Cultural Competence, Family Dynamics, and Social Determinants
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Slander
A false statement of fact that is spoken or communicated orally.
Libel
A false statement of fact that is written, printed, or otherwise fixed in a permanent form.
The Burden of Proof Required
The statement was a false, defamatory factual claim, not a statement of opinion. The statement was communicated to a third party. The statement was about the plaintiff and could be understood as such by others. The plaintiff suffered harm to their reputation or finances as a result of the statement.
Health disparity
A particular type of health difference that is closely linked with social, economic, and/or environmental disadvantage.
Social determinants of health
The aspects of the non-medical conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age that affect health functioning and quality of life outcomes.
Marginalized groups
Groups that are more likely to have poor health outcomes and die earlier.
Intersectionality
Research and policy model used to study complexities of people's lives and experiences.
Privilege
A category that represents advantages held by certain groups in society.
Oppression
A category that represents disadvantages faced by certain groups in society.
Racial identity
An individual's sense of belonging and identification with a particular racial group.
Ethnic identity
An individual's sense of belonging to an ethnic group, characterized by shared cultural, social, linguistic, and often religious factors.
Acculturation
The cultural modification or merging of people by adapting to or borrowing traits of a different culture, typically the dominant one.
Assimilation
Process through which individuals or groups from one culture adopt the customs, values, and behaviors of another culture, often resulting in a loss of their original cultural identity.
Cultural Care
Emphasizes the need to provide care based on an individual's cultural beliefs, practices, and values.
Cultural competence
Professional health care must be culturally sensitive, culturally appropriate, and culturally competent to meet the multifaceted health care needs of each person, family, and community.
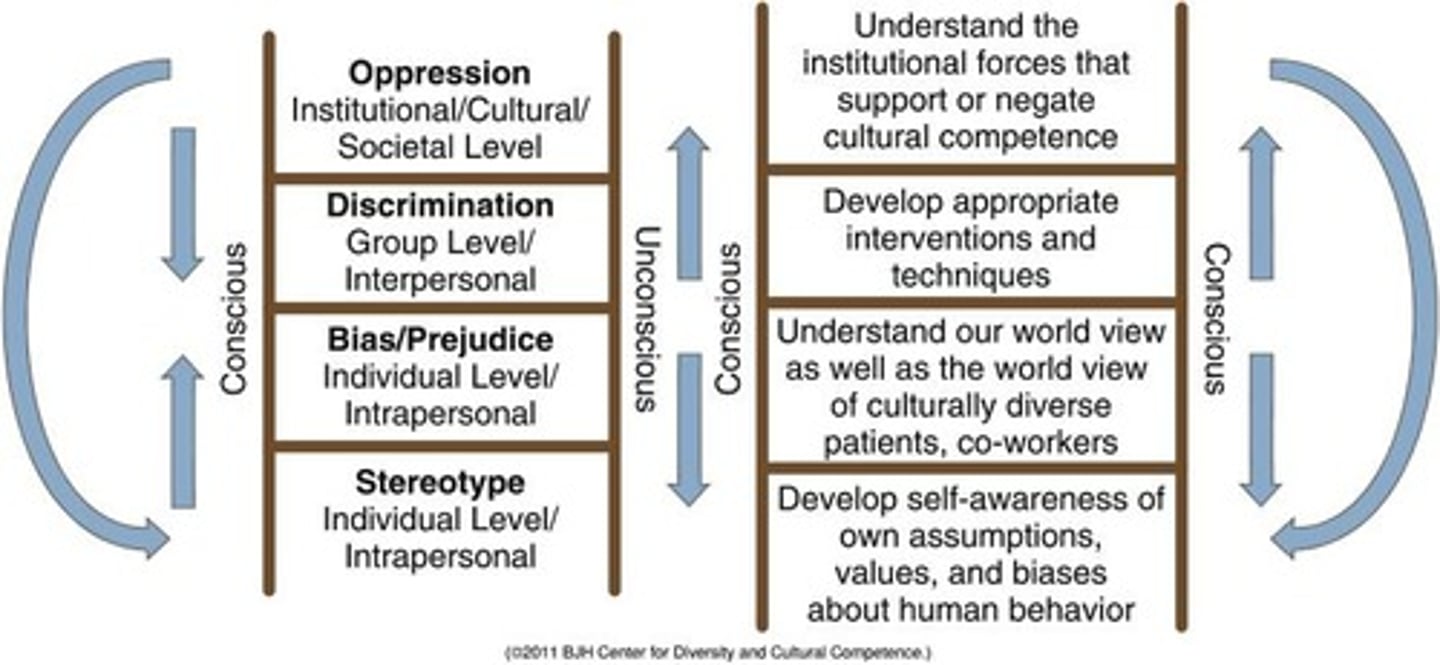
Unconscious bias
Bias we are unaware of and that happens outside our control, influenced by our personal background, cultural environment, and personal experiences.
World view
The way an individual perceives and interprets the world around them.
Emic
An insider's perspective on a culture.
Etic
An outsider's perspective on a culture.
Culturally congruent care
Care that is based on an individual's cultural beliefs, practices, and values.
Common stressors
Factors that impact family functioning across the lifespan.
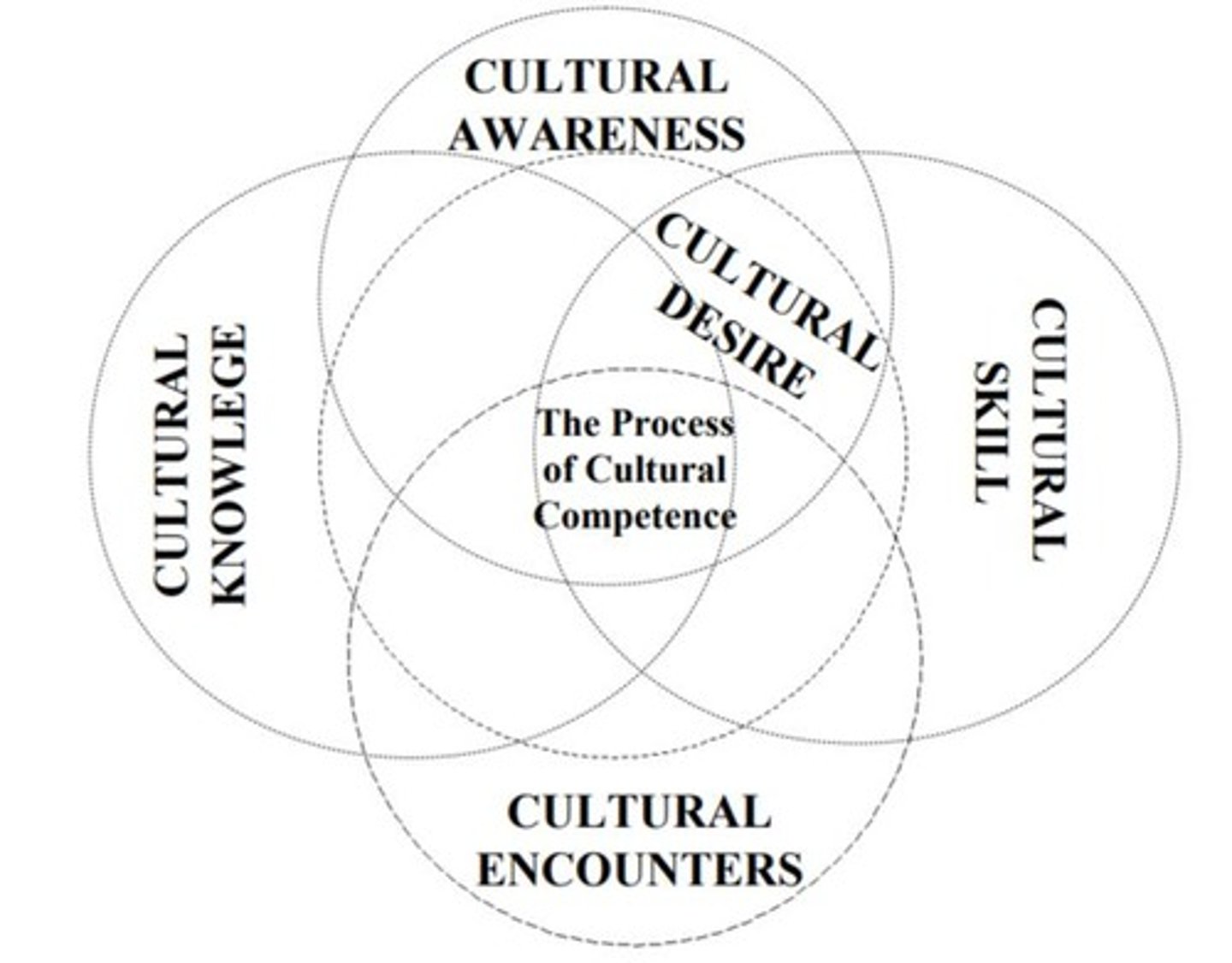
Cultural awareness
Self-examination of one's biases toward other cultures and an in-depth exploration of one's own cultural and professional background
Cultural knowledge
Learning or becoming educated about the beliefs and values of other cultures and diverse ethnic groups
Cultural skill
Ability to effectively engage with patients from diverse cultural backgrounds
Cultural encounters
Experiences that provide opportunities to engage with individuals from different cultures
Cultural desire
Having the motivation to engage patients so that you understand them from a cultural perspective
LEARN Model
A framework for understanding and addressing cultural differences in healthcare
Iceberg analogy tool
A metaphor illustrating that deeply held values reside 'underneath the iceberg' and are not immediately visible

Family durability
System of support and structure within a family that extends beyond the walls of the household
Family resiliency
Ability to cope with expected and unexpected stressors
Family diversity
Uniqueness of each family unit
Family dynamics
Interactions between family members that are affected by a family's makeup, structure, function, problem solving, and coping
Concept of family
Families represent more than a set of individuals. A family is more than a sum of its individual members.
Definition of family
A family is what an individual believes the family to be, including a set of interacting individuals related through biology or enduring commitments
Family forms
Patterns of people considered by family members to be included in a family
Factors influencing family forms
Family caregivers, poverty, housing insecurity, domestic violence
Structure and Function
Structure is based on the ongoing membership of the family and the pattern of relationships; family function involves the processes used by a family to achieve its goals
Family as context
Health and development of individual family members
Family as patient
Family patterns and processes
Family as a system
Both family members and family unit
Attributes of healthy families
Genetic factors, living with acute or chronic illnesses, diseases or trauma, end-of-life care
Family-centered care
Applying the nursing process and critical thinking to develop and implement family-centered nursing care
Family Assessment
A family-centered approach that establishes a working relationship with the patient and family
Planning Family-Centered Care
Work together with patients and their families to develop plans of care that all members clearly understand and mutually agree to follow
Evaluating the Outcomes of Family Care
Obtaining the family's perspective of care provided and if it met the family's needs
Explain the "LEARN" model
L: listen (listen with empathy and understanding to the patients problems)
E: explain (explain your own perception of the problem from a clinical stand point)
A: acknowledge (acknowledge differences and similarites between both perspectives)
R: recommend (recommend treatment options include; cultural and medical best perspectives)
N: negotiate (negotiate an agreement for a treatment plan that works for both nurse + patient)