Ch.20 ❤️
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Heart circulation
Double cardiovascular system
Congestive Heart failure
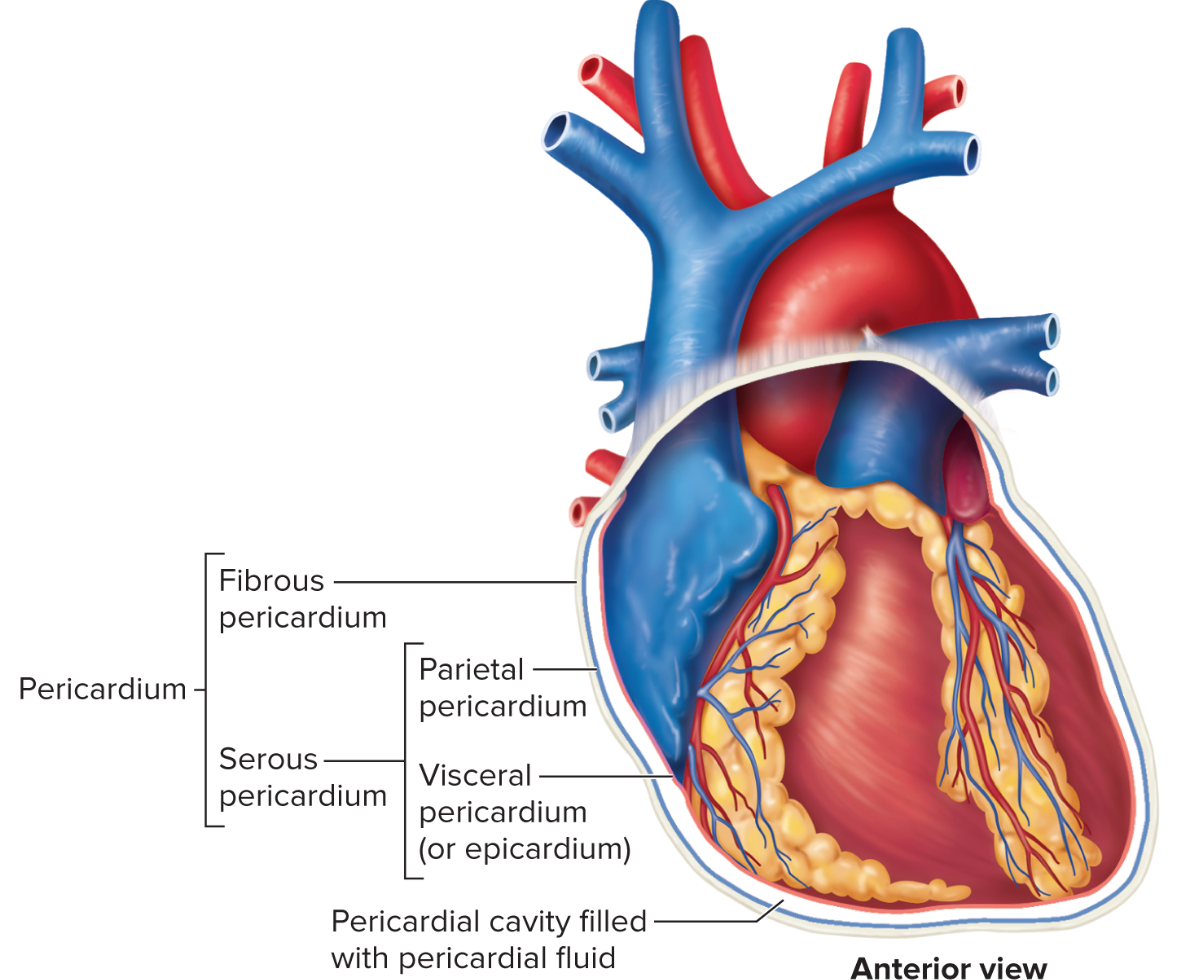
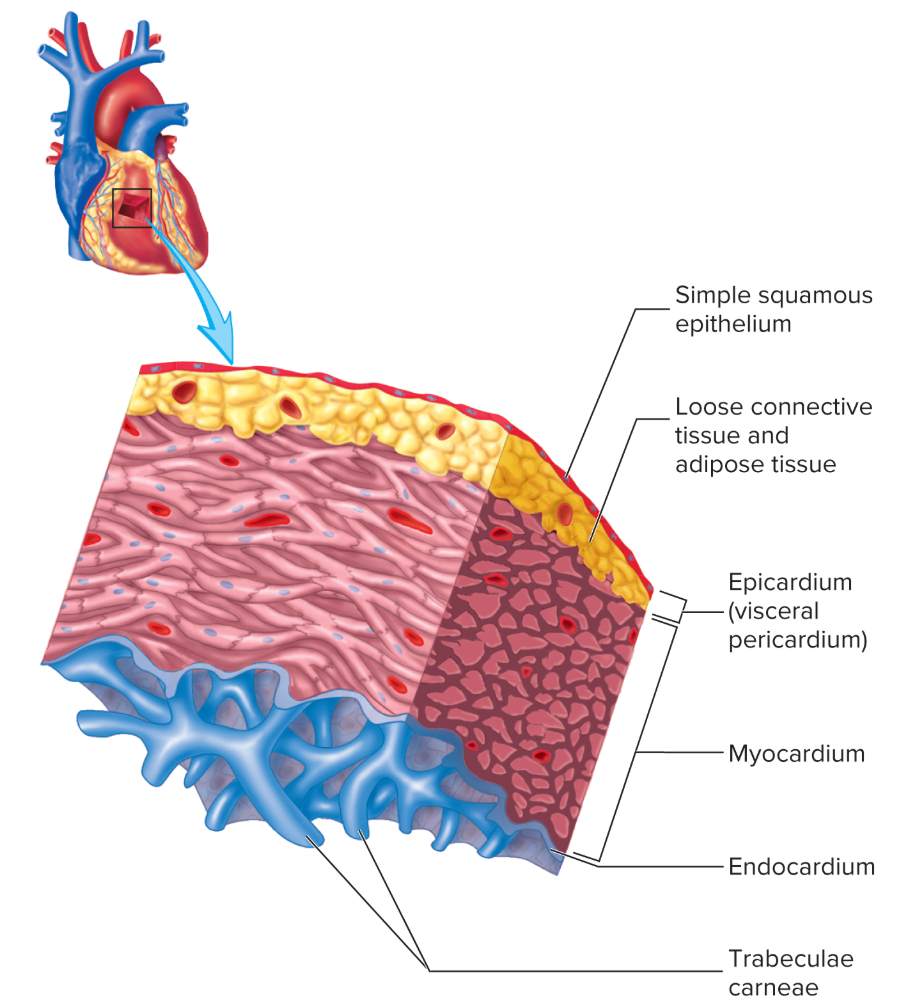
Layers of Heart
in → out
Endocardium (simple squamous & connective tissue)
Myocardium
Parietal Pericardium
Pericardial cavity = pericardial fluid
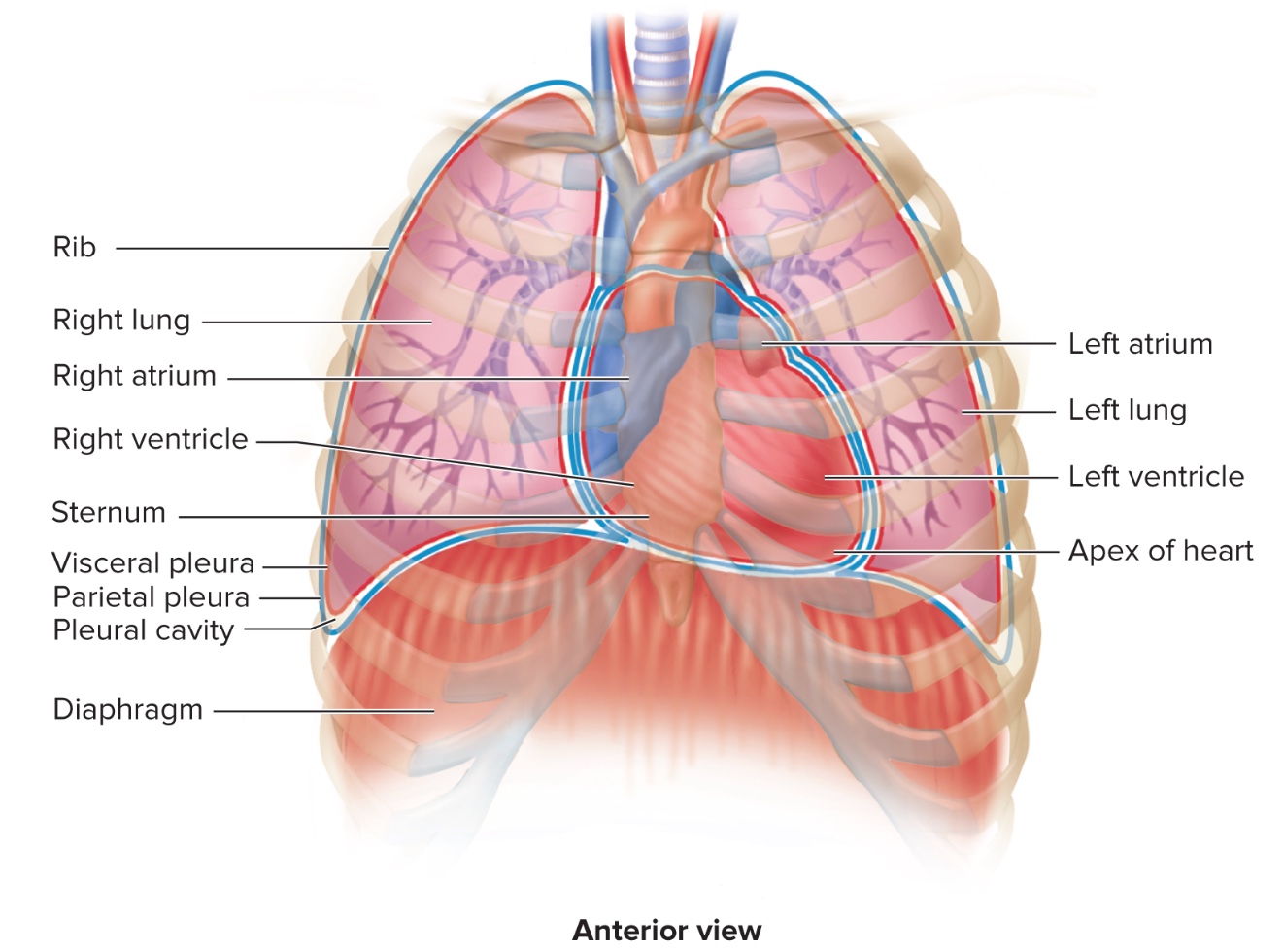
Where is the Heart?
b/t Lungs at MEDIASTINUM = b
Why are the ventricles the same size?
to stop congestion = same volume → ventricles same size but the left has more myocardium
Functions of Heart Skeleton - Passive 80% filling of ventricles & delay?
Vacuum - atria contracting 20% into ventricles rest is like a medicine dropper
1. Electrical insulator b/t atria & ventricles
delay → skeleton stops action potential from going straight to ventricles
anchors myocardium → spiral structure alows most output
Valve seat - memo
how do we prevent congestion on RIGHT atria?
fibrous connective tissue - chordae tendineae f that attached to papillary muscles on the ventricles
- attatch to flap of atriventricular valve
when heart contaracts blood preasurre pushing up - papillary will keep it from inverting(prolapsing)
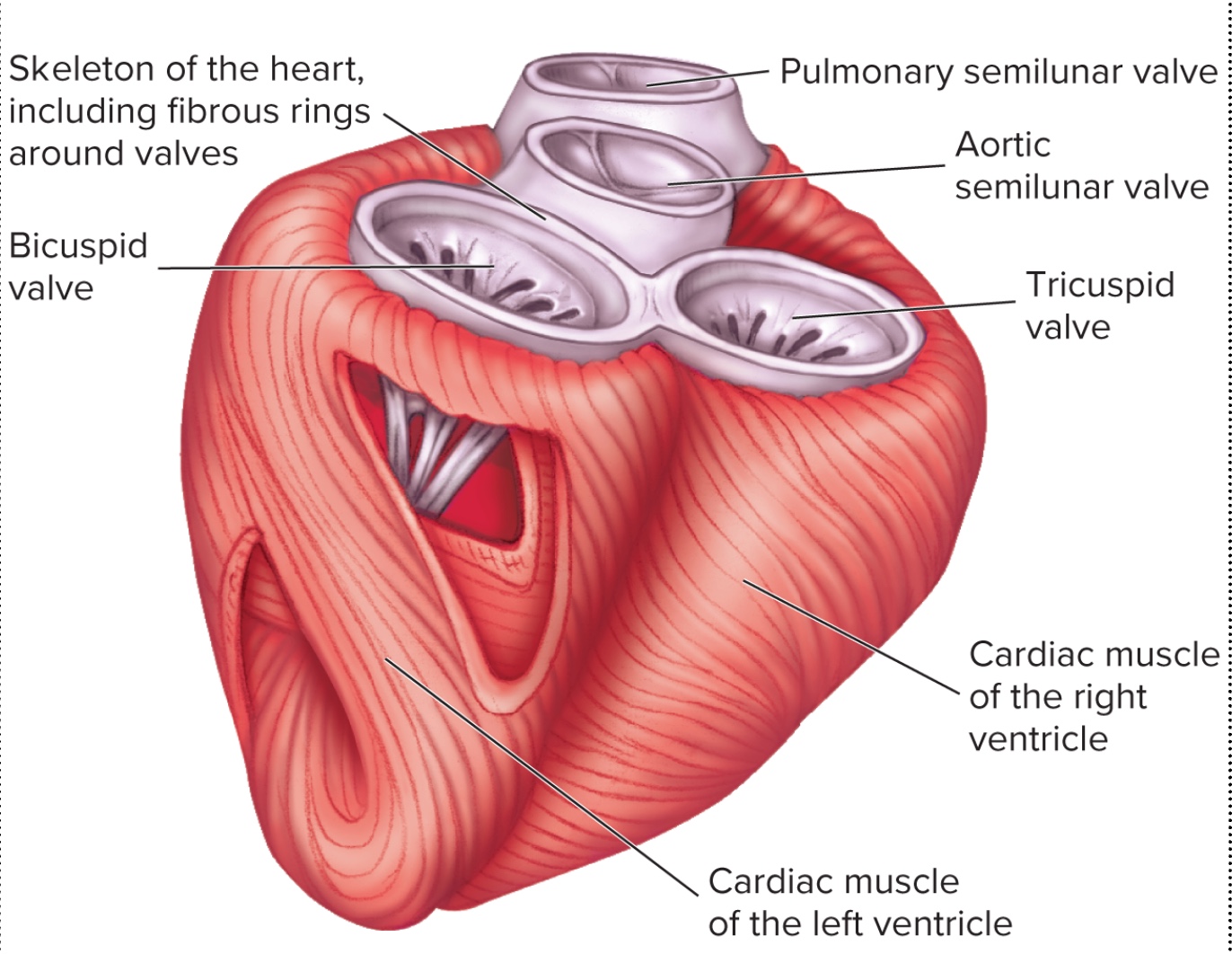
Heart skeleton
InterATRIAL septum
Foramen ovalis → Fossa ovalis after birth
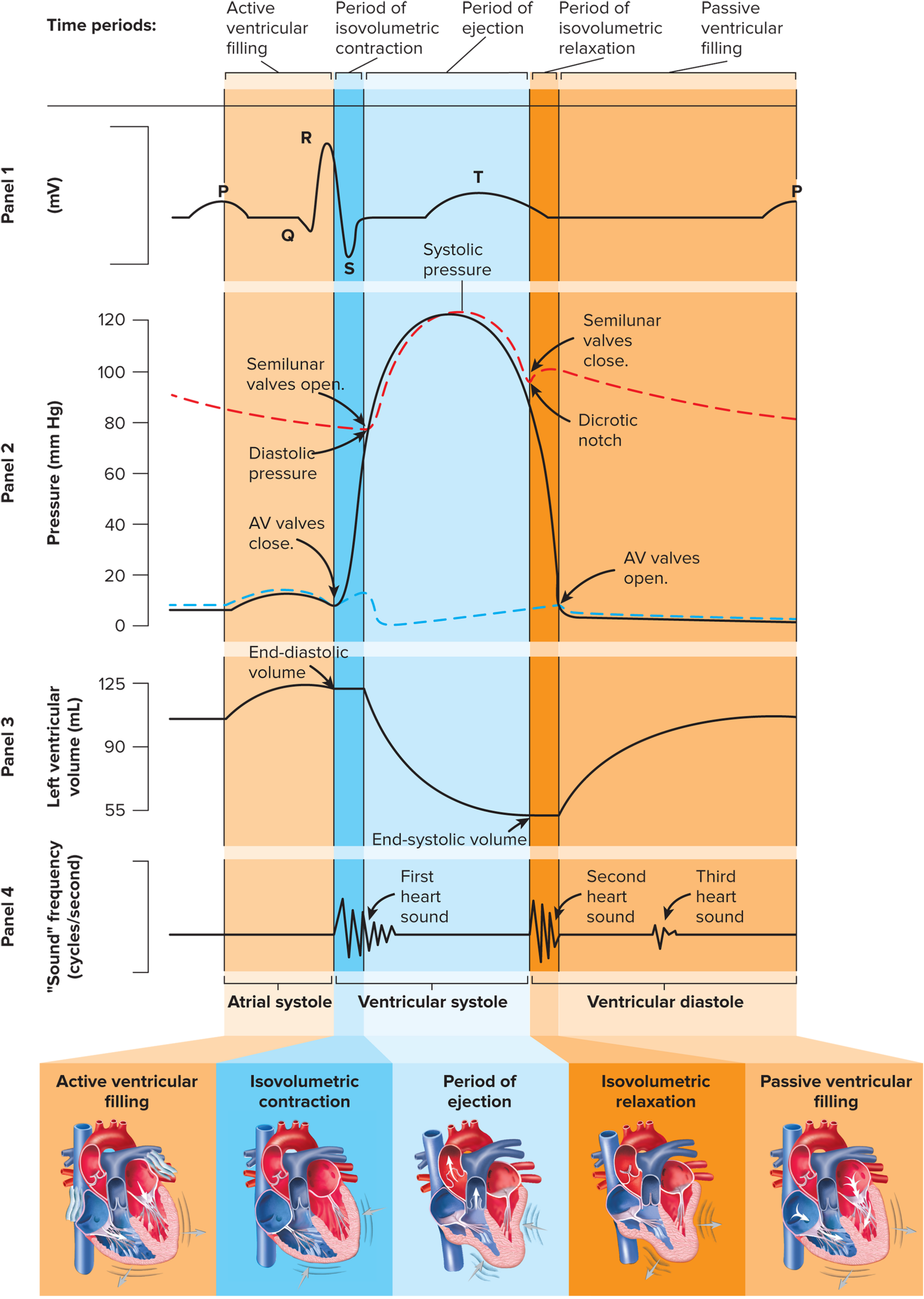
Heart sounds
LUB - AV valves CLOSIN
DUB - Semilunar Pulmonary & aortic valves CLOSING w/ more force
Left side Ventricular preassure - 10 torr which increases to 120?
Heart murmurs - Valve disease LESS CARDIAC OUTPUT → CONGESTIVE HR FAILURE
Valvular STENOSIS
- hardening & Narrowing
Result - pump faster/harderValvular incompetence/Regurgitation
Closes weird - blood goes back → flaging sound
CONGESTIVE HR FAILURE → Chronic disease on Cardiac Output that could lead to Respiratory problems etc all because of different pressure equlization
Coronary Circulation
Blood supply to myocardium
coronary arteries taking blood to capillary muscle
Cardiac Cycle
Mid diastole - ventricles = relaxing & expanding
- Passive filling 80%, 20% atria contractionEnd of systole/start of distole - ventricles relax and their preassure drops (L 120→80) when this occurs semiluar valves close
- all 4 valves shut → isovolumetric relaxation and we have end systolic volume =70ml
Stroke volume
SV- volume of blood pumped out Left Ventricle (& right V) EACH BEAT
SV= EDV(150ml)-ESV(70ml) = 80ml/stroke
Cardiac Output
volume of blood pumped our of LV in 1min
CO= stroke volume x stroke rate
CO= 80ml/stroke x 70 stroke/mins = 5,600 ml/min AT REST
Average Human has how much blood?
~5500ml of blood
avg human 165 lbs 5’8
Can stroke volume and cardiac output change? look over this
Yes, increased or decrease
Action potentials
Membrane resting potential = average cell potential energy = -70mv , inside = 12 Na+ , 155 K+ 155 protein-, Outside = 145 Na , 4 K+ , 0 protein
Na/k Pump = To keep them at the proper distribution to stop equalization through diffusion and maintain charge
Cardiac Muscle (myocardium) consists of
Single cells w/ nucleus
connected by INTERCALATED DISCS
Autorhythmic (myogenic contractions) '
Generates OWN action potentialsFibers=branched
Intercalated discs → thanks to gap junctions myocardium → connects them as two big cells (atria/ventricles) because theres no membrane
adhesion fibers stronger than membrane
HIGHLY permeable
Skeletal muscle fiber - connected to neurons
2 types of Myocardium
Contractile cell→ pump
Conductive cell→ specialized myocardium = generate & conduct AP
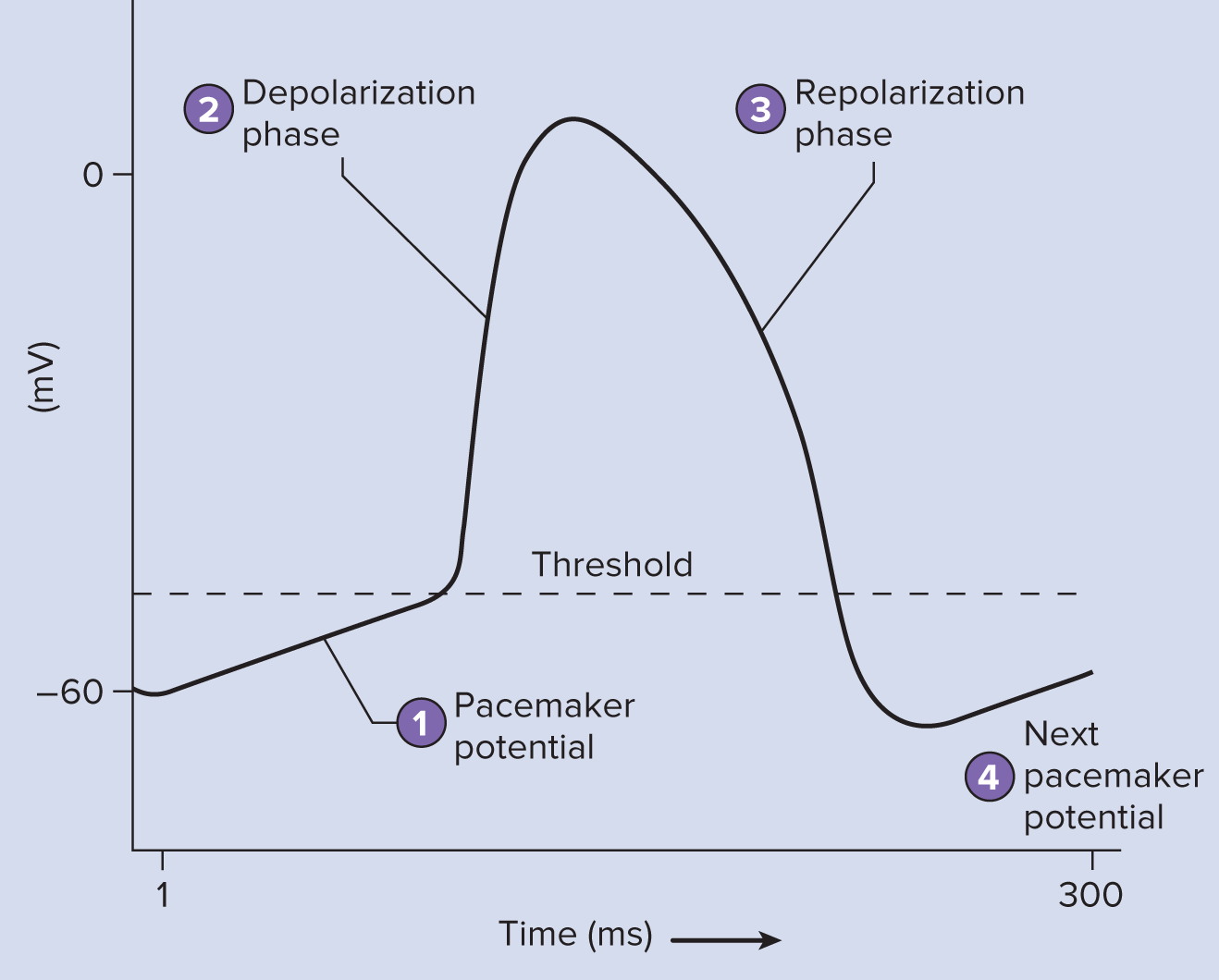
Pacemaker Sinoatrial node (SA)
No resting potential
NO NEED FOR EXTERNAL STIMULUS = no neuron connection
Rate is 100-120bpm
Na continuously leaks gets to threshold +50
Ca++ chennels open & leaks → spike UP Depolarization (two charges make it quicker)
+20 Na channelscloses
K open K goes out cell → -60 → K channels close → K UP

Contractile cells
Resting potential -90 → +20
If it wasn’t under ANS → 110 bpm
Long refractory period → avoids cramping, allows Contraction→ Relax
Electrical flow
SA node sets pace by generating PP (55-200bpm)
intermodal fibers 1m/sec - conduct AP → ATRIA & AV node
AV node 0.1 m/sec
Delays AP
Cardio skeleton = electrical insulator so AP goes through AV bundle → bundle branches→ purkinje fibers
4-6 = 8-10 m/sec
AV bundle in septum
bundle branches each ventricle
Purkinje fibers
myocardium of ventricles
moderate → slow→sonic speed
Contractile cells
conducts pacemaker potentials and leads it to contractile cells