Ch 1 intro to child development
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Reasons to learn about child development: Raise children
Research improves it. Building empathy for diverse popul of children (regardless of extreme circumstances)
Spanking worsens behavioral problems. Better way:Turtle technique (retreat to “shell” to cool down to manage anger) and expressing sympathy
Reasons to learn about child development: Choosing social policies
Research helps decide on social issues
No screen time for first 24 months
Playing violent video games DOES NOT affect aggression!
NICHD has interview protocols that improves the quality of children’s courtroom testimony
Helps teachers, counselors, and other professionals understand + emphasize w children facing difficulties ex. Poverty, discrimination, etc. → effective care
Reasons to learn about child development: Understand human nature
Age to start learning.
Can early rearing be overcome?
What contributes to differences among children in personality and intellect (Nativists vs empiricists)
Romanian Adoption Study: Adopted after what age has most deficit?
Recovery depends on timing of adoption (best when adopt before 6 m)
Adopted after 6 months → persistent deficits
Adopted after 24 months → Atypical intellectual + social development + abnormal development of prefrontal cortex and low activity of amygdala
Romanian Adoption Study: If not adopted, how will the children turn out?
Even worse physical, intellectual, social development than adopted late
worse in controlling emotions and forming friendships
Use mental health services more
Kauai Longitudinal Study: Are the prenatal & birth complications correlated to mental issues?
Yes, ONLY if the children also grew up in poor rearing conditions
Kauai Longitudinal Study: How do children w BOTH poor bio and envi (“at-risk”) develop?
⅔ developed serious learning or behavior problems by age 18.
⅓ developed resilience, growing into adults who loved well, worked well, and played well
3 Goals of learning children in the past (which is similar to present)
To help people become better parents
To improve children's well-being
To understand human nature
What do Plato and Aristotle think in common about long-term welfare of society?
Both believed that the long-term welfare of society depended on raising children properly, but they disagreed on how that should be done
What did Plato think abt knowledge?
emphasized self-control and discipline
Children are born with innate knowledge
Foundation for the Nativist (nature) and/or Core Knowledge theories
What did Aristotle think abt knowledge?
fitting child rearing to the needs of the individual child
believed that knowledge comes from experience
Foundation for both Constructivist and Empiricist (nurture) theories
What did John Locke think about knowledge?
Like Aristotle, saw the child as a tabula rasa (mind starts at blank state) means knowledge has to be learned
Children should be disciplined, then gradually increasing freedom.
Foundation for Empiricist Theories
What did Jean-Jacques Rousseau think about knowledge?
Children are inherently curious
Parents and society should give child max freedom from the start
Foundation for Constructivist Theories
Empiricist theory
Mind started at 0, Knowledge comes from experience.
Nurture (envi)
Develop continuously
Key thinker: John Locke (philosophy), Behaviorists, Aristotle
Constructivist theory
Children actively build (construct) knowledge thru interaction w envi.
Develop in stages
Interpret experience using existing mental structure (assimilation vs accommodation)
Key thinker: Jean-Jacques R., Piaget, Aristotle
Charles Darwin’s contributions abt child development
Wrote abt his son, and noted achievements in vision, hearing, touch, anger, affection, moral sense, emergence of ideas, reasoning (prolly dont have to memorize)
Proposed theory of evolution like:
Attachment to mothers
Innate fears
Sex differences
Aggression and altruism
Learning mechanisms
Nature vs Nurture theme in child devel.
All human characteristics are created through interaction of genes and environment.
Schizophrenia most likely when have a schiz parent + adopted into toxic family envi
Epigenetics: Interactions of exp/envi on gene expression
Methylation (Biochem process, influ by stress): Infant’s mom stress → influ amount of methylation in child’s gene 15 yrs later
Active vs. Passive theme in child devel.
Active
Do they select their envi or shape their own devel.?
Have preferences in info, innately curious, motivated to learn?
Passive
Do they need to be motivated by rewards or punishments?
The Active Child: Three of the most important contributions during children's first years
Selective attention, language practice, and play
These roles increase as they grow older.
The Active Child: New borns vs toddlers in devel.
Newborns
Prefer things that move and make sounds; pay particular attention to mom's face (Selective attention)
Strengthens bond and exp w mom
Toddlers (1- and 2-year-olds): Internally motivated to learn & practice talking. Self-speech (esp when they’re alone)
The Active Child: How children play before 2, after 2, and older
<2 y/o: Early play (learn abt physics and social dynamics)
>2 y/o: Fantasy play (learn abt emotional and social)
Older children’s play: More organized and with rules (self-control, follow rules, emotional regulation)
Development as continuous or discontinuous
Continuity view: Change is uniform, gradual quantitative (ex. Like pine tree growing taller)
Discontinuity view: Change can be rapid, qualitatively different stages across the lifespan (like butterfly) (Jean Piaget – “stage” theorist)
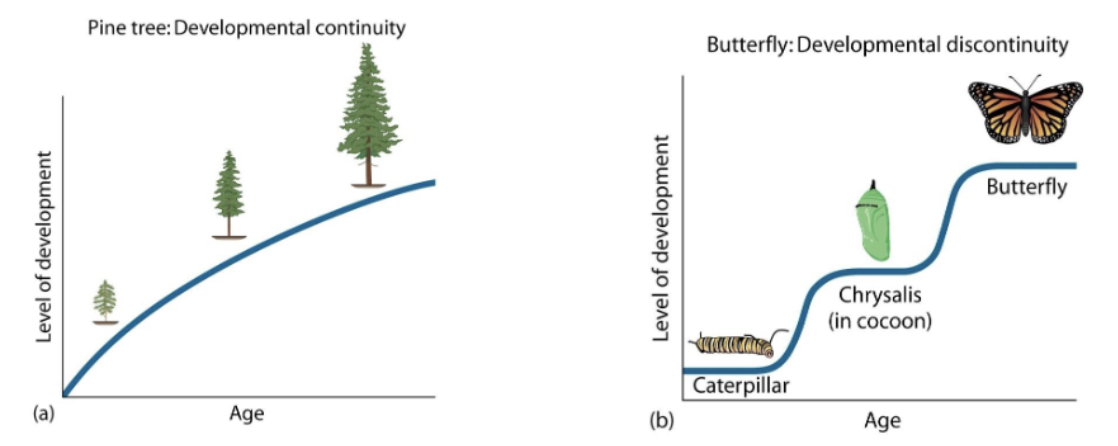
Is development fundamentally continuous or fundamentally discontinuous?:
It depends on how you look at it and how often you look
How do genome & envi interact?
Nature/Nurture
Continuing Transaction - Epigenetics
Timing
Critical/Sensitive Periods
A critical period
A behavior develops abnormally if lack of certain envi influences in a time window (ex. Adopt before 6 m into good envi → develop normal)
Experience Expectant
Those envi influences that are expected, and necessary for normal development (e.g. human faces, human language are needed for social, cognitive, etc. development)
Experience Dependent
Those envi influences that lead to more general learning and indv diff (toys, specific foods, specific words)
What is Effortful Attention (EA) and what are mechanisms involved?
Voluntary control over emotions and thoughts, and it’s an interaction of multiple mechanisms.
Neural: activity in limbic area + anterior cingulate + prefrontal cortex for effortful control
Genetic: Specific genes are linked to EA, effects are mediated by parenting quality.
Experiential Learning and training can improve their EA and intelligence tests
Sleep’s role for learning in first 18 months vs 24 months
First 18 months:
Sleep supports more w learning frequently occurring patterns (ex. routines, lang rhythm)
Sleep modulates more in Cortex
24 months+
Sleep supports more w learning specific, singular events
Sleep modulates more in Hippocampus (event-based memory)
Bronfenbrenner’s Bioecological Model
Child development is strongly shaped by directly interacted people (parents, teachers, peers), and also shaped by social institutions (school, media, gov, etc.)
Less visibly shaped by History, economy, cultural beliefs & values
Cross-cultural study: When do children start sleeping alone in US vs Guatemala?
US: sleep alone after 6 months → reflect independence and self-reliance
Mayan: children sleep with mothers until age 2 or 3 → reflect interdependence
Within-culture SES study: Children in poverty are more likely to
Have serious health problems (infancy)
Have social/emotional and behavioural problems (childhood)
Do worse in school (childhood and adolescence)
Poverty in Canada
More in Indigenous
5% of children live in poverty, but decreasing
Scarr's 4 factors that make children differ from each other
Genetic (even in twins)
Treatment by parents and others
Reactions to similar experiences
Choices of environments (choose their own friends, activities)
Resilience children (despite poverty) are more likely to have… (3)
Positive qualities (e.g., high intelligence, easy going)
Close relationship with at least one parent.
Close relationship with at least one other supportive adult (e.g., grandparent, teacher)
How do children's beliefs about intelligence hugely impact on their learning?
Some children think intelligence is Fixed, some think it grows
Think learning will make them “smarter” or overcoming obstacles can lead to success → improve learning and grades
Key criteria in creating good research measures
Relevance to hypotheses
Reliability
Validity: Internal (test cause-and-effect), External (generalizability)
Replicability:
Large sample size
Preregistration
More collaboration (ex. ManyBabies Consortium)
Interview/Questionnaire pros and cons
Pros: Can reveal subjective experience, flexible, cheap.
Cons: Maybe biased, memories can be inaccurate
Naturalistic Observation pros and cons
Pros: Real, see social interaction
Cons: Context varies, not so generalizable, diff to know what’s the most influential
Structured Observation (in lab)
Pros: Ensures all children's behaviors are observed in the same context. Allows controlled comparison.
Cons: Context is less natural. Reveals less about subjective experience than interviews
Correlation and causation
Important goal of child-development research
Determine how variables are related to one another through
Associations
Cause–effect relations
How experimental designs draw causation
Random asm
Experimental control
Cross-sectional design pros and cons
Compare children of different ages on a given behavior/characteristic over a short period
Pros: Quick and easy, see diff b/w age group
Cons: Cohort effects, doesn’t tell indv stability
Longitudinal pros and cons
Pros: See degree of stability of individual diff and children's patterns of change
Cons: Difficult to keep all participants in the study. Repeated testing can threaten external validity.
Microgenetic pros and cons
Children are observed intensively over a relatively short period while a change is occurring.
Pros: Can clarify the process of change. See change patterns over short periods.
Cons: Doesn’t tell typical patterns of change over long periods.