anatomy lecture 4 YAY
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
what is the basic function of all muscle tissue?
generating force (muscle tension)
what is the function of intercalated discs?
facilitate coordinated heart contraction and electrical conduction
what muscle type is made up of long, multinucleated cells arranged parallel to one another?
skeletal muscle tissue
what do skeletal muscles do?
extend nearly the entire length of muscle
what is skeletal muscle attached by?
connective tissue to skeleton
what is one distinct feature of cardiac muscle cells?
they are branched with one to two nuclei
what do intercalated discs do?
join adjacent cells and permit coordination of contraction
what do intercalated discs contain?
gap junctions and desmosomes
what links smooth muscle tissue?
gap junctions
types of muscle tissue (image)
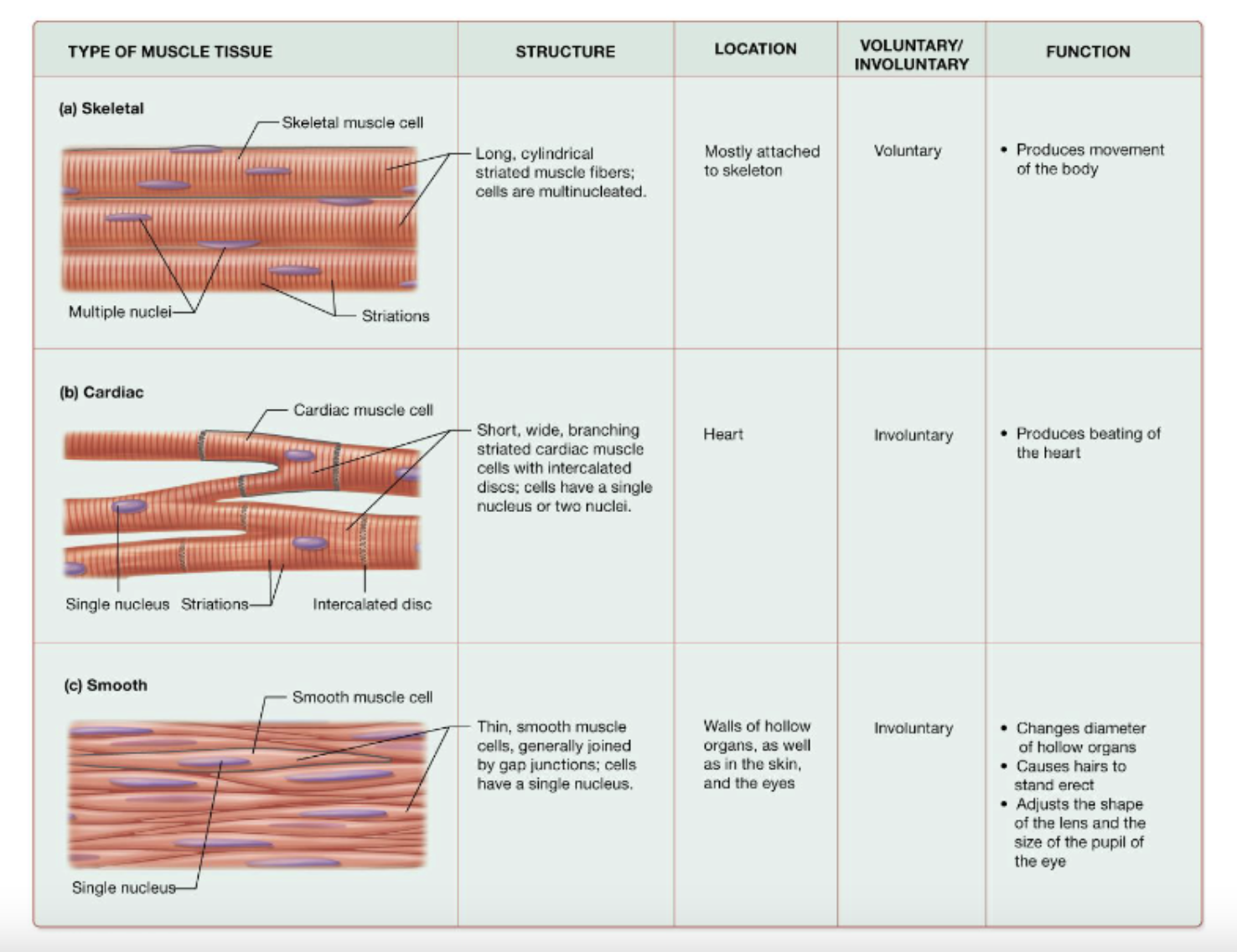
what are the properties of muscle cells?
contractility, excitability, and conductivity, extensibility, and elasticity
what is contracility?
ability to contract (does not involve shortening of cell) and proteins in cell draw closer togehter
what is excitability?
ability to respond to stimulus (chemical, mechanical stretch, or local electrical signals)
what is conductivity?
ability to conduct electrical charges across entire plasma membrane
what is extensiblility?
ability to be stretch (up to 3 times resting length) without rupturing
what is elasticity?
ability to return to original length after stretching
what does the prefix sarco mean?
related to muscle
function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum (3)
lipid and carbohydrate synthesis, calcium (ca2+) storage, and detoxifying agent
function of sarcoplasmic reticulum
storing and releasing calcium ions (Ca2+)
function of rough endoplasmic reticulumn (3)
protein synthesis, bank of calcium, deliver calcium to myofibril for muscle contraction
what does the term tendon mean?
muscle to bone
what happens if you do flexion for biceps?
the triceps will relax
what happens if you do extension for triceps?
the biceps will relax
function of terminal cisternae? (2)
help deliver calcium to the sarcoplasm and are storage sites for calcium ions (Ca2+)
function of (transverse) T-tubles?
conduct impulses from the surface to the interior of the muscle fiber, helping calcium ions move for muscle contraction
what are the different kinds of myocyte (muscle cell)?
sarcoplasm, sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum
what is the sarcoplasm?
myocyte’s cytoplasm
what is the sarcolemma?
myocyte’s plasma membrane
what is a triad?
a structure consisting of terminal cisternae and transverse (T) tubles
what is cytosol?
the liquid part of a cytoplasm
what is the mitochondria?
powerhouse of cell
what is each myofibril made up of?
thousands of myofilaments
what proteins are present in myofibril?
contractile, regulatory, and structural proteins
function of contractile proteins
generate tension
function of regulatory protiens
dictate when a fiber may contact
function of structural proteins
maintain proper myofilament alignment and fiber stability
what are the three types of myofilaments
thick, thin, and elastic
what are thick filaments?
bundles of contractile protein myosin
what are thin filaments?
proteins actin, tropomyosin, and troponin
what are elastic filaments?
single massive, spring-like structural protein (titin)
function of elastic filaments
stabilizes myofibril structure and resists excessive stretching
what is myosin?
thick filament, has tail and big head connected by a neck
what does the head of myosin do?
has active site that binds with actin
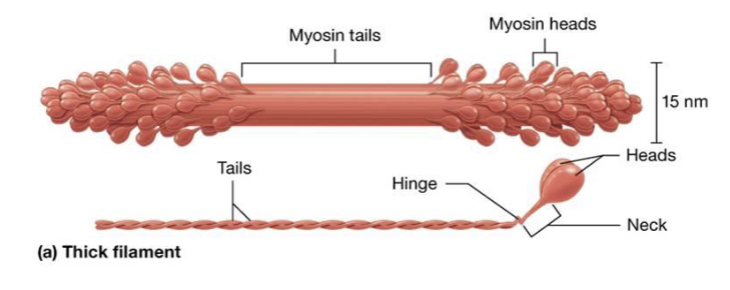
what does actin have and what does it bind with?
it has an active site that binds with myosin heads
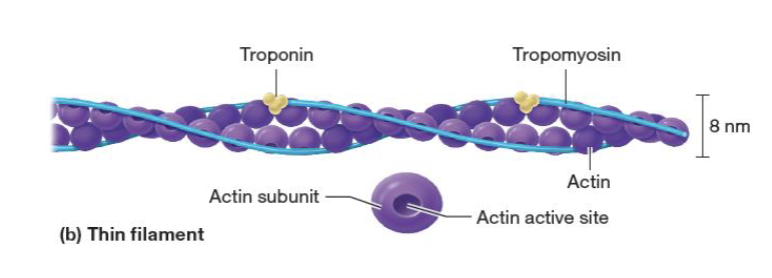
what happens to myosin and actin at the time of contraction?
the head of myosin attaches to actin’s active site and myosin pushes actin to the midline
what does tropomyosin do?
operates as security of actin active site and pins actin in place
function of troponin
pins tropomyosin in place
what is the unit function of a muscle?
sarcomere
myofilament arrangement of sarcomere image
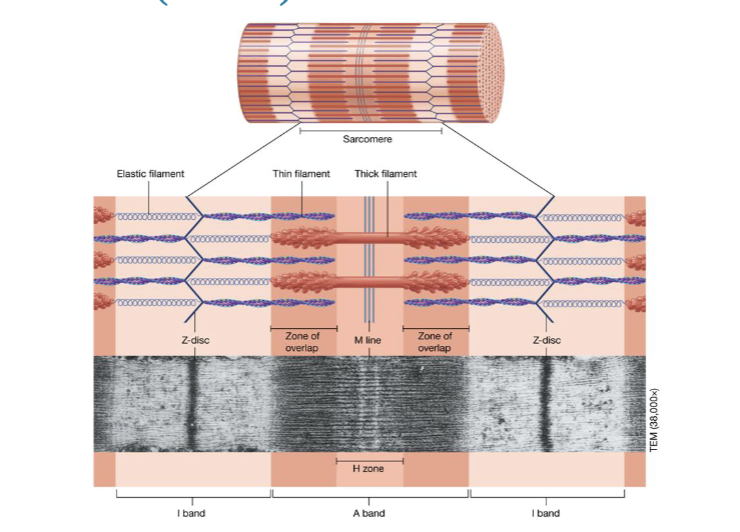
what is the A band?
the whole length of myosin
whats the I band?
the lighter region containing only thin actin filaments
what does the I band do at the time of contraction?
shrinks and decreases in length
what is the zone of overlap?
overlapping actin and myosin
where is H zone found?
H zone is found in the middle of an A band IF there is a zone of overlap in the A band
what is the M line?
the middle of myosin
what is the Z disc?
found in the middle of I band and serves as the anchoring point for actin filaments in the sarcomere, the fundamental unit of muscle contraction
what form a fascicle?
multiple muscle fibers surrounded by endomysiumq
what is each fascicle surrounded by?
perimysium
what makes up a skeletal muscle?
bundles of fascicles surrounded by epimysium
what come together at the end of muscle to form a tendon?
perimysium and epimysium
what layer of thick connective tissue encloses skeletal muscles?
fascia
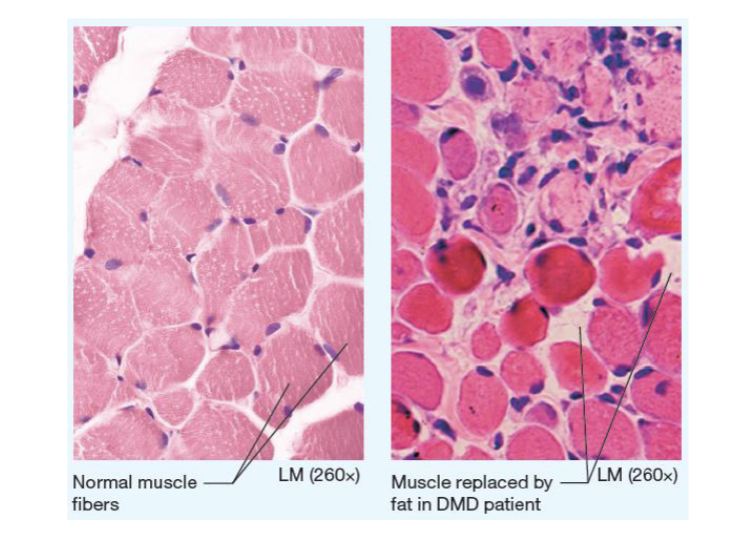
what is duchenne muscular atrophy?
a progressive and severe muscle-wasting disease primarily affecting boys, caused by a lack of the protein dystrophin
relaxed vs contracted sarcomere
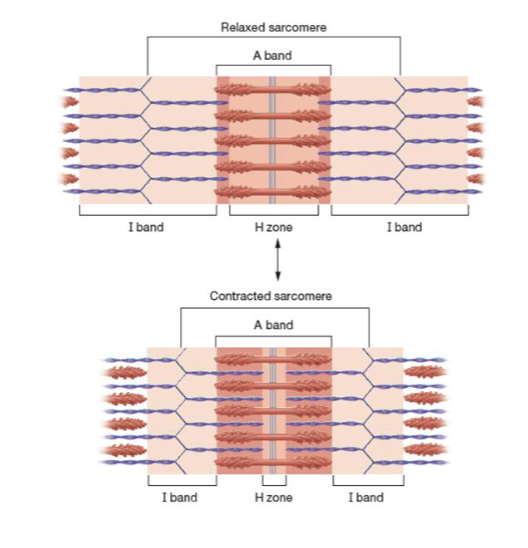
what does sarcomere extend from?
one Z-disc to the next
what do myosin heads to?
attach to actin, pull thin filaments toward M line, bring Z-discs close togher
what makes the neuromuscular junction?
synpase between motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber
function to the neuromyscular junction
transmits nerve impulse/action potential from neuron to sarcolemma of muscle fiber
what does the axon terminal contain?
synaptic vesicles filled with neurotransmitter acetycholine (ACh)
what do neurotransmitters allow?
cell to cell communication
where is the synaptic cleft? what is it filled with?
space between axon terminal and muscle fiber, filled with collagen fibers and gel that anchors neuron in place
describe the motor end plate
folded surface that has many ligand-gated Na+ channels
what opens ligand-gated channels?
ACh is a ligand that does so, allowing Na+ to diffuse into muscle cell
when does neural transmission to a muscle fiber cease?
when acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft
what are the muscle contraction phases?
excitation phase, excitation-contraction coupling, contraction phase
what is the excitation phase?
the process where a muscle cell receives and transmits an electrical signal, leading to a muscle contraction
what is excitation-contraction coupling?
the physiological process that transforms an electrical stimulus into a mechanical response, specifically muscle contraction
what is the contraction phase?
when a muscle generates tension, leading to shortening or movement of the muscle
why is calcium important for acetylcholine?
calcium is needed in order for acetylcholine to be released
why is calcium needed at the time of contraction for troponin
calcium binds troponin
what releases calcium ions?
sarcoplasmic reticulumn
what is hydrolysis of ATP responsible for?
recocking of myosin heads
why does myosin bind to ATP?
to release myosin heads from actin active sites
When does the release of ADP and Pi from myosin occur?
during the power stroke
when do the myosin heads return to their relaxed/low-energy state?
the power stroke
what does the power stroke do?
pulls the thin filaments toward the M lines
what are the sequence of events that occur in preparation for contraction?
Action potential arrives at triad, calcium is released from the terminal cisternae,
calcium binds to troponin, tropomyosin exposes the actin active sites
explain the cross bridge cycle briefly
myosin head binds to actin and forms a cross-bridge, pulls on actin filament resulting in power stroke, then detaches to bind to a new active site
what is crossbridge detachment?
myosin head separates from the actin filament
what causes myosin heads to be reactivated?
ATP binding and hydrolosis
why do calcium channels in the SR close during muscle fiber contraction?
the resting membrane potential is restored
what happens to calcium during muscle fiber relaxation?
calcium is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulumn
when acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft degrades acetylcholine, what happens?
ligand-gated sodium channels close
what does sarcolemma repolarization during relaxation do?
restores the resting membrane potential
what aspect of muscle relaxation requires ATP?
pumping calcium ions back into sarcoplasmic reticulum
what is rigor mortis?
progressive stiffening (contraction) of skeletal muscles that begins 3-4 hours after death
what happens to muscle fibers during rigor mortis?
muscle fibers are unable to relax without ATP
what is a muscle twitch?
smallest musle contraction
what are the three phases of twiches?
latent, contraction, relaxation, and refractory period
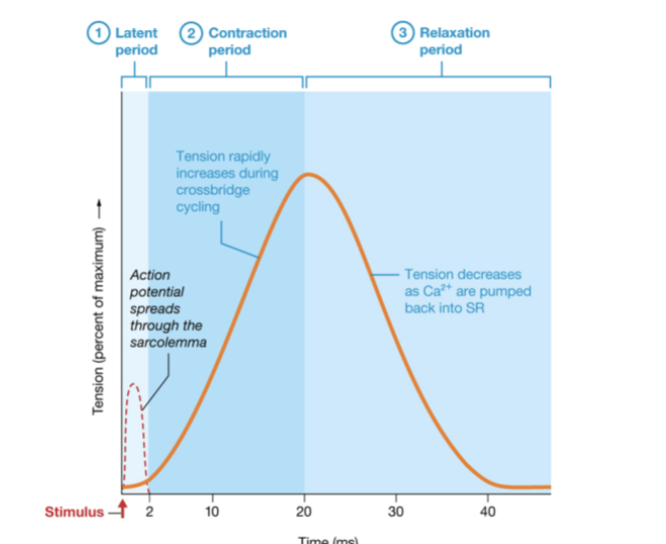
what does the latent period do?
time for action potential to propagate across sarcolemma
what does the contraction period do?
repeated crossbridge cycles generate tension