IMC Unit 2: Derivatives
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is a forward contract
A contract between a buyer and a seller to exchange an underlying asset on a future date, at a price agreed today
• Traded OTC
What is a futures contract
Exchange-traded forward, with standardised contract specifications
What is specified in a futures contract
a specific quantity and quality of a specified asset;
on a fixed future date;
at a price agreed today
What terminology is used for futures contracts
Buyer/Long
Seller/Short
Underlying
Futures price
Delivery
Who in a futures contract benefits when prices rise and fall
Buyers (‘longs’) gain if prices RISE
Sellers (‘shorts’) gain as prices FALL
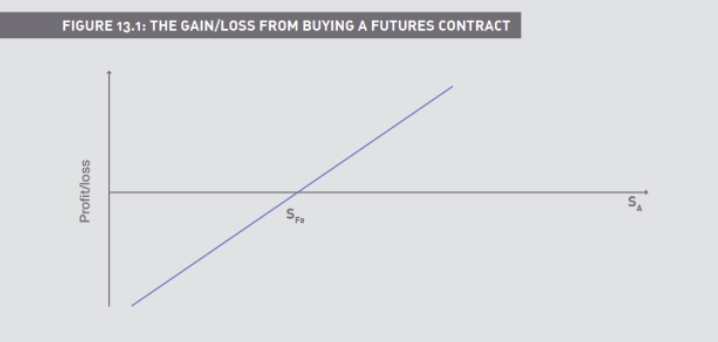
Futures price vs. cash price (and the concept of ‘arbitrage’
Exploiting price differences between futures and cash markets to make risk-free profit.
xyz
What are the Uses of futures
Hedging
Speculation
Examples of futures contracts
Short-term interest rate futures (‘short sterling’ futures)
• Fix an interest rate on a (notional) deposit of £500,000 for three
months (3mth SONIA)
• Cash settled
• Priced at 100 minus the rate
• Long profits if rates fall, so use to hedge a DEPOSIT
• Short profits if rates rise, so use to hedge a LOAN
• Long bond futures
• Take or make delivery of £100,000 nominal of a UK gilt
• Physically delivered
• Actual gilt delivered: ‘cheapest to deliver’ (CTD) gil
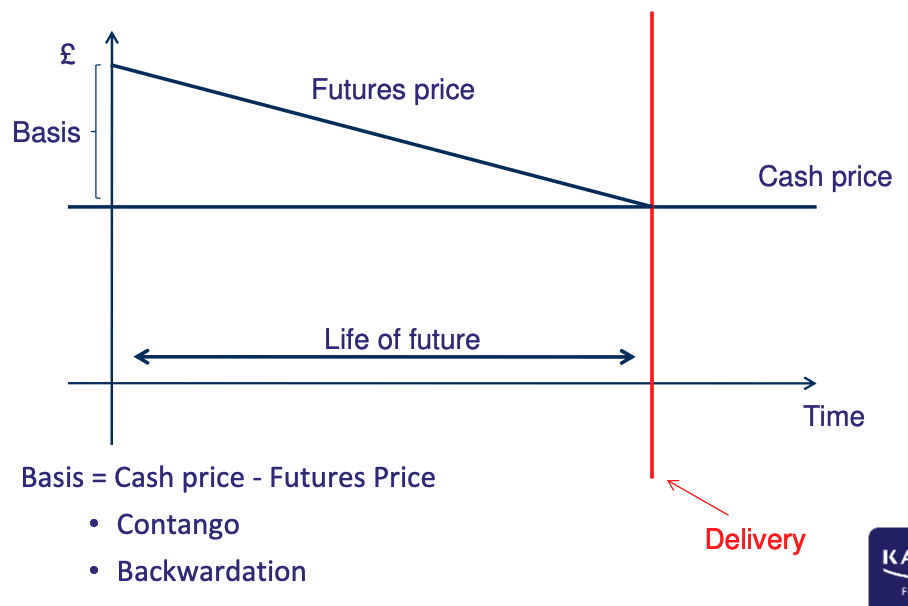
How is Basis calculated
Basis = Cash Price – Futures Price.
It indicates the difference between spot and futures market prices.
What is Contango
When futures price is higher than cash price—often due to storage costs or expectations of rising prices.
What is Backwardation
When futures price is lower than the current cash price—common when there's immediate high demand or scarcity.
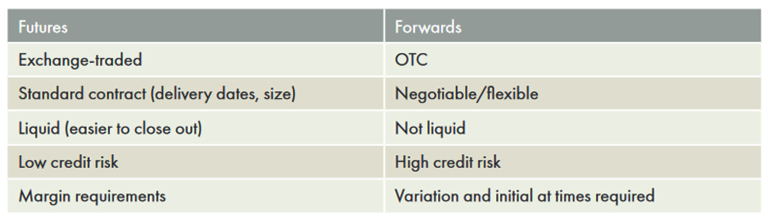
What are the differences between Forwards and Futures
What is a swap (contract for difference)
Agreement to exchange a series of cash flows
Traded OTC
What is an Option
A contract between a buyer and a seller giving the RIGHT to exchange an underlying asset for a pre-agreed price
Exchange-traded or OTC
What is specified in a Options contract
a particular asset;
at a particular price;
on or before a specified date
What terminology is used in options contracts
Put/Call
Buyer/Long/Holder
Seller/Short/Writer
Underlying
Premium
Expiry
• European-style: exercise AT expiry
• American-style: exercise ON OR BEFORE expiry
Long a 150p call, premium 6p
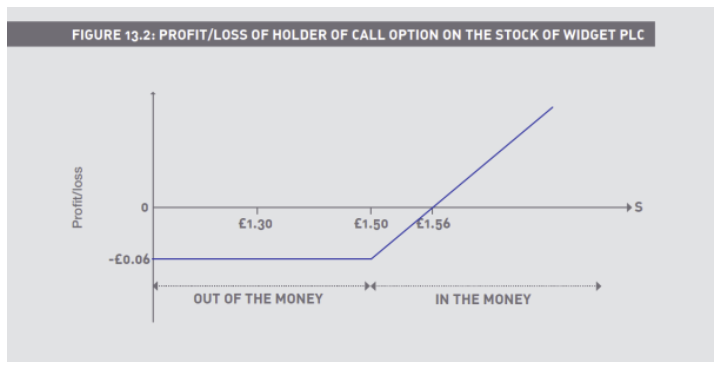
Short a 150p call, premium 6p
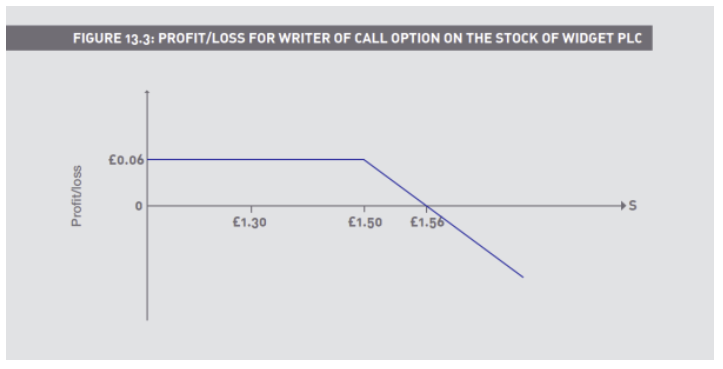
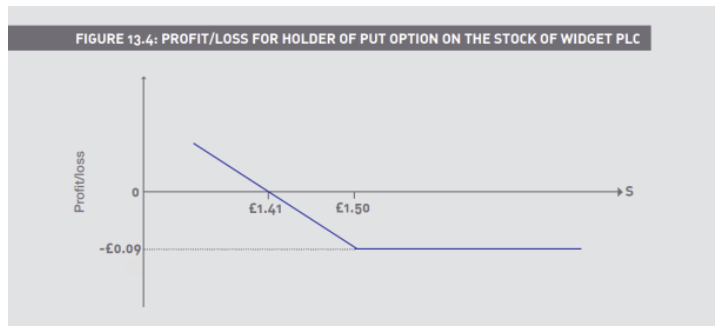
Long a 150p put, premium 9p
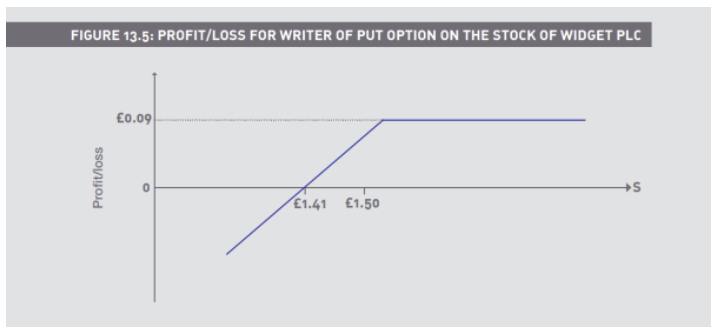
Short a 150p put, premium 9p
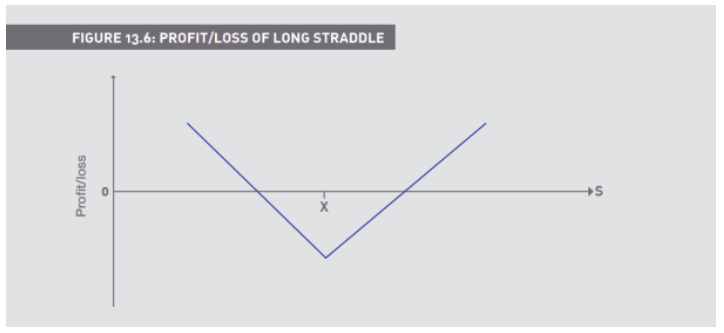
How does a Straddle work
Combines a put and a call on the same underlying, with the same expiries and the SAME strikes
(Straddle) Long a 550 call for 37, and a 550 put for 3
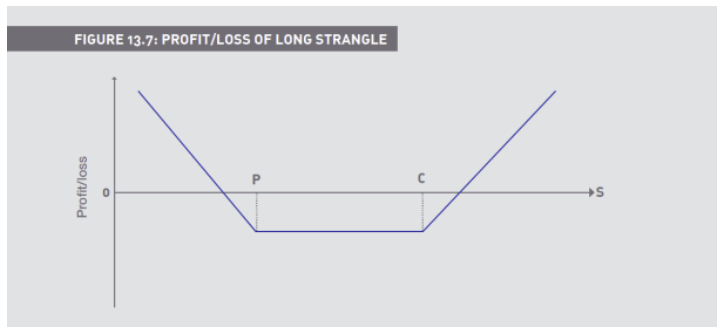
How does a strangle work
Combines a put and a call on the same underlying, with the same expiries and the DIFFERENT strikes
(Strangle) Long a 500 put for 18, and a 600 call for 1
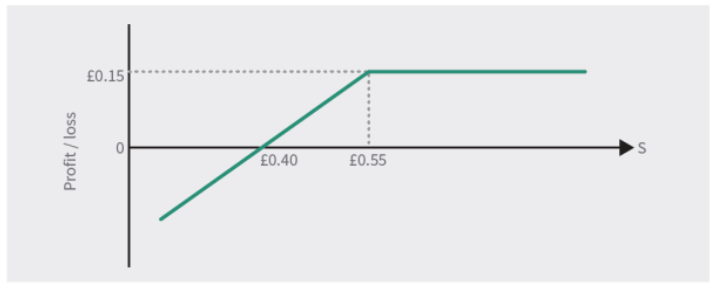
How does a covered call work
Sell a call (short call) against an existing, or simultaneously purchased holding of the underlying (long the underlying
(Covered Call) Long a share at 50p, and sells a 55 call for 10
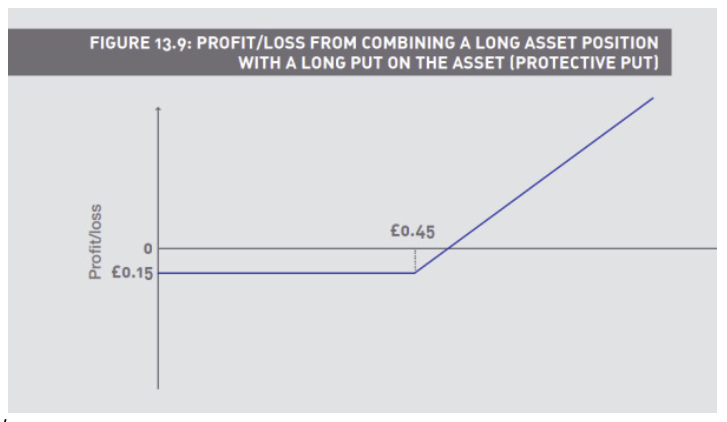
What is Protective Put
Buy a put (long put) against an existing, or simultaneously purchased holding of the underlying (long the underlying
(Protective Put) Long a share at 50p, and buys a 45 put for 10
What is the role of clearing houses for derivatives
Act as CENTRAL COUNTERPARTIES and guarantee the performance of contracts
What is Initial Margin
Goodwill Deposit
What is Variation Margin
Daily marking-to-market of contract
What model do Uncleared Transactions for derivatives use
ISDA Standard Initial Margin Model (ISDA SIMM®)
What is Aggregate Average Notional Amount (AANA)
A firm must calculate the average notional value of its non-cleared derivatives over a set period.
What happens If AANA exceeds €8 billion,
The firm becomes subject to margin requirements.
Intial Margin
How much is each FTSE 100 futures contract valued at
£10 per index point
What is the formula for hedging with futures

A fund manager has a well diversified portfolio of UK equities valued at £50m. The FTSE 100 index is currently standing at 6,350, and the FTSE100 future is trading at 6,400.
How many contracts does the fund manager need to sell to hedge the
portfolio?
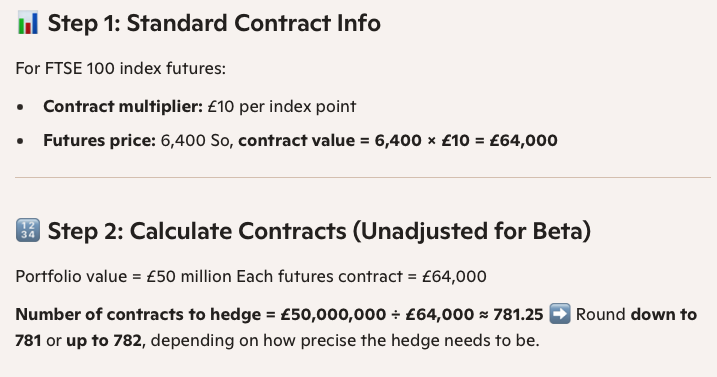
A fund manager has a well diversified portfolio of UK equities valued at £50m. The FTSE 100 index is currently standing at 6,350, and the FTSE100 future is trading at 6,400.
How would the answer change if the portfolio has a beta (ß) of 1.20
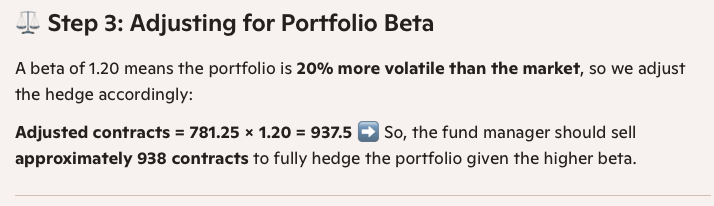
What is the formula for hedging with futures
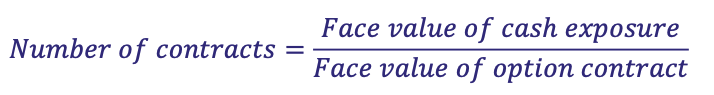
A fund manager has a well diversified portfolio of UK equities valued at £50m. The FTSE 100 index is currently standing at 6,350, and the FTSE100
6,100 puts are quoted at 40.
How many long puts does the fund manager need to hedge the portfolio?
A fund manager has a well diversified portfolio of UK equities valued at £50m. The FTSE 100 index is currently standing at 6,350, and the FTSE100
6,100 puts are quoted at 40.
How would the answer change if the portfolio has a beta (ß) of 1.20

What is the formula for Option Premium

What is the intrinsic value and time value in the BP 460 Aug call? Question
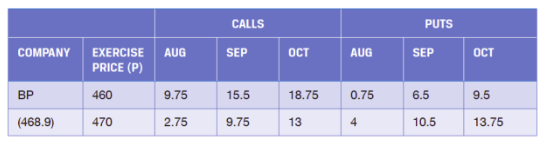
What is the intrinsic value and time value in the BP 460 Aug call?

What factors affect option premiums (and associated measures of how ‘sensitive’ option premiums are to changes in these factors
Cash price (Delta)
Time to expiry (Theta)
Volatility of share price (Vega)
Discount rate (Rho)
What is stock lending
Securities temporarily transferred from a lender to a borrower for a fee
Borrowers provide lenders with collateral
Who does the legal title transfer to in a stock lending arrangement
Borrower
‘Manufactured dividends’
What is Short Selling
Borrowing securities and selling them, in the hope that prices will fa
What are the types of contracts for differences
Interest rate swaps
Equity swaps
Inflation swaps
Currency swaps
What is an Interest rate swaps
The exchange of a fixed rate of interest and a variable rate (usually SONIA)
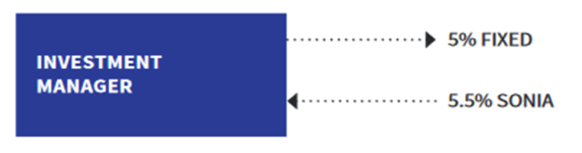
What is an example of an Intereset rate swaps
A fund manager wanting to remove exposure to a rise in SONIA buys a swap (becomes the ‘fixed rate payer’
What is an equity swap
One party pays another the return on equities (or an equity index) in exchange for a fixed return
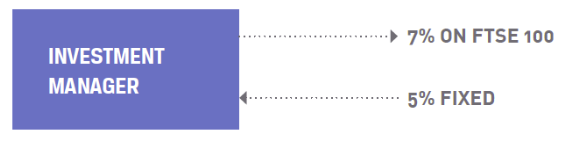
Why would a fund manager do a equity swap
To remove equity exposure
What is an inflation swap
Transfer inflation risk
Variable rate reset by reference to an inflation index
What is a currency swap
Two parties swap fixed (or floating) interest in one currency for fixed (or floating) interest in another, to hedge underlying liabilities in the respective currencies
What is a Convertible Bond / Preference Share
Allow investors to convert their holding into a pre-specified amount of equity
Generally trade at a higher price than equivalent non-convertible bonds (and hence lower yield)
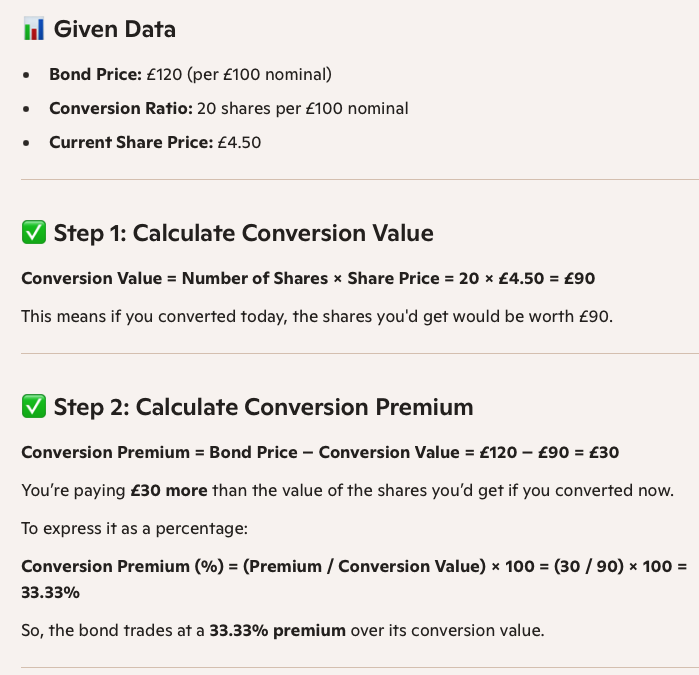
What is the formula for conversion value

A convertible bond is trading at £120 (per £100 nominal), and offers the holder the right to convert into 20 ordinary shares (per £100 nominal). The current share price is £4.50.
What is the conversion value and the conversion premium
What is a Warrant
Give the holder the right to buy a certain number of NEW SHARES in the issuer at a fixed exercise price
(so INCREASE the number of issued shares on exercise)
What is a Traded Option
Give the holder the right to buy a certain number of EXISTING shares in the issuer at a fixed exercise price (so DO NOT increase the number of issued shares on exercise)
Generally shorter lives than warrants
What is a Covered Warrant
Issued by investment banks
Call (buy) and put (sell) covered warrants availabl
What is a Credit Default Swap
A buyer pays a premium to a seller for protection against bond default
What happens if a default occurs
The seller receives the bond and pays the face value to the buyer (physical settlement); or
The seller pays agreed notional principle to the buyer (cash settlement)