[O Chem] Hydroxy
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
[ACIDITY]
The strength of an acid depends on the stability of its…
conjugate base. A more stable conjugate base will dissociate to a greater extent, producing more H+ ions.
[ACIDITY]
Compare the relative acidities of alcohols, phenols, and water.
alcohol < water < phenol
The presence of electron-donating alkyl group increases the intensity of the negative charge on the oxygen atom in the alkoxide anion. This makes alkoxide less stable than OH-.
The p-orbital of the oxygen atom in phenol overlaps with the adjacent pi electron cloud of the benzene ring, allowing the negative charge on the oxygen to delocalise into the benzene ring, reducing the intensity of the negative charge. This makes phenoxide more stable than OH-.
[PREPARATION]
How do you prepare an alcohol from an alkene?
Electrophilic addition
H2O (g), H3PO4 catalyst, high temp and pressure
cold conc. H2SO4, followed by H2O (l), heat
[PREPARATION]
How do you prepare an alcohol from a halogenoalkane?
Nucleophilic substitution/alkaline hydrolysis
NaOH (aq), heat
[PREPARATION]
How do you prepare alcohols from carbonyl compounds?
Reduction
LiAlH4 in dry ether
NaBH4 in methanol
H2, Ni catalyst, high temp and pressure
Aldehyde → 1º alcohol
Ketone → 2º alcohol
[PREPARATION]
How do you prepare alcohols from carboxylic acids?
Reduction
LiAlH4 in dry ether
Carboxylic acids → primary alcohols
[EXTENTION]
Why must reduction with LiAlH4 be conducted in dry ether?
LiAlH4 will react with water and must hence be in anhydrous conditions.
[REACTIVITY]
What makes alcohols electrophilic?
The electronegative oxygen polarises the C-OH bond towards the oxygen atom, making the carbon atom electron-deficient.
[REACTIVITY]
What makes alcohols nucleophilic? Explain if they are strong or weak nucleophiles.
The lone electron pair on the oxygen atom.
Weak nucleophiles as alcohol molecules are uncharged and the highly electronegative oxygen atom strongly attracts the lone pair, making it less available for donation.
[REACTIVITY]
How may the nucleophilicity of alcohols be increased?
Acid-metal displacement/redox with sodium metal to generate an alkoxide ion.
[REACTIONS]
How do alcohols react with reactive metals? What are the products formed?
Acid-metal displacement/redox to give alkoxide salts and H2 (g).
[REACTIVITY]
Do alcohols react with bases such as hydroxides and carbonates?
No as alcohols are neutral compounds.
[REACTIONS]
How do you form esters from alcohols? Is the alcohol acting as a nucleophile or electrophile?
Condensation/nucleophilic acyl substitution, nucleophile
RCOOH: RCOOH, conc. H2SO4 catalyst, heat under reflux.
RCOCl: RCOCl, r.t.p.
[EXTENSION]
What are the two functions of H2SO4 in condensation between alcohols and carboxylic acids?
Dehydrating agent removes H2O, shifting the position of equilibrium to the right by LCP hence increasing the yield of the ester
Supplied H+ to catalyse the reaction
[EXTENSION]
Why does the condensation reaction between an alcohol and acyl chloride require milder conditions and proceed to completion, but requires heat, a catalyst and is reversible between an alcohol and acyl chloride?
Acyl chlorides are more reactive.
The -OH group in the carboxylic acid is electron donating by resonance, making the carboxyl carbon less electron deficient and electrophilic.
The -Cl group in the acyl chloride is electron withdrawing by induction, making the carbonyl carbon less electron deficient and electrophilic.
The C-Cl bond is also weaker than the C-OH bond.
[EXTENSION]
Is the formation of esters from alcohols and carboxylic acids or acyl chlorides preferred?
Acyl chlorides. the reaction has a higher yield.
[REACTIONS]
How do you form an ether from a halogenoalkane?
Redox: alcohol, Na(s)
Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution: alkoxide, halogenoalkane, r.t.p.
[REACTIONS]
How do you form alkenes from alcohols?
Elimination
excess conc. H2SO4, heat
conc. H3PO4, heat
Al2O3, heat
[REACTIONS]
How do you form halogenoalkanes from alcohols?
Nucleophilic substitution.
Dry HX (g), heat, anhydrous ZnCl2 for HCl
PX3 (l for Cl, s for Br and I), heat
PCl5 (s)
SOCl2 in pyridine, heat
[REACTIONS]
How do you form aldehydes from alcohols?
Oxidation of 1º alcohols
K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, heat with immediate distillation
[REACTIONS]
How do you form carboxylic acids from alcohols?
Oxidation of 1º alcohols
KMnO4/K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, heat under reflux
[REACTIONS]
How do you form ketones from
Oxidation of 2º alcohols
KMnO4/K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, heat under reflux
[EXTENSION]
What are some possible side reactions that can occur due to KMnO4?
Side-chain oxidation
Oxidative cleavage
[TESTS]
List the 4 tests that can be used to identify alcohols
Nucleophilic substitution: PCl5 (all alcohols)
Oxidation: KMnO4/K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, heat (1º and 2º alcohols)
Oxidation: iodoform (methyl alcohol)
Redox: Na(s) (all alcohols)
[TESTS]
For a test for alcohols with PCl5, state the following
Species required for positive test
Reagents and conditions
Type of reaction
Observations
Alcohols
PCl5(s)
Nucleophilic substitution
White fumes of HCl
[TESTS]
For a test for alcohols with KMnO4/K2Cr2O7, state the following
Species required for positive test
Reagents and conditions
Type of reaction
Observations
1º or 2º alcohol
KMnO4/K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, heat
Oxidation
Purple KMnO4 decolourises/Orange K2Cr2O7 turns green
(1º and 2º alcohols can be further distinguished using 2,4-DNPH)
[TESTS]
For a test for alcohols with CI3, state the following
Species required for positive test
Reagents and conditions
Type of reaction
Observations
Methyl alcohol
I2(aq), NaOH(aq), warm
Oxidation
Decolourisation of brown iodine solution, pale yellow precipitate of CHI3
[TESTS]
Write out the mechanism for iodoform reaction with methyl alcohols. Hence, write out a balanced equation for the reaction.
RCH(OH)CH3 + 4I2 + 6OH- → RCOO- + CHI3 + 5I- + 5H2O
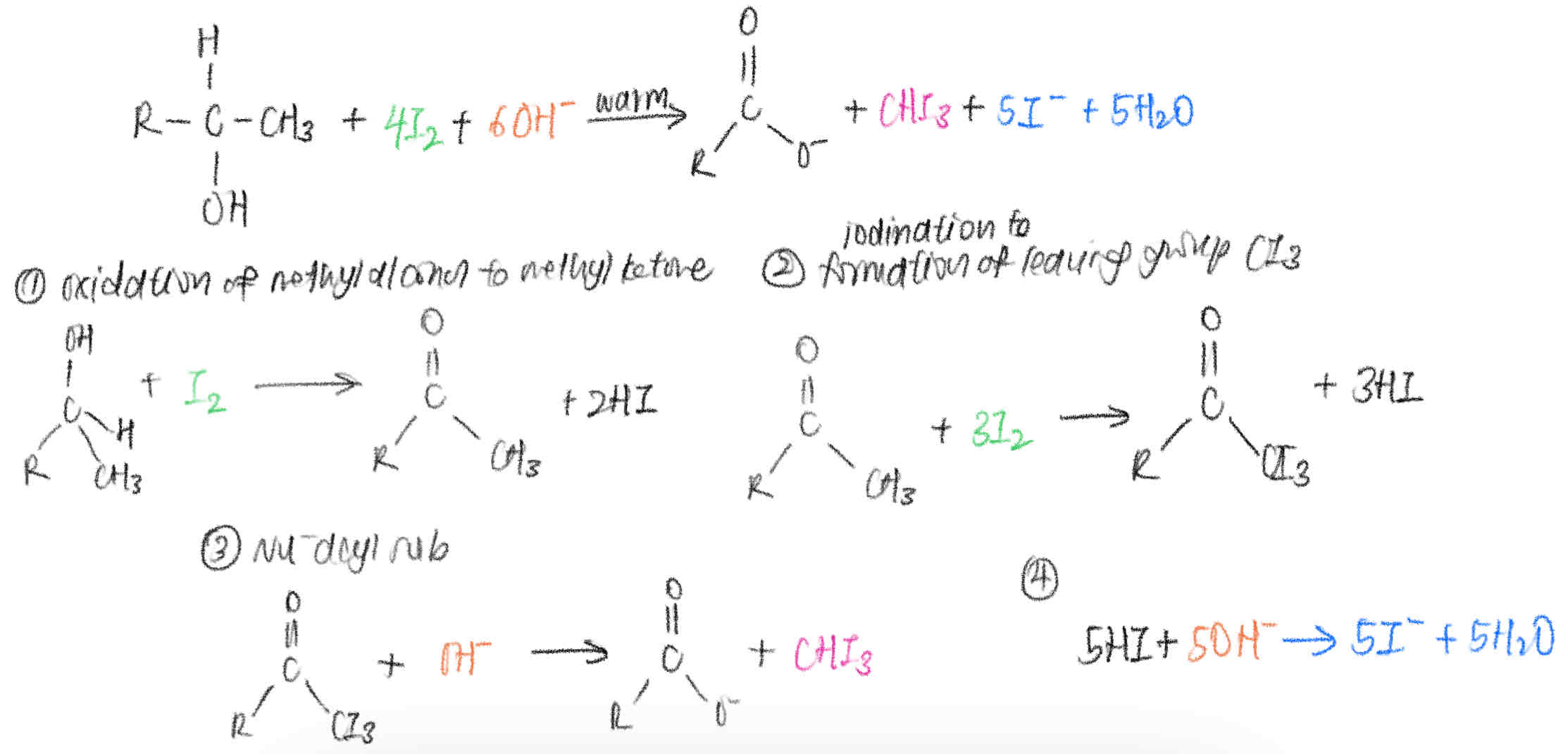
[ELUCIDATION]
List 3 types of step-down reactions
Oxidative cleavage
Benzene side-chain oxidation
Iodoform
[TESTS]
For a test for alcohols with Na(s), state the following
Species required for positive test
Reagents and conditions
Type of reaction
Observations
Alcohol
Na(s), r.t.p.
Redox/acid-metal displacement
Effervescence of colourless, odourless gas that extinguishes a burning splint with a ‘pop’ sound
[REACTIVITY]
Explain the reactivity of phenol as an electrophile and nucleophile
Electrophile: Non-electrophilic. The lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of phenol delocalises into the benzene ring, giving the C-O bond partial double bond character, making it difficult to break → does not undergo nucleophilic substitution of -OH
Nucleophile:
The ring is more nucleophilic than benzene. The lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of phenol delocalises into the benzene ring, increasing the electron density of and activating the ring → more reactive to electrophilic substitution at the benzene ring (milder conditions, tri-sub in aqueous medium)
The hydroxyl oxygen is less nucleophilic than in an alcohol. The lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom of phenol delocalises into the benzene ring, making them less available for nucleophilic attack → cannot undergo condensation with COOH
[REACTIVITY]
How do you increase the nucleophilicity of the hydroxyl oxygen in phenol?
Formation of phenoxide ion through redox reaction with Na(s) or neutralisation reaction with NaOH(aq)
[REACTIONS]
How do you form phenoxide ions from phenol?
Redox/acid-metal displacement: Na(s), r.t.p.
Neutralisation/acid-base reaction: NaOH (aq), r.t.p.
[REACTIONS]
How do you form phenyl esters from phenol?
Form phenoxide ion through redox/neutralisation reaction: Na(s)/NaOH(aq), followed by condensation/nucleophilic acyl substitution: RCOOH, r.t.p.
Condensation/nucleophilic acyl substitution: RCOCl, r.t.p.
[REACTIONS]
How do you obtain a monobrominated phenol? What do you observe?
Electrophilic substitution. Br2 in CCl4, r.t.p.
Orange-red Br2 decolourises
[REACTIONS]
How do you obtain a tribrominated phenol? What do you observe?
Electrophilic substitution. Br2(aq), r.t.p.
Orange Br2(aq) decolourises, white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromophenol observed
[REACTIONS]
How do you obtain mono-substituted nitrophenol from phenol?
Electrophilic substitution. Dilute HNO3(aq), r.t.p.
[REACTIONS]
How do you obtain poly-substituted nitrophenol from phenol?
Electrophilic substitution. Conc. HNO3(aq), r.t.p.
[EXTENSION]
Why is phenol able to undergo triple substitution in aqueous medium?
Ion-dipole interactions with water molecules help stabilise the carbocation intermediate, lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
[TESTS]
List 2 confirmatory tests for phenol.
Electrophilic substitution with Br2(aq)
Complex formation with neutral solution of FeCl3(aq)
[TESTS]
For a test for phenols with FeCl3, state the following
Reagents and conditions
Type of reaction
Observations
Neutral solution of FeCl3(aq)
Complex formation
Violet complex observed
[TESTS]
For a test for phenols with Br2(aq), state the following
Reagents and conditions
Type of reaction
Observations
Br2(aq), r.t.p.
Electrophilic substitution
Orange Br2(aq) decolourises, white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromophenol observed
[TESTS]
Why is aqueous bromine used to test for phenols instead of bromine in CCl4?
Tribromophenol produced is insoluble in water due to the hydrophobic benzene ring, forming a white ppt in aqueous medium. However, tribromophenol can form favourable id-id interactions with non-polar CCl4 solvent, and no white ppt will be formed.
Phenol can dissociate in aqueous medium to form phenoxide which undergoes electrophilic substitution more readily with bromine due to the negative charge on the oxygen, making the benzene ring more electron rich than phenol in aqueous medium. Phenol cannot dissociate in CCl4 as CCl4 is not a phenol acceptor. Hence, only one bromine atom can be substituted on the benzene ring in CCl4 as opposed to three in aqueous medium.