Unit Two: American Revolution to Constitution (EOC)
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Natural Rights
God-given rights that everyone who is human possess.
Social Contract Theory
People consented to surrender some freedoms in exchange for protection of their rights.
Federalist
Supporter of the U.S. constitution and strong central government.
Anti-Federalist
Against the U.S. constitution and feared strong central government.
Boycott
A form of protest where people refuse to buy goods or services from a particular company or country.
Repeal
To revoke a law or act of legislation.
Thomas Jefferson
Primary author of the Declaration of Independence.
Thomas Paine
England-born political philosopher and writer who supported revolutionary causes in America.
Benjamin Franklin
American ambassador working in Europe (France) to secure a military alliance.
John Adams
American ambassador working in Europe (Netherlands) to secure a loan.
John Locke
British philosopher who believed all individuals naturally possess certain rights.
Baron von Steuben
Experienced Prussian officer who taught drills to the milita the Valley Forge.
Marquis de LaFayette
A young French nobleman who served as a critical link for the military alliance.
John Burgoyne
A commander who lost to Washington because he did not know the geography.
Horatio Gates
Placed the canons on Bemis Heights Ridge; turning points of the Revolution.
Crispus Attucks
One of the Americans killed at the Boston Massacre.
Valley Forge
Training location during the winter of 1777; terrible weather conditions.
French and Indian War
Conflict was fought between France and Britain over control of North America.
Crossing the Delaware
Surprise Christmas Day attack where the milita was able to defeat the Hessians.
Treaty of Paris 1763
Results in France losing Canada and the Ohio River Valley.
Battle of Trenton
Plan was to use the River to arrive at Trenton.
Battle of Saratoga
Plan was to split the colonies but the British general didn’t know the terrain.
Treaty of Paris 1763
American independence is gained and land is acquired.
Yorktown
Surrender location of General Cornwallis.
Land of Ordinance 1765
Method for dividing land and creating townships.
Articles of Confederation
Created a simple “league of friendship” between the states.
Proclamation of 1763
Prohibited colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains.
Northwest Ordiance
Procedure for adding new states to the union.
Stamp Act
Required every official document, newspaper, etc to have one attached to it.
Intolerable Acts
A combination of five acts; also done as a response to the Boston Tea Party.
Common Sense
Simple persuasive essay about Independence that everyone should understand.
Federalist Papers
Series of essays to convince New Yorkers the Constitution would protect and strengthen the United States.
Committee of Correspondence
Sent information to other colonies about their anti-British activities.
Great Compromise
Settled disputes between large states and small states.
Committee of 5
Appointed by the Continental Congress to draft the Declaration.
3/5th Compromise
States were permitted to count a portion of their slaves toward the population.
Sons of Liberty
Led by Samuel Adams; protesting and boycotting; and at times violent.
Daughters of Liberty
Helped boycott British goods by making cloth and refusing British tea.
Shays’ Rebellion
Led an angry group of farmers to attack the Massachusetts Courthouse.
How did the French and Indian War lead to the American Revolution?
It caused Britain to impose taxes on the colonies to pay for war debt, leading to colonial resistance and eventually revolution.
How are John Locke and Thomas Jefferson similar in their philosophy?
They both believed in natural rights.
What was the significance of the crossing of the Delaware River and the victory at Trenton?
It proved America could win, increased nationalism, and helped regain control of New Jersey.
How did Shays’ Rebellion demonstrate the weakness of the Articles of Confederation?
It showed its inability to raise a sufficient military force.
What did the Anti-Federalists want added to the U.S. constitution?
Bill of Rights

What does this picture depict?
Stamp act
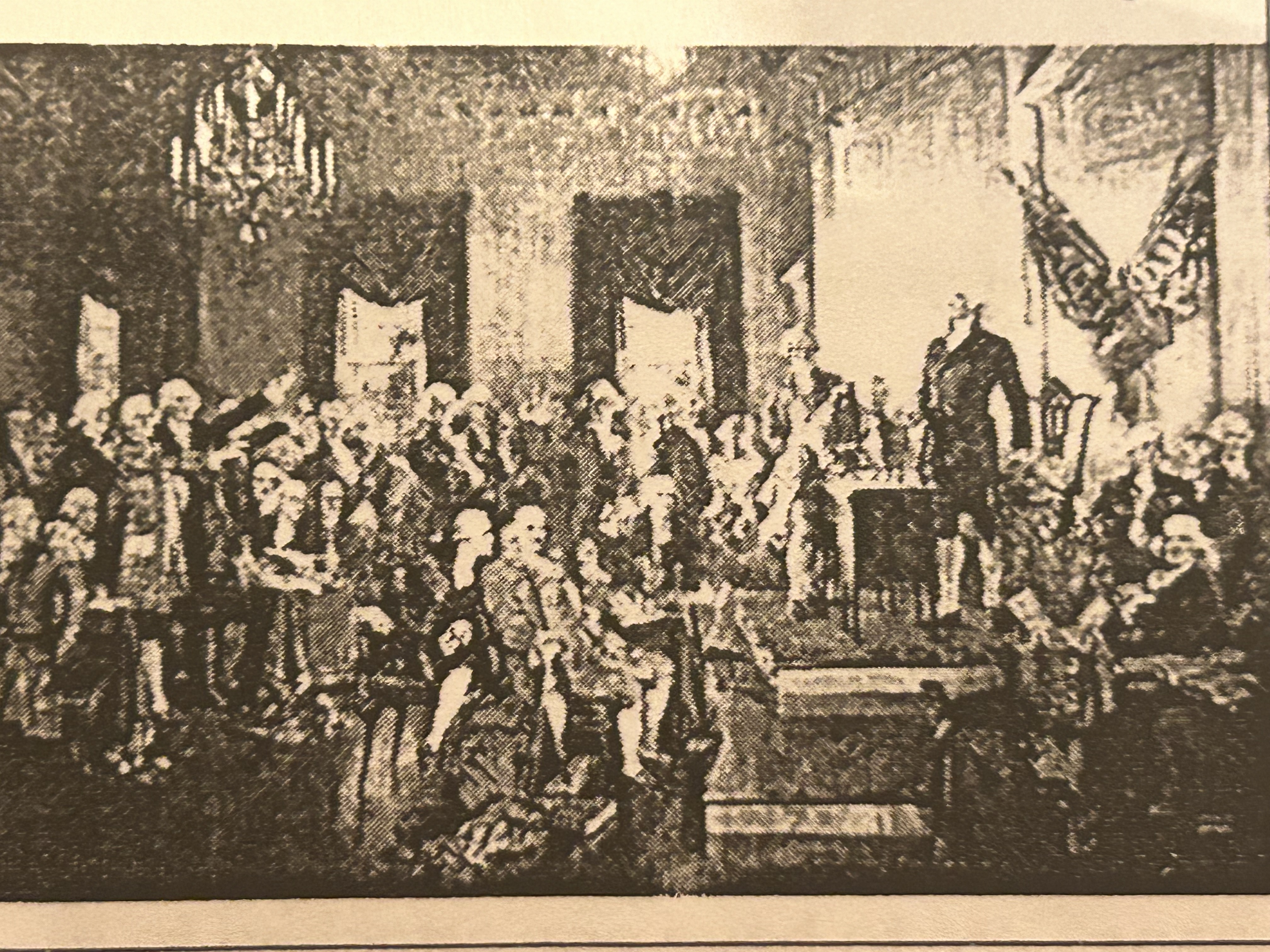

What does this picture depict?
1st Continental Congress
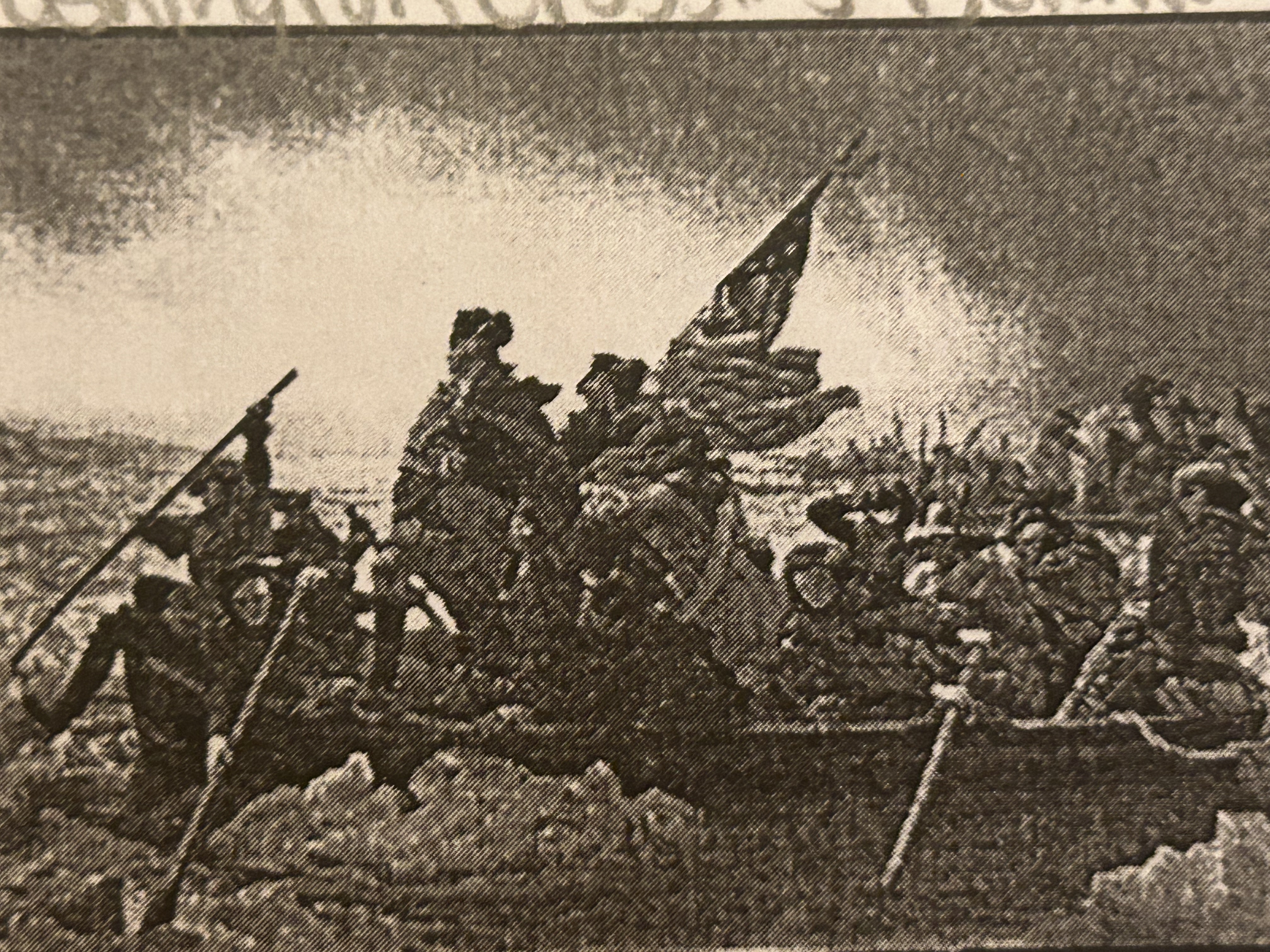

What does this picture depict?
Washington crossing Delaware
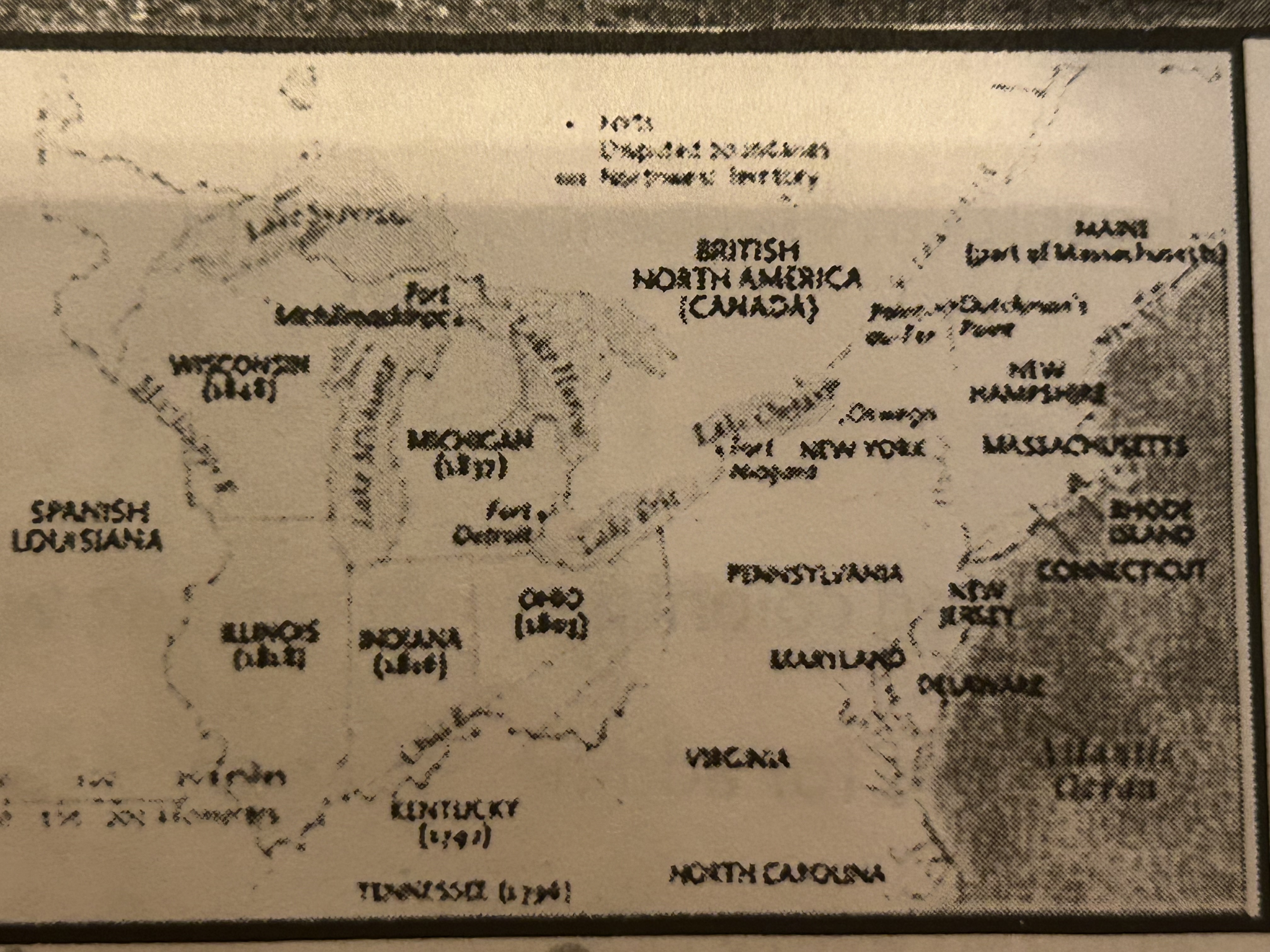
What does this picture depict?
Battle of Saratoga