APH Ch 1 introduction to A+P
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Anatomy
deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts
Physiology
studies the functions of body parts
function relies on its
structure
apoptosis
programmed cell death
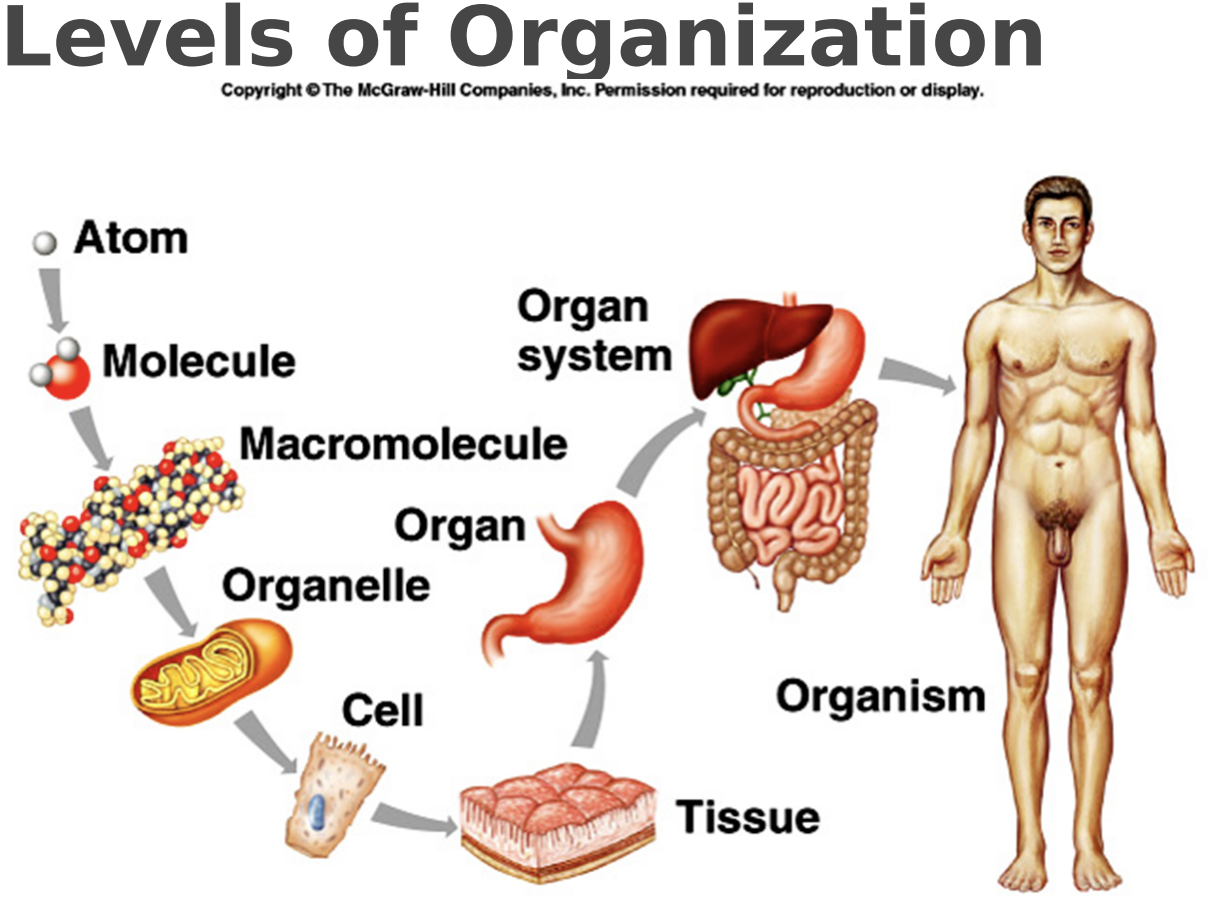
macromolecules
lipid, protein, nuclei acid, carbohydrates
organelle
vesicles, cytoplasm, cytosol, lysosome, peroxisome, vacuoles, membrane, golgi apparatus, ER, ribosome, mitochondria, nucleus
cell
smallest unit of life
Diagnostic tools
x-ray
MRI
ultrasoun
CT scan
PET scan
Atoms
are the simplest level
Two or more atoms comprise a
molecule
Macromolecules
are large, biologically important molecules inside cells
Organelles
are aggregates of macromolecules used to carry out a specific function in the cell
Cells
are the basic living unit
Tissues
are groups of cells functioning together
Groups
of tissues form organs
organ systems
Groups of organs function together as
organism
Organ systems functioning together make up an
metabolism
break down/ buildup of molecules
Movement (internal or gross)
move around in environment (food, blood, etc)
Responsiveness (reaction to internal or external change)
body ability to respond to change (hunger, shiver, sickness, sweating, pupil dilation)
Growth (increase in size without change in shape)
if you change shape you change the function
Reproduction (new organisms or new cells)
making more of yourself (pregnancy)
Respiration (use of oxygen; removal of CO2)
breathe in oxygen
breathe out carbon dioxide
Digestion
(breakdown of food into simpler forms)
Absorption
(movement of substances through membranes and into fluids)
Circulation (movement within body fluids)
blood, lymph nodes
Assimilation
(changing nutrients into chemically different forms)
Excretion (removal of metabolic wastes)
urination, poop, sweat out of pores
interelated DAA
digestion, absorption, assimilation
Water (required for metabolic reactions, for transport of substances, for temperature regulation)
assimilation, digestion, circulation
Food (nutrients needed to supply energy and raw materials for building new living matter)
growth, assimilation, digeston, absorbstion
Oxygen (used in releasing energy from nutrients)
respiration
Heat (a byproduct of metabolism; its presence governs the rate at which reactions occur)
responsiveness, circulation
Pressure (force required to facilitate movement of air or fluids)
blood pressure, respiration, pressure inside vs outside your body
Normal vital signs change with
age, sex, weight, exercise tolerance, and overall health (physically active/ fit)
Blood pressure: 90/60 mm/Hg to 120/80 mm/Hg
normal resting condition range
contract #/ release #
Breathing: 12 - 18 breaths per minute
brain can manipulate
Pulse: 60 - 100 beats per minute
high or low at rest
Temperature: 97.8 - 99.1 degrees Fahrenheit / average 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit
higer if working out/ fever
103 degrees is bad
Maintenance of a stable internal environment
is called
homeostasis
Homeostasis is regulated through control
systems which have
receptors, a set point and effectors in common
stimulus
change occurs in internal environment (in or outside body)
receptors
pick up change in environment
control center (set point)
change is compared to the set point
effectors
(muscles or glands)
response (change is corrected)
correcting the change
positive feedback loop (can not be controlled)
to keep going beyond the set point
child birth or blood clots
negative feedback loop (can be controlled)
to stop once set point is reached
sweating
anatomical position
how it lies in the body not how you are seeing it / facing forward palms up toes forward
cranial cavity
houses brain
vertebral canal
houses spinal cord
thoracic cavity
houses lungs and heart
diaphragm is the
dividing point between thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
diaphragm
muscle that allows air to fill lungs (can cause hiccups)
abdominalpelvic cavity
abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
abdominal cavity
houses liver
pelvic cavity
houses reproductive organs
cavities hold
organs (viscera)
mediastinum
separates thoracic cavity from right to left
appendicular portion
upper and lower limbs
axial portion
head, neck, and trunk
dorsal (back)
posterior
ventral (front)
anterior
The dorsal cavity can be divided into the
cranial cavity and vertebral canal
The ventral cavity is made up of a
thoracic cavity and an abdominopelvic cavity,
separated by the diaphragm
visceral pleura
pleural cavity
parietal pleura
lungs
visceral pericardium
pericardial cavity
parietal pericardium
heart
visceral peritoneum
peritoneal cavity
parietal peritoneum
abdominal plevic
visceral
organ itself / covering of organ
parietal
cavity / covering inside a cavity (membrane)
sagittal section divides the body into
right and left portions
transverse (“cross section” )section divides the body into
superior and inferior portions
coronal section divides the body into
anterior and posterior sections
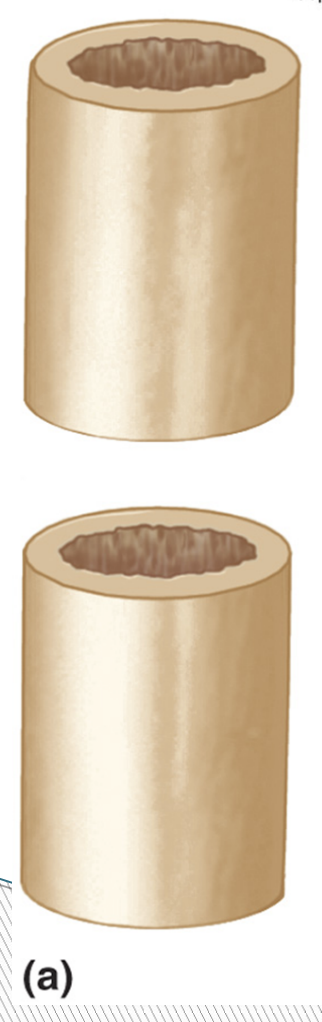
cross section
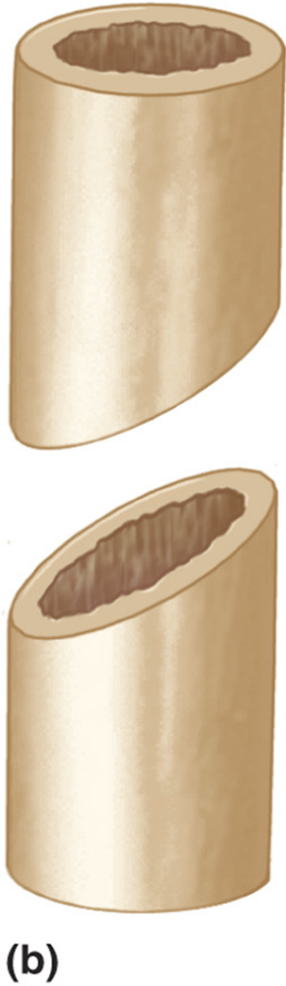
oblique diagonal cut

longitudinal cut
Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
GL
gallbladder
liver
Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
A
appendix
Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
SS
spleen
stomach