Lecture 8: Lab Testing, Acute & Chronic Injury Cirrhosis
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Liver Blood supply
Dual blood supply via:
Hepatic Artery from Aortic Celiac trunk
Portal Vein from GI tract
Venous drainage via Hepatic Vein into IVC
Portal Triads at periphery carry Portal Vein + Hepatic Artery + Bile Ductule
Arterial & Venous blood mix in the sinusoids & collect at the Central vein of lobule (Central vein region, Zone 3, is the most hypoxic region)
Sinusoids are lined by endothelial cells with gaps between them (Fenestrae)
Hepatic Plates (the hepatocytes between sinusoids) are 1-2 layers thick
Liver Specialized Cells
Kupffer cells are resident liver Macrophages attached to endothelial cell surfaces
Beneath endothelium is space of Disse with Stellate Cells (Ito cells)
Stellate cells store fat & fat-soluble vitamins like Vit A & produce extracellular matrix Type III collagen (Reticulin) for structural support
If activated by inflammation, can differentiate into Myofibroblasts & produce Type I Collagen (Scar tissue)
Acute Liver failure Labs
Increased Ammonia → Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hypoglycemia
Severe bleeding (Lab: ↑ PT/INR)
Chronic Liver Disease
Hypoalbuminemia → ↓ oncotic pressure → Ascites, Edema
Impairs breakdown of Estrogen → Feminization in men
Drug choices & dosages must be adjusted
If impaired excretory functions
In GI tract, ↓ bile acids → fat malabsorption (Steatorrhea) & deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
In Blood, ↑ Bile acids → Pruritus; ↑ Cholesterol → Xanthomas
If impaired conjugation or excretion of Bilirubin (Cholestasis) → ↑ Bilirubin → Jaundice, Biliary cirrhosis
Enterohepatic Circulation of Bile Acids
Bile Acids: secreted into the duodenum; most reabsorbed in ileum for reuse
Bilirubin: Small amounts of unconjugated Bilirubin along with urobilinogen are reabsorbed from the colon into the blood
Drugs: Some drugs are reabsorbed & re-excreted in the bile
↑ in severe Hepatocyte injury or death
AST, ALT, LD
↑ in Bile ductal obstruction/bile ductal epithelial injury
Total Bilirubin
Conjugated Bilirubin (Direct)
ALP
GGT
to assess for Liver Failure
Albumin, PT, Ammonia
Aminotransferases
used to detect Hepatocyte injury
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): Not specific; may be from Liver, Skeletal muscle, heart, kidney, RBCs, pancreas
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): Clinically specific to liver
Hepatocyte Injury/Death
Cytosolic enzymes released; elevated in serum
AST & ALT + Lactate Dehydrogenase
Hepatocyte necrosis likely if:
AST, ALT > 10x upper limit normal
AST and ALT are >> ALP (Alkaline phosphatase)
AST > 2x ALT in Alcoholic liver disease
AST > ALT in Cirrhosis
Elevations may be due to toxins, drugs, hepatitis, metabolic diseases, poor perfusion
Minor elevations occur in biliary obstructive diseases
Tests for Bile duct obstruction & Bile ductal epithelial injury
Hyperbilirubinemia Bilirubin, particularly the Conjugated form (Direct)
GGT: ↑ in biliary obstruction disproportionately to AST & ALT
GGT is localized to luminal cell membranes of bile canaliculi & bile ductal cells & is the only enzyme specific to liver
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP):
↑ 3-5 X in extrahepatic & usually < 3 X, for intrahepatic cholestasis
ALP is found in Bile duct canalicular cells, Bone & Placenta
Children have reference range above adults
Hypercholemia (↑ serum Bile Acids) & ↑ Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia) in bile obstruction
Increased unconjugated bilirubin
Hemolysis
Increased unconjugated and conjugated
Hepatocyte pathology
Indirect (Unconjugated) Hyperbilirubinemia
↑ Hemolysis
↑ LD; AST may be mildly elevated, ALT normal; ALP normal
Resorption of blood from internal bleeding (hematoma)
Hereditary unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemias (Normal ALP, GGT, AST, ALT, LD)
Gilbert common; benign
Crigler-Najjar Type II; benign (but Type I is lethal in newborns)
Unconjugated bilirubin predominates over conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia in advanced liver disease (not enough cells to conjugate!):
Cirrhosis of the liver
Hepatitis, late in disease
Acute liver failure
Direct (Conjugated) Hyperbilirubinemia
Urinary bilirubin also ↑ as it is water-soluble
Hepatitis, acute or early
Intrahepatic cholestasis due to deficiency of bile pump/transporter proteins
Bile duct obstruction
Intrahepatic biliary disease: obstruction due to cancer, abscess, etc.
Extrahepatic obstructions
Hereditary: Dubin Johnson, Rotor syndromes
Physiologic Jaundice of the Newborn (Neonatal Jaundice)
Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia
Transient, usually mild
Noted 2-3 days after birth, peaks in about a week
Due to immature Liver at birth (conjugating enzyme level low)
Exacerbated by breast feeding (milk contains deconjugating enzymes; unconjugated bilirubin in baby's gut gets reabsorbed)
Phototherapy, blue light, that converts unconjugated bilirubin into water soluble Lumibilirubin
Kernicterus (Bilirubin Encephalopathy)
unconjugated bilirubin levels are >20 mg/dL
Unconjugated bilirubin can cross the blood-brain barrier as it is lipid-soluble
permanent neurologic damage or death
Physiologic Jaundice of the Newborn
Crigler-Najjar
Increased in unconjugated bilirubin
Type I: Absent conjugating enzyme activity; Fatal in neonatal period
Type II: Reduced conjugating enzyme; generally mild; occasional Kernicterus; Rx with phenobarbital if Bili > 15-20
Phenobarbital ↑ hepatic glucuronosyl transferase activity
Gilbert Syndrome
Increased in unconjugated bilirubin
Innocuous; ↓ conjugating enzyme activity
↑ Conjugated bilirubin
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome → Innocuous; impaired canalicular secretion of conjugated bilirubin due to mutation in drug efflux channel (Multidrug Resistance Protein 2/MRP2)
Pigmented cytoplasmic globules in cytoplasm → liver black
Rotor Syndrome → innocuous
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
Synthesized & excreted by the biliary tract
Elevated in bile duct obstruction, external & internal (extra- or intra-hepatic)
External obstruction results in the highest elevations of ALP & is accompanied by a parallel rise in direct (conjugated) bilirubin
Moderate elevations ≈2x normal
Space-occupying lesions (primary & metastatic tumors to the Liver or Bone)
Intrahepatic biliary tract disease
Hepatic congestion (heart failure); Hepatic injury (hepatitis)
Non-liver ALP sources: Osteoblasts (bones in growing kids/teens), Placenta (pregnancy), Intestines
Gamma Glutamyl Transpeptidase (GGT)
manufactured by bile ducts; specific to liver
Elevated with Alcohol ingestion even w/o liver disease due to microsomal induction
Obesity
Cholestasis
Decreased bile flow due to impaired secretion by hepatocytes or to obstruction of bile flow through the intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts
increased serum concentrations of:
Conjugated bilirubin, Bile acids/salts, Cholesterol
↑ Direct (Conjugated) bilirubin; Cholesterol; ALP
Jaundice, Pruritus due to retained bile acids, skin Xanthomas
Acute liver failure
Encephalopathy & Coagulopathy that occurs < 6 months (usually < 2 months) after the initial liver injury & in absence of preexisting liver disease
Causes: Acetaminophen overdose, Drugs/toxins, Hep A, Hep B, Autoimmune hepatitis, Hep E
AST, ALT > 10x upper limit normal & are >> ALP
Jaundice & Icterus, N&V
↑ Bilirubin: mostly conjugated, but ↑ unconjugated too
Coagulopathy: prolonged PT/INR & PTT
Easy bruising, intracranial hemorrhage, DIC
Hepatic Encephalopathy: ↑ serum Ammonia
Confusion, stupor, coma, Asterixis "liver flap"
Hepatorenal Syndrome: ↓ urine output, ↑ BUN & Creatinine
Fetor Hepaticus: foul smelling breath due to portosystemic shunt of Thiols (organosulfurs)
Two pathogenetic patterns of Acute Liver Failure
Massive necrosis
Diffuse Microvesicular Steatosis:
AST, ALT not massively elevated (not due to necrosis)
Seen in Fatty Liver of Pregnancy, some Drugs (valproate, tetracycline), Reye syndrome (aspirin to children) or idiosyncratic
Mechanism is acute metabolic failure due to impaired mitochondrial Fatty Acid β-oxidation
Chronic Liver Failure
Encephalopathy & Coagulopathy
background of other complications of inadequate liver function occurring after a long-standing (> 6 months) liver illness
Cirrhosis: Nodules of hepatocytes completely surrounded by fibrous (collagenous) tissue
Portal hypertension
Persistent Cholestasis can result in retention of Bile Acids in blood with Pruritus (Itching)
Impaired breakdown of Estrogen: Palmar Erythema (due to vasodilation), Spider Angiomas of skin, Hypogonadism (menstrual irregularities, testicular atrophy) & Gynecomastia
Causes of Cirrhosis
Chronic Hep B, Hep C, NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis), Alcoholic Liver Disease
Cirrhosis-associated Immune Dysfunction syndrome
immunocompromised & have ↑ susceptibility for spontaneous bacterial infections, hospital-acquired infections, & infections from uncommon pathogens
Portosystemic shunting impairs liver clearance of gut-derived bacteria in the portal circulation
↓ phagocytic activity
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis (SBP) in the Ascitic fluid, Urinary tract infection, Pneumonia, Bacteremia, & soft tissue infection
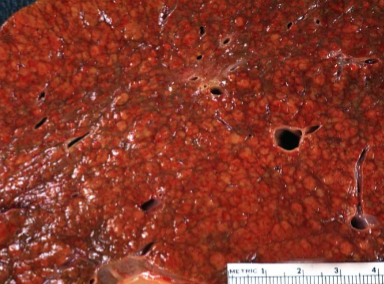
Cirrhosis
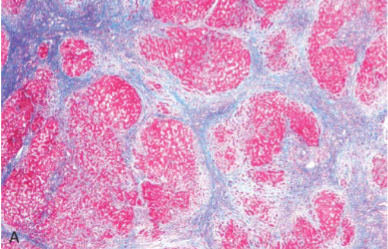
Cirrhosis
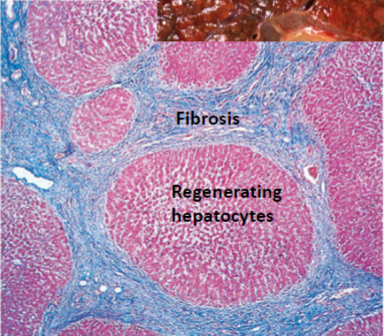
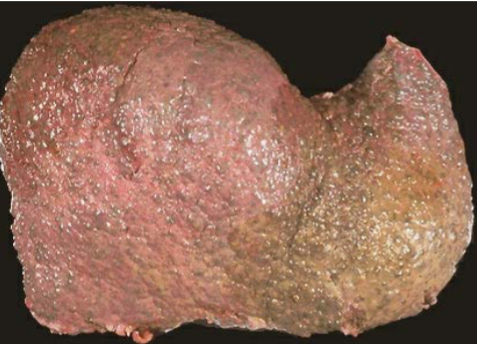
Cirrhosis
liver is shrunken with a “hobnail” capsule & micronodular cut surface
Cirrhosis Morphology
Diffuse involvement of entire liver by regenerating hepatocyte nodules surrounded by dense bands of scar
Ductular reaction (proliferation of reactive bile ducts within the fibrotic septa)
Some Regression of fibrosis may occur (eg, treated Hep C, EtOH abstinence) via thinning of fibrous scars
Hyperestrogenemia in advanced Chronic Liver disease
Pathogenesis: inability to break down Estrogen
Palmar erythema (due to vasodilation)
Spider angiomas (may be due to ↑VEGF)
Hypogonadism & Gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men)
Secondary Amenorrhea in women
Portal Hypertension
Increased pressure in Portal Vein → ↑ resistance to Portal blood flow
Cirrhosis (intrahepatic) is the most common cause
In Cirrhosis, resistance to portal flow at the level of sinusoids is due sinusoidal disruption from scarring & Arteriolar vasoconstriction due to ↓ NO production by sinusoidal endothelial cells
Causes include pre-, intra- & post- hepatic
Four major consequences of portal hypertension are:
Formation of Portosystemic venous shunts/varices
Hepatic encephalopathy
Ascites
Congestive splenomegaly
Portosystemic venous shunts
Portal Hypertension is an impedance to return of blood to the IVC & causes development of, & use of, portocaval anastomoses to decompress the portal circulation
Rectum → Hemorrhoids
Esophagogastric Junction (producing Esophageal & Gastric Varices): often rupture, causing massive bleeding, death
Periumbilical/Abdominal wall venous collaterals (producing Caput Medusa)
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Ammonia toxic to CNS accumulate due to impaired liver function + shunting of blood around liver
Severe Hepatocyte loss or impairment reduces liver’s capacity to detoxify Ammonia into Urea
Biggest source of Ammonia is the GI tract from bacterial & enterocyte metabolism of Glutamine
With significant portosystemic shunting, Ammonia bypasses the liver
GI enema with Lactulose traps ammonia
Ascites
Caused by cirrhosis; normally are Transudates; may seep through diaphragm to cause hydrothorax
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis, an ascitic fluid infection without an evident intra-abdominal surgically treatable source, presumably by transmigration of bacteria through the gut wall
Suspect if cirrhotic patient develops fever, abdominal pain/ tenderness to palpation, altered mental status, or hypotension
Rx if Paracentesis fluid PMNs > 250/mm3, or if + Leukocyte Esterase or + Nitrite
Splenomegaly
Hypersplenism sequestration → Thrombocytopenia or Pancytopenia
Schistosomiasis
common cause of Portal Hypertension
Intrahepatic “Pipestem Fibrosis” due to granulomatous inflammation to eggs within intrahepatic branches of the portal vein
Indications for TIPS procedure (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) for Rx of Portal Hypertension
Uncontrolled variceal hemorrhage from esophageal or gastric varices that do not respond to endoscopic or medical management
Refractory Ascites
Hepatic pleural effusion (Hydrothorax)