Quarterly #1 Sem 2
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintain dynamic equilibrium in the body. Organisms maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment despite fluctuating external conditions.
Negative feedback loop!
Set point
Midpoint or target point in homeostasis. While there are normal fluctuations, the body’s systems will usually attempt to go back to this point.
Stimulus
Anything (an object, event, or change) that causes a reaction or response in an organism or system, triggering a physical or behavioral change
Ex) Seeing light (a stimulus) causing your pupil to constrict
Receptor
(The detector) A specialized cell or group of cells that detects that specific stimulus and converts it into a nerve signal.
Negative Feedback Loop
Feedback to a control mechanism that increases or decreases a stimulus instead of maintaining it.
In other words, if a level is too high, the body does something to bring it down, and conversely, if a level is too low, the body does something to make it go up.
Predominant mechanism used in homeostasis.
Positive Feedback Loop
Maintains the direction of the stimulus, possibly accelerating it.
Ex) Childbirth, blood clotting
Ectotherms
Animals that rely on external temperatures to set their body temperature
Endotherms
Animals that rely on internal sources for maintenance of relatively constant body temperature in varying environmental temperatures
Thermoregulation
The vital physiological process by which the body maintains a stable core temperature (typically 37∘C or 98.6 ∘ F) by balancing heat production and loss
Homeostatic Control System Sequence
Stimulus → Sensor → Control (change is compared to the set point)→ Effector (The control center sends signals to the effector which then performs an action (e.g., releases insulin, shivers) to counteract or enhance the initial stimulus.
Anatomy
Study of body’s internal and external structures, and relationship between body’s parts
• Traditionally subdivided into gross & microscopic
Anatomy affects physiology
Physiology
Study of how these structures work as an integrated whole
• Focuses on the chemical, electrical & physical process of the body
• Traditionally deals with organs and organ systems
Asymmetrical Animals
Animals with no pattern or symmetry; an example is a sponge.
Radial Symmetry
Describes when an animal has an up-and-down orientation: any plane cut along its longitudinal axis through the organism produces equal halves, but not a definite right or left side.
Bilateral Symmetry
A plane cut from front to back separates the animal into definite right and left sides.
Sagittal plane
Divides the body into right and left portions.
Frontal plane
Separates the front from the back.
Transverse plane or cross section
Divides the animal into upper and lower portions.
Dorsal Cavity
Contains the cranial and the vertebral (or spinal) cavities.
Ventral cavity
Contains the thoracic cavity, which in turn contains the pleural cavity around the lungs and the pericardial cavity, which surrounds the heart. Also contains the abdominopelvic cavity, which can be separated into the abdominal and the pelvic cavities.
Epithelial tissues
Cover the outside of organs and structures in the body and line the lumens of organs in a single layer or multiple layers of cells. Smooth inner lining.
Epithelia composed of a single layer of cells is called simple epithelia; epithelial tissue composed of multiple layers is called stratified epithelia
Squamous
Flat, irregular round shape
Located in:
Simple: lung alveoli, capillaries
Stratified: skin, mouth, vagina (think about where the body faces abrasion)
Cuboidal
Cube shaped, central nucleus
Located in:
glands, renal tubules
Columnar
Tall, narrow, nucleus toward base; tall, narrow, nucleus along cell
Located in:
Simple: digestive tract
Pseudostratified: respiratory tract (think where cilia needs to help move stuff)
Transitional
Round, simple but appear stratified
Located in:
Urinary bladder
Connective Tissues
Made up of a matrix consisting of living cells and a nonliving substance, called the ground substance. Contains blood vessels.
The organic portion or protein fibers found are either collagen, elastic, or reticular fibers.
Fibers provide strength to the tissue, preventing it from being torn or separated from the surrounding tissues.
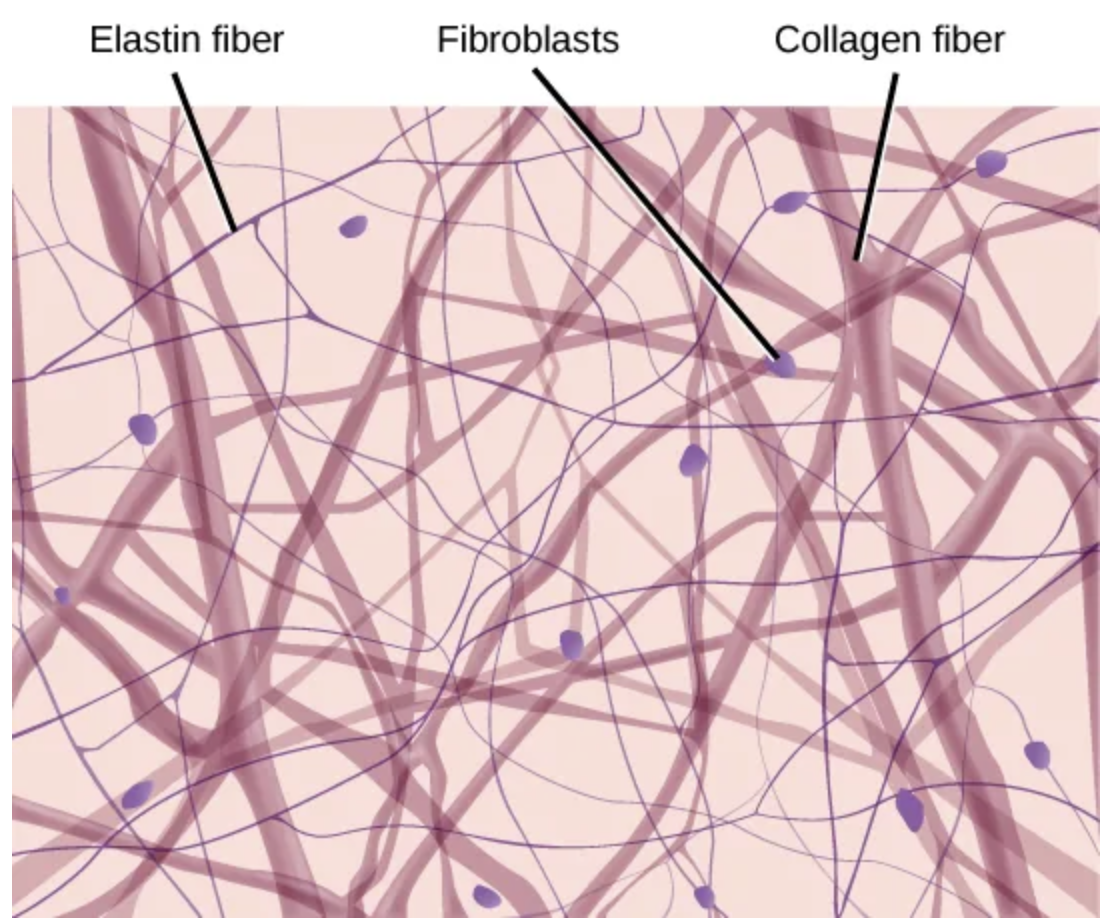
Loose/areolar
Connective tissue
Cells: Fibroblasts, macrophages, some lymphocytes, some neutrophils
Fibers: Collagen, elastic, reticular
Location: Around blood vessels; anchors epithelia
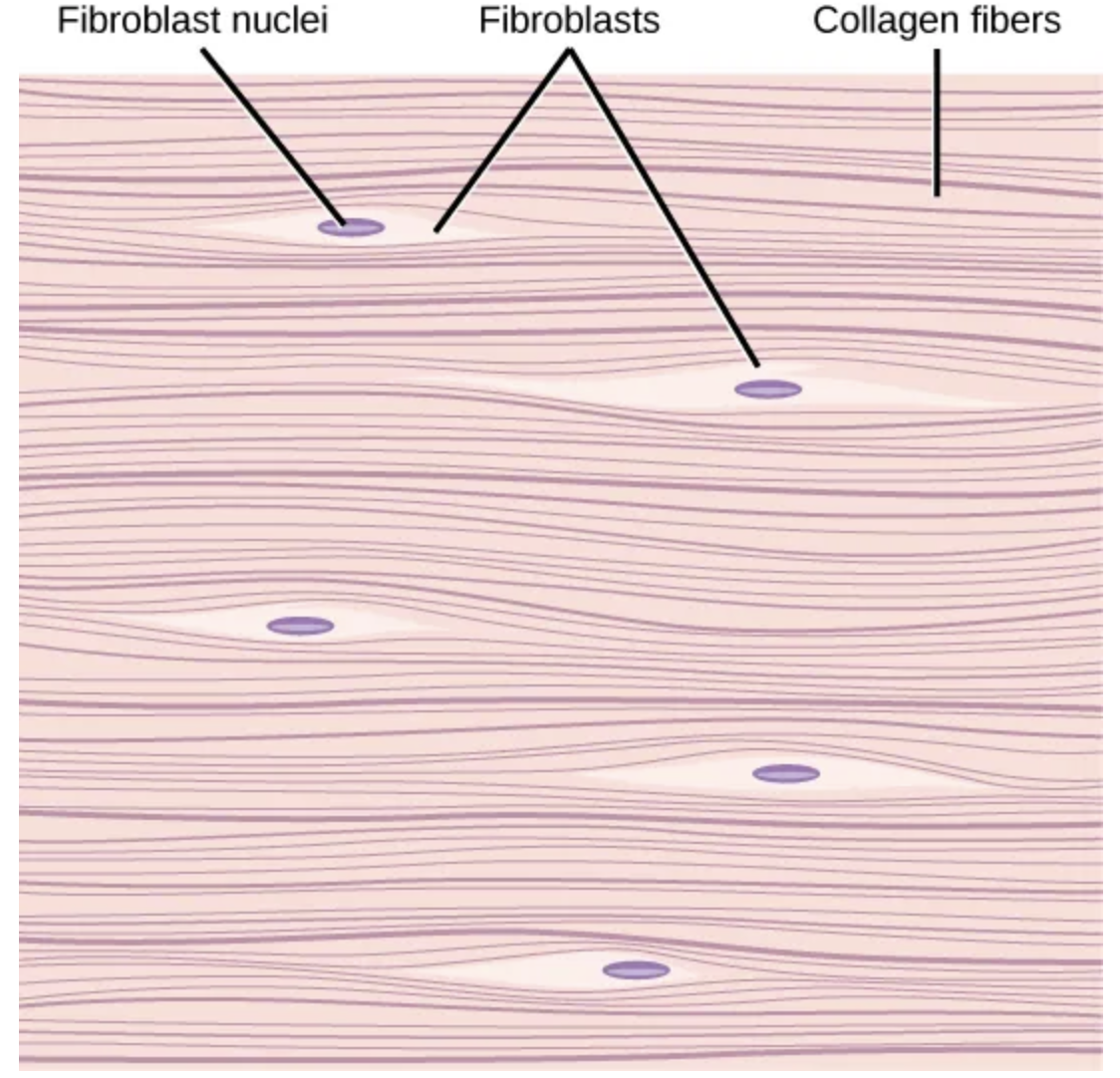
Dense, fibrous
Connective tissue
Cells: Fibroblasts, macrophages
Fibers: Mostly collagen
Location:
Irregular: skin
Regular: tendons, ligaments
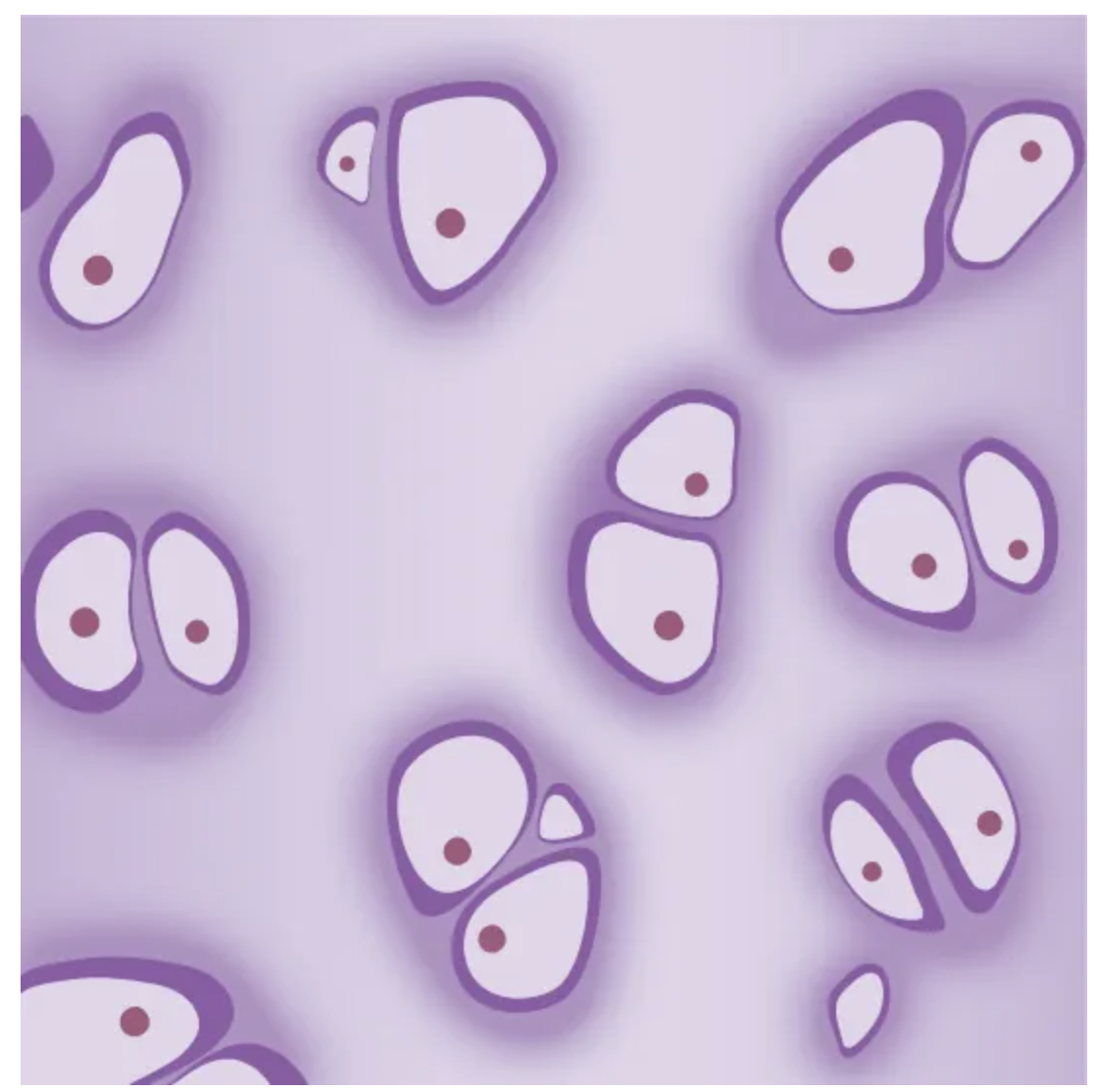
Cartilage
Connective Tissue
Cells: chondrocytes, chondroblasts
Fibers:
Hyaline: The collagen fibers are very thin and spread out, so you usually don’t see them easily under a microscope. Resulting properties: smooth, flexible, good at reducing friction and absorbing shock
Fibrocartilage: Large amount of collagen, thick, densely packed collagen fibers that are clearly visible. Resulting properties: Very strong, resistant to compression and pulling forces
Location: Shark skeleton, fetal bones, human ears, intervertebral discs
Bone
Connective Tissue
Cells: Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
Fibers: (Some) collagen, elastic
Location: Vertebrate skeletons
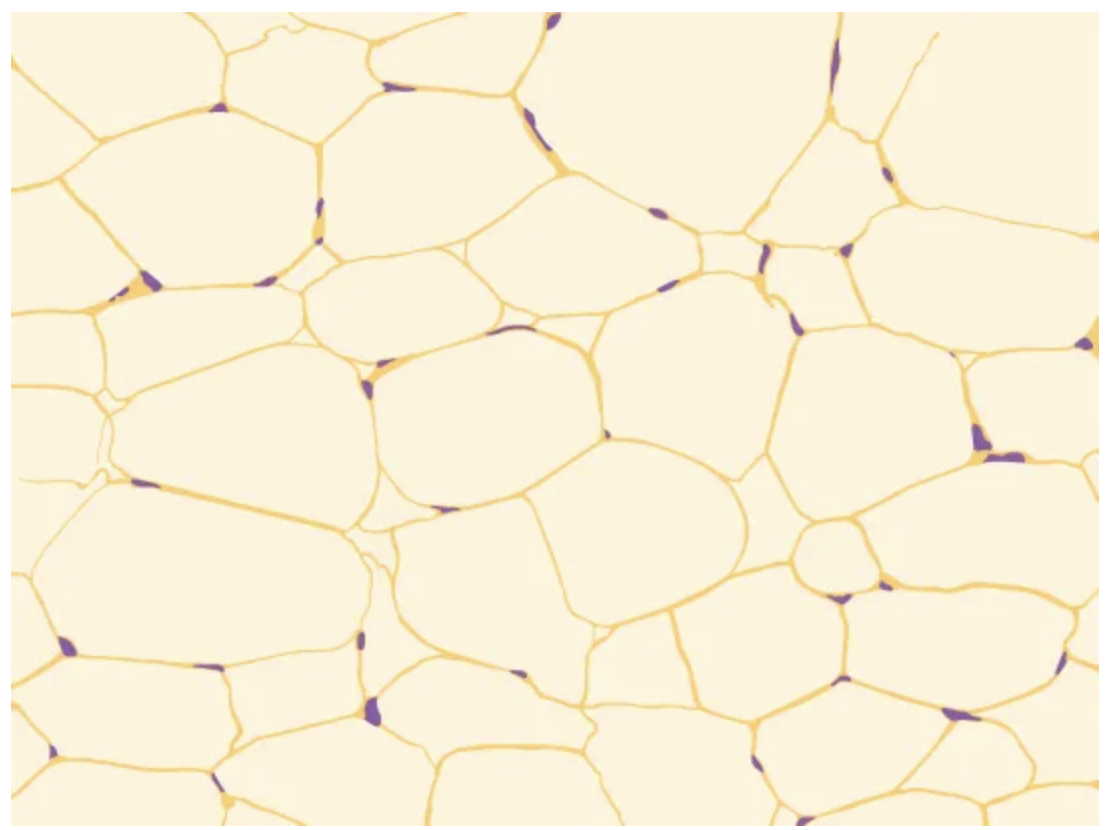
Adipose
Connective tissue
Cells: Adipocytes
Fibers: Few
Location: Adipose (fat)
Blood
Connective tissue
Cells: Red blood cells, white blood cells
Fibers: None
Location: Blood
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac
Smooth muscle
Does not have striations in its cells, has a single, centrally located nucleus. Non-striated as it lacks the banded appearance of skeletal and cardiac muscle.
Constriction of smooth muscle occurs under involuntary, autonomic nervous control and in response to local conditions in the tissues.
Neuron
The structural and functional unit of nervous tissue
Skeletal muscle
Muscle has striations across its cells caused by the arrangement of the contractile proteins actin and myosin.
These muscle cells are relatively long and have multiple nuclei along the edge of the cell. Skeletal muscle is under voluntary, somatic nervous system control and is found in the muscles that move bones.
Cardiac Muscle
Found only in the heart. Has cross striations in its cells, but cardiac muscle has a single, centrally located nucleus.
Not under voluntary control but can be influenced by the autonomic nervous system to speed up or slow down.
Has intercalated discs: which assist in passing electrical impulse efficiently from one cell to the next and maintains the strong connection between neighboring cardiac cells.
Nervous Tissue
Made of cells specialized to receive and transmit electrical impulses from specific areas of the body and to send them to specific locations in the body.
Clinical Care
Prevention, treatment, and management of illness and the preservation of mental and physical well- being through the services offered by medical and allied health professions; also known as health care
Clinical care team
Consists of the health professionals with the training and skills needed to provide high-quality, coordinated care specific to the patient’s clinical needs and circumstances
Epidemic / Outbreak
Occurrence in a community or region of cases of an illness, specific health-related behavior, or other health-related event clearly in excess of normal expectancy.
(Both terms are used interchangeably)
• epidemic usually refers to a larger geographic distribution of illness or health-related events
Public Health Approach
Surveillance → Risk Factor Identification → Intervention Evaluation → Implementation
John Snow
Best known for his work tracing the source of the cholera outbreak and is considered the father of modern epidemiology.
Three core functions of public health
Assessment, policy development, assurance
Epidermis (skin layer)
Forms the surface of the skin
Stratified squamous epithelium
Dermis (skin layer)
Forms a deeper skin layer
• composed of dense connective tissue with many resilient elastic fibers and strong
collagen fibers
• contains hair follicles, oil and sweat glands, muscle cells, nerves, sensory receptors,
and blood vessels
Integumentary system
The body's largest organ system, comprising the skin, hair, nails, and glands, which acts as a protective, regulatory barrier
Pathogen
Agents, usually microorganisms, that cause diseases in their hosts
Include bacteria, protists, fungi and other infectious organisms.
Innate immunity
Occurs naturally because of genetic factors or physiology; it is not induced by infection or vaccination but works to reduce the workload for the adaptive immune response.
No “memory”
External barriers (skin/exoskeleton, acidic environment, secretions, mucous membranes, hairs, cilia) internal barriers (phagocytic cells, natural killer cells, defensive proteins, inflammatory response)
Macrophage
A large phagocytic cell that engulfs foreign particles and pathogens.
Lymphocytes
Leukocytes that are histologically identifiable by their large, darkly staining nuclei; they are small cells with very little cytoplasm. Can kill cells infected with viruses or tumor cells (abnormal cells that uncontrollably divide and invade other tissue).
T cells
Lymphocytes that mature in the thymus gland.
Kill infected cells or help other immune cells
B cells
Lymphocytes that mature in the bone marrow.
Make antibodies
Lymphatic System
Involved in innate and adaptive immunity
• consists of a network
• lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymph
Circulating lymph
Collects
• microbes, parts of microbes, and microbial toxins
• transports them to lymphatic organs
• macrophages in lymphatic organs engulf the invaders
• lymphocytes may mount an adaptive immune response
Perforin
A destructive protein that creates a pore in the target cell.
Adaptive Immunity
An immunity that occurs after exposure to an antigen either from a pathogen or a vaccination.
Activated when the innate immune response is insufficient to control an infection.
Antigen
Foreign molecules recognized by our immune systems
• elicit the adaptive immune response
Active immunity
Occurs when the body is exposed to an antigen and responds by producing its own antibodies and memory cells
Humoral immune response
An adaptive immune response in which B cells produce antibodies that circulate in blood and lymph to target antigens.
Cell-mediated immune response
The part of the adaptive immune system that uses T cells (not antibodies) to fight infected or abnormal cells.
Microphages
A large white blood cell that locates and eats particles such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Use a process known as phagocytosis to destroy unwanted particles in the body.
Include neutrophils and eosinophils.
Normally in blood but can leave bloodstream to enter infected or injured tissue
Macrophages
Specialized white blood cell that acts as the body's "clean-up crew" and first responder, engulfing and digesting pathogens (like bacteria), dead cells, and debris, while also coordinating other immune cells and promoting tissue repair and homeostasis
Derived from monocytes
• pervade almost every body tissue
Mast Cells
Immune cells in connective tissues that act as the body's "alarm system," releasing chemicals to fight infections and parasites, but also causing allergies and anaphylaxis when triggered inappropriately.
Secrete histamine and heparin
Interferons
Small proteins released by activated lymphocytes, macrophages, infected cells
• Cause normal cells to produce antiviral compounds
• May also stimulate macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells into action
Antigens
Foreign molecules recognized by our immune systems
• elicit the adaptive immune response
Effector Cells
Selected lymphocyte cells multiply into clones of short-lived effector cells, specialized for defending against the antigen that triggered the response
Clonal selection
When a specific antigen shows up, it “selects” the one lymphocyte that matches it, that cell multiplies, and the clones become fighters now (effector/plasma cells) and rememberers later (memory cells).
Think: Find → Copy → Fight → Remember
Plasma cells (B-cell effector cells)
If the selected lymphocyte is a B cell, its effector cells are called plasma cells.
Plasma cells:
Secrete large amounts of antibodies
Target that specific antigen
Plasma cells = antibody factories
Memory cells (long-term immunity)
Some clones become memory cells instead of effector cells.
Memory cells:
Live a long time
Respond faster and stronger if the antigen returns
This is why you don’t get sick again (or get much milder illness).
Helper T-cells
1. Receptors recognize the self–nonself complexes
2. Interaction activates the helper T cells
3. Then cytotoxic T cells attack body cells that are infected with pathogens and B cells
Cytotoxic T cells
Only T cells that kill infected cells
• bind to infected body cells and destroy them
• play a role in protecting the body against the spread of some cancers
Self-/non-self discrimination
The immune system’s ability to tell your own cells (“self”) from foreign invaders (“non-self”).
When do T-cells learn self-/non-self discrimination?
During embryonic or newborn stages of life in the thymus.
What happens to T-cells that recognize self-antigens?
They are eliminated in the thymus by clonal deletion.
Clonal deletion
The removal of self-reactive T-cell clones to prevent autoimmunity.
If it fails → Self-reactive T-cells persist and can cause autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune diseases
Occur when the immune system turns against the body’s own molecules
Include:
lupus
rheumatoid arthritis
insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
multiple sclerosis
Immunodeficiency diseases
Occur when an immune response is defective or absent
Allergies
Produced when body mounts massive inflammatory response to foreign substance (allergen) that is not in itself harmful
Triggers release of histamine and heparin
“Over-reaction” by body
• Response ranges from mild to life-threatening (sneezing vs. asthma)
Passive immunity
Transfer of antibodies from one individual to another to provide temporary protection against pathogens
Ex: Breastfeeding
Axon
The long threadlike part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells.
Dendrite
The branched, tree-like extensions of a neuron that receive chemical and electrical signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body
Open circulatory system
System in which the blood is mixed with interstitial fluid and directly covers the organs
Pumps hemolymph into body cavities where it directly bathes organs before returning to the heart, making it a low-pressure and less efficient system.
Found in: All arthropods and most mollusks
Closed circulatory system
System in which the blood is separated from the bodily interstitial fluid and contained in blood vessels
Found in: vertebrates, earthworms, squids, and octopuses
Arteries (arterioles)
Carry blood away from the heart to body organs and tissues; most high O2
Veins (venules)
Return blood to the heart; most high CO2
Have valves
Double circulation
Blood is pumped a second time after it loses pressure in the lungs
Pulmonary circuit
Carries blood between the heart and gas exchange tissues in the lungs
Systemic circuit
Carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body
Three chambered heart
Exists in: Amphibians & Reptiles
Consists of:
• Two atria
• Right – receives blood from body
• Left – receives blood from the lungs
• One ventricle
• Sends blood out of the heart
Four chambered heart
Consists of:
• Two atria
• Right – receives blood from body
• Left – receives blood from the lungs
• Two ventricles
• Right – sends blood to lungs
• Left – sends blood to body
• No mixing, divided sides
• Right = No O2
• Left = O2
“Lub” sound
When valves between atria and ventricles close
• Valves = atrioventricular (bi- & tricuspid)
“Dub” sound
Produced by closing of valves between ventricles and arteries
• Valves = Semi-lunar (aortic & pulmonary)
Capillaries
Thin walls consisting of a single layer of epithelial cell
• Narrow = about as wide as one red blood cell
• Allows RBCs to squeeze through
• exchange gas and fluid with the interstitial fluid
• Only 5-10% f the time is blood flowing through
Blood Pressure
Force blood exerts on vessel walls
• depends on cardiac output and resistance of vessels to expansion
• decreases as blood moves away from the heart
Systolic Pressure
Ventricular contraction
Top # in blood pressure reading
Diastolic pressure
Low pressure between contractions.
Bottom # in blood pressure reading
Hypertension
Simply means high blood pressure.
The heart has to work harder, weakening the heart over time
Arteriosclerosis
(Umbrella term)
Increased plaque formation from tiny ruptures
“Hardening of the arteries”
Arteries become thick, stiff, and less elastic
Happens with aging, hypertension, diabetes
Reduces the artery’s ability to expand
Broad term that includes several conditions
Think: overall stiffness
Atherosclerosis
Increased risk of blood clot formation
“Fatty hardening of the arteries”
Caused by plaque buildup (fat, cholesterol, calcium)
Plaque forms inside the arterial wall
Narrows the artery → reduced blood flow
Can lead to heart attacks, strokes
Think: plaque clogging