CHP 19 - KIDNEYS
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
most important functions of kidneys
homeostatic regulation of the water and ion content of the blood
balancing intake of ions and water with their excretion in the urine
how much plasma do the kidneys filter out each day
180 L of plasma a day
how much cardiac output goes into kidneys
20%
what do afferent arterioles control
inflow
function of glomerulus
filtration
function of efferent arterioles
controls flow
function of peritubular capillaries
reabsorption
function of vasa recta
reabsorbtion
2 layers of the kidneys
outer cortex
inner medulla
the outer cortex of the kidney contains
80% of nephrons
short cortical nephrons
all bowmans capsules
proximal and distal tubules
the inner medulla contains
20% of nephrons
long justamedullary nephrons
loops of henle
collecting ducts
function of bowmans capsule
site of plasma filtration with the glomerulus
what is glomerulus and plasma filtration referred to as together
renal corpuscle
loop of henle contains
descending limb
ascending limb
function of collecting ducts
converge and drain into renal pelvis
distal nephrons contain
distal tubule and collecting ducts
filtration of kidneys
fluid from blood into lumen of the nephron
occurs at renal corpuscle
filtered plasma is called filtrate - excreted unless reabsorbed
reabsorption at the kidneys
most reabsorbtion occurs in the proximal tubules
only 1.5 are excreted
active or passive transport
materials in the filtrate are passed back into the blood
occurs with peritubular cappilaries
secretion at the kidneys
transfer of molecules from the extracellular fluid into lumen of the nephron
enables the nephron to enhance excretion of a substance
depends mostly on membrane proteins for transport
active process moving against concentration gradients
materials from blood into lumen of tubule
occurs with peritubular capillaries
4 steps of the kidneys
filtration
reabsorption
secretion
excretion
how much plasma is filtered in the nephron
about 20%
how much plasma flows into peritubular capillaries
80%
what is filtration fraction
percentage of total plasma that enters the renal corpuscle and filters into the tubule
where does filtration is kidneys occur
renal corpuscle (glomerulus and bowmans capsule)
what are the 3 filtration barriers of renal corpuscle
pores in endothelium
basal lamina
foot processes of podocyte (epithelia of bowmans capsule)
what is the hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus
pressure exerted by the blood within the glomerular capillaries. This pressure drives the filtration of plasma from the blood into the Bowman's capsule, forming the initial filtrate that will become urine
what two forces oppose glomerulus hydrostatic pressure
colloid osmotic pressure
bowman’s hydrostatic pressure
what is capsular hydrostatic pressure
The pressure exerted by the fluid already present in Bowman's capsule (about 10–15 mmHg).
what is colloid osmotic pressure
The osmotic pull of proteins (mainly albumin) in the blood plasma that resists the filtration of water (about 25–30 mmHg)
what regulates glomerulus filtration rate
renal blood flow
blood pressure
permeability of bowmans capsule
what is the hormone that influences glomerulus filtration rate
angiotensin 2 - powerful vascontrictor
regulation of GFR inflow: if the afferent arteriole constricts what is the effect on
renal blood flow
hydrostatic pressure in bowmans
glomerulus filtration rate
RBF - decreases
hydrostatic pressure in bowmans - decrease
GFR - decreases
regulation of GFR inflow: if the afferent arteriole dilates what is the effect on
renal blood flow
hydrostatic pressure in bowmans
glomerulus filtration rate
renal blood flow - increases
hydrostatic pressure in bowmans - increases
glomerulus filtration rate - increases
regulation of GFR outflow: if the efferent arteriole constricts what is the effect on
renal blood flow
hydrostatic pressure in Bowmans
glomerulus filtration rate
renal blood flow - stays the same
hydrostatic pressure in Bowmans - increases
glomerulus filtration rate - increases
what is myogenic response for glomerulus filtration regulation
intrinsic ability of vascular smooth muscle to respond tp pressure changes
constricts or dilates
what is tubuloglomerular feed for glomerulus filtration regulation
local control pathway where fluid flow through tubule influences GFR
paracrine control
what is the juxtaglomerular apparatus
specialized structure in the nephron of the kidney that plays a critical role in regulating blood pressure, blood volume, and the filtration rate of the glomerulus
located at the point where the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) comes into close proximity to the afferent and efferent arterioles of the glomerulus.
granular cells secrete??
renin
what are macula densa cells
cells that create a barrier between the tubular system and arteriole system
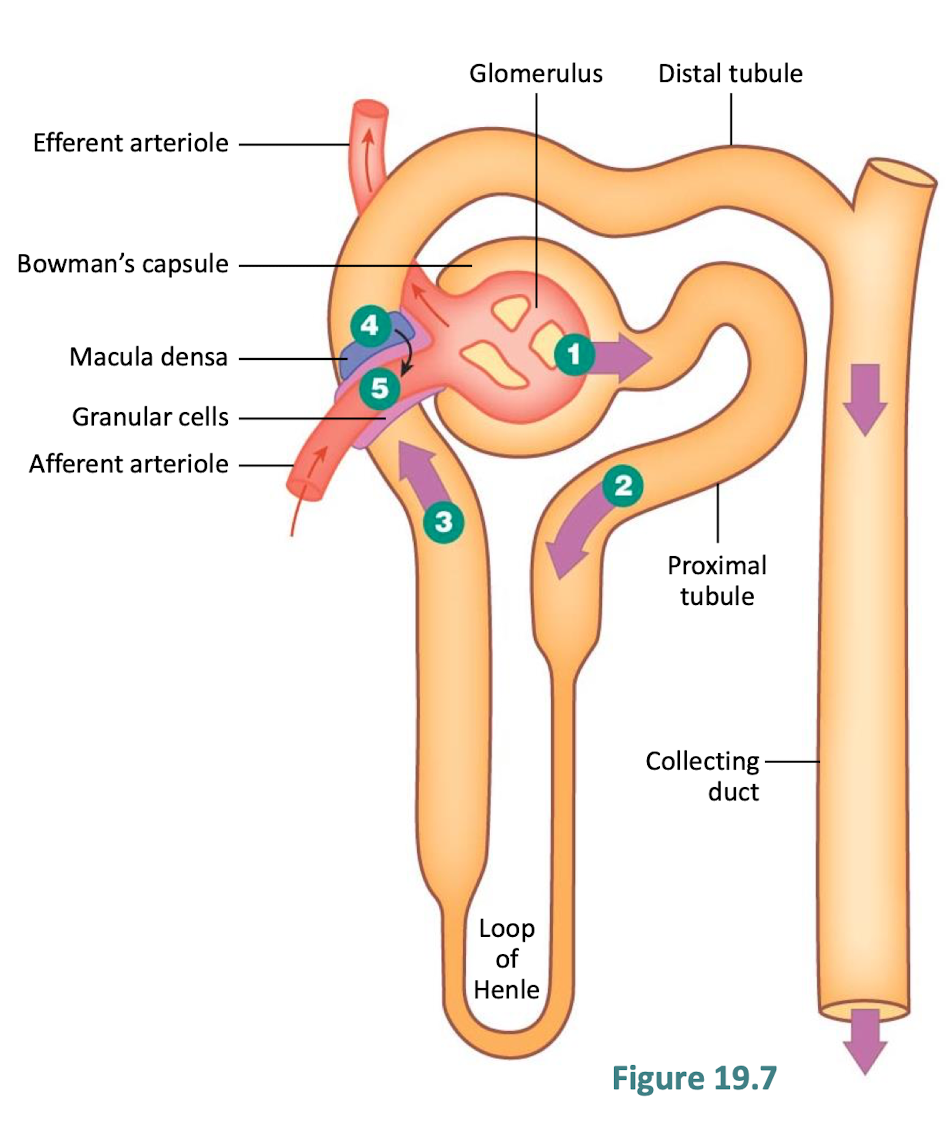
explain the steps
GFR increases
flow through tubule increases
flow past macula densa increses
paracrine the macula densa to afferent arteriole
afferent arteriole constricts
GFR decreases
4 steps of tubular reabsorption in the kidneys
Na+ is reabsorbed via active transport
electrochemical gradient drive anion reabsorption (gets more negative)
water moves by osmosis following solute reabsorption
the concentration of other solutes increases as fluid volume in lumen decreases
4b. Permeable solutes are reabsorbed by diffusion or by the paracellular pathway