FINC 4660 ETFs
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Traditional ETFs strategy
Passive investment strategy tracking an index
Ex.
SPY, MDY, Dow Diamonds, Nasdaq QQQQ
Other types of ETFs
Leveraged (LETFS)
Actively managed ETFs
ANTs (active non transparent ETFs)
What ETFs offer
-Diversification
-Low cost
-Tax Efficiency
-Transparency
-Stock like trading features
Net asset value
Assets - liabilities divided by shares outstanding of an investment fund
Intraday indicative value
Estimated value of an ETFs NAV updated every 15 seconds
Sponsor of ETF
Entity that creates the ETF
Authorized participant (arbitrageur)
Acquires the securities the ETF wants to hold, obtain and create the underlying shares
Creation unit
Block of new shares issued by an etf ranging from 25000 - 600000
In kind transactions vs cash transactions
Shares of underlying basket for ETF shares vs redeeming cash for ETF shares
If the price of an etf is greater than the ETF
Buy the basket and short the ETF
Profit = P - NAV
If the price of the ETF is less than the NAV
Buy the etf and short the basket
Profit = NAV - P
Premium on ETF
((P - NAV) / P )* 100
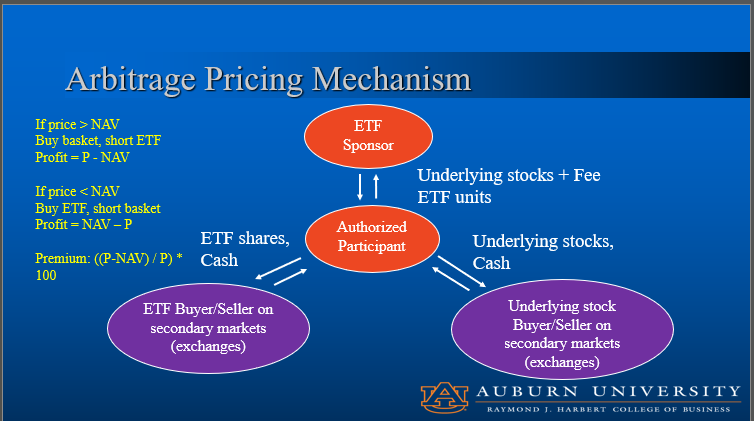
Study this
Graph
Barriers to ETF arbitrage
-Decreased transparency of ETF holding
-Low liquidity of underlying securities
-Time differences in trading ETF and underlying securities
-Restrictions on in kind transactions
Actively managed ETF characteristics
New and fast growing
Concerns about price efficiency
Mainly operate in bond category
ANTs
Disclose holdings quarterly, not daily
More meaningfully pursue active strategy with lack of transparency
Limited to investments that trade simultaneously as the fund itself
Sponsors required to provide additional info on the creation and redemption baskets
Leveraged ETFs
Promise to pay shareholders a multiple of the daily change of the underlying assets
Uses derivatives rolled quarterly
Frequent rebalancing
Used for short term trading strategies
LT returns differ substantially from promised return
ETF passive investment concern
No fundamental analysis
No corporate governance
ETF increase volatility in underlying securities concern
Brought by arbitrage pricing mechanism and rebalancing of LETFs
ETF liquidity concerns
Increased trading in illiquid markets may lead to increased volatility
ETF exogeneous negative price shock risks
Lead to panic selling by institutions that face redemption from investors
ETF leverage concern
Rebalancing adds upward price pressure in good times and downward pressure in bad times
ETF Counterparty risk concern
LETFs, ETFs using synthetic replication