Edexcel a level biology topic 1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
carbohydrates
molecules which only consist of hydrogen carbon and oxygen,
they are three types of chains,
monosaccharides
disaccharides
polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
such as glucose it contains 6 carbon atoms and there is alpha or beta glucose
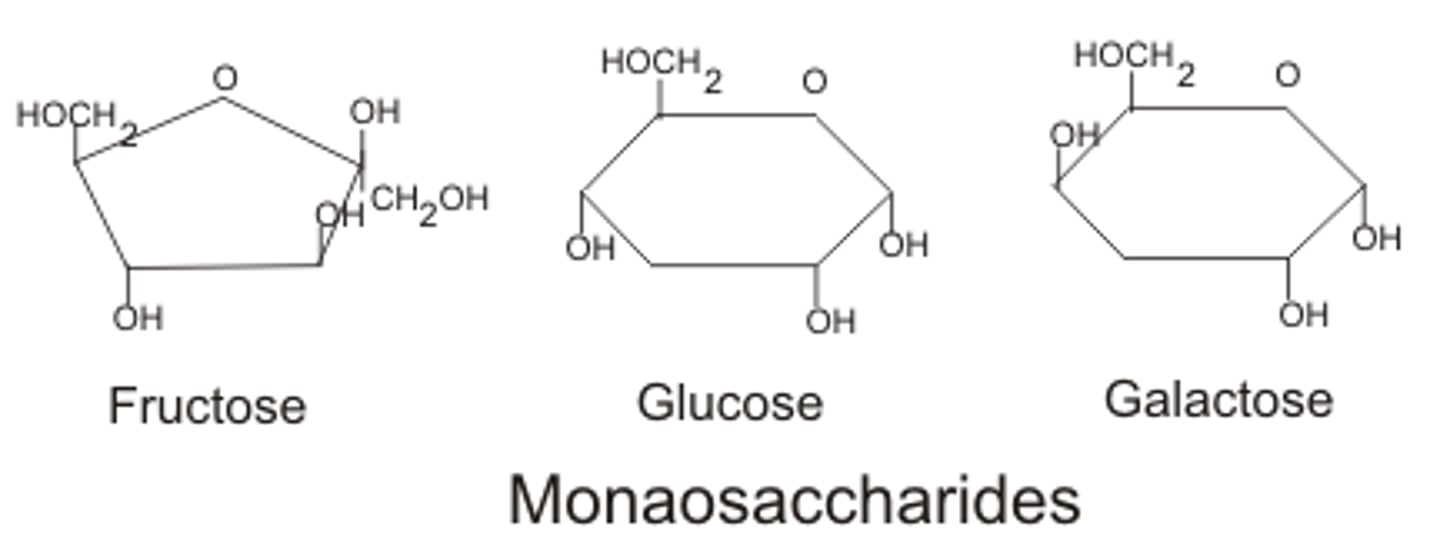
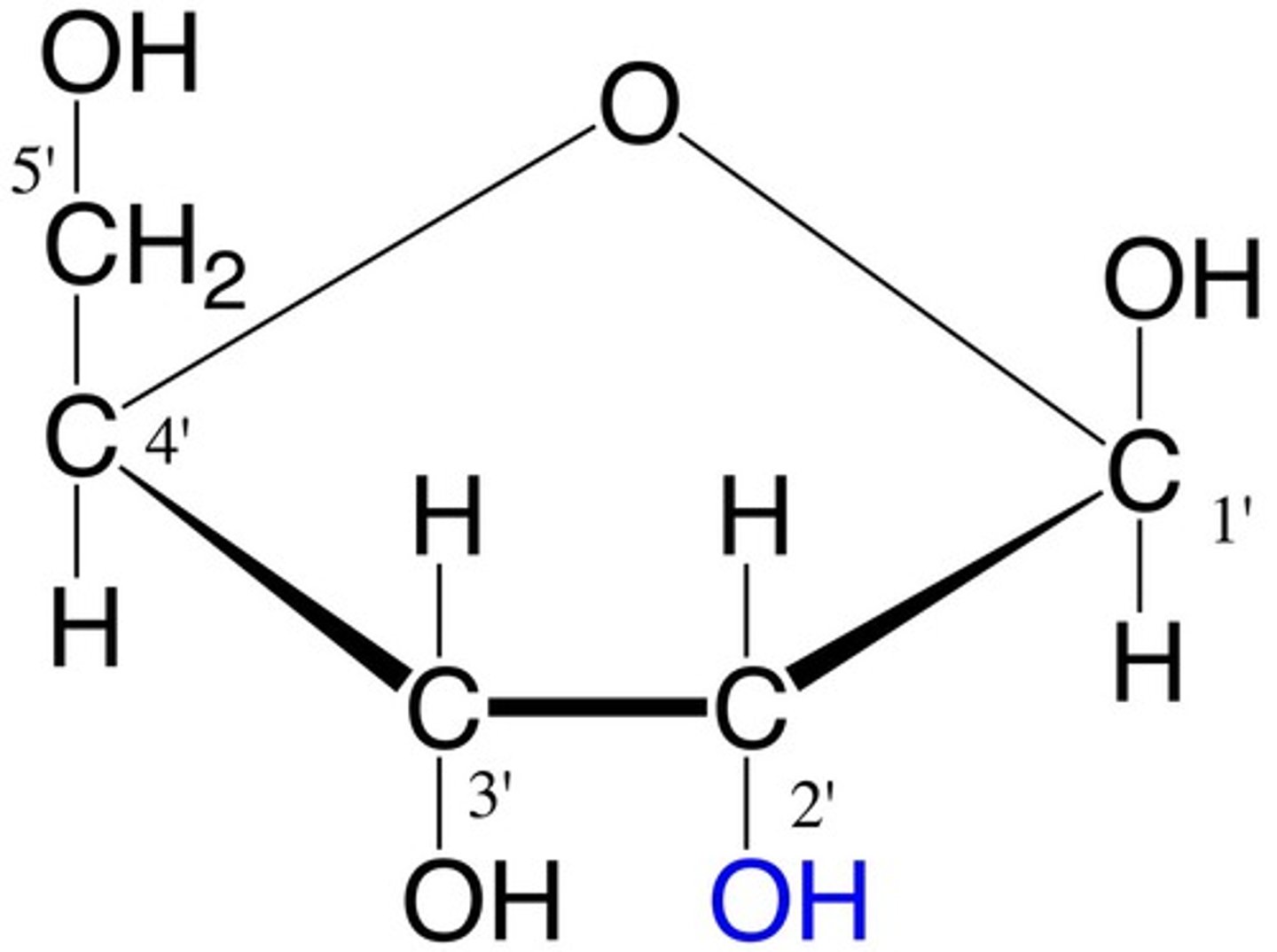
ribose
monosaccharide
its a pentose sugar used in RNA.
DNA contains an isomer of ribose called deoxyribose.
disaccharides
maltose- two glucose molecules
sucrose- fructose and glucose
lactose- glucose and galactose
polysaccharides
long chains of monosaccharides
such as glycogen and starch which are made up of alpha glucose
cellulose made up beta glucose.
Both formed via condensation
glycogen
made up of 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, it contains a lot of energy branches so it can be hydrolysed and energy can be release quickly.
its also compact so storing it is much easier
starch
stores two polysaccharides
amylose-is an unbranched molecule made up of 1-4 glycosidic bonds, it is also coiled and very compact so it can store a lot of energy
amylopectin- branches and made up of both 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, so enzymes are able to digest the branched chains so it is made for quick energy release, it is compact however not as compact as amylose
cellulose
long, unbranched beta glucose monomers, joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds.
contains microfibrils and microfibres held together by hydrogen bonds
lipids
saturated lipids c-c single bonds and are found in animals
unsaturated made up of c=c double bonds and are found in animals, they have a lower melting point compared to saturated lipids, because of the weaker intermolecular forces and branched hydrocarbons aren't as compact so they have more kinks.
properties of lipids
they're water proof/hydrophobic
compact and release energy quicker than carbs.
non polar
thermal insulation
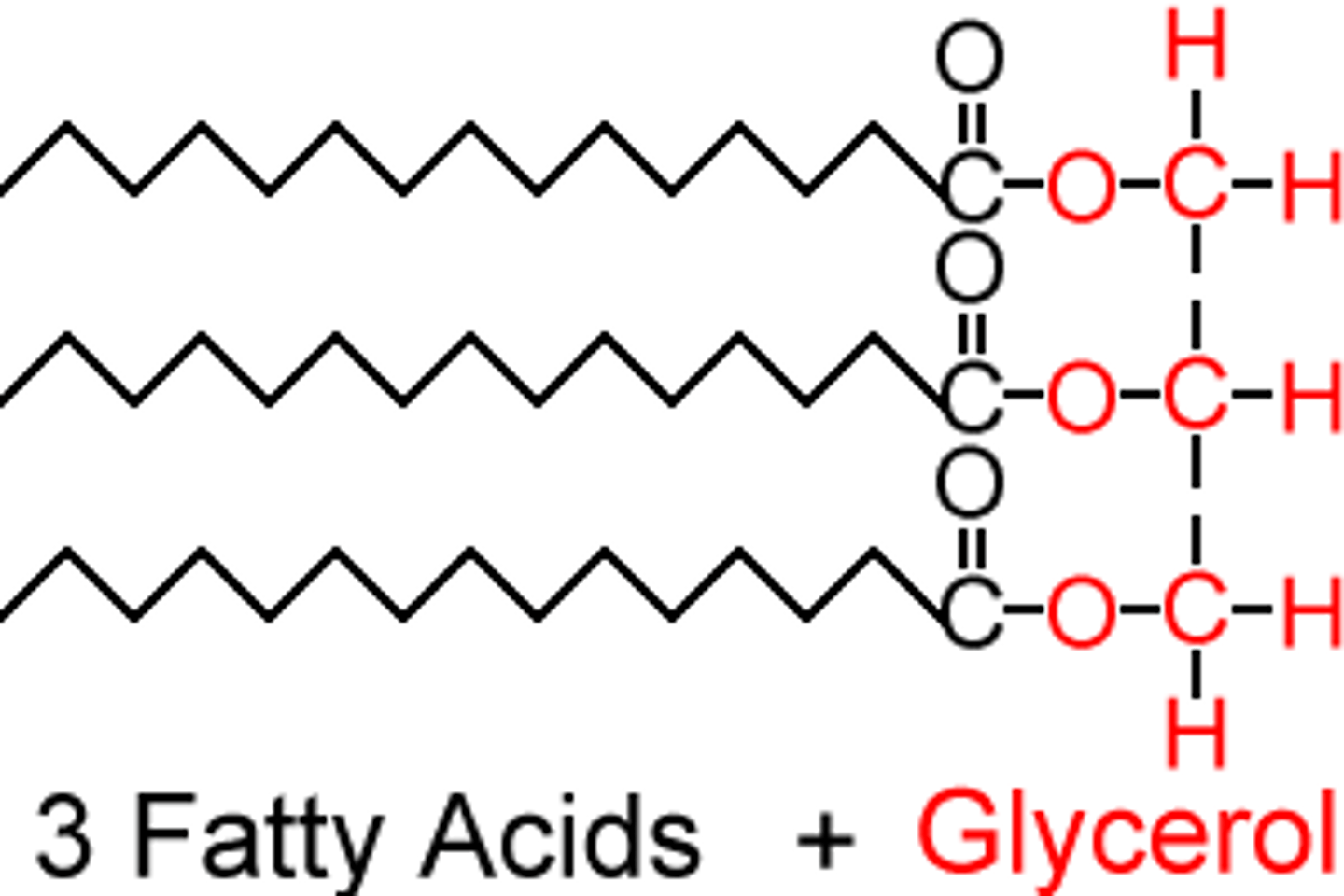
triglycerides
made up of 3 fatty acids, one glycerol and are joined by ester bonds which are formed in the condensation reaction.
They're used as energy reserves in both plant and animals.
protiens
they contain an anime group and a carboxyl group.
theyre joined by a peptide bond in condensation reaction
primary structure-is the linear sequences of the amino acids
secondary structure-formed by folding by folding the polypeptide chains in alpha or beta helix, it only contains hydrogen bonds.
tertiary structure-3d folding of the secondary structure into a complex shape, joined by either hydrogen or ionic bonding
quaternary-3d arrangement of more than one polypeptide
fibrous proteins
Very little teritary/quaternary structure - mainly secondary structure.
Occasional cross-linkages which form microfibres for tensile strength
Insoluble
Used for structural purposes
such as collagen high tensile strength from hydrogen bonds, collagen forms structure of the bones the cartilage and connective tissues
globular protien
complex tertiary/quaternary structure
forms colloids in water
many uses e.g hormones
e.g haemoglobin which is water soluble, consisting of 4 polypeptide chains.
DNA and protein synthesis
DNA nucleotide contains a deoxyribose, phosphate group and the organic base A,T,C,G.
Pyrimidines-single ring structure, uracil, cytosine and thymine
purines-adenine and guanine
pyrimidines are smaller with only one nitrogen containing ring, whereas purines have more than one.
transcription
hydrogen bonds break via dna helicase and the dna uncoils.
one of the dna strands acts as a template making mRNA this is antisense strands, the coding strand is the sense strand, which has the same nucleotide sequence as the stand being synthesised.
free floating nucleotides line up on the template strand by complimentary base pairing, and adjacent molecules are joined together by phosphodiester bonds, thus forming the molecule RNA, which is catalysed by RNA polymerase.
mRNA the moves out of the nucleus via the nuclear pore, into the ribosomes ready for the next stage of protein synthesis.
Translation
mRNA attaches on the ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
a tRNA molecule, which has the specific amino acid binding site, binds to the mRNA via its anticodon.
Hydrogen bonds form between the anticodon of the tRNA and the codon of mRNA.
a second tRNA molecule binds to the mRNA and the two amino acid forms a peptide bond
a third tRNA joins and the first one leaves the ribosomes.
this process has repeated thus leading the formation of the polypeptide chains until the stop codon has reached the mRNA.
enzymes
they're biological catalysts, increasing the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy pathway., including both anabolic and catabolic reactions.
the active site is the area of the enzymes where only the substrate binds, meaning enzymes are specific where the substrate binds to.
However when an enzyme and substrate forms a complex, the structure of the enzyme is distorted so that it fits the substrate complex, known as the induced fit model.
inhibitors
used to slow down a chemical reaction, there are two types competitive inhibition and non competitive inhibition.
competitive inhibition- when the inhibitor competes with the substrate molecule for the active site, therefore preventing it from binding, it can be reversed by increasing the substrate concentration.
non competitive inhibition- where the inhibitor doesn't bind the active site, yet binds to the allosteric site, this changes shape of the enzyme which decrease the reaction rate.Increasing substrate does not decrease the rate of reaction.
inorganic ions
they're required for plant growth.
nitrate ions-required to make DNA and amino acids
calcium ions- required for calcium pectate for the middle lamellae of the plants
phosphate ions- required to make ATP and ADP, also DNA and RNA.
magnesium ions- needed to produce chlorophyll
Water
polar molecule due the uneven distribution of the charge, so metabolic reactions can occur.
high specific latent heat- a lot of energy is required to change the temperature, therefore no temperature fluctuations which can be dangerous for animals that live in the rivers.
maximum density- ice is less dense than water, which is an insulating layer in colder regions, where on the top layer of the ice has been melted off.