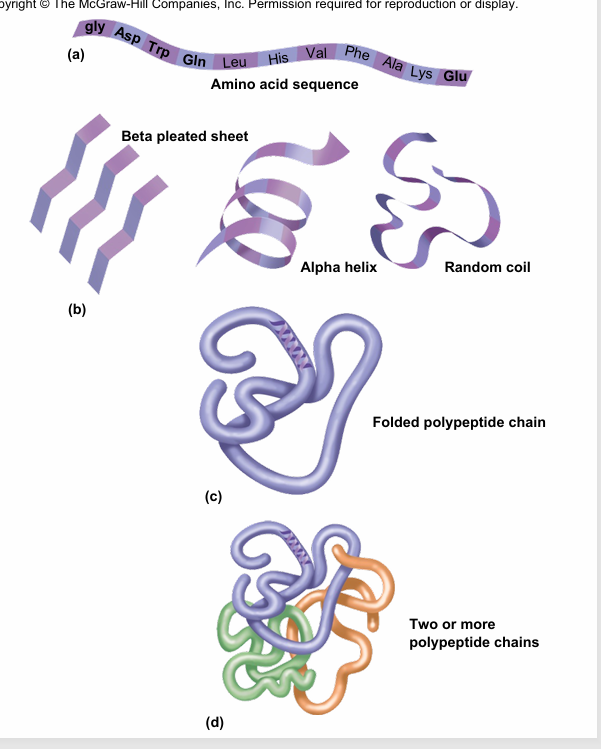
quaternary structure
is the association of more than one polypeptide chains coming together to make a protein
Ex of quaternary structure- hemoglobin
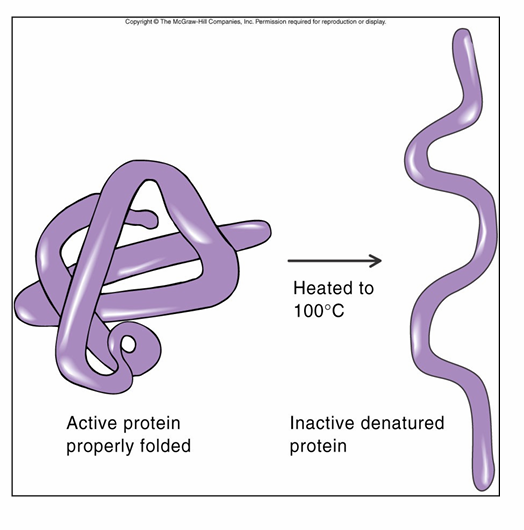
Protein Denaturation
– causes loss of 3D structure
– protein unravels and looses function
– can be caused by
• heat
• acids
• bases
• harsh chemicals
•mechanical action
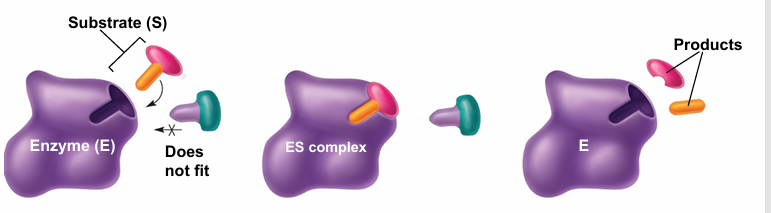
enzymes
• Nearly always proteins
• Biological catalysts critical for life
• Active site
• Substrate(s) – acted on by enzymes to make products
• Cofactors – often required (ATP, NADH, etc)
DNA
• DNA is genetic material of all organisms and of many viruses
• Carries instructions for synthesis of RNA and proteins; controls synthesis of all molecules in an organism
RNA
• functions in protein synthesis (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA)
• is the genetic material of some viruses
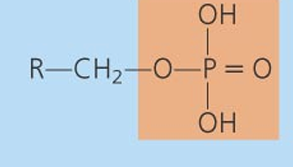
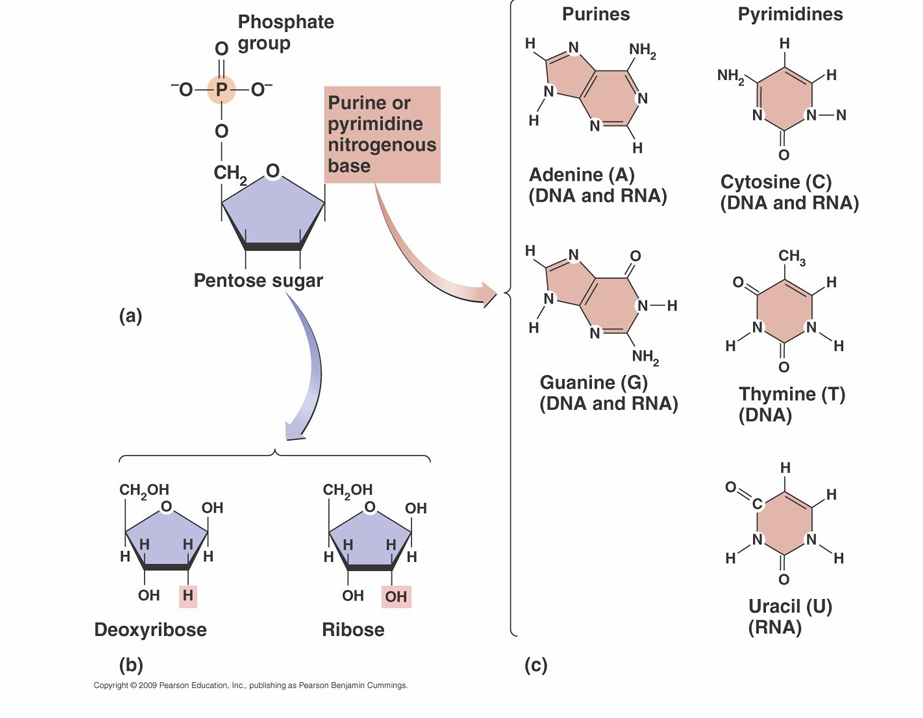
Nucleotides
• Monomers that make up nucleic acids
• Composed of three parts
– Phosphate
– Pentose sugar: deoxyribose or ribose
– One of five cyclic nitrogenous base
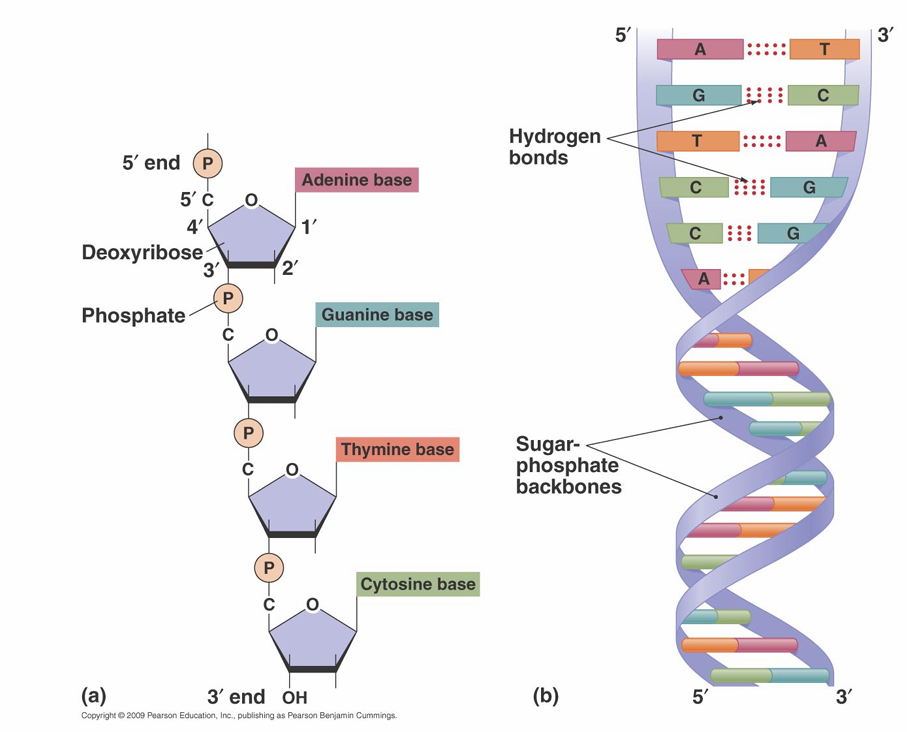
Nucleic acid structure
• H bonds form between C and G and between T and A in DNA
– Two H bonds form between U and A in RNA
• DNA is double stranded in most cells and viruses
– Two strands are complementary
– Two strands are antiparallel
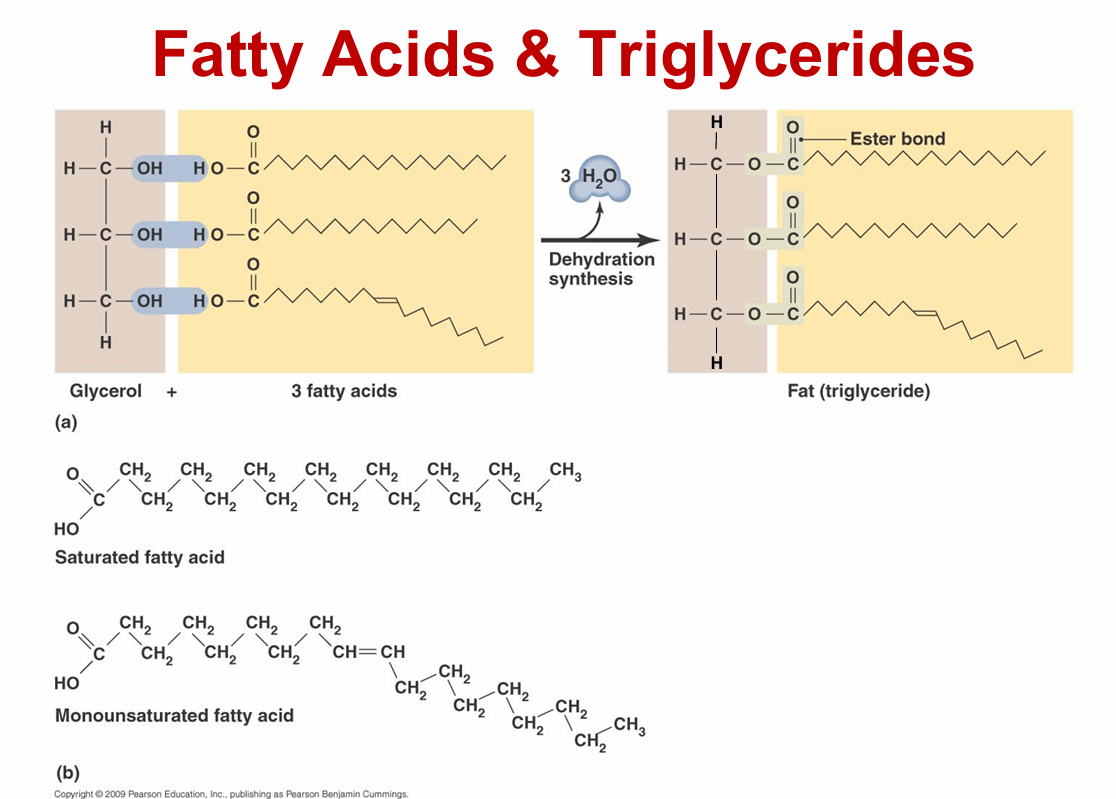
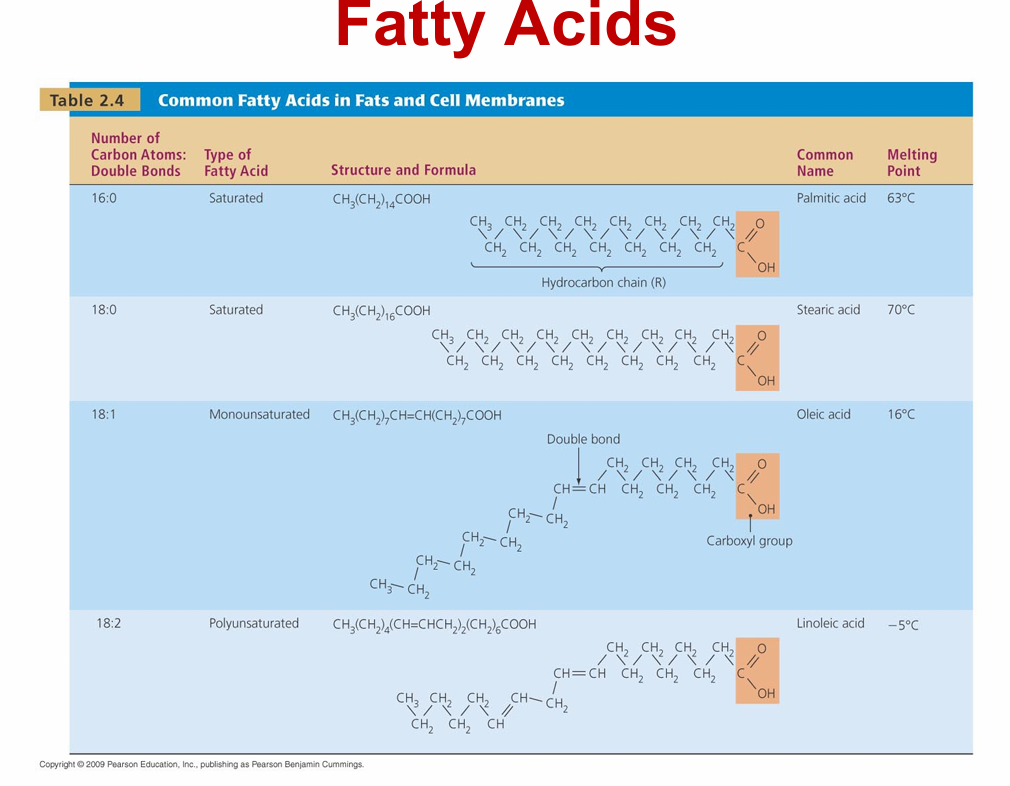
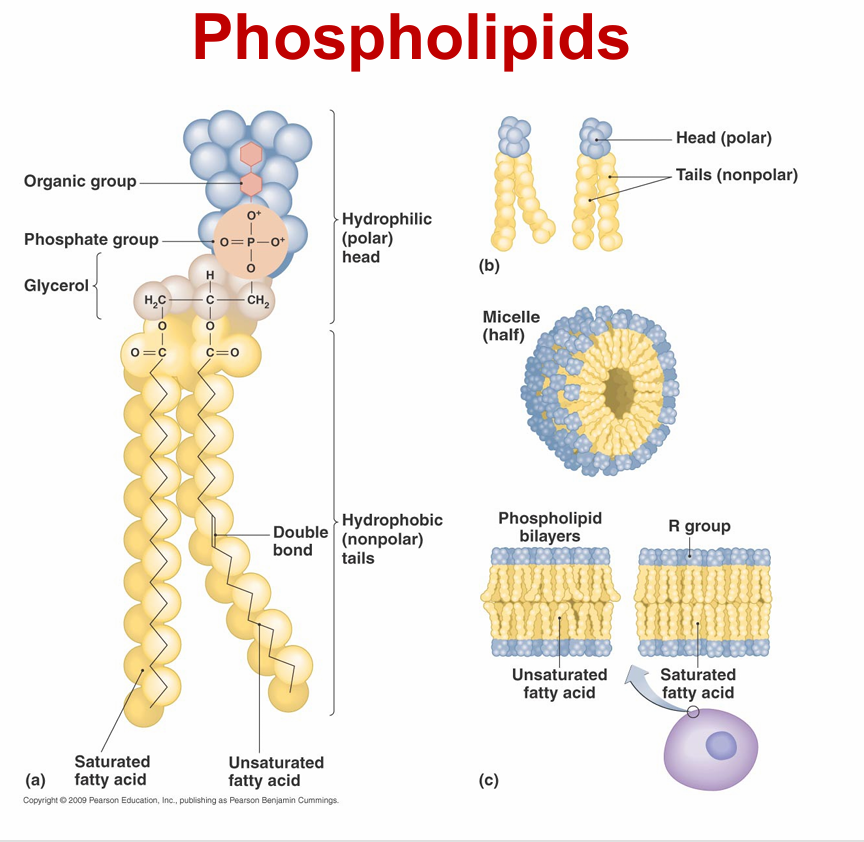
lipids
– Not composed of regular subunits, but are all hydrophobic
– Four groups
• Fats
• Phospholipids
• Waxes
• Steroids
sterols
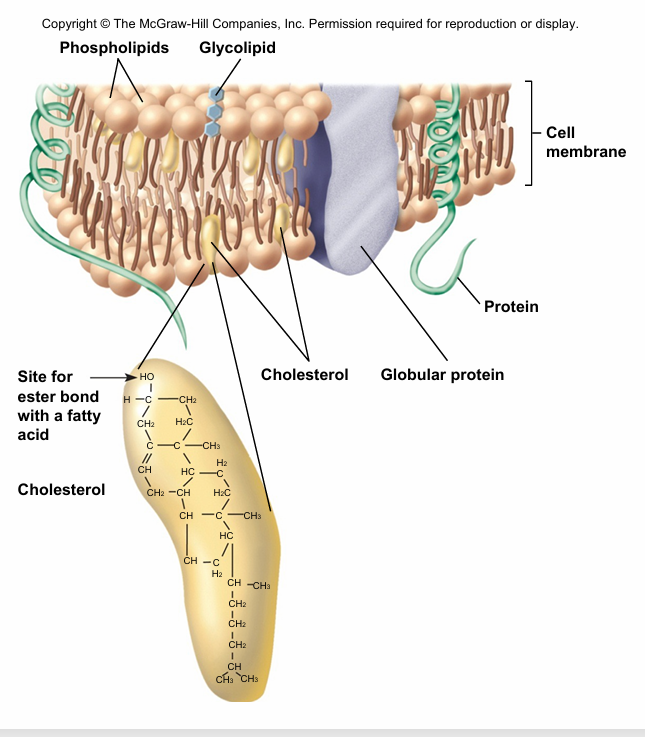
• Multi-ring structure
• Used in membranes cholesterol
• Bile acids (help digest food)
• Hormones ( chemical signal released by the cell)
macromolecules
plasma membrane composed of phospholipids
cell wall made out of carbohydrates
flagella made out of protein
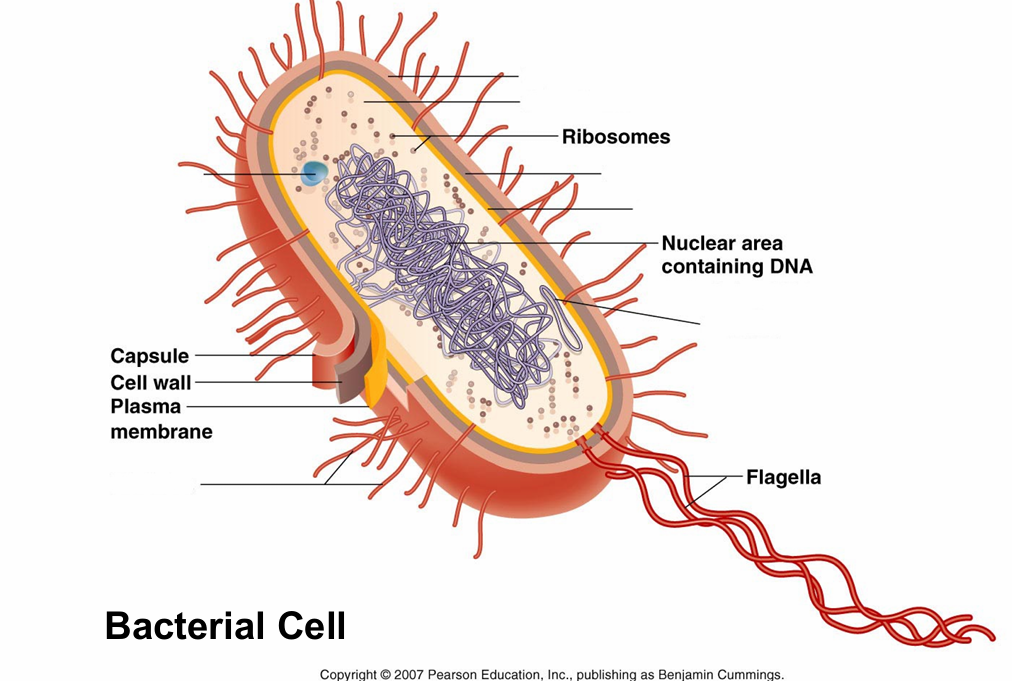
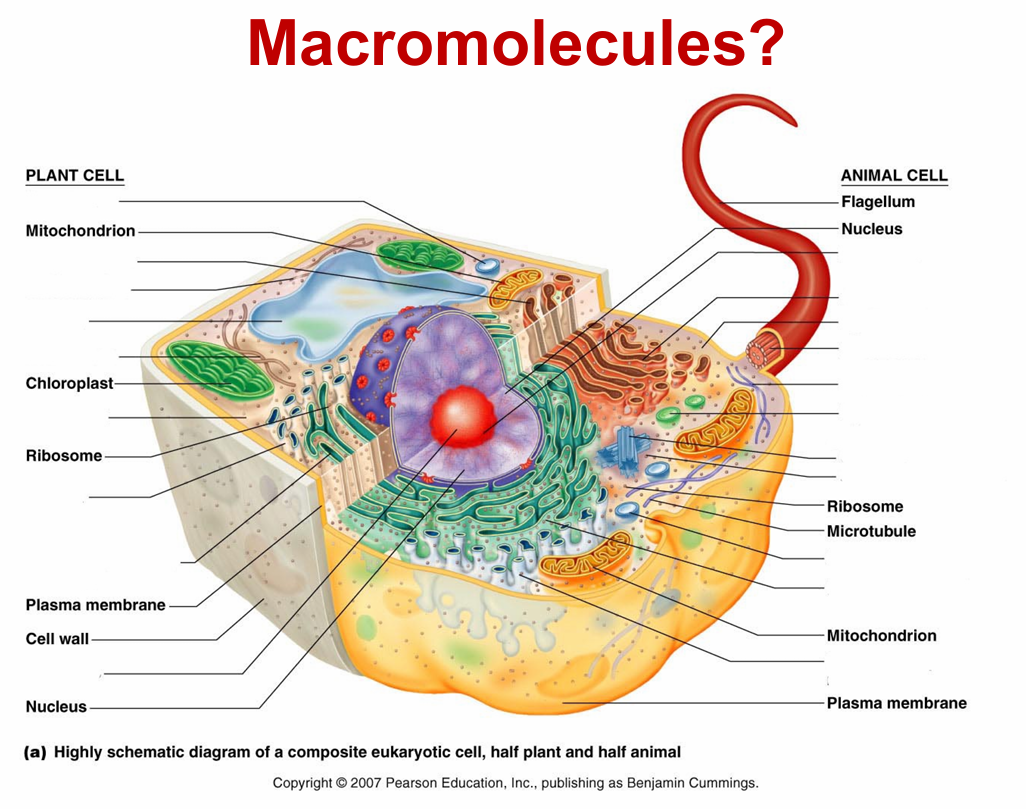
cells
• The fundamental unit of life is the cell
• All cells:
– Have a cytoplasmic membrane
– Have chromosomes made of DNA
– Have ribosomes for protein synthesis
– Reproduce to form progeny cells
– Obtain energy from their environment
eukaryotic cells
– Animals, plants, fungi, and protists
– Have a nucleus and cellular organelles
– Tend to be large
Prokaryotic cells
– Bacteria and Archaea
– No nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
– Tend to be smaller
DNA monomer unit us
nucleotides
amino acids monomer unit is
polypeptide or protein
cofactors
something an enzyme needs in order to do it’s job
Example:(ATP, NADH)