Topic 1: Lifestyle, Health, and Risk
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
What do cells need to survive?
* Constant supply of reactants
2
New cards
How do single- celled organisms get the supply of reactants?
* Gain O2 and glucose directly from surroundings
* Molecules can diffuse to all parts of the cell quickly due to short diffusion distances
* Molecules can diffuse to all parts of the cell quickly due to short diffusion distances
3
New cards
Why can large organisms not operate in the same way?
* Made up of many layer of cells so time taken for substances such s glucose and oxygen is too long
* Diffusion distance too great
* High energy requirements so delivery of reactants needs to happen quickly
* Diffusion distance too great
* High energy requirements so delivery of reactants needs to happen quickly
4
New cards
How do large organisms get their supply of reactants?
* The exchange surfaces are connected to a mass transport system
* eg. lungs connected to circulatory system
* eg. lungs connected to circulatory system
5
New cards
What is mass transport?
* The bulk movement of gases or liquids in one direction, usually via a system of vessels and tubes
* The circulatory system is a mass transport system
* The circulatory system is a mass transport system
6
New cards
What do mass transport substances help to do?
* Bring substances quickly from one exchange site to another
* Maintain diffusion gradients at exchange sites and between cells and their fluid surroundings
* Ensure effective cell acctivit by supplying reactants and removing waste products
* Maintain diffusion gradients at exchange sites and between cells and their fluid surroundings
* Ensure effective cell acctivit by supplying reactants and removing waste products
7
New cards
What does water do in terms of transport?
* The medium in which all metabolic reactions take place in cells and in which all substances are transported around the body
8
New cards
What is water composed of?
* One Oxygen atom covalently bonded (sharing e-) with two Hydrogen atoms
9
New cards
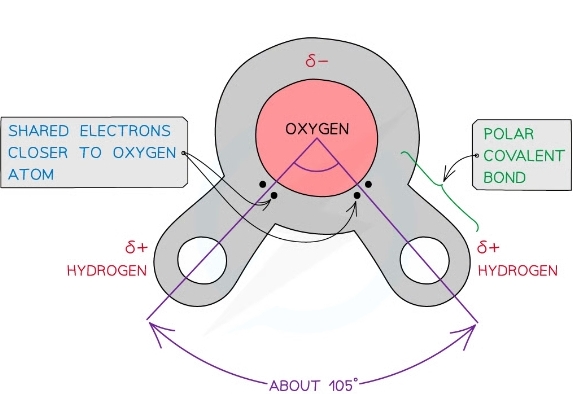
Dipolar nature of water
* Uneven sharing of electrons
* O attracts the electrons more strongly than the H atoms
* Weak -ve charge on the O atom
* Weak +ve charge on the H atoms
* Therefore H2O is a polar molecule
* O attracts the electrons more strongly than the H atoms
* Weak -ve charge on the O atom
* Weak +ve charge on the H atoms
* Therefore H2O is a polar molecule
10
New cards
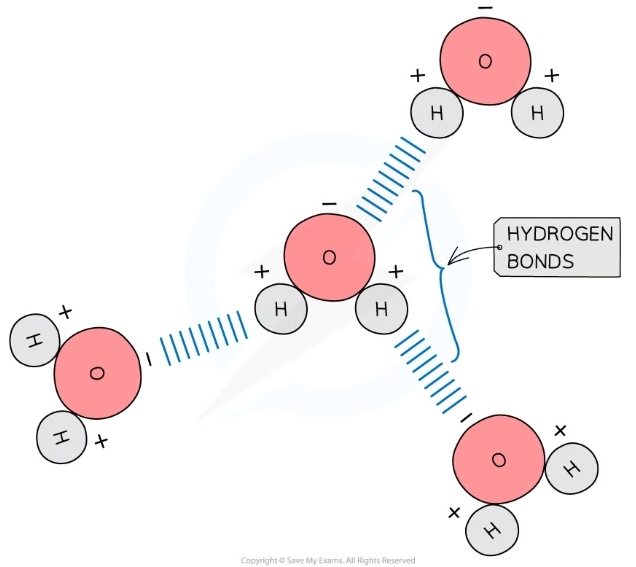
Result of the dipolar nature of water
* Hydrogen bonds form between the +ve and -ve Q regions of molecules as a result of the polar nature of water
* Hydrogen bonds are weak when few in number so constantly breaking and reforming
* Molecules flow past each other in a liquid state
* Hydrogen bonds are weak when few in number so constantly breaking and reforming
* Molecules flow past each other in a liquid state
11
New cards
What prooperties of water (due to its polar nature) make it good for transporting substances?
* It isCohesive
* It is a solvent
* It is a solvent
12
New cards
What is cohesion?
* The attraction of water molecules to each other
* This is due to the H bonds
* Water molecules pull other water molecules along due to adhesion
* This is due to the H bonds
* Water molecules pull other water molecules along due to adhesion
13
New cards
What is adhesion?
* Water can hydrogen bond to other molecules
* Water adheres to the sides of a vessel due to adhesion
* Water adheres to the sides of a vessel due to adhesion
14
New cards
How do adhesion and cohesion help transport?
* Water molecules pull other water molecules along due to cohesion
* Water adheres to the sides of a vessel due to adhesion
* This means that water flows easily
* Water adheres to the sides of a vessel due to adhesion
* This means that water flows easily
15
New cards
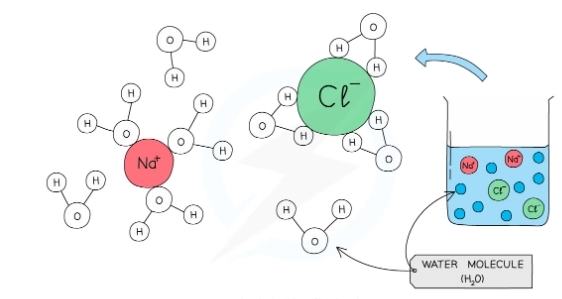
What makes water a solvent?
* It is a polar molecule meaning many ions dissolve in it
16
New cards
How do ions dissolve in water?
* +ve part of water (H) attracted to the -ve charged patticles
* -ve part of water (O) attracted to the +ve charged particles
* This causes the surrounding molecules to break aprt (dissvolve)
* -ve part of water (O) attracted to the +ve charged particles
* This causes the surrounding molecules to break aprt (dissvolve)
17
New cards
What is the purpose of dissolving ions?
* Allows chemical reactions to occur within cells as the dissolved solutes are more chemicaly reactive when they are free to move about
* Metavolites can be transported efficiently in a dissolved state
* Metavolites can be transported efficiently in a dissolved state
18
New cards
What is a circulatory system?
* A system which transports fluids containing materials needed by the organism as well as waste materials that need to be removed
19
New cards
What happens in a closed circulatory system?
* Blood is pumped around the body and is always contained within a network of blood vessels
20
New cards
What happens in an open circulatory sytem?
* The blood, or blood equivalent, is inside the body cavity and bathes the organs
21
New cards
What is a double circulatory system?
* They have two loops
* One to the lungs and one to the body
* One to the lungs and one to the body
22
New cards
What is a single circulatory system?
* They have one loop that includes the lungs and the body
23
New cards
What type of circulatory systems do humans have?
* Closed, double circulatory system
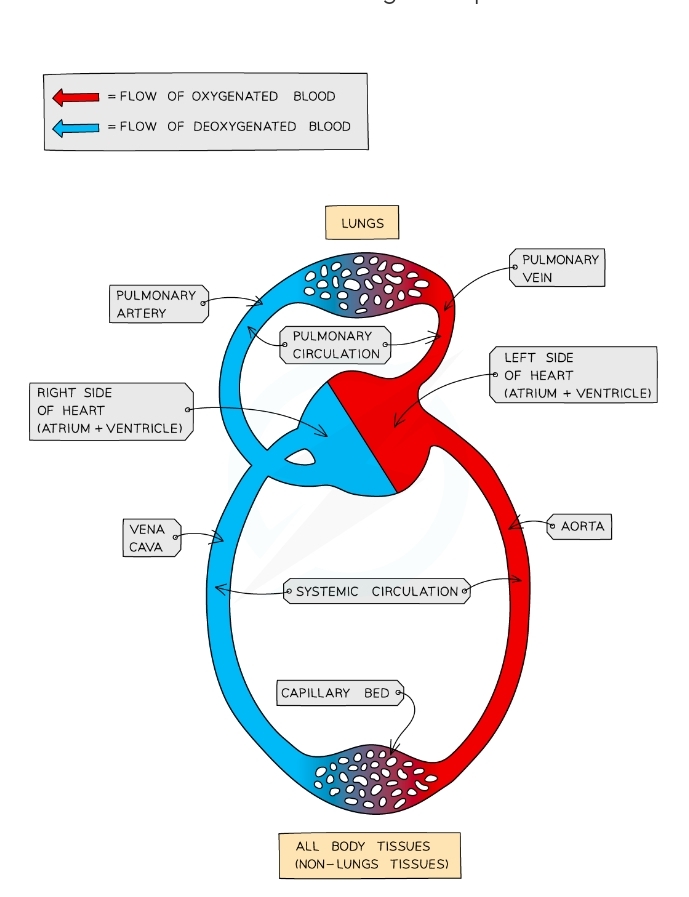
* Right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange (pulmonary circulatory system)
* Blood returns to the left side of the heart so oxygenated blood can be pumped at high pressure around the body (systemic circulatory system)
* Right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange (pulmonary circulatory system)
* Blood returns to the left side of the heart so oxygenated blood can be pumped at high pressure around the body (systemic circulatory system)
24
New cards
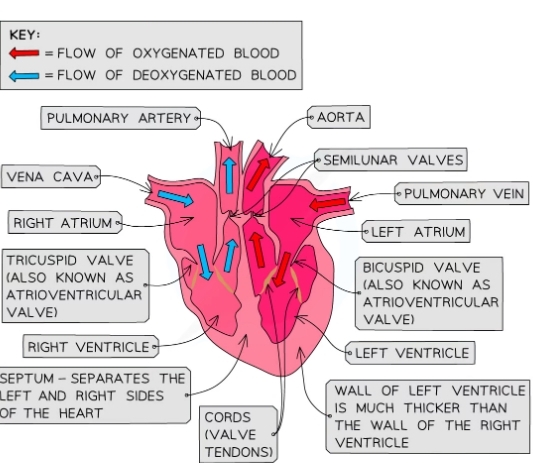
Structure of the heart
* Divided into four chamber
* Top 2 chambers are the atria
* The bottom 2 chambers are ventricles
* Left and right sides of the heart are separated by a wall of muscular tissue called the septum
* Protected in the chest cavity by the pericardium, a tough and fibrous sac
* Top 2 chambers are the atria
* The bottom 2 chambers are ventricles
* Left and right sides of the heart are separated by a wall of muscular tissue called the septum
* Protected in the chest cavity by the pericardium, a tough and fibrous sac
25
New cards
What is the role of the septum?
* Ensures blood doesn’t mix between the left and right sides of the heart
26
New cards
What are the roles of valves in the heart?
* Keep blood flowing forward in the right direction and for maintaining the correct pressure in the chambers of the heart
27
New cards
What separates the right atrium and right ventricle
* An AV valve called the tricuspid valve
28
New cards
What separates the left atrium from left vetricle
* An AV valve called the bicuspid valve
29
New cards
What separates the right vantricle from the pulmonary artery
* Semilunar valve called the pulmonary valve
30
New cards
What separates the left ventricle and the aorta
* Semilunar valve called the aortic valve
31
New cards
When do valves open?
* Open when pressure of the blood behind them is greater than the pressure in front
32
New cards
When do valves shut?
* Shut when the pressure in front of them is greater than the pressure behind them
* Preventing the backflow of blood
* Preventing the backflow of blood
33
New cards
How are the valvesattached to the walls of the heart
* By valve tendons (cords)
* Prevent the valves from flipping inside out under high pressure
* Prevent the valves from flipping inside out under high pressure
34
New cards
How have the ventricles adapted to their function?
* Thicker walls than atria to pump blood out of the heart
* Atria only pump blood into ventricles and are assisted by gravity ig
* Atria only pump blood into ventricles and are assisted by gravity ig
35
New cards
Left vs right ventricle
* Left ventricle:Thicker muscle than right ventricle for strong contraction to pump blood all the way around the body
* Right ventricle only has to pump blood to the nearby lungs
* Right ventricle only has to pump blood to the nearby lungs
36
New cards
Function of AV valves
* Prevent backflow of blood from ventricles into atria
37
New cards
Function of the SL valves
* Prevent backflow of blood from the aorta or pulmonary artery into the ventricles
38
New cards
Function of the vena cava
* Brings deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart
39
New cards
Function of the pulmonary vein
* Bring oxygenated blood from the lungs into the heart
40
New cards
Function of the pulmonary artery
* Takes deoxygenated blood to the lungs
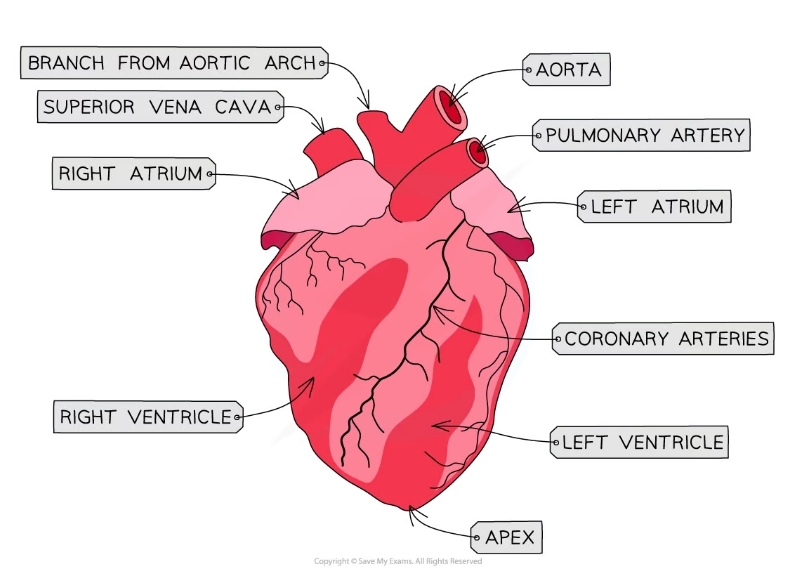
41
New cards
Function of the aorta
* Takes oxygenated blood into the body
42
New cards
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
* Run across the surface of the heart
* supplies blood to the heart muscle
* supplies blood to the heart muscle
43
New cards
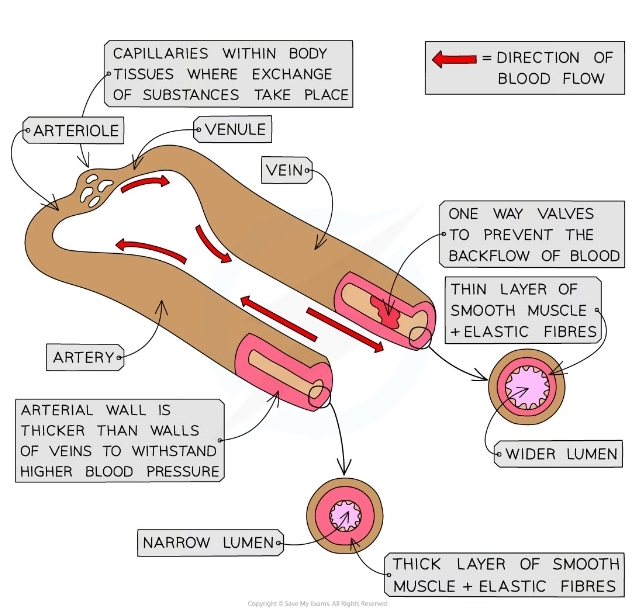
Function of the arteries
* Transport blood away from the heart, usually at high pressure, to the tissues
44
New cards
What are arterioles?
* Arteries branch into narrower blood vessels called arterioles which transport blood into capillaries
45
New cards
What do veins do?
* Transport blood to the heart, usually at low pressure
46
New cards
What do venules do?
* These narrower blood vessels transport blood from the capillaries to the veins
47
New cards
What do capillaries do?
* Microscopic blood vessels that carry blood to the cells
48
New cards
What is the lumen?
* The central cavity of an intestine or blood vessel through which the blood flows
* Arteries have a narrow lumen and veins have a wider lumen
* Arteries have a narrow lumen and veins have a wider lumen
49
New cards
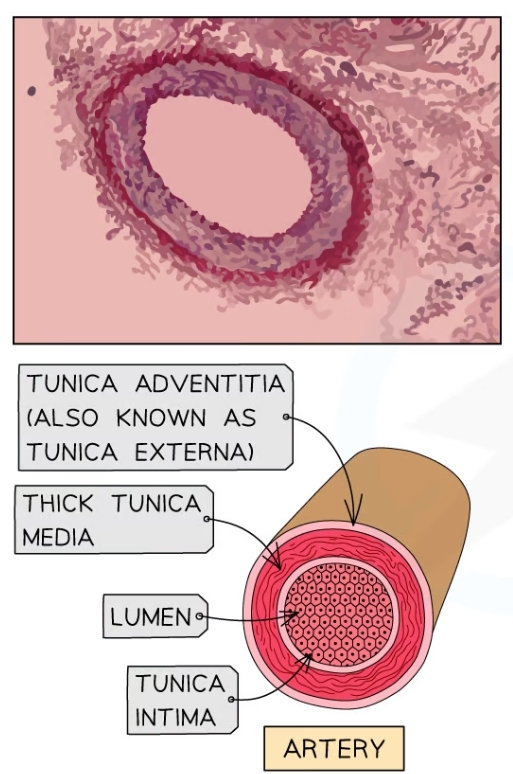
Properties of the artieries?
* Tunica intima
* Endothelium
* Tunica media
* Smooth muscle
* Elastic tissue
* Tunica externa
* Contains collagen
* Narrow lumen to maintainn high bloof pressure
* Pulse present so they stretch to accomodate increased volume of blood with every heartbeat
* Endothelium
* Tunica media
* Smooth muscle
* Elastic tissue
* Tunica externa
* Contains collagen
* Narrow lumen to maintainn high bloof pressure
* Pulse present so they stretch to accomodate increased volume of blood with every heartbeat
50
New cards
Features of the endothelium (tunica intima)
* One cell thick and lines the lumen of all blood cells
* Smooth to reduce friction for blood flow
* Endothelium highly folded, so it can expand under high pressure
* Smooth to reduce friction for blood flow
* Endothelium highly folded, so it can expand under high pressure
51
New cards
Features of the tunica media
* Thick layer of smooth muscle and elastic tissue
* Muscle strengthens the artieris so they can withstand high pressure
* Muscle can contract to constrict and narrow the lumen to reduce blood flow
* Elastic tissue maintains blood pressure as it stretches and recoils to even out fluctuations in pressure
* Muscle strengthens the artieris so they can withstand high pressure
* Muscle can contract to constrict and narrow the lumen to reduce blood flow
* Elastic tissue maintains blood pressure as it stretches and recoils to even out fluctuations in pressure
52
New cards
Features of the tunica externa
* Contains structural protein collagen
* Strong so protects blood vessels from damage by over-stretching
* Strong so protects blood vessels from damage by over-stretching
53
New cards
Function of the veins
* Recieve blood that has passed through capillary networks and send it to the heart
54
New cards
Propoerties of veins
* Smooth muscle and elastic layer
* Lumen
* valves
* noo pulse due to increased distance from the heart
* Lumen
* valves
* noo pulse due to increased distance from the heart
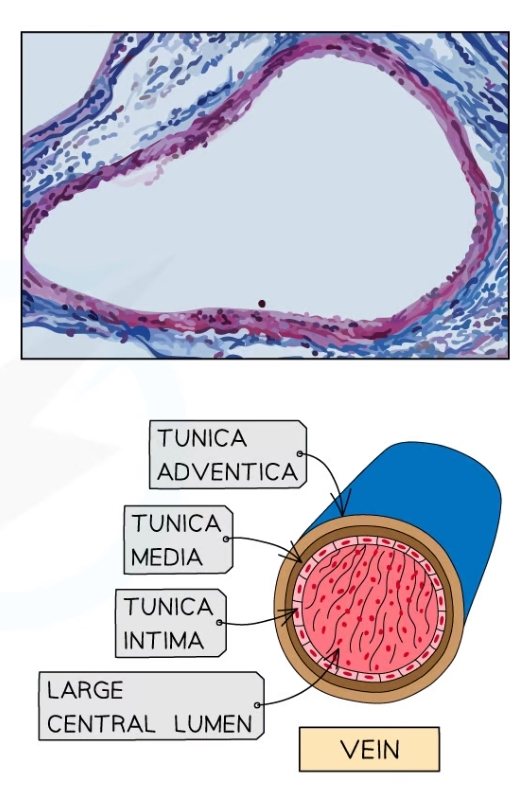
55
New cards
Smooth muscle and elastic tissue in veins?
* Much thinner as veins don’t need to withstand the high pressure
56
New cards
Lumen in the veins
* Wider in the veins than in the artery
* Ensures blood returns to the heart at adequate speed
* Reduces friction between the blood and endothelium of the vein
* Ensures blood returns to the heart at adequate speed
* Reduces friction between the blood and endothelium of the vein
57
New cards
How does the larger lumen in the veins affect speed of blood flow?
* The rate of blood flow slower in veins but in a larger lumen the volume of blood delivered per unit of time is equal to that of the arteries
58
New cards
What is the purpose of valves in the veins?
* Prevents backflow of blood, helping blood return to the heart
59
New cards
Properties of the capillaries?
* thin walls which are permeable
* narrow lumen
* Wall is a single layer of endothelial cells
* narrow lumen
* Wall is a single layer of endothelial cells
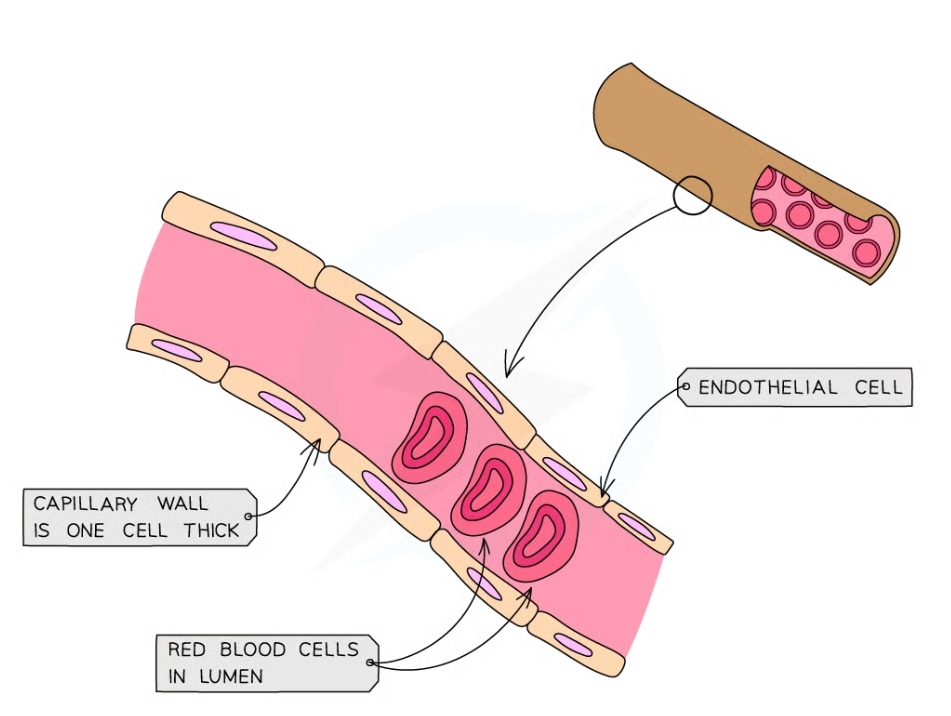
60
New cards
What is a capillary bed?
* Exchange surfacea
* Large number of capillaries that branch between cells
* Showrt diffusion distance so substances dffuse quicker
* Large number of capillaries that branch between cells
* Showrt diffusion distance so substances dffuse quicker
61
New cards
Why is the lumen narrow in a capillary?
* Red blood cells travel in a single file line
* Forces blood to travel slower which provides more time for diffusion to occur
* Forces blood to travel slower which provides more time for diffusion to occur
62
New cards
Feature of the capillary cell wall?
* One cell thick which Reduces diffusion distance for O2 and CO2
* Single layer of endothelial cells
* They have pores which allow blood plasma to leak out and form tissue fluid
* White blood cells can squeeze through these pores to combat infection
* Single layer of endothelial cells
* They have pores which allow blood plasma to leak out and form tissue fluid
* White blood cells can squeeze through these pores to combat infection
63
New cards
Steps of the cardiac cycle
* Atrial systole
* Ventricular systole
* Atrial and ventricular diastole
* Ventricular systole
* Atrial and ventricular diastole
64
New cards
Atrial systole
* Walls of atria contract
* Volume decreases
* Pressure decreases causes AV valve to open
* Blood forced into ventricles
* Ventricles relaxed
* Volume decreases
* Pressure decreases causes AV valve to open
* Blood forced into ventricles
* Ventricles relaxed
65
New cards
Ventricular systole
* Walls of ventricle contract
* Ventricular volume decrease
* Ventricular pressure increases
* Pressure in ventricles greater than in atria so AV valve close, prevent backflow of blood
* Pressurein ventricles greater than in the veins so SL valves open
* Blood forced into arteries
* Arial diastole
* Ventricular volume decrease
* Ventricular pressure increases
* Pressure in ventricles greater than in atria so AV valve close, prevent backflow of blood
* Pressurein ventricles greater than in the veins so SL valves open
* Blood forced into arteries
* Arial diastole
66
New cards
Cardiac Diastole
* Ventricles and atria both relaxed
* SL valves close as pressure in veins greater than in ventricles
* Atria fill with blood
* AV valves open
* Blood flows passively into ventricles
* SL valves close as pressure in veins greater than in ventricles
* Atria fill with blood
* AV valves open
* Blood flows passively into ventricles
67
New cards
Cardiac Cycle Graph
* The lines of the graph = pressure of left ventricle atrium and aorta
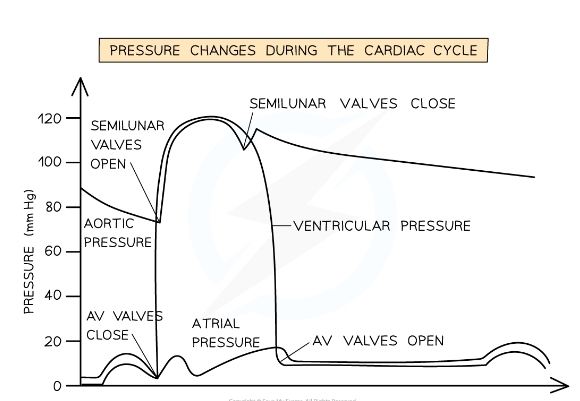
68
New cards
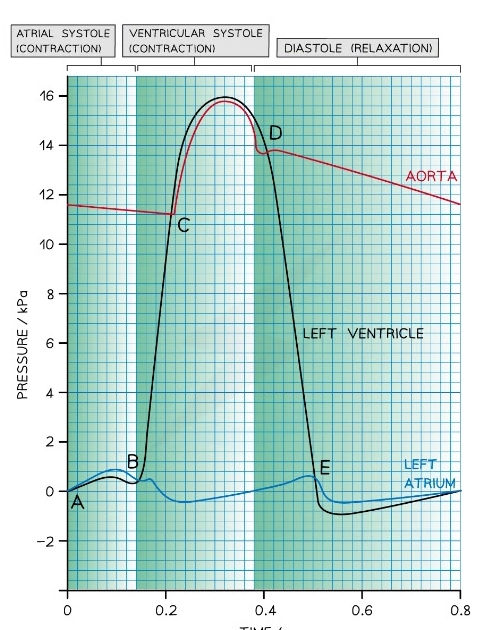
Whta stage of the cardiac cycle does point A represent?
* End of diastole
* Atrium has just filled with blood
* Higher pressure in the atrium so AV valve open
* Atrium has just filled with blood
* Higher pressure in the atrium so AV valve open
69
New cards
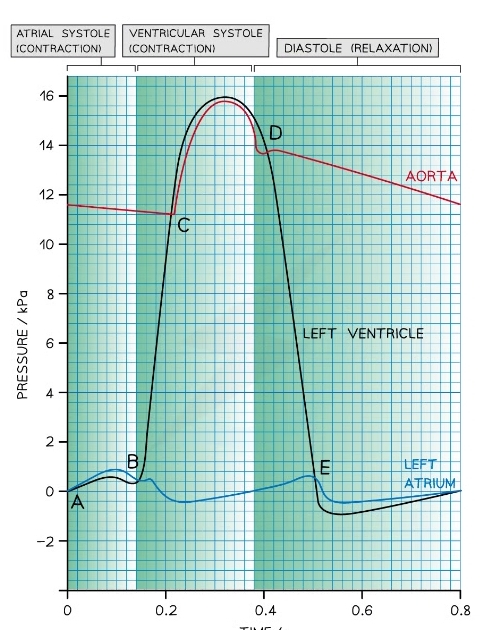
What stage of the cardiac cycle is between point A and B?
* Arial systole
* Atrium contracts
* Ventricle pressure increases as it fills with blood
* AV valve remains open
* Atrium contracts
* Ventricle pressure increases as it fills with blood
* AV valve remains open
70
New cards
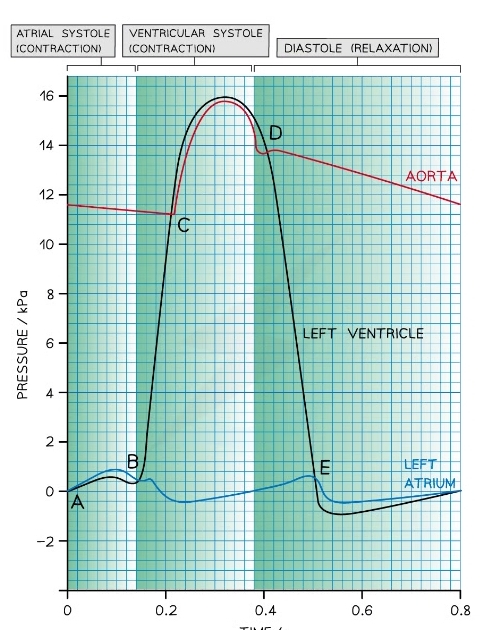
What stage of the cardiac cycle occurs at point B?
* Begining of ventricular systol
* Ventricle contracts
* Atrium pressure drops
* Pressure in ventricle> than in atrium so AV valve closes
* Ventricle contracts
* Atrium pressure drops
* Pressure in ventricle> than in atrium so AV valve closes
71
New cards
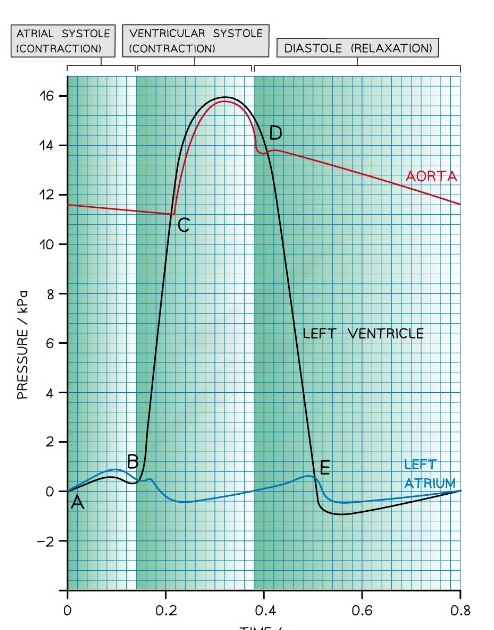
What stage of the cardiac cycle is at point c
* Ventricular systole
* Ventricle continues to contract
* Aortic valves opens as pressure in ventricle> pressure in aorta
* Blood forced into aorta
* Ventricle continues to contract
* Aortic valves opens as pressure in ventricle> pressure in aorta
* Blood forced into aorta
72
New cards
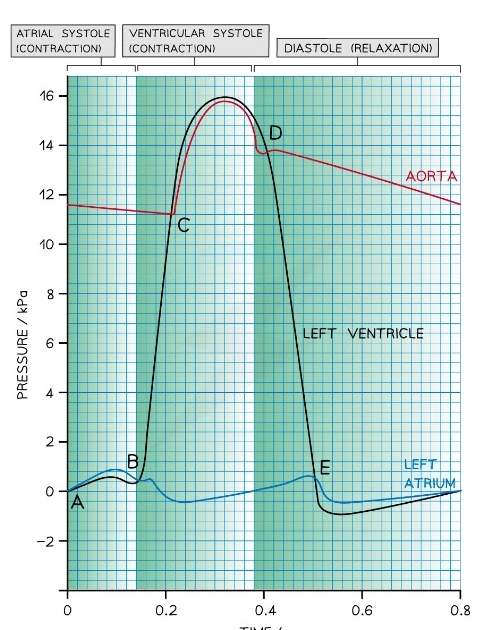
What stage of the cardiac cycle is at point D?
* The begining of diastole
* Ventricles relax
* Aortic valve closes as pressure> pressure in ventricle
* Ventricles relax
* Aortic valve closes as pressure> pressure in ventricle
73
New cards
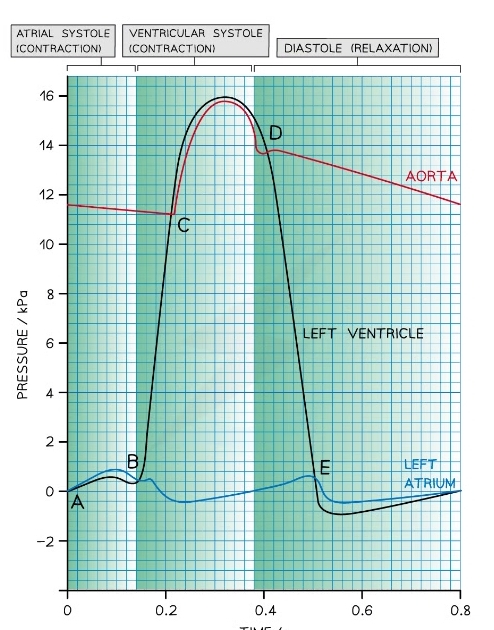
What stage of the cardiac cycle is at point D-E?
* Ventricle remains relax and ventricular pressure still decreases
* Blood flows into the relaxed atrium form pulmonary veins
* Blood flows into the relaxed atrium form pulmonary veins
74
New cards
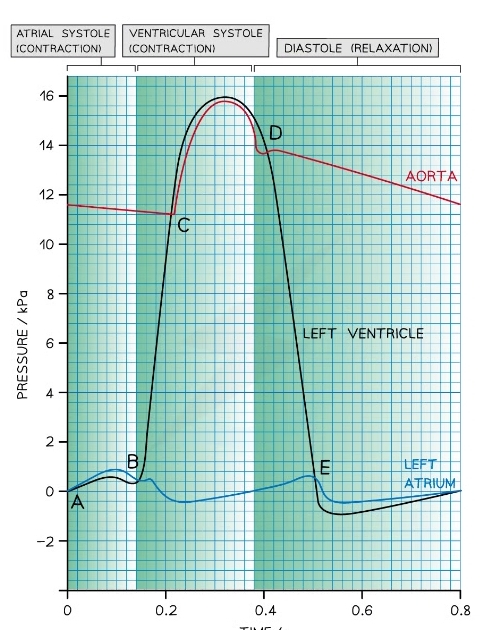
What stage of the cardiac cycle is at point E?
* AV valve opens as pressure in atrium> pressure in ventricle
75
New cards
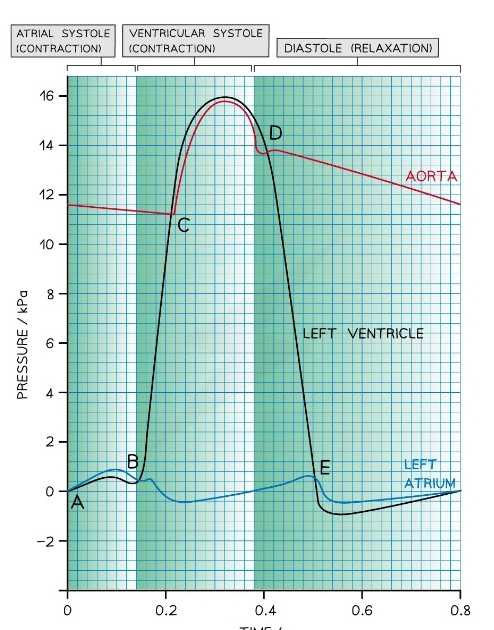
What happens in cardiac cycle after point E
* Late diastole
* here is a short period of time during which the **left ventricle expands** due to relaxing muscles
* This increases the internal volume of the left ventricle and **decreases the ventricular pressure**
* At the same time, blood is flowing slowly through the newly opened AV valve into the left ventricle, causing a **brief decrease in pressure** in the left atrium
* The pressure in both the atrium and ventricle then **increases slowly** as they continue to fill with blood
* here is a short period of time during which the **left ventricle expands** due to relaxing muscles
* This increases the internal volume of the left ventricle and **decreases the ventricular pressure**
* At the same time, blood is flowing slowly through the newly opened AV valve into the left ventricle, causing a **brief decrease in pressure** in the left atrium
* The pressure in both the atrium and ventricle then **increases slowly** as they continue to fill with blood
76
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
What factors can influence heart rate?
What factors can influence heart rate?
* Drugs
* Caffeine
* Alcohol
* Sex i.e. male or female
* Weight
* Height
* Temperature
* Diet
* Dehydration
* Caffeine
* Alcohol
* Sex i.e. male or female
* Weight
* Height
* Temperature
* Diet
* Dehydration
77
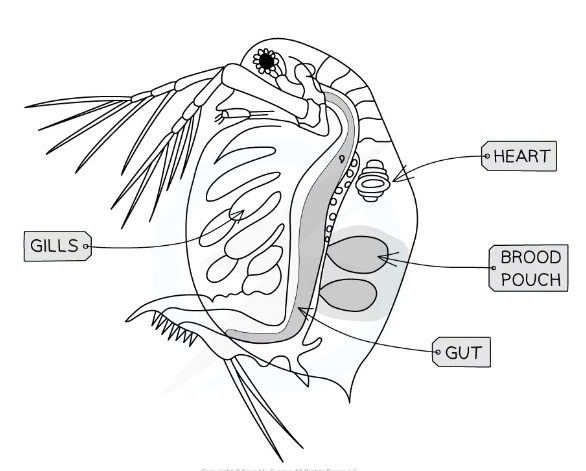
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
What are daphnia?
What are daphnia?
* Small aquatic vertebrates
78
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
Why are daphnia suitable for this expriment?
Why are daphnia suitable for this expriment?
* Transparent bodies so their internal organs can be observd using a light microscope
79
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
Apparatus
Apparatus
* Light microscope
* Cavity slide
* Culture of *Daphnia*
* Pipette
* Caffeine solutions at a range of concentrations
* Distilled water
* Stop watch
* Cavity slide
* Culture of *Daphnia*
* Pipette
* Caffeine solutions at a range of concentrations
* Distilled water
* Stop watch
80
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
Method
Method
1. Prepare five different concentrations of caffeine solution and a control solution of distilled water
* The serial dilution technique could be used here
2. Add some pond water into the well of a cavity slide and add three drops of distilled water
3. Select a large *Daphnia* and use a pipette to carefully transfer it to the cavity slide
* You can also use a Petri dish if you do not have access to a cavity slide
4. Place the cavity slide onto the stage of a microscope and observe the animal under low power
* The beating heart is located on the dorsal side just above the gut and in front of the brood pouch
5. Use a stopwatch to time 20 seconds, and count the number of heart beats
* The heart beat of *Daphnia* is very rapid, so you can count the beats by making dots on a piece of paper
6. Count the dots and express heart rate as number of beats per minute
* Multiply by three to convert beats per 20 seconds into beats per 60 seconds
7. Return the *Daphnia* to the stock culture
8. Repeat steps 3-7 with at least 5 other *Daphnia* individuals
9. Repeat steps 3-8 with different caffeine concentration solutions
81
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
Variations
Variations
* You can also investigate the effect of
* Temperature
* Other chemicals such as alcohol (1% ethanol solution)
* Temperature
* Other chemicals such as alcohol (1% ethanol solution)
82
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
Results
Results
* To analyse your results it is best to draw a graph
* Take an average of the heart rate repeats for each caffeine concentration
* Plot average heart rate (y axis) against caffeine concentration (x axis)
* The graph should show a positive correlation; as caffeine concentration increases, heart rate increases
* Take an average of the heart rate repeats for each caffeine concentration
* Plot average heart rate (y axis) against caffeine concentration (x axis)
* The graph should show a positive correlation; as caffeine concentration increases, heart rate increases
83
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
Ethical considerations
Ethical considerations
* Less sophisticated nervous system so don’t feel paint the same way
* Cannot give consent
* Cannot express pain
* Cannot give consent
* Cannot express pain
84
New cards
Core practical 1: Investigating heart rate
How to miniimise poential harm of the daphniia
How to miniimise poential harm of the daphniia
* Handle gently
* Examination preiods should e kept as short as possible
* Animals should be returned promptly to the holding tank
* Extreme ranges of variables tested should be avoided
* Examination preiods should e kept as short as possible
* Animals should be returned promptly to the holding tank
* Extreme ranges of variables tested should be avoided
85
New cards
What is atherosclerosis?
* Narrowing of the lumen in the arteries due to a build up of plaque
* Hardening of the arteries
* Progressive disease
* Hardening of the arteries
* Progressive disease
86
New cards
What is a progressive disease?
* A disease that gets worse over time
87
New cards
Steps of atherosclerosis
* Damage to the endothelium (due to high blood pressure), cholesterol accumulates and oxidises causing an inflammatory response
* Lipids and cholesterol accumulate in the damaged area
* White blood cells (macrophages) enter the endothlium, attempt to digest cholesterol and turn into foam cells
* Foam cells degenerate and form the atheroma t on the endothelium wall
* Plaque ruptures and platelets accumulate and form a plaque called an atheroma
* Atheroma narrows lumen of the artery, raising lood pressure and reducing blood flow
* Plaque hardens over time further reducing easticity of artery wall
* Lipids and cholesterol accumulate in the damaged area
* White blood cells (macrophages) enter the endothlium, attempt to digest cholesterol and turn into foam cells
* Foam cells degenerate and form the atheroma t on the endothelium wall
* Plaque ruptures and platelets accumulate and form a plaque called an atheroma
* Atheroma narrows lumen of the artery, raising lood pressure and reducing blood flow
* Plaque hardens over time further reducing easticity of artery wall
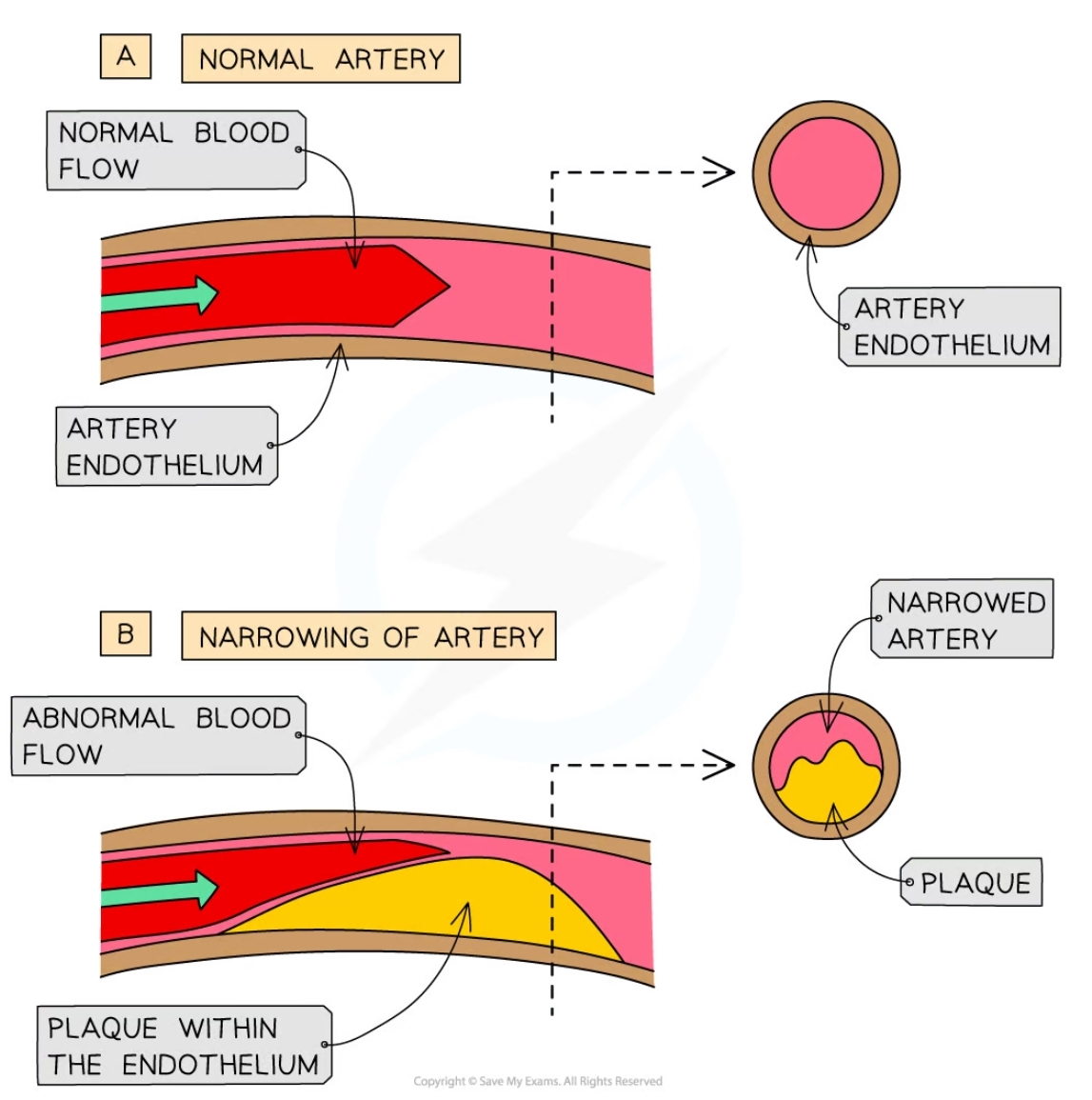
88
New cards
What is the pupose of blood clotting?
* Prevents excess blood loss and prevents entry of pathogens
* Provides a barrier (scab) so healing can occur
* Provides a barrier (scab) so healing can occur
89
New cards
What causes the formation of a blood clot?
90
New cards
91
New cards
92
New cards
93
New cards
94
New cards
95
New cards
96
New cards
97
New cards
98
New cards
99
New cards
100
New cards