Ch 26: Seed Plants
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
evolutionary history of seed plants order
first land plants
first vascular plants
first seed plants
forests of seedless vascular plants dominate swampy land
first gymnosperms
gymnosperms forests replace lycophyte and fern forests
cycads and conifers dominate landscape
flowering plants appear
flowering plants begin to diversity
did seed plants come before or after vascular plants?
after
female gametophyte: seeds and pollen as an evolutionary adaptation to dry land
the egg
endosperm-producing cell (supports the growth of the embryo)
embryo: produced from the diploid zygote, grows into the sporophyte when seed germinates
seed: offers the embryo protection, nourishment, and a mechanism to maintain dormancy, allow plants to disperse the next generation through both space and time
male gametophyte: seeds and pollen as an evolutionary adaptation to dry land
pollen grands (contain the sperm of the plant)
protected from dessication
not dependent on water to reach the female organs
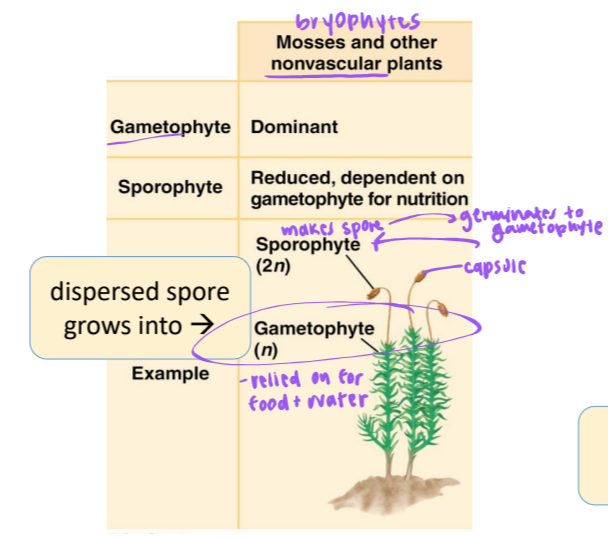
gametophyte-sporophyte relationship in Bryophytes (mosses and other nonvascular plants)
gametophyte: dominant
sporophyte: reduced, dependent on gametophyte for nutrition
dispersed spore grows into: gametophyte
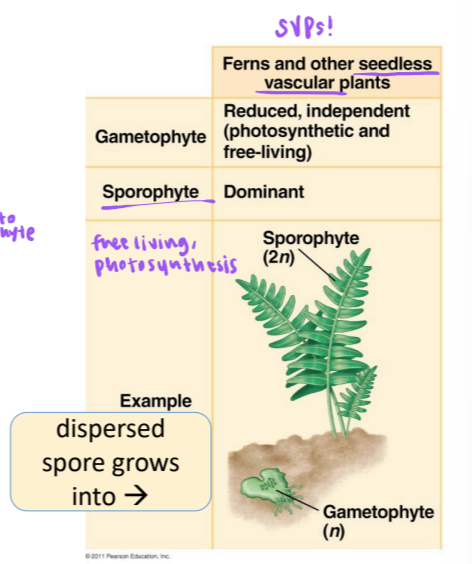
gametophyte-sporophyte relationship in SVPs (ferns and other seedless vascular plants
gametophyte: reduced, independent (photosynthetic and free-living)
sporophyte: dominant
dispersed spore grows into: gametophyte
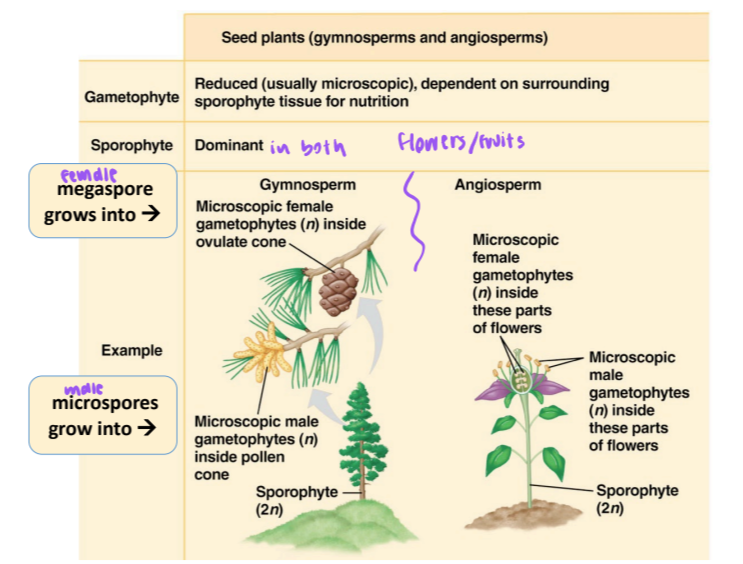
reproductive adaptations of seed plants (reduced gametophyte) (seed plants gymnosperms and angiosperms)
gametophyte: reduced (usually microscopic), dependent on surrounding sporophyte tissue for nutrition
sporophyte: dominant
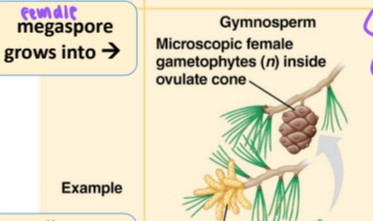
in gymnosperms, what does the megaspore grow into?
microscopic female gametophytes (n) inside the ovulate cone

in gymnosperms, what does the microspore grow into?
microscopic male gametophytes (n) inside pollen cone

in angiosperms, what does the megaspore grow into?
microscopic female gametophytes (n) inside these parts of flowers
in angiosperms, what does the microspore grow into?
microscopic male gametophytes (n) inside these parts of flowers
reproductive adaptations of seed plants 1
reduced and retained gametophytes
seed plants are heterosporous
megaspores (grow into female gametophytes)
microspores (grow into male gametophytes)
both gametophytes mature within sporangis
highly reduced in size
protected from drying and UV
retained
instead of the sporangia releasing spores, the gametophytes grow within the sporangia itself
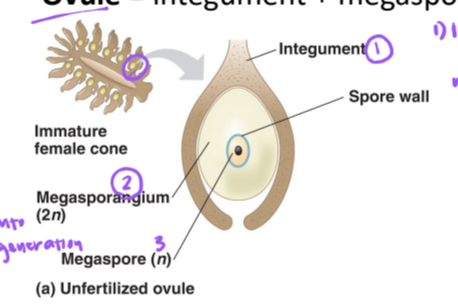
ovule
integument + megasporangium + megaspores
integument
protective layer of sporophyte tissue, protects the megasporangium
microphyle
small opening in the integument of the ovule, through sperm are able to access the egg
megaspore germinates within _____, develops into tiny female __________, produces egg which will eventually be fertilized
ovule, gametophyte
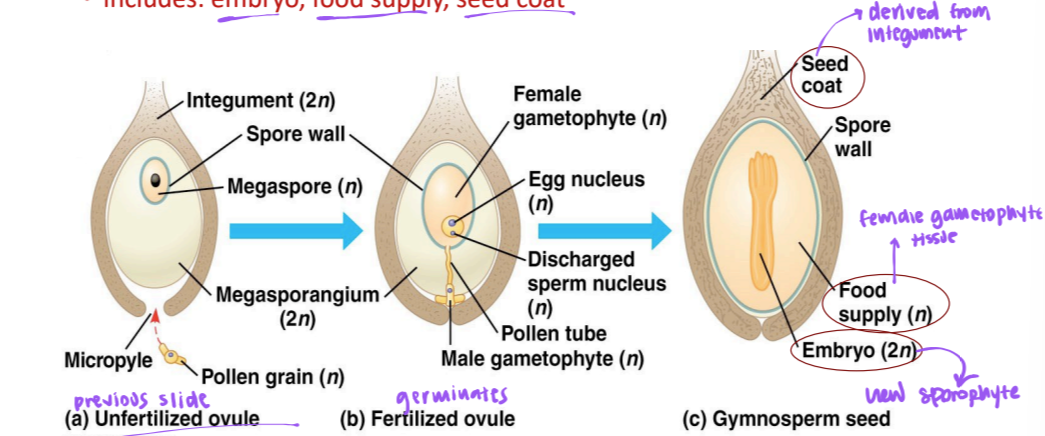
seeds
develops from fertilized ovule
includes embryo, food supply seed coat
what structure is the seed coat derived from?
integument
what tissue is the food supply derived from?
female gametophyte tissue
pollen grains def
male gametophyte surrounded by pollen wall (partly secreted by sporophyte)
pollen grains
capable of long dispersal, tough & resistant, & sperm nuclei does not require external H2O for fertilization
sporopollenin in the pollen wall protects pollen grains
pollination
pollen grain germinates → pollen tube → sperm discharged into female gametophyte
pollination
transfer of a pollen to a part of the seed plant that contains the ovule
sporopollenin
in the pollen wall protects pollen grains
does sperm nuclei require external H2O for fertilization?
no
gymnosperms characteristics
naked seeds (partially sheltered by sporophylls)
separate male and female gametes
pollination by wind
tracheids
life cycle involves alternation of generations
reduced male and female gametophytes
dominant sporophyte
all are heterosporous
male and female reproductive organs can form in cones or strobili
monoecious or dioecious
monoecious
male and female sporangia on same plant
dioecious
on separate plants
tracheids
lignified cells in the xylem of vascular plants
true or false. in gymnosperms, male and female reproductive organs can only form in cones.
false. in gymnosperms, male and female reproductive organs can only form in cones or strobili
what is the dominant in gymnosperms?
sporophyte
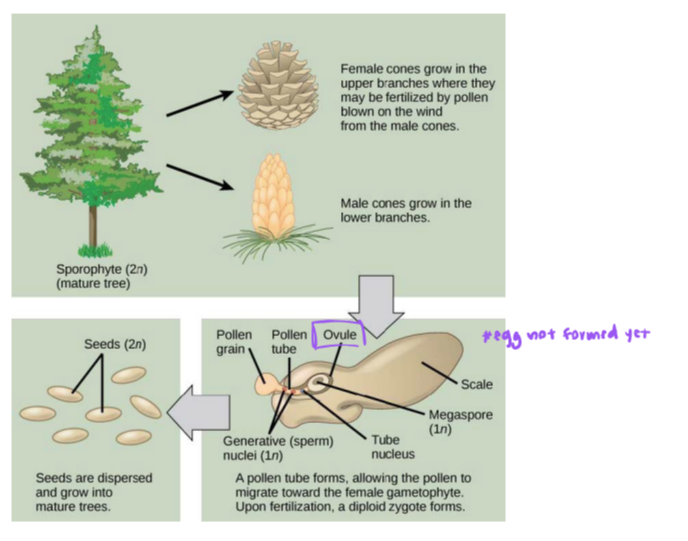
life cycle of a conifer (gymnosperm)
female cones grow in the upper branches where they may be fertilized by pollen blown on the wind from the male cones
male cones grow in the lower branches
seeds are dispersed and grow into mature trees
seeds (2n)
a pollen tube forms, allowing the pollen to migrate toward the female gametophyte. upon fertilization, a diploid zygote forms
pollen grain, pollen tube, ovule, scale, megaspore (n), tube nucleus, generative nuclei (sperm -1n)
5 phyla of extant seed plants
gymnosperms:
coniferphyta
cyacdophyta
gnetophyta
ginkophyta
angiosperms
anthophyta
2 primtive gymnosperms
cyacdophyta and cinkgophyta
coniferphyta
gymnosperms: conifers
most diverse gymnosperms today
“cone-bearers”
male pollen cone (sperm not motile0
female ovulate cone
monoescions
dominate high altitudes & latitudes in N. hemisphere
most are evergreen w/ needle-like leaves
coniferphyta ex.
pine fir, spruce, sequiias
most diverse gymnosperms
coniferophyte
cycadophyta
gymnosperms: cycads
100 species
fern-like or palm-like fronds radiate from central stem
central female and male cones
with flagellated sperm
beetles are involved in pollination of some cycads
dioecious
which gymnosperm phylum has flagellated sperm?
cycadophyta
ginkgophyta
gymnosperms: ginkgos
one extant tree: Ginkgo biloba
herbal medicine
with flagellated sperm
dioescious
female sporophylls, not cones
male sporophylls, in strobili
sporophylls are modified leaves: modified to carry sporangis
which gymnosperm has flagellated sperm?
ginkgophyta
what is the one extant tree of ginkgophyta?
Ginkgo biloba
gnetophyta
gymnosperms: gnetophytes
3 distinct genera:
Gnetum in tropics, Welwitschia in SW Africa deserts, Ephedra in US deserts
male & female strobili; sperm not motile
Ephedra - herbal medicine (Ephedrine)
amphetamine!
where is Gnetum found?
gnetophyta
tropics
where is Welwitschia found?
gnetophyta
SW Africa deserts (Namib desert)
where is Ephedra found?
gnetophyta
U.S. deserts
angiosperms key innovation
flowers and fruits
flower
structure specialized to facilitate sexual reproduction
success mainly due to coevolution with pollinators
function of flowers
to ensure pollination
to protect a developing embryo
male flower parts
stamen
anther
filament
female flower parts
stigma
carpel
style
ovary
sepals (calyx)
green leaf-like appendages that enclose the rest of the flower
calyx + corolla
perianth (non-reproductive system)
petals
brightly colored appendages that aid in attracting pollinators
stamen
collectivelyc alled androecium
filament
stalk that holds up pollen-producing sac
anther
terminal sac that produces pollen
carpel
aka “pistil” - known collectively as gynoecium
stigma
sticky tip of carpel that receives pollen
style
long tube leading from stigma to ovary
ovary
structure at base of the carpel that produces ovules
ovules becomes fruit after fertilization
ovules
develop into seeds if fertilized
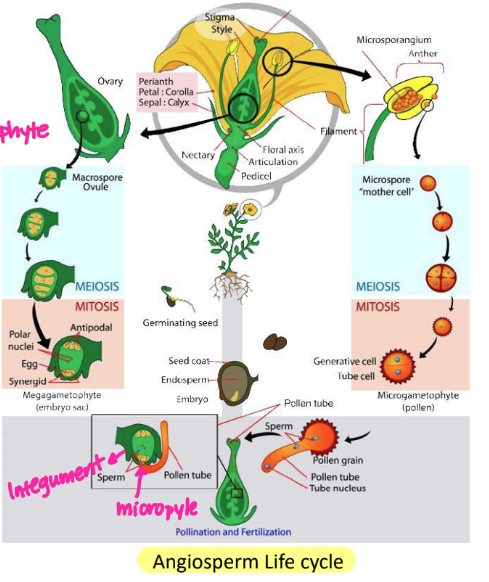
angiosperm: life cycle 1
microsporangia → male sporocycts (2n) → microspores (n) (pollen grains)
pollen grains: 1 generative cell, 1 tube cell
____ contains ovule, ovule contains ___________
ovary, megasporangium
angiosperm: life cycle 2
ovule → megasporangiusm → megasporocyte (2n) → (meiosis) → 4 megaspores (n) → only large megaspores survives → (mitosis 3x) →8 nuclei distributed among 7 cells of gemale gametophyte → 3 cells at one pole become egg and 2 synergids (remaining 3 cells become antipodal cells) , center cell → 2 polar nuclei
angiosperms: double fertilization with 2 sperm nuclei
happens in ALL angiosperms
one fuses w/ egg, forming zygote (2n)
one fuses w/ 2 central nuclei (polar nuclei), forming endosperm (3n) food supply in seed
fruit
mature ovary of a flower, thickens around seeds
may include some additional tissues as well
may be fleshy or dry
protects seeds
main function is enhancing seed dispersal
embryo
radicle (small root)
1 or 2 leaf like organs : cotyledons
cotyledons
transmits broken down food reserves from endosperm (storage site) to the embryo
basal
diverged from other angiosperms early in the history of the group
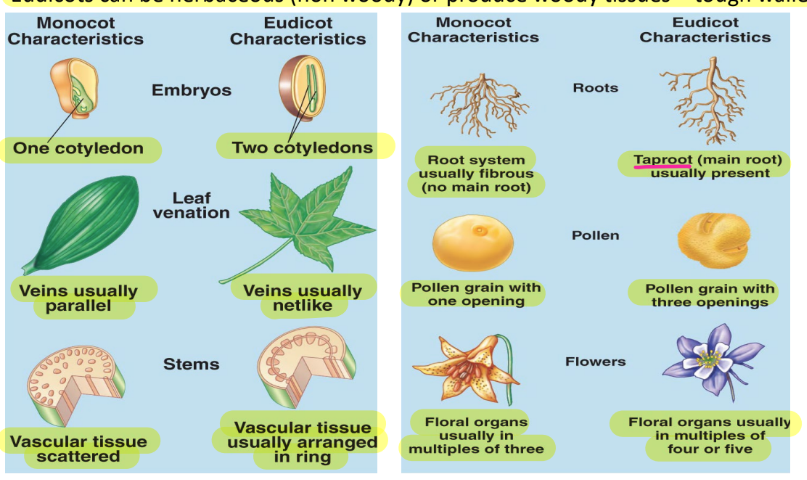
2 big gorups of angiosperms
monocots and eudicots
monocots ex
orchids, palms, lilies, grasses, corn, rice, sugarcane
dicots ex.
oaks, peas, roses, potatoes
true woody tissue is ______ found in monocots
rarely
eudicots can be _______ (non woody) or produce woody tissues - tough walled xylem cells
herbaceous
Seed Plants & People
Almost all food & beverages & spices
(80% calories globally!)
Wood products, including paper
Fuel
Fiber for clothing, rope
cotton, linen, jute, hemp
Secondary compounds:
countless drugs & medicines
perfumes
latex rubber
Ornamental plants
what percentage of prescription drugs contain an active ingredient from plants?
25%