BIO - GENETICS/EPIGENETICS STUDY SET
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Gametes
Sex cells. These are the only types of human cells produced by meiosis, rather than mitosis
sexual reproduction
2 parents give rise to offspring that have uniquecombinations of genes inherited from the 2 parents
Chromosomes
packaged DNA
Locus
a specific location of a gene on a certain chromosome
Heredity
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity and variation
Genes
Units of heredity, and are made up of segments of DNA
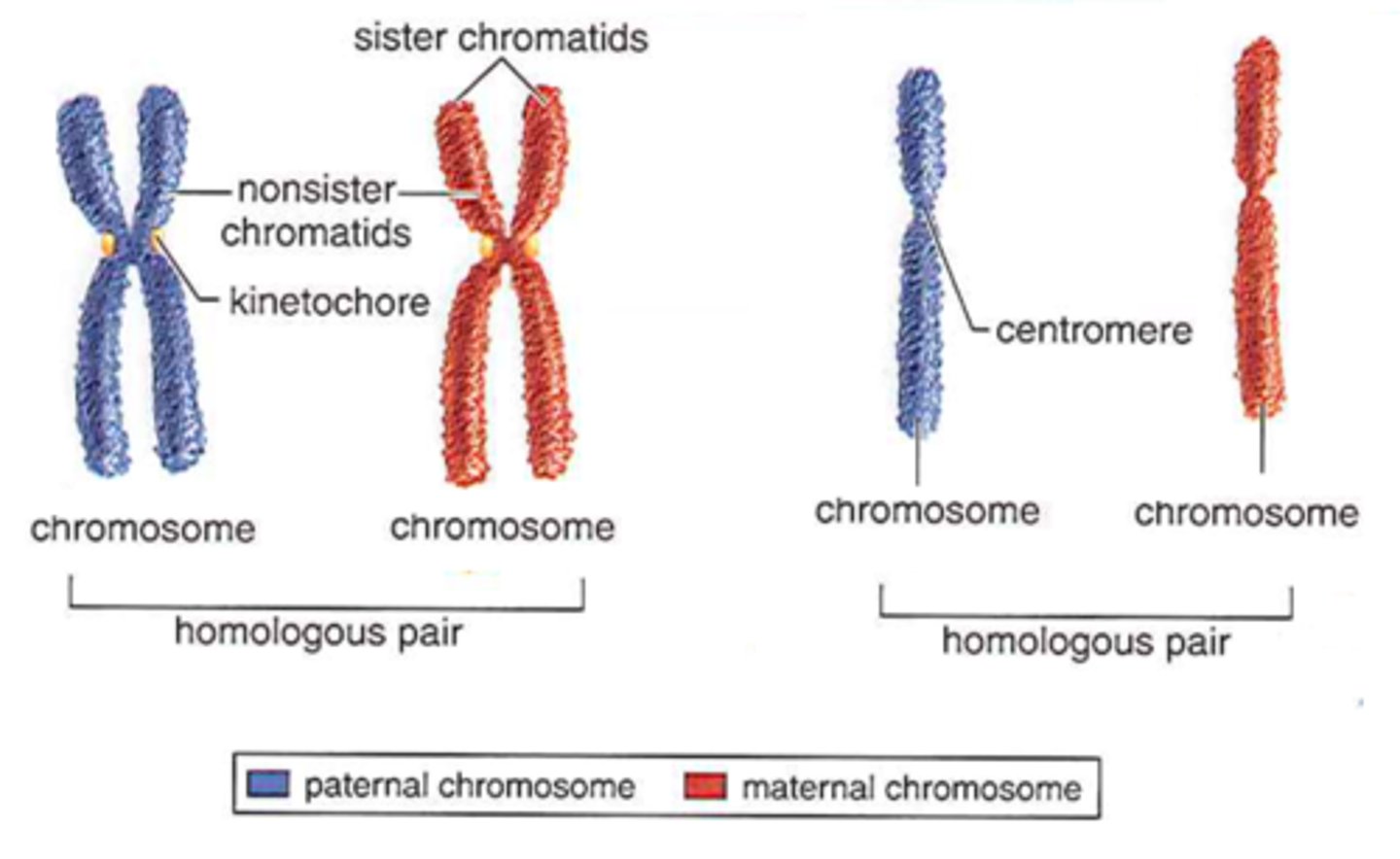
A karyotype
ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
homologous or homologs
pairs of sister chromatids
each pair comes from maternal and parental genes
trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes. (aka character)
true-breeding
plants that produce offspring of the same variety when they self-pollinate
hybridization
mating or crossing of two different true-breeding varieties
P generation
the parental generation, true-breeding parents
F1 generation
the first filial generation, hybrid offspring from the P generation
F2 generation
the second filial generation, offspring from the self-pollination of the F1 generation
alleles
the alternative versions of a gene
dominant allele
the allele which determines the organism's appearance if two alleles at a locus differ
recessive allele
the allele which has no noticeable effect on the organism's appearance if two alleles at a locus differ
law of segregation
the two alleles for a heritable character segregate during gamete formation, ending up in different gametes
Punnett square
a diagrammatic device used for predicting allele composition of offspring from a cross between individuals of known genetic makeup
homozygous
a pair of identical alleles for a gene
heterozygous
two different alleles for a gene
phenotype
the observable trait from the genetic makeup
genotype
the genetic makeup of a trait
test cross
breeding an organism of unknown genotype with a recessive homozygote, revealing the genotype of said organism
monohybrid
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
dihybrid
cross involving two traits
law of independent assortment
each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation
complete dominance
phenotypes of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are indistinguishable
incomplete dominance
phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of individuals homozygous for either allele
codominance
phenotypes of both alleles are exhibited in the heterozygote because both alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways
pleiotropy
The ability of a single gene to have multiple phenotypic effects.
epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
polygenic inheritance
an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character
pedigree
family tree showing the occurrence of heritable characters in parents and offspring over multiple generations
carriers
heterozygotes that transmit the recessive allele to their offspring
Sex-linked gene
A gene located on a sex chromosome; can be X-linked or Y-linked
X-linked inheritence
X-linked genes are passed to daughters by both mother and father as females are XX. For males, only the mother provides the X-linked gene and the father provides the Y-linked gene as the mother only has X-linked genes and the father can only give Y-linked genes if the result is male progeny
X-inactivation
During embryonic development of females, one of the X chromosomes (randomly chosen) is inactivated by methylation
Barr body
The inactive X chromosome of the developing female condenses into this and lies along the inside of the nuclear envelope
Linked genes
Located on the same chromosome and therefore tend to be inherited together during cell division
Genetic recombination
The production of offspring with a new combination of genes inherited from the parents
Recombinants
A genetic cross that yields offspring with a different phenotype from either parent
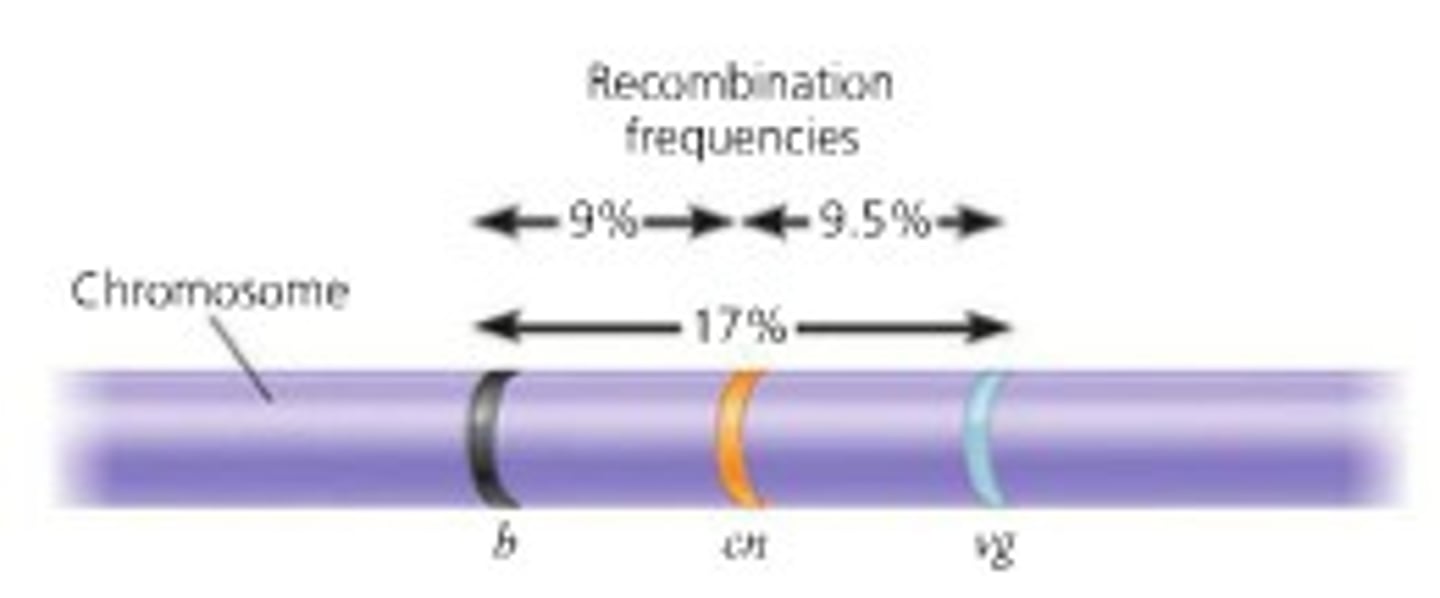
Linkage map
A genetic map that is based on the percentage of crossover events
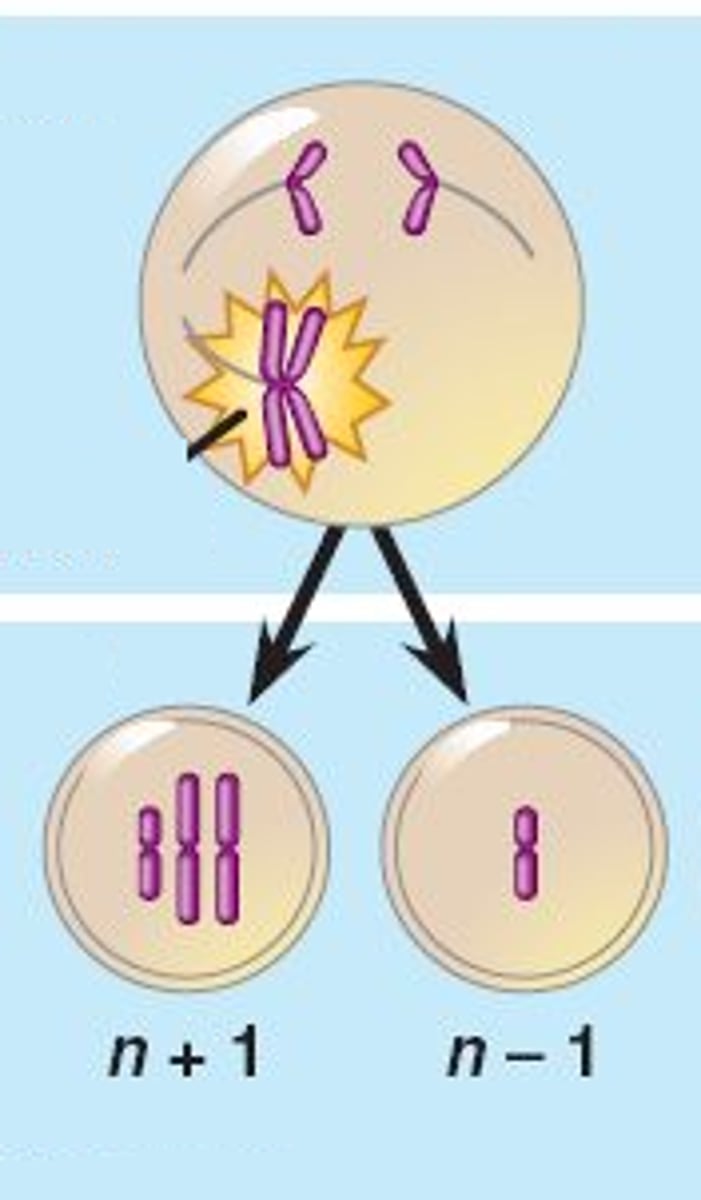
Nondisjunction
Occurs when the members of a pair of homologous chromosomes do not separate properly during meiosis I resulting in one gamete receiving two copies of a chromosome, while the other gamete receiving none
recombination frequency
With respect to two given genes, the number of recombinant progeny from a mating divided by the total number of progeny. Recombinant progeny carry combinations of alleles different from those in either of the parents as a result of independent assortment of chromosomes or crossing over.
extranuclear inheritance
extranuclear genes are found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Defects in mitochondrial DNA can reduce cell's ATP production. Mitochondria typically passed to zygote all come from mother, so all related diseases are mother inherited. (Note: new research may refute this.)
phenotypic plasticity
the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.
gene penetrance
likelihood that an organism will actually express its inherited genotype.
gene expressivity
the degree to which the phenotype is expressed in an organism
Epigenetics
the study of influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
gene regulation
ability of an organism to control which genes are transcribed in response to the environment
Heterochromatin
DNA that is densely packed around histones. The genes in heterochromatin are generally inaccessible to enzymes and are turned off.
Euchromatin
The less condensed form of eukaryotic chromatin that is available for transcription.
DNA methylation
The addition of methyl groups to bases (cytosine) of DNA after DNA synthesis (genes turned off); may serve as a long-term control of gene expression.
DNA acetylation
The addition of acetyl groups to histone complexes to loosen them, increasing transcription (genes turned on)
transcription initiation
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region of DNA strand, and synthesis begins
transcription suppression
The blocking of RNA polymerase from binding to the promotor region, thus suppressing transcription
promotor region
portion of a gene that signals for RNA polymerase to start transcription
transcription factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription; can be activators or suppressors
enhancer region
Binding site far upstream of gene. Turns transcription on HIGH.
terminator region
the nucleotide sequence at the end of a gene that signals the end of transcription
operator region
the region of DNA where a repressor protein binds, to block transcription
lac operon
a gene system whose operator gene and three structural genes control lactose metabolism in E. coli
alternative splicing
Post-translational RNA modification process in which exons can be joined in various combinations.
RNA interference
small pieces of RNA can shut down protein translation by binding to the messenger RNAs that code for those proteins
mRNA degradation
the lifespan of mRNA determines how much protein it can produce- only lasts hours to a few weeks
Transposons
(jumping genes) short strands of DNA capable of moving from one location to another within a cell's genetic material; sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity and genome size
Ubiquitin
A small protein that is covalently linked to other cellular proteins identified for breakdown by the proteosome; marked for degradation (death)
Proteasomes
A giant protein complex that recognizes and destroys proteins tagged for elimination by the small protein ubiquitin.
Agouti mouse study
a landmark epigenetic experiment showing how maternal diet (especially methyl donors like folic acid) during pregnancy dramatically changes offspring's coat color (yellow/obese vs. brown/lean) and disease risk (obesity, diabetes) without altering their DNA, proving environmental factors can switch genes on or off via methylation, a key concept in epigenetics and developmental health (Dr. Jyrtle at NCSU!!)
What does gene regulation do?
It turns genes on and off rapidly, allows for flexibility & reversibility, regulates cell differentiation, allows cell to adjust to changing environment, adjusts levels of enzymes for synthesis & digestion
What are the points of control for gene expression?
1. packing/unpacking DNA
2. transcription
3. mRNA processing
4. mRNA transport
5. translation
6. protein processing
7. protein degradation
What is DNA Packing?
Degree of packing of DNA that regulates transcription, DNA tightly wrapped around histones, no transcription, genes turned off
What is heterochromatin?
darker DNA (H) = tightly packed
What is euchromatin?
lighter DNA (E) = loosely packed
What does DNA methylation do?
It blocks transcription factors which involves the addition of methyl groups (–CH3) to cytosine on the DNA strand causing a tightening of the strand around histones, which shuts down transcription→ genes turned off. It is a nearly permanent inactivation of genes.
How does DNA methylation differentiate cells?
DNA methylation differentiates cells by silencing genes that are not needed anymore.
What does histone acetylation do?
It unwinds DNA allowing gene access, it involves the attachment of acetyl groups (–COCH3) to histones, it causes conformational change in histone proteins which unwind, it allows for transcription factors have easier access to genes, and genes get turned on
What is transcription initiation and suppression?
It is regulation of the start of transcription. It is regulated by non coding sequences of DNA (the “junk). It involves transcription factors, enhancers, and terminators.
What is the promoter?
The promoter is the area upstream of a gene where RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription with the help of general transcription factors
What is a transcription factor?
transcription factors are molecules (generally proteins) that help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter region of the DNA. They can be activators or repressors, which help other general TF and RNA polymerase assemble and bind to the promoter, ultimately controlling whether or not transcription occurs
What is an enhancer?
An enhancer is a distant control sequences on DNA (further upstream from the gene)- helps with “enhanced” rate (high level) of transcription
What is a terminator?
A terminator marks the end of the gene and thus the end of transcription
What does Post-transcriptional control involve?
Post-transcriptional control involves Alternative RNA splicing, RNA interference, and mRNA degradation.
What is Alternative RNA splicing?
Alternative RNA splicing is where introns are removed and exons are pasted together by the spliceosome to make the final mRNA strand. The mRNA can be spliced in different ways resulting in different gene expressions.
What is RNA Interference?
RNA interference is where small pieces of RNA can shut down protein translation by binding to the messenger RNAs that code for those proteins.
What is mRNA degredation?
mRNA degradation is where the mRNA lifespan determines number of proteins which only lasts from hours to a few weeks.
What is a transposon?
A transposon is a sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations and altering the cell's genetic identity and genome size
What does the protein life cycle consist of?
The protein life cycle consists of protein processing and protein degredation
What does protein processing consist of?
Protein processing consists of folding, cleaving, adding sugar groups, targeting for transport
What does protein degradation consist of?
Protein degradation consists of ubiquitin “death tag” which marks unwanted proteins with a label, and labeled proteins are broken down rapidly in "waste disposers" called proteasomes
What is the takeaway of the Agouti mouse study?
The agouti mouse study shows that environmental factors (especially maternal diet) can change gene expression without changing DNA sequence, leading to differences in traits like coat color, obesity, and disease risk.
How do the changes occur in the Agouti mouse study?
These changes occur through epigenetic modifications—mainly DNA methylation of the agouti gene—which can silence or activate genes and may persist across generations.