Ch 9 Kinship,Family, and Marriage
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
China One Child Policy
strictly limited each family to one child; lead to preference of male children, infanticide of females, and later economic/care economy turmoil
Kinship
the system of meaning and power created to determine who is related to whom and to define their mutual expectations, rights, and responsibilities
nuclear family
a kinship unit of a mother, father, and their children
descent groups
a kinship group in which primary relationships are traced through certain consanguineal (blood) relatives
most European/North American cultures do not use descent to organize social groups
lineages
a type of descent group that traces genealogical connection through generations by linking persons to a founding ancestor
clan
a type of descent group based on a claim to a founding ancestor but lacking genealogical documentation
matrilineal
constructing a descent group though female ancestors
patrilineal
tracing kinship through male ancestors
unilineal descent
build kinship though either one line (females or males) or the other
ambilineal/bilateral
descent groups that trace kinship through both mother and father
ex: samosas,maori, Hawaiians, etc
patrilineal descent group
a kinship group in which membership passes to the next generation from father to son
ex: The Nuer( E.E.Evans-Pritchard)
ego
the central character and starting point in tracing kinship relationships
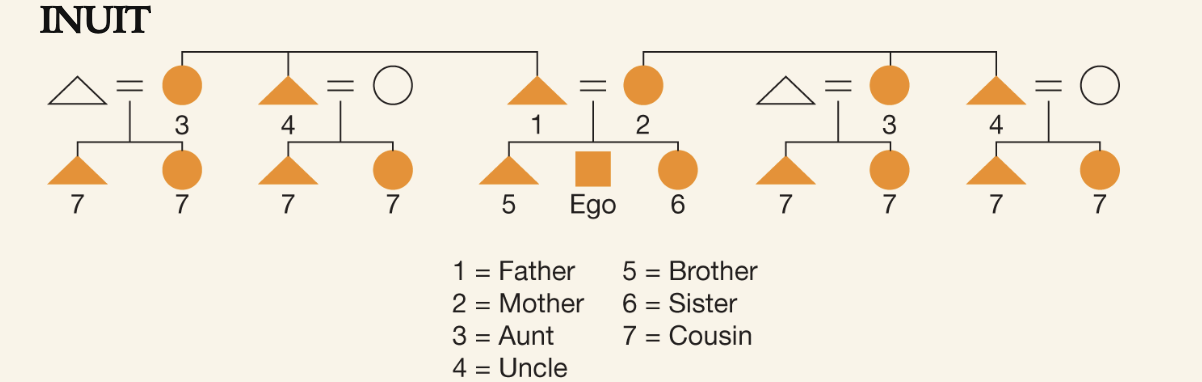
Inuit Kinship
Only members of the nuclear family are given distinct terms, aunts and uncles are distinguished from parents but not by side of the family, all cousins are lumped together
most common in Europe and North America
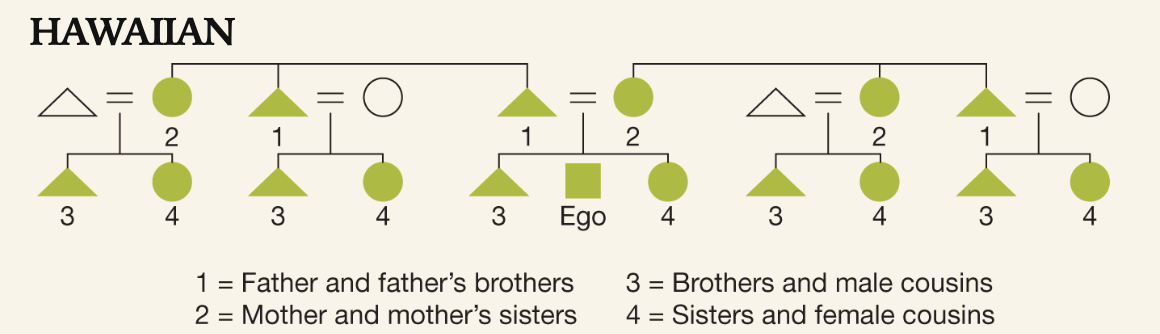
Hawaiian Kinship
the nuclear family is deemphasized, and relatives are distinguished only by generation and gender( least complicated)
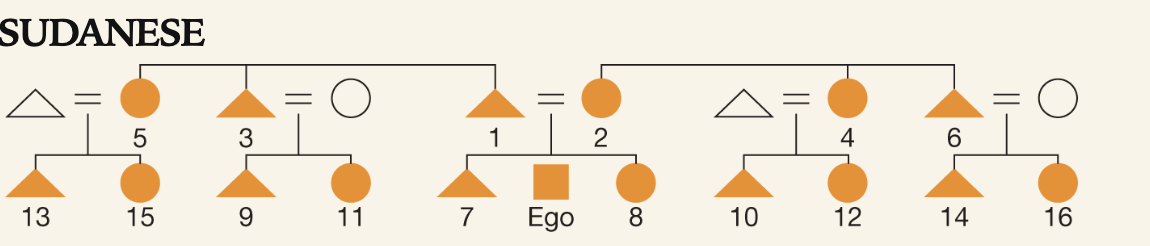
sudanese kinship
Each category of relative is given a distinct term based on genealogical distance from ego; eight different cousin terms which are distinguished from ego’s brother and sister ( most complex)
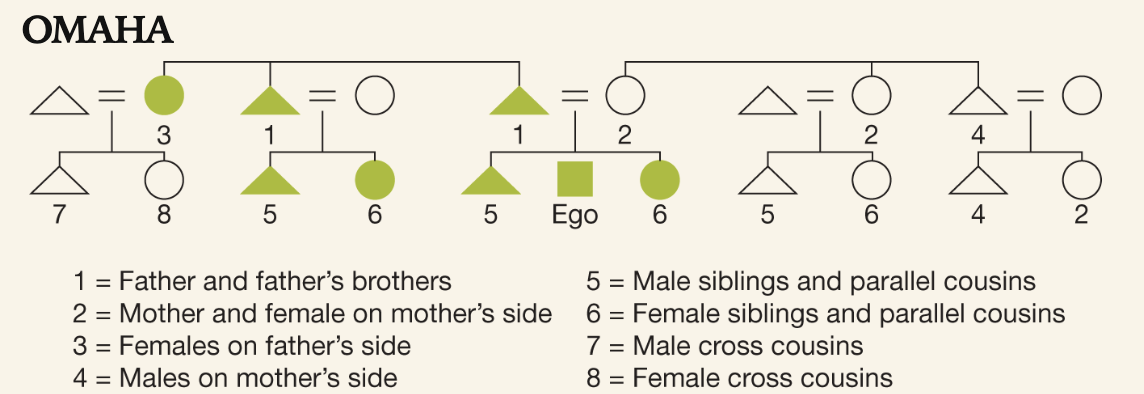
Omaha kinship
Tracks kinships through patrilineal descent (distinguishing between cousins takes importance)
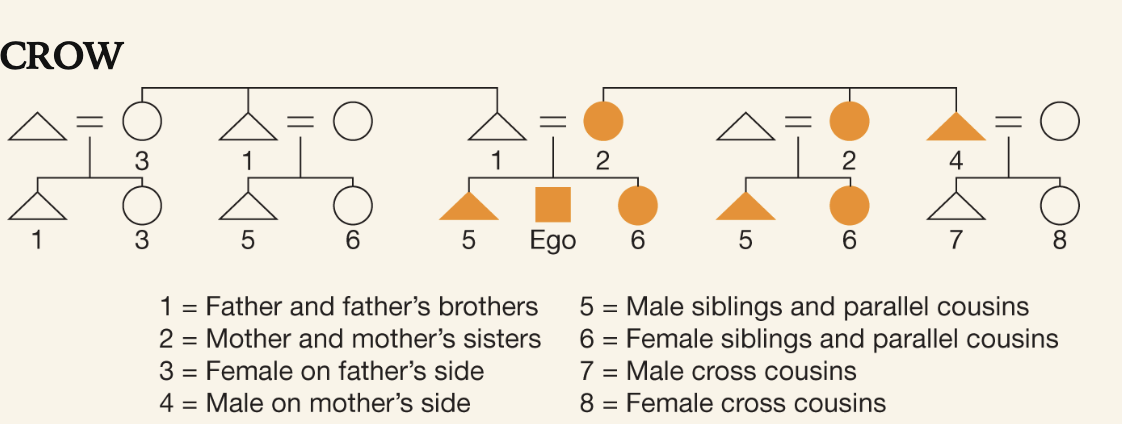
Crow Kinship
Tracks kinships through matrilineal descent (distinguishing between cousins takes importance)
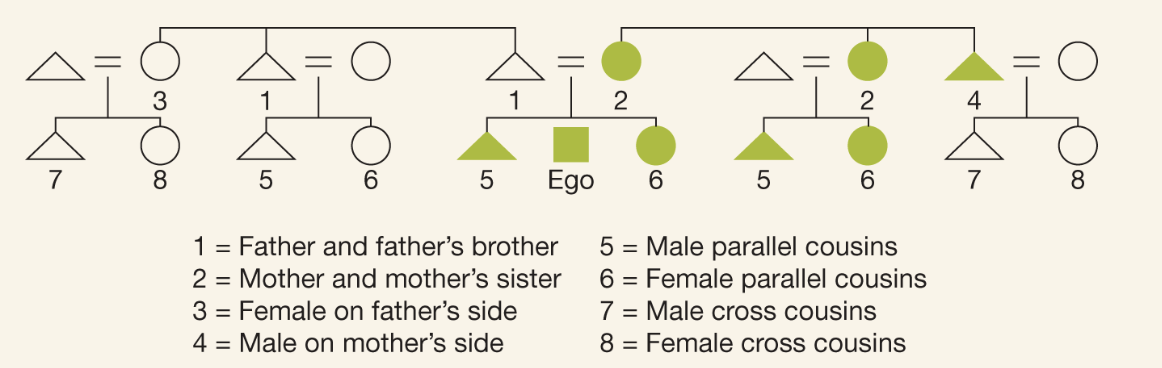
Iroquois Kinship
system can be traced either matrilineally or matrilineally. Same term is used for father and father’s brother and for mother and mother’s sister, reflecting shared membership in lineages
The Nuer
follow Sudanese kinship system and patrilineal descent.
bilateral kinship relationships creased by marriage are often just as important as those created through descent
affinal relationships
a kinship relationship established through marriage and/or alliance, not through biology or common descent
marriage
socially recognized relationships that may involve physical and emotional intimacy, sexual pleasure, reproduction and raising children, mutual support/companionship, and shared legal rights to property and inheritance.
may also serve to create connection, communication, and alliance between groups
arranged marriages
marriage orchestrated by the families of the involved parties; marriage is a social obligation and symbol of commitment larger kinship group
still common in Asia, the Pacific, Middle East, and Africa
Companionate marriage
Marriage that’s foundations are in love, intimacy and personal pleasure, not social obligation
polygyny
several marriages involving one man and two or more women
Nuer of Sudan and Brahmans of Nepal
Polyandry
marriages between one women and two or more men
Nayar of India and Nyimda of tibet and Nepal
Monogamy
marriage between one man and one woman, or two people of the same sex.
serial monogamy
when monogamous marriages follow one after the other
incest taboo
rules that forbid sexual relations with certain close relatives( nuclear family members)
universal but origins are unclear(instinctive horror or biological repercussions)
cross-cousins
children of a mother’s brother or a father’s sister
parallel cousins
children of a father’s brother or a mother’s sister
exogamy
marriage to someone outside the group
endogamy
marriage inside the group
kindred exogamy
avoidance, either by law or power of tradition, with certain relatives
bridewealth
the exchange of cattle, cash, or other goods as a gift from the groom and his kin to the bride’s kin
seen as compensation to the brides family; also to establish reciprocal rights and obligation, give legitimacy to children, etc
popular in Middle East and africa
dowry
the bride’s family gives gifts to the groom’s family on the occasion of marriage
often used to establish a household and as compensation to husband for taking on the responsibility of a wife(women have lower social status)
common in India
the langkawi of Malaysia
example of how kinship can be acquired throughout life as eating and living together, in the house and hearth, builds kinship
fictive kin
members of close interpersonal circles that become kin as they are willing to participate in a system of mutual support
ex: Carol Stack’s The Flats African American community in Chicago
family of orientation
the people with whom we grow up and develop life skills with
family of procreation
the people in which we reproduce and raise our own children with
Chosen families
the decision of whether or not to have children, creating family when one can’t biologically produce offspring due to infertility or sexuality
phratry
a unilinear descent group of three or more clans that supposedly share a common ancestry
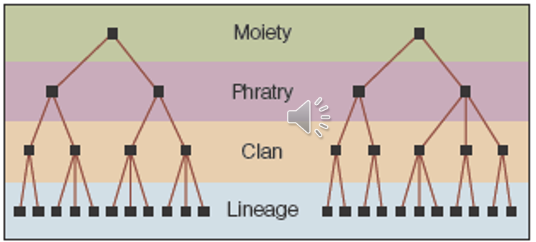
moieties
the two major descent groups formed when a society is devised into two halves where each had consist of one or more clans
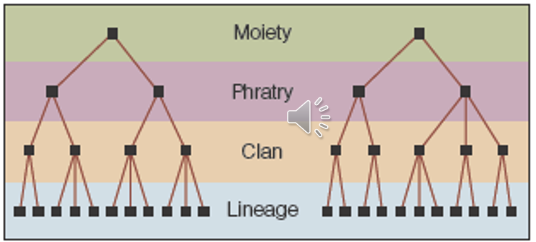
kindred
a large group that is reduced to a small circle of paternal and maternal relatives
bride service
groom provides fixed services to his wife’s family for a fixed period of time, compensation for the loss of her labor
neolocal residence
when bride/groom establish a new residence/household
matrilocal residence
when the bride/groom live with the bride’s family
patrilocal residence
when the bride/groom live with the groom’s family