Unit 4: Biological Bases of Behavior
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:00 PM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
2
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
3
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system)
4
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight (arouses)
5
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest (calms)
6
New cards
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
7
New cards
pituitary gland
Under the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands (master gland)
8
New cards
adrenal gland
Just above the kidneys and secretes hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress (adrenaline)
9
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers made by endocrine glands
10
New cards
lateralization
brain hemispheres are functionally different
11
New cards
corpus callosum
neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and allowing communication between them
12
New cards
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the corpus callosum
13
New cards
brain plasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing or building new pathways
14
New cards
neuron
nerve cell
15
New cards
synapse
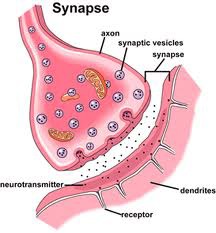
16
New cards
reuptake
neurotransmitters that didn't bind to receptor sites are taken back into the synaptic vesicles
17
New cards
neurotransmitters
chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another
18
New cards
acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter involved in learning, memory and muscle movement (linked the Alzheimer’s)
19
New cards
serotonin
neurotransmitter that affects hunger, sleep, arousal, and mood
20
New cards
dopamine
neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system (linked to Parkinson’s, too little dopamine vs and schizophrenia, too much dopamine)
21
New cards
endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure
22
New cards
resting potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse
23
New cards
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
24
New cards
all-or-nothing principle
Once action potential reaches threshold, either fires or doesn't
25
New cards
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
26
New cards
stimulant drugs
drugs that stimulate or excite the central nervous system (ex. caffeine, cocaine)
27
New cards
depressant drugs
drugs that tend to slow down the central nervous system (ex. alcohol, Xanax)
28
New cards
hallucinogens
distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input (ex. LSD, cannabis)
29
New cards
opiates
depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety (ex. heroin)
30
New cards
circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle (ex. wakefulness, body temp)
31
New cards
agonist drug
mimics and enhances a neurotransmitter's effect
32
New cards
antagonist drug
binds to a receptor and blocks a neurotransmitter's effect
33
New cards
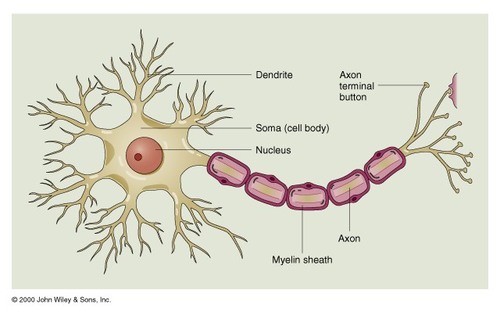
dendrites, cell body, axon, axon terminals/terminal buttons (contains neurotransmitters)
parts of a neuron
34
New cards
afferent neurons
sensory neurons ("as")
35
New cards
efferent neurons
motor neurons ("em")
36
New cards
left hemisphere
controls the right side of the body; analytical, language, math
37
New cards
right hemisphere
controls the left side of the body; creative, intuitive, spacial
38
New cards
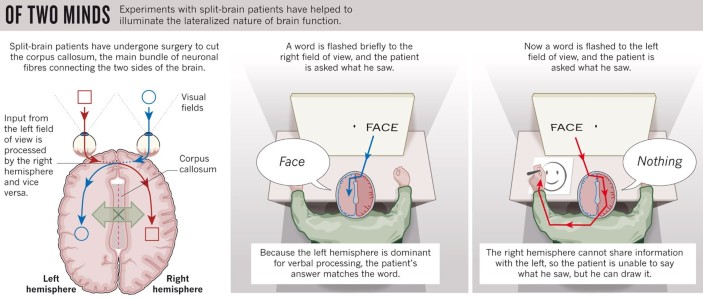
effect of split brain
able to say the word on right side of the dot but only able to draw the word on the left side of the dot
39
New cards
parallel processing
process many aspects simultaneously, used to process well-learned info and solve familiar problems
40
New cards
NREM 1
falling asleep, brain still active but everything is slowing down, high amplitude theta wave
41
New cards
NREM 2
light sleep, less aware of surroundings, sleep spindles, eye movements stop, body temp drops
42
New cards
NREM 3
deep sleep, muscles completely relaxed, brain consolidates memories, delta waves
43
New cards
REM
rapid eye movement, vivid dreams occur, brain consolidates emotional memories, brain activity similar to when awake but body paralyzed
44
New cards
GABA
inhibitory neurotransmitter that blocks signals going through neurons, good for calming stress and anxiety
45
New cards
norepinephrine
excitatory neurotransmitter important in controlling alertness, wakefulness, mood, and attention
46
New cards
thalamus
part of brain stem that is the sensory switchboard, directs all sensory messages except smell
47
New cards
medulla
part of brain stem that controls heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing
48
New cards
reticular formation
part of brainstem that controls alertness
49
New cards
limbic system
system that consists of hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala (associated with emotional drives, memory formation, sexual drive, etc.)
50
New cards
hippocampus
part of brain that processes explicit memories for storage
51
New cards
hypothalamus
controls endocrine system and regulates homeostasis
52
New cards
amygdala
linked to emotion and helps us remember emotionally charged events
53
New cards
motor cortex
generate signals to direct the movement of the body (part of frontal lobe)
54
New cards
somatosensory cortex
responsible for receiving and processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain (part of parietal lobe)
55
New cards
frontal lobe
speaking, muscles movements, making plans, abstract thinking
56
New cards
parietal lobe
receive sensory input for touch and body position
57
New cards
temporal lobe
processes speech, sounds, and smells and stores long-term memory
58
New cards
occipital lobe
receive info from visual fields
59
New cards
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for planning, judgements, and not fully developed until around 25
60
New cards
neural plasticity
the capacity of the nervous system to modify itself, functionally and structurally, in response to experience and injury
61
New cards
pons
part of the brainstem that relays information between different parts of the brain, controls breathing, regulates sleep and arousal, and controls facial sensation and movement
62
New cards
cerebellum
helps coordination, motor control, balance, and movement
63
New cards
cerebral cortex
interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres
64
New cards
activation-synthesis theory
dreams are random neurological firings that have no particular meaning
65
New cards
information-processing theory
we organize our memories as we sleep so our dreams, which often contain elements from what we experienced that day, are a byproduct of that process
66
New cards
Freud’s wish-fulfillment theory
when wishes can't or won't be fulfilled in our waking lives, they are carried out in dreams
67
New cards
latent content
underlying meaning of symbols in dream
68
New cards
manifest content
actual literal subject matter of the dream
69
New cards
somatic nervous system
muscles under conscious control
70
New cards
sleep apnea
stop breathing during sleep
71
New cards
narcolepsy
hard time staying awake during the day
72
New cards
insomnia
trouble sleeping