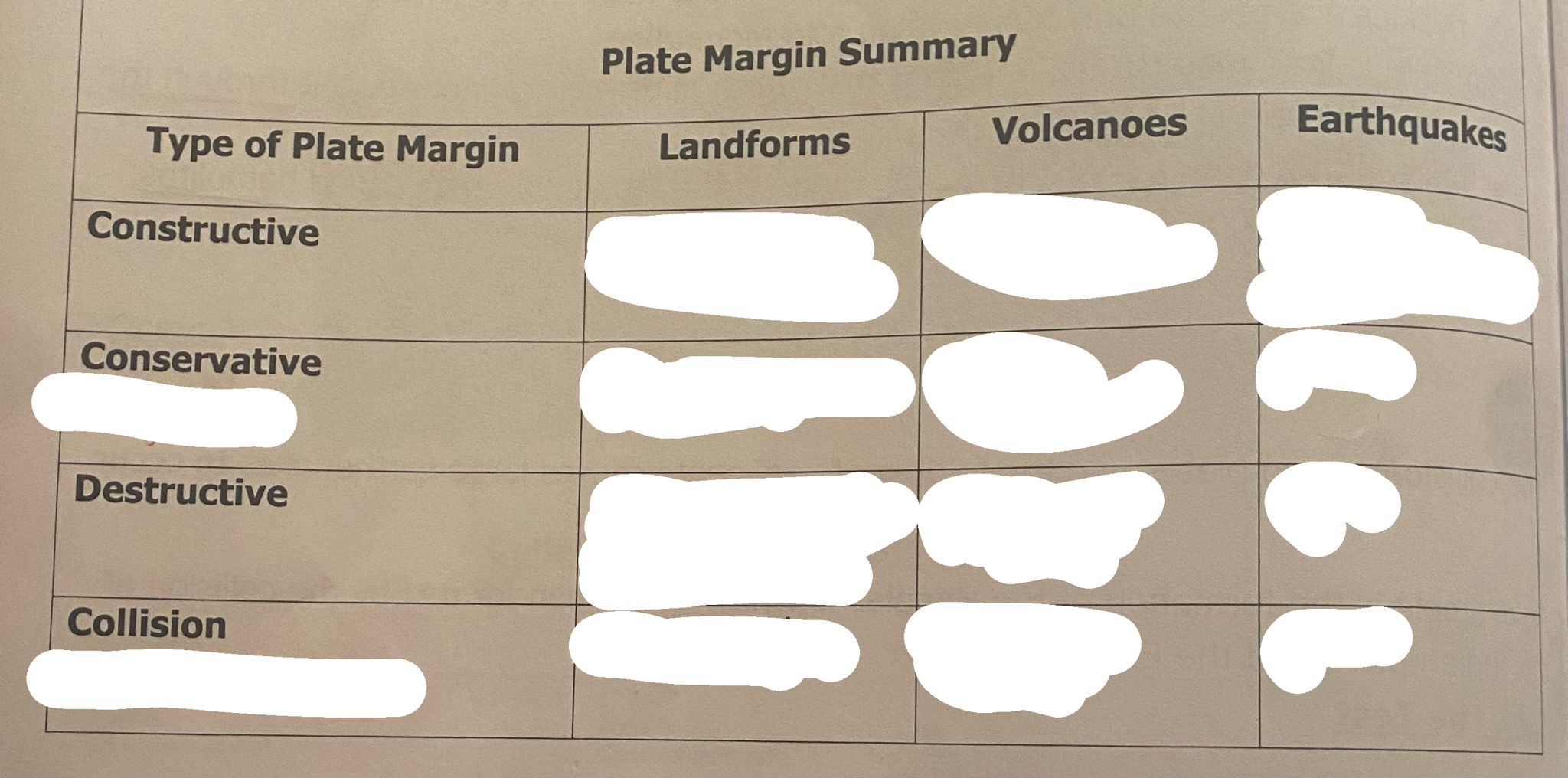
earthquakes
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
How are convection currents made
Tectonic plates float on the mantle.
Radioactive decay in the core generates huge amounts of heat.
The heat generated by the core keeps the magma in the mantle in a semi-molten state.
Magma closest to the core is heated, becomes less dense and rises towards the crust.
When the rising magma reaches the crust, it spreads out below the crust,
This then creates a dragging effect on the tectonic plates
and causes them to move slowly.As the magma moves below the crust, it begins to cool and its density increases.
Eventually it sinks back to the core where it is reheated.This is a convection current.
Convection currents in the mantle cause the slow movement of tectonic plates
How do plates move when magma rises
The diverge/ pull apart
What happens when magma sinks
They converge/ are pulled towards each other
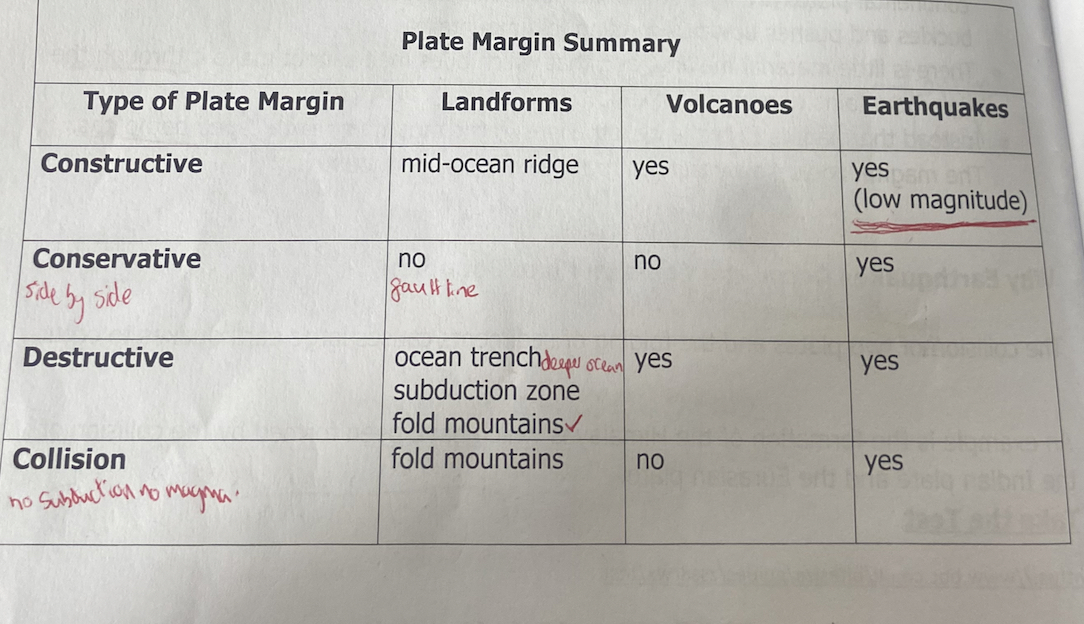
What happens at a constructive place margin
(Divergent plate margin = constructive)
Plates move away from each other
examples of constructive plays boundary
North American plate and Eurasian plate centre of the Atlantic Ocean
plate Movement at a constructive plate boundary
Radioactive decay in the core generates heat which heats the magma in the mantle.
In the mantle there are convection currents rising which cause two plates floating on the mantle to move slowly away from each other.
What is a mid ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater volcanic mountain range formed at a constructive plate margin
Reasons why a mid ocean ridge forms at a constructive plate boundary
When convection currents rise in the mantle and cause two plates to move apart, a small gap is created.
Magma from the mantle seeps / oozes slowly upwards to plug the narrow gap created.
Basic lava is erupted along the fissure (cracks) and where there are pools of particularly active magma, the magma will gently erupt through underwater volcanoes.
This magma which oozes onto the seabed is runny, so it spreads far before cooling and becoming solid.
• Over time and with repeated eruptions, the magma that is erupted cools and becomes solid rock. This new rock builds up over a long time to form an underwater mountain range called a mid-ocean ridge.
Reason why earthquake happens at a constructive plate boundary
• Low magnitude earthquakes are caused when the crust is disturbed by the rising magma or as it is slowly moving apart.
What are volcanoes found along ridge called
Smokers . Some of the volcanoes continue to grow with every eruption until they break the surface and form small islands. Example Surtsey, Iceland.
Example of a conservative plate boundary
Pacific plate and North American plate (San Andreas fault) West Coasr of Usa
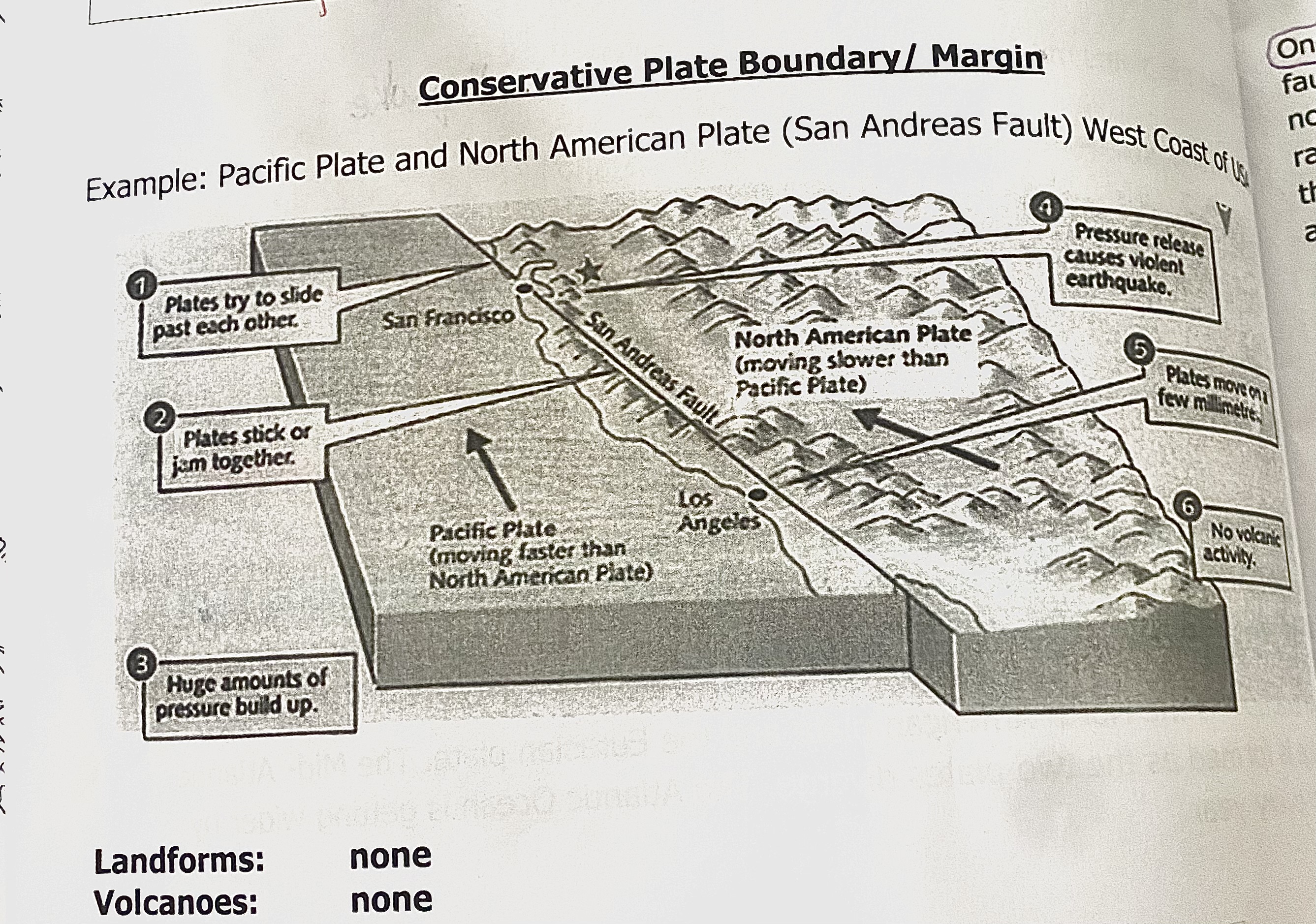
Plate movement at a conservative plate boundary
Radioactive decay in the core generates heat which heats the magma in the mantle.
Convection currents in the mantle cause plates floating on the mantle to slide past each other.
In some cases the plates might be moving in two different directions, or the plates could be moving in the same direction but at different speeds.
Reason why earthquakes happen at a conservative plate boundary
The movement of plates against each other is not smooth. There is a lot of friction.
When two plates grind past each other, they sometimes lock/ stop moving.
When plates are locked, the convection current is continuing below the plates.
Over time, tension/ pressure builds up.
when there is enough tension/ pressure built up, the plates suddenly move and the built up tension is released as Seismic waves
When this happens, the crusts shakes. This is an earthquake.
When plates are locked for a long time, there is the potential for a lot of tension/ pressure to have built up, so there is a risk of a high magnitude earthquake.
When the plates are moving, no tension/ pressure is building up so there is very little risk of an earthquake.
Example of destructive plate boundary
Nazca plate and South American plate
Plate movement of destructive plate boundary
Radioactive decay in the core generates heat which heats the magma in the mantle.
Convection currents in the mantle fall, causing two plates, one oceanic crust and one continental crust to move towards each other.
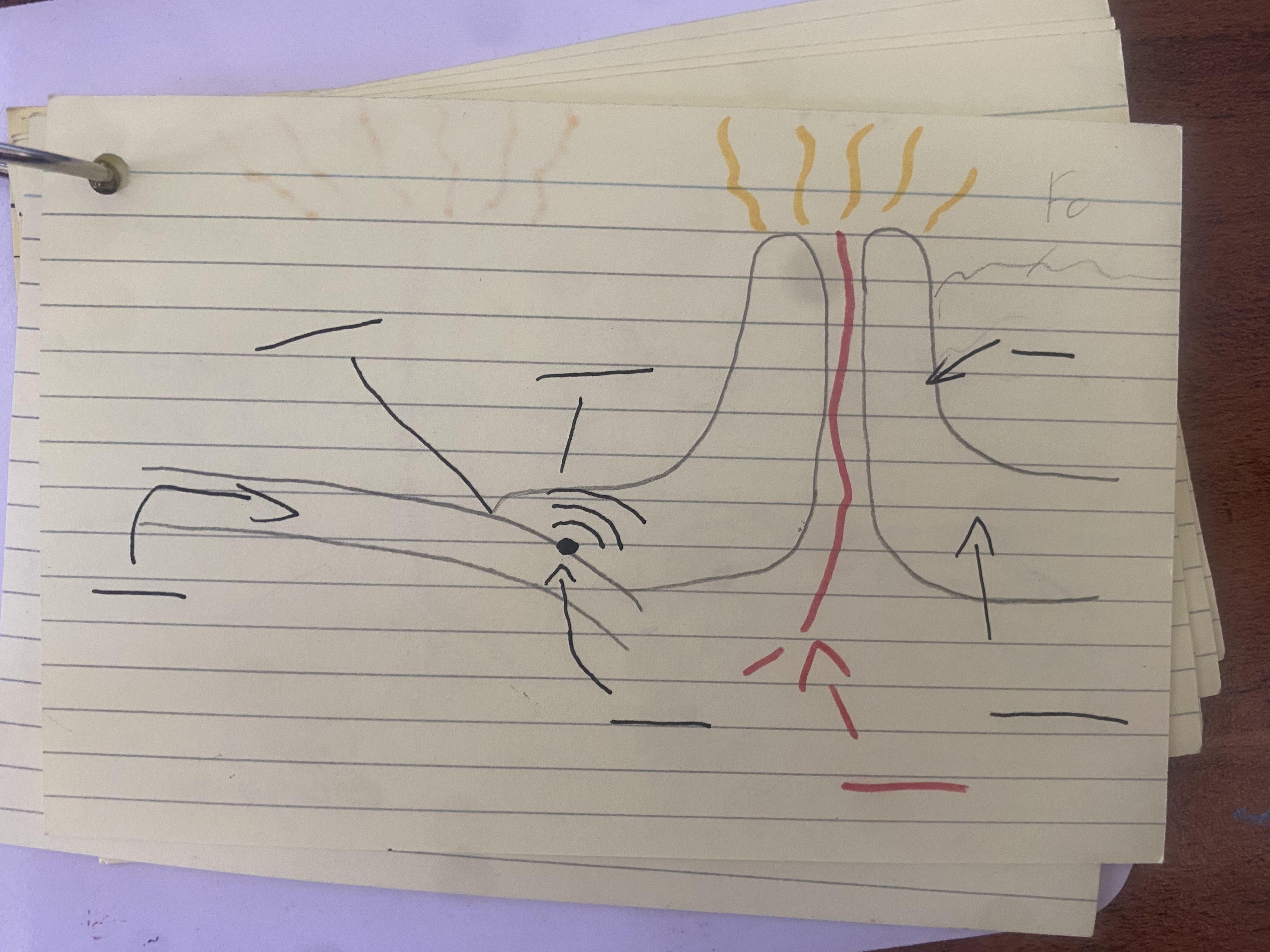
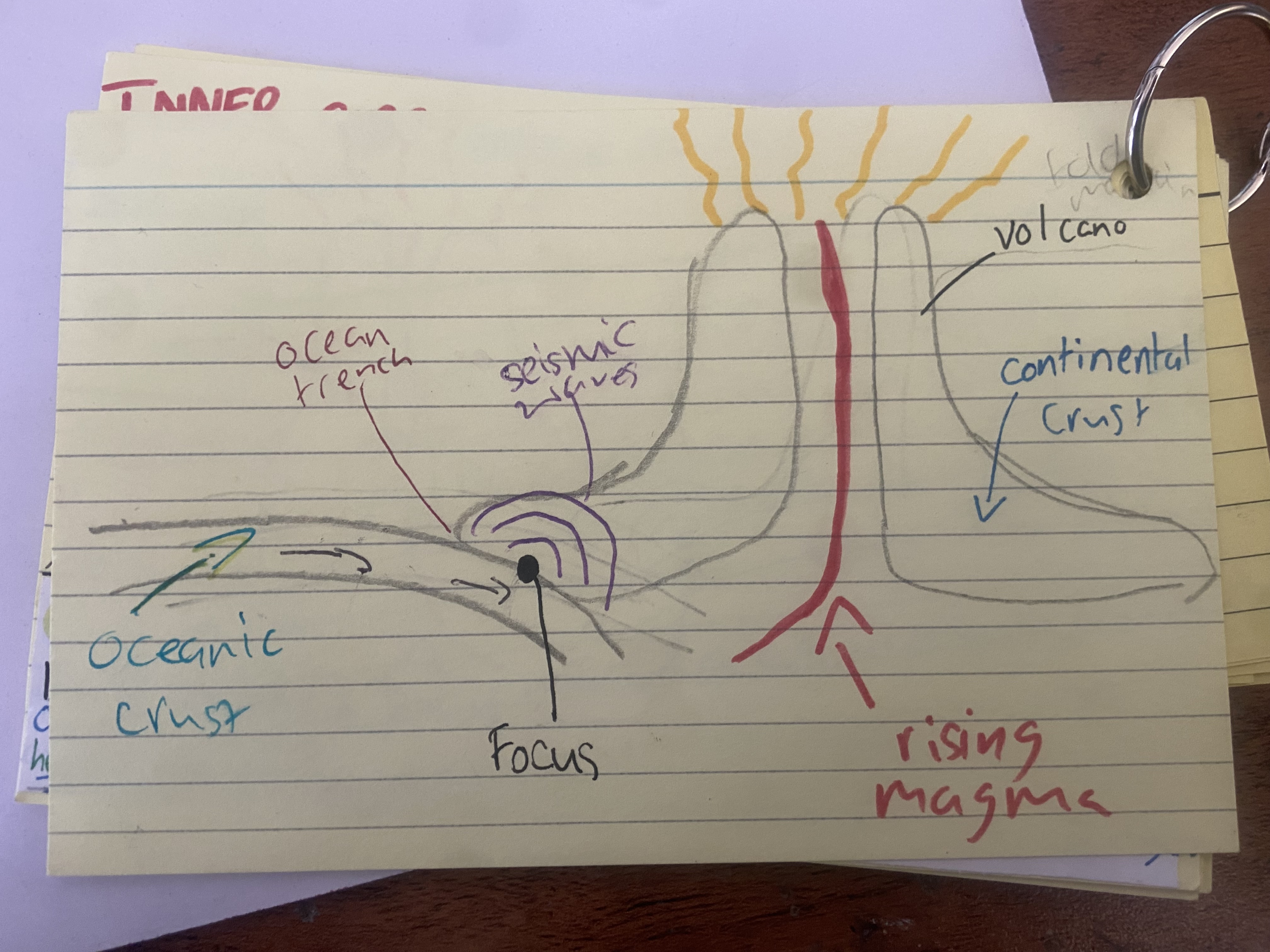
Reasons why there’s a subduction zone and ocean trench at a destructive plate boundary
The oceanic crust is heavier that the continental crust so it subducts into the mantle at an angle of 45°.
Where the oceanic crust moves under the lighter continental crust, there is a significant dip in the seabed called an ocean trench.
Reasons why fold mountains form at a destructive plate boundary
• Fold mountains form at a destructive plate margin where oceanic crust is moving towards continental crust.
Continental crust is lighter so it is not sub-ducted. The oceanic crust subducts as it more dense/ heavier than the continental crust.
The huge pressure caused by the two plates pushing into each other cause the end of the thick continental crust to buckle/ twist/ fold to form a range of fold mountains.
Sometimes parts of fold mountains are formed from sedimentary rock. These rocks form on the seabed and since they are so light, they are not dragged under by the subducting oceanic crust. Instead the sedimentary rocks are scraped and fused on to the edge of the continental crust so the pressure causes these rocks to buckle/ twist/ fold too.
Reasons why there’s volcanoes at a destructive plate boundary
Falling convection currents cause two plates to move towards each OTHER.
The heavier oceanic plate is subducted underneath the continental plate.
The end of the subducting oceanic crust moves into the mantle where magma is at very high temperatures - this, along with friction between the plates, causes the oceanic crust to melt.
The melting/ destruction of the end of the oceanic crust produces extra magma which is full of gases
This magma is lighter than the surrounding magma so rises up.
The pressure within the mantle increases due to the gas and extra magma. Eventually this leads to a violent volcanic eruption. Composite volcanos as it breaks through weaknesses in the crust
The volcanoes that form are made from hardened acidic lava and are steep sided.
Reasons why earthquakes happen at a destructive plate boundary
Falling convection currents cause two plates to move towards each OTHER.
The heavier oceanic plate is subducted underneath the continental plate.
The movement between plates is not smooth.
Friction can cause plates to become stuck.
Over time, tension/ pressure builds up.
Suddenly when there is enough tension/ pressure built up, the oceanic crust suddenly moves and the built up tension is released. Seismic waves spread from the focus.
When this happens, the crust shakes. This is an earthquake.
Earthquakes happen along the subduction zone.
Plate movement at a collision plate boundary
plate Movement at a Collision Plate Boundary
• Radioactive decay in the core generates heat which heats the magma in the mantle.
Convection currents in the mantle causes two continental plates floating on the mantle
to move towards each other.
How Fold Mountains Form at a Collision Plate Boundary
Falling convection currents cause plates to move towards each other. The two continental plates are light and so do not sink. Instead the sediment between them buckles and pushes upwards forming fold mountains.
There is little material melting, and that which does melt cannot make it through the high mountains to create a volcano.
Instead the magma forms large intrusions in the mountain range called batholiths.
The magma cools slowly to form granite cores to the mountains.
Why earthquakes occur at a collision Plate boundary
The collision of two plates and the folding of sediments causes large earthquakes to occur.
Distribution of fold mountains
Fold mountains are found along either a destructive plate margin where oceanic crust moves towards continental crust or a collision plate boundary. They are found on western sides of North (Rockies) and South America (Andes). There is an east/west belt through the Mediterranean Sea (Alps) into Asia (Caucasus) and northern India (Himalayas). There are very few fold mountains in Africa except on the NW Coast (Atlas Mountains). Fold mountains do not form at constructive, conservative or at oceanic-oceanic destructive plate margins.