Chapter 1: Overview of Blockchain Technology and Concepts
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Centralized
Has only a single copy of the ledger.
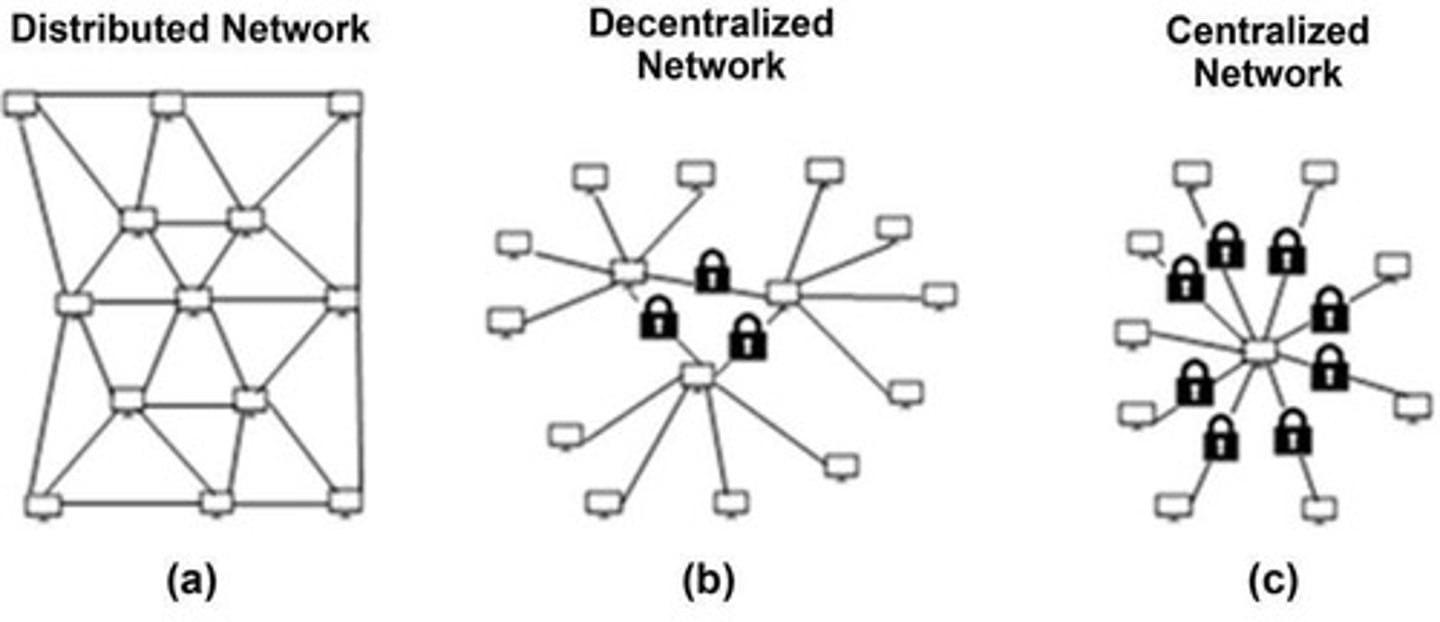
Decentralized
A trustless environment where all members get the same copy of the ledger.
Distributed
Indicates all members holding a fragment of the ledger.
Painpoints of centralization model
Includes central authority, single point of failure, data tampering, claim dispute, audit compliance, expensive, and vulnerable.
Blockchain history
In 1982, David Chaum proposed a blockchain-like protocol, which became the roots for cryptocurrency.
Satoshi Nakamoto
Conceptualized blockchain and introduced Bitcoin in 2008.
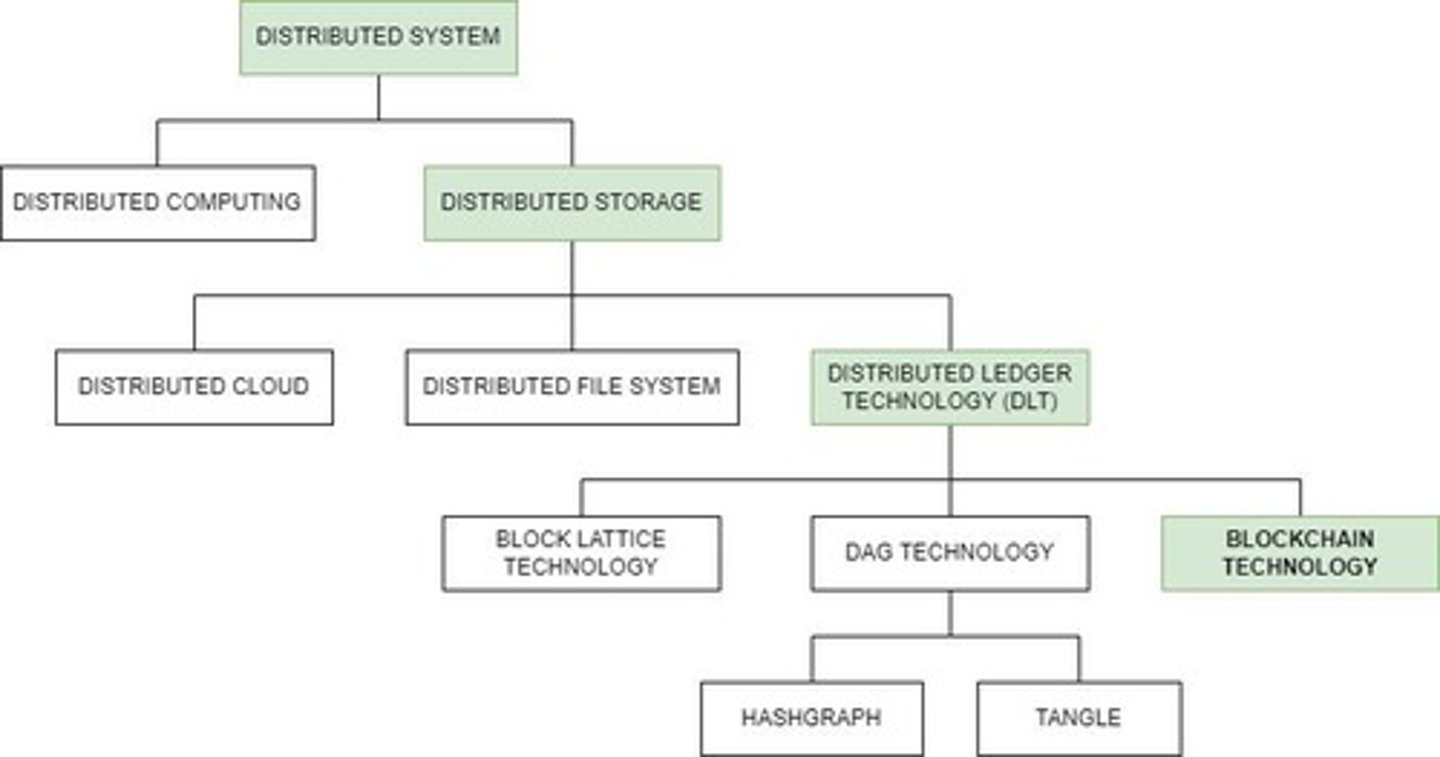
Blockchain
Can be defined as a distributed ledger, a consensus protocol, or a membership protocol.
Ledger
Tracks ownership of things such as gold, beads, cash, etc.
Distributed trust
No need to trust any designated centralized authority to maintain the ledgers; everyone keeps a copy of the ledger.
Consensus
Participants must agree on who gets to extend the blockchain and how, reaching a distributed consensus on all changes.
Decentralization
Potentially avoids a single point of failure.
Persistency
Provides tamper-proof after adding into the blockchain.
Anonymity
Solves the trust problems in blockchain.
Auditability
Allows everyone to verify the ledger.
Trusted Data
Data that is final and has no dispute.
Relational database vs. distributed ledger
Differentiate between the two types of data storage systems.
Data storage in centralized system
Compare and contrast with data storage in distributed system.
Blockchain technology
Define the technology that underpins cryptocurrencies.
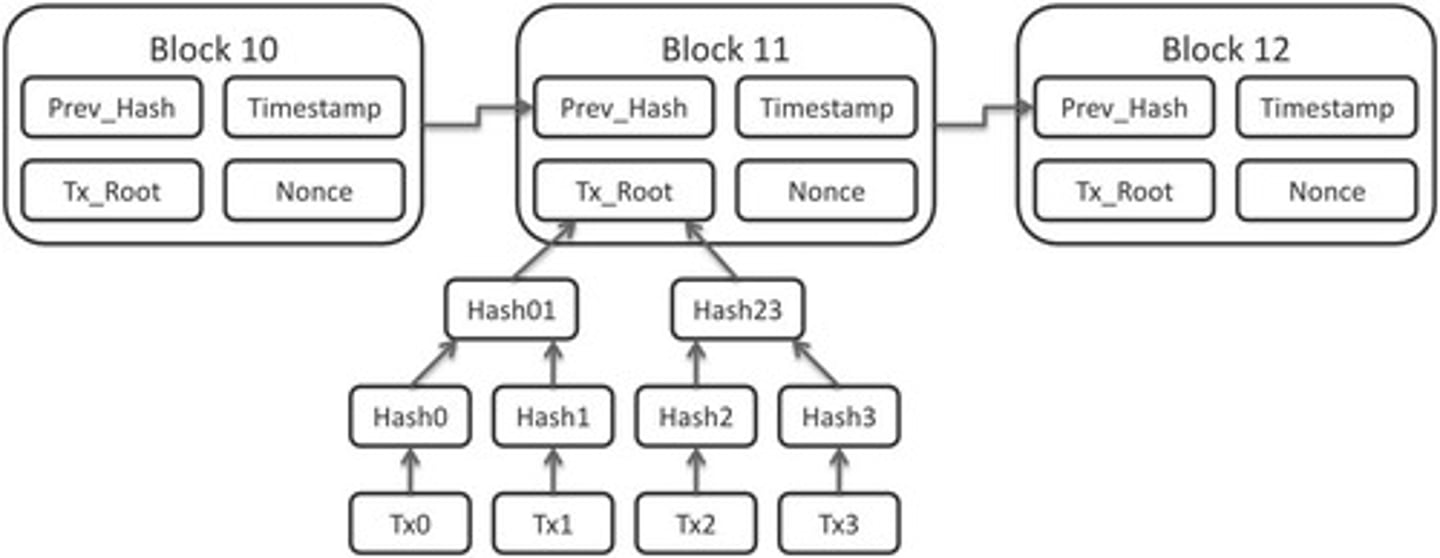
Block
Define the term related to the structure of blockchain.
Characteristics of blockchain
Explain the key features that define blockchain technology.