Pathophysiology: Cell Metabolism
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
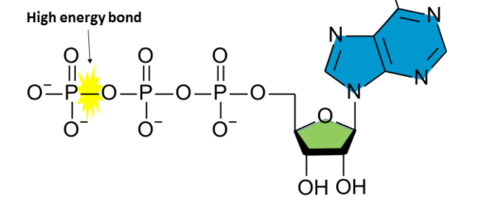
ATP
adenosine triphosphate, the body’s main source of energy largely synthesized from carbohydrates
Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, Oxidative Phosphorylation
What are the three steps of carbohydrate metabolism?
Anabolic Reaction
requires energy (ATP)
-building things up
-sugar → large carbohydrates
Catabolic
release energy (ATP)
-breaking things apart
-large carbs → sugars
energy carrier, third
ATP is an ______ ______. The energy needed to make reactions go are found in the medial oxygen and _____ phosphate in the tail’s third phosphate group.
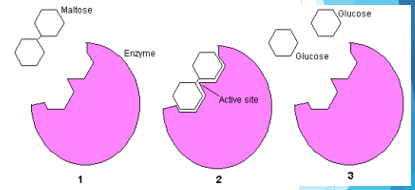
Enzymes
catalyzes metabolic reactions
-are proteins 99.9% of the times, can also be ribozymes (RNAs)
-structure dictates function
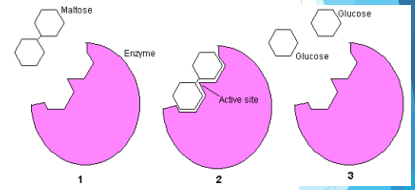
Substrate-specific
The active site of a molecule is ________-_______, meaning one enzyme fits in one specific type of substrate. This is good because it prevents improper functioning of enzymes. The shape of the active site is determined by what amino acids make up the protein.
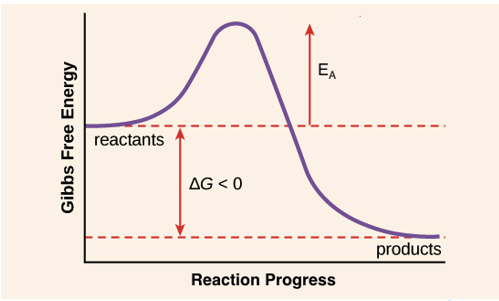
Activation Energy
the energy required for a reaction to take place
-to reach this in a time-effective manner, you need an enzyme
Small Molecule Binding
Regulates enzymes
-without them, these reactions would occur at random times and drain the cell/body of energy
Cofactors
promote enzyme function by binding to the protein and stabilizing its structure
-ex ions (Mg, Fe) and small molecules
Coenzymes
promote enzyme function
-ex coenzyme A in metabolism
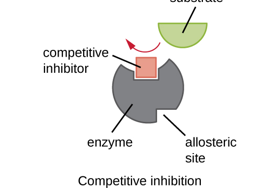
Competitive Inhibitor
binds in the active site, blocking the substrate from binding and halting enzyme function
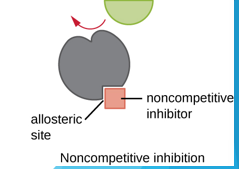
Non-Competitive (allosteric) Inhibitor
binds outside the active site, changes the shape of the active site and prevents the substrate from binding
Cytoplasm and mitochondria
Production of energy occurs in the _____________ and ___________
stored or used immediately
Glucose must be ________ or _______ ________
Glycogen
stored form of glucose found most often in the liver
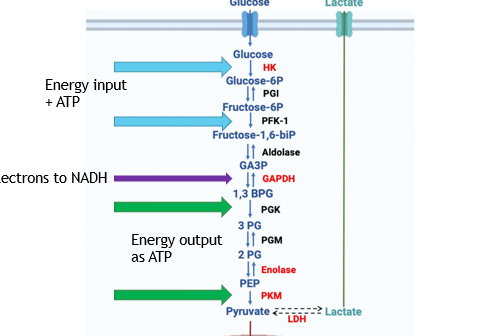
Glycolysis
a set of 10 chemical reactions that start with glucose + 2 ATP and ends with pyruvate + electrons + 4 ATP
-net 2 ATP
-electrons are carried by NADH to ETC
Pyruvate, Citric Acid Cycle
The goal of glycolysis is not to produce ATP but rather to produce _________, which is the molecule required to start the ________ ______ ________
Allosteric Regulation
Binding of small molecules outside the active site
-Does the reaction happen?
-At what speed does it happen?
Products
Enzymes in glycolysis are regulated by __________ of glycolysis
Hexokinase
binds to glucose very tightly and is good for generating energy with very little glucose in the body; means cells can still undergo glycolysis if glucose is in low supply
-Answers the question of does glycolysis happen?
Liver Hexokinase
the exception to the role of hexokinase, does not bind well to glucose because glycogen is produced in this organ
PFK
-inhibited by ATP, activated by ADP
-more active when there is less energy in the cell
-ATP binds to allosteric site, blocking PFK and halting glycolysis
-ADP activates PFK and kick starts glycolysis
-Answers the question of “how fast does glycolysis occur”
ATP and acetyl-CoA
Pyruvate kinase is inhibited by?
-done to prevent pyruvate from being turned into lactate and burning muscle, no need to finish glycolysis if these are already in excess
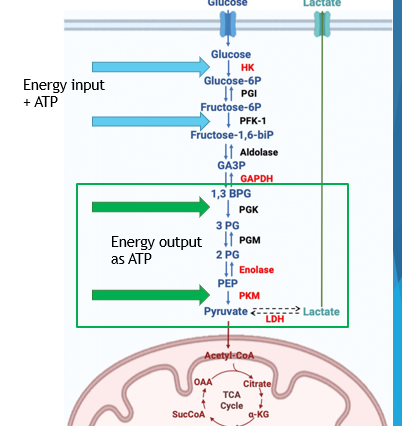
Fat
Glycolysis is sometimes inhibited when ___ can be used as an energy source
-___ metabolism = acetyl CoA production, blocks glycolysis
Oxygen
Glycolysis can also be inhibited by _______
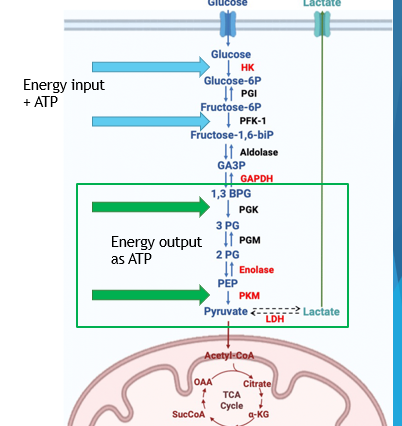
Aerobic Metabolism
will only happen if oxygen is in the cell, proceed to Citric Acid cycle in mitochondrial lumen
Anaerobic Metabolism
no/low oxygen present
proceeds to fermentation or lactic acid production
Fermentation
form of anaerobic metabolism where acetaldehyde is produced and turned into ethanol, releasing CO2
-should not happen in humans
-common in beer and wine making
Lactic Acid Production
form of anaerobic metabolism that is more common in humans, results in the burning of muscles
Recycle electron carriers
The goal of anaerobic metabolism is to _____ ______ ______ that can pick up the electrons produced during glycolysis and eventually get into aerobic respiration
Lactate Dehydrogenase
converts pyruvate to lactate → lactic acid
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
pyruvate → acetaldehyde → ethanol
releases carbon dioxide
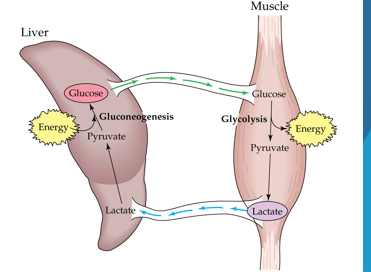
Oxygen Debt
not enough oxygen to function through the Citric Acid Cycle
-oxygen required to restore energy stores
-energy to convert lactate back to glucose
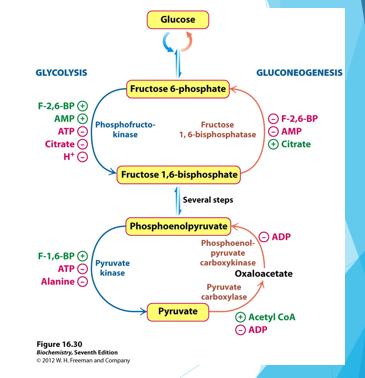
Gluconeogenesis
What process helps fight the oxygen debt by converting lactate into glucose within the liver?
Requires energy
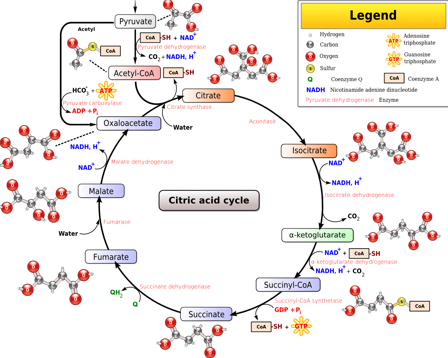
Citric Acid Cycle
occurs in the lumen of the mitochondria, goal is to get electrons to the electron transport chain
-in: pyruvate and acetyl-CoA
-out: electrons, GTP, CoA
-components of this cycle are used elsewhere in the cell, like citrate in semen
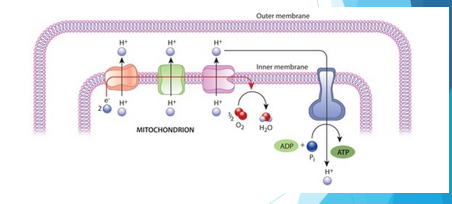
Electron Transport Chain
proteins embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
-electrons are passed from one protein complex to the next, decreasing energy with each passage
-H+ ions pumped across the membrane, and electrons are accepted by oxygen
-generates 32 ATP
CoQ Deficiency
metabolic disease caused by the lack of coenzyme Q synthesis
-loss of electron shuttle in ETC, preventing the cell from making all of the ATP it needs
-results in the breakdown of skeletal muscles
-can be treated with CoQ supplements or riboflavin
Chronic Lactic Acidosis
metabolic disease caused by a genetic deficiency in ETC subunits, rendering them unable to function
-causes a build-up of lactic acid in tissues due to lack of respiration
-results in tissue acidification
-pH can be regulated by IV fluid
Gluconeogenesis
making new glucose, reverse synthesis of glucose from pyruvate or other intermediates
-while most cells just get their glucose from the blood, some tissues rely heavily on glucose and need to perform this process
ex brain, muscles, liver
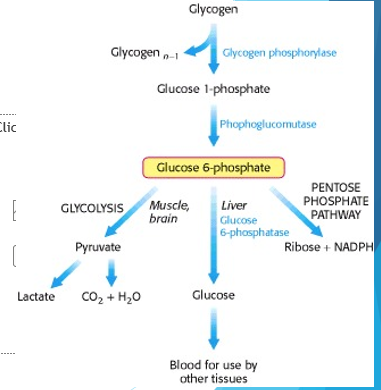
Glycogen
storage form of glucose found in the liver, separate stores can also be found in the muscles and brain
-does this to prevent high blood glucose, which can lead to many conditions
-allows for quick glucose mobilization when necessary
Glycogen Synthase
adds new glucose molecule to growing carbohydrate chain
Glucagon
the hormone that mediates the release of glucose from glycogen
Glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway
Glucose-6-Phosphate has three fates…
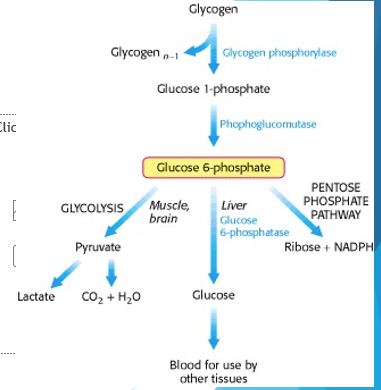
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
generates ribose and NADPH, support production of antioxidants and synthesis of other biomolecules like DNA or RNA
Liver and pancreas
What organs regulate blood glucose?
Insulin and glucagon
What hormones regulate blood glucose?
Type 1 Diabetes
diabetics that are unable to produce insulin or an adequate amount of insulin
Type 2 Diabetes
diabetics have no response to insulin
Proteins
_________ can contribute carbons to the Citric Acid Cycle if needed, however, this is a last ditch effort
Lipid Metabolism
occurs in the mitochondria once per two carbons, which go to produce Acetyl CoA through beta oxidation
-also releases electrons for the ETC
-carnitine acts as a carrier across the mitochondrial membrane
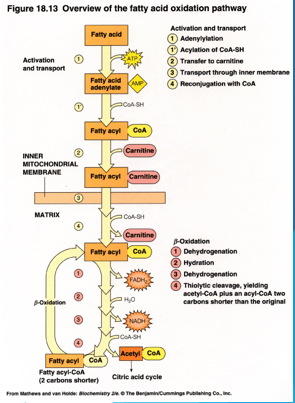
FADH2 and NADH
These are also produced via fatty acid oxidation
2 ATP
One molecule of FADH2 results in _ ATP
3 ATP
One molecule of NADH results in _ ATP
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
can occur in Type I Diabetics when their cells don’t get a signal about there being sugar in the blood, preventing them from taking it out of the bloodstream. The cells then switch to fatty acid metabolism, producing ketones
-can cause hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, acidosis, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, swelling of the brain, coma, and death
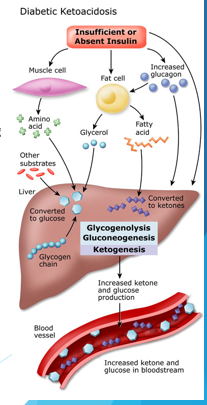
Glucagon
________ is also in excess in diabetic ketoacidosis, meaning type I diabetics cannot modulate or metabolize glucagon. Their cells use triglycerides or amino acids for energy. Also stimulates conversion of fatty acids to ketones, resulting in the “sweet breath” some diabetics have
Ammonia
an important enzyme substrate converted to glutamate, glutamine, asparagine
-used in amino acid and nucleotide synthesis
Transamination
amines transferred from one molecule to another, substituting for a ketone
-requires a variety of coenzymes like pyridoxine and pyridoxal phosphate
Essential Amino Acids
amino acids that cells cannot synthesize, must be consumed dietarily
Histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine
What are the essential amino acids?
conditional amino acids
In times of stress, we must also consume _________ ____ ______ like arginine, cysteine, glycine, and glutamine
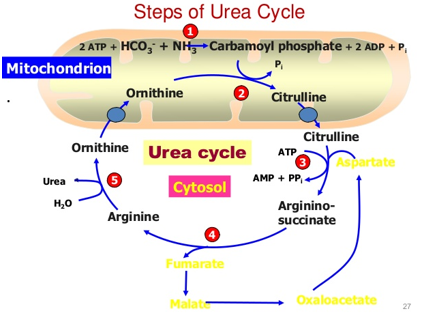
Urea Cycle
important for amino acid degradation
-produces urea from ammonia, which is not good for the body
-required to clear ammonia from the blood, typically through urination
-coupled with the TCA cycle