ap micro unit 5
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
factor market
market in which firms purchase the factors of production (resources) from households (businesses)
businesses
In a factor market, the _________ are demand
households
In a factor market, the _________ are supply
Marginal revenue product
the change in total revenue associated with one additional unit of input
MRP
MR x MP
Marginal cost of labor
the cost to the firm of hiring one more worker
MCL
Wage/MP
MRP
In a Factor market, the firm's demand for labor is the ________ because it is the maximum that the firm is willing to pay for that quantity of labor
MRP > Wage
In a factor market, you only hire workers where ____________
Value of Marginal Product
MP x Price
MR
If the firm is selling to a perfectly competitive market then Price =
derived demand
business demand that ultimately comes from the demand for consumer goods (increase in demand for housers = increase in demand for carpenters)
economic rent
any amount above the minimum needed to bring a resource into use
wage - opportunity cost
economic rent
equilibirum
In the labor market, the ____________ is the intersection of supply/demand and established the wage paid
unemployment
When at equilibrium, there is no ______________
minimum
In a labor market, the _______ wage goes above the equilibrium wage
unemployment
The gap between the quantity of workers at the equilibrium wage and the quantity of workers at the minimum wage
Perfectly Competitive Factor Market
A large number of buyers in the factor market - Each firm is acquiring a very small amount of resources compared to the entire market - competing for labor, workers have identical skills
wage takers
In a Perfectly Competitive Factor Market, the firms are ________ ______________
marginal factor cost
marginal resource cost is aka (cost of hiring an additional worker)
wage
In perfect competition, MRC =
any number
In perfect competiiton, the firm can hire ___ _________ of workers at the equilibrium wage (perfectly elastic)
marginal revenue product
the change in total revenue associated with one additional worker
MRP
MP x MR
MP x P
value of marginal product
MRP
_______ is the maximum wage a firm is willing to pay at x number of workers, also the demand for labor
increasing
Always hire if MRP is ___________
MRP = MRC
Profit Maximizing in perfect comp
MRP > MRC
hire as long as
MRP
A change in the market wage moves the firm's MRC, this changes ________ of last worker in market graph
profit maximizing quantity
A change in the firm's MRP shifts the firm's demand, this changes the market's _______ ________ _________
Least Cost Combination
A combination of two or more resources in such a way that the resource cost of producing a given level of output is a minimum
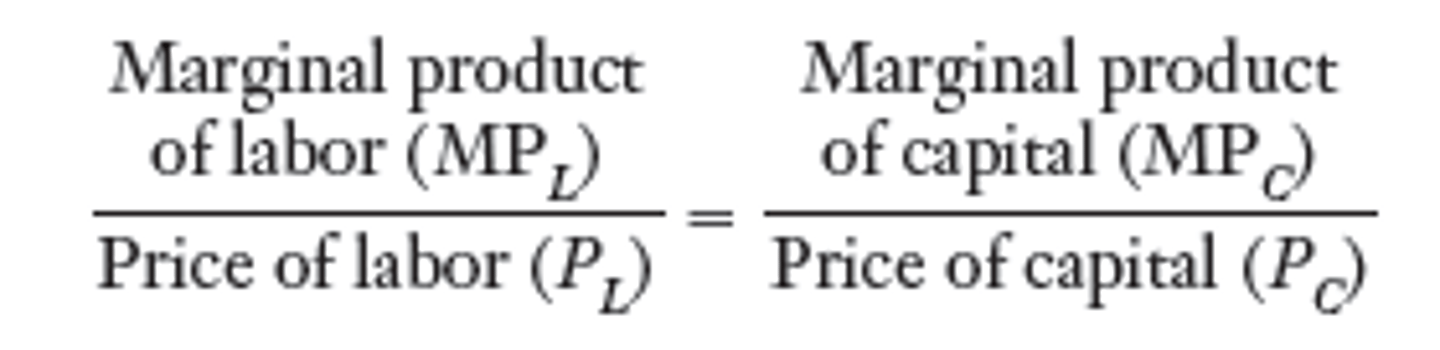
Profit Maximizing Combination
Marginal Revenue Product of Labor / Price of Labor = Marginal Revenue Product of Capital / Price of Capital = 1
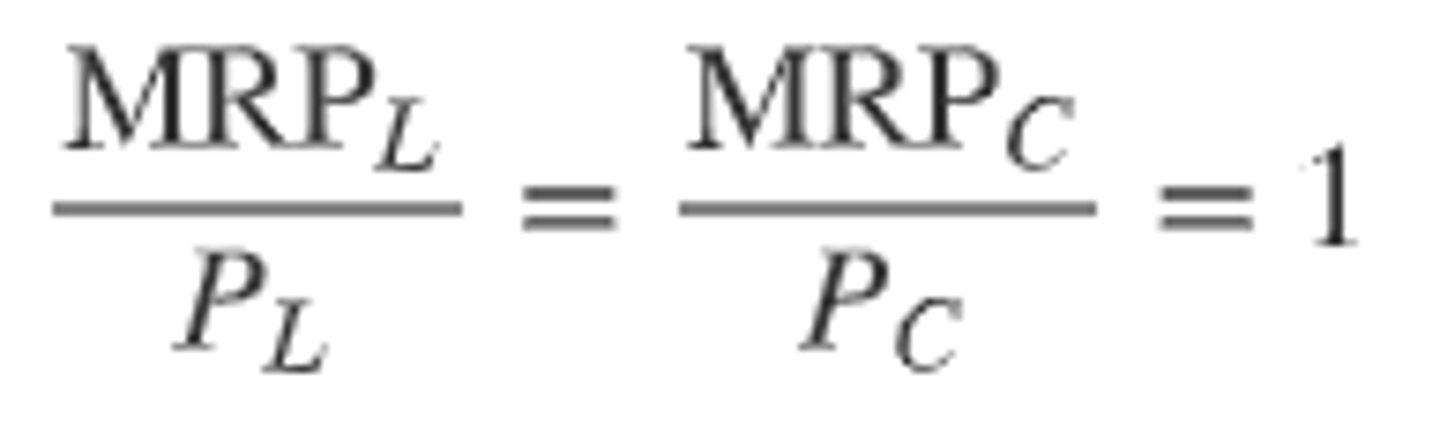
monopsony
a market structure in which there is only a single buyer of labor (employer), there are no alternative employers, and high barriers to entry
market
In a monopsony, the firm's supply equals the _______ supply
MRP = MRC
hire where
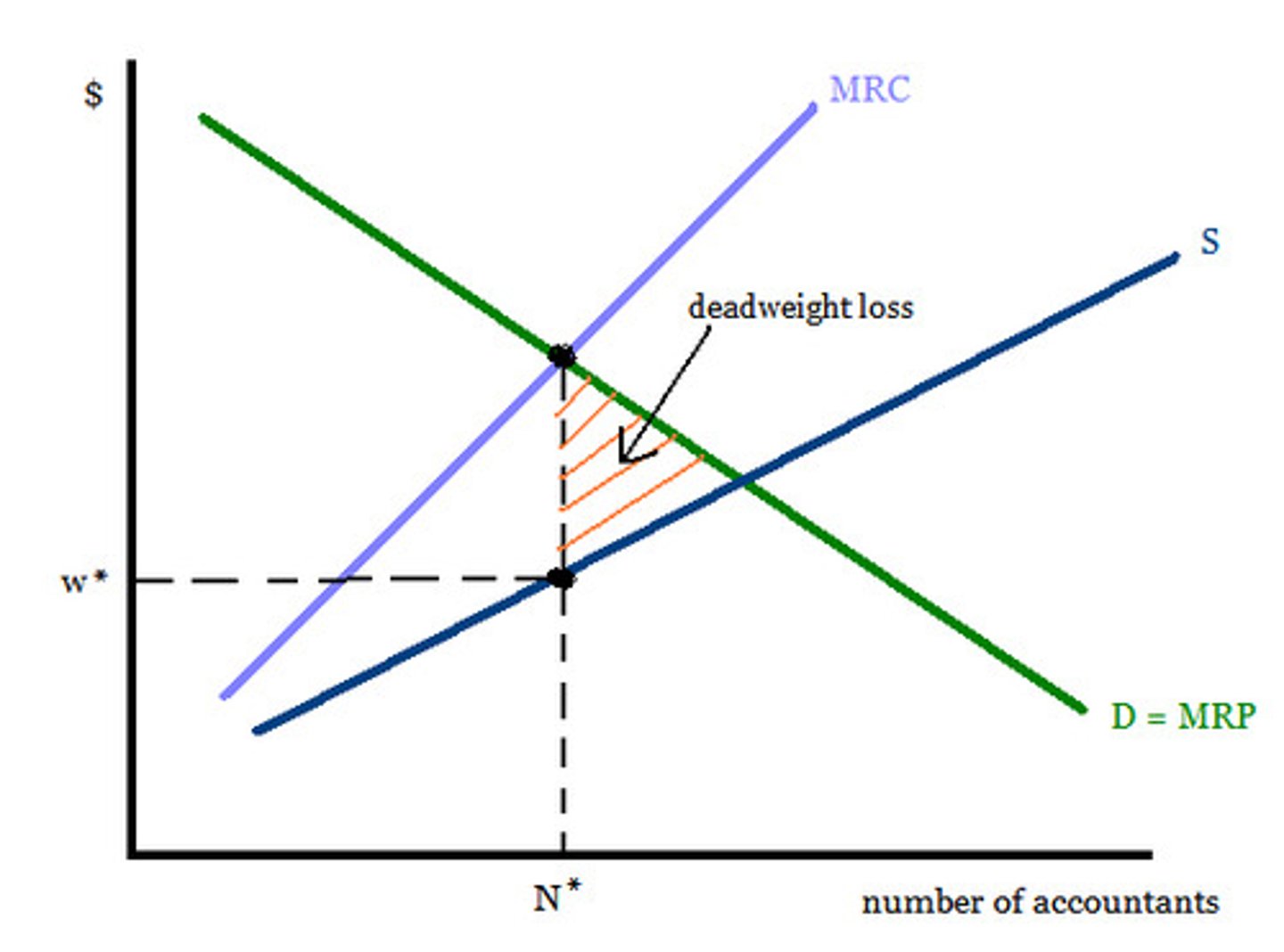
lower wages and lower quantity
Compared to a competitive market, monopsonies pay ________ (this creates deadweight loss)
minimum wage
In a monopsony, the _______ _______ is the intersection between supply and demand.
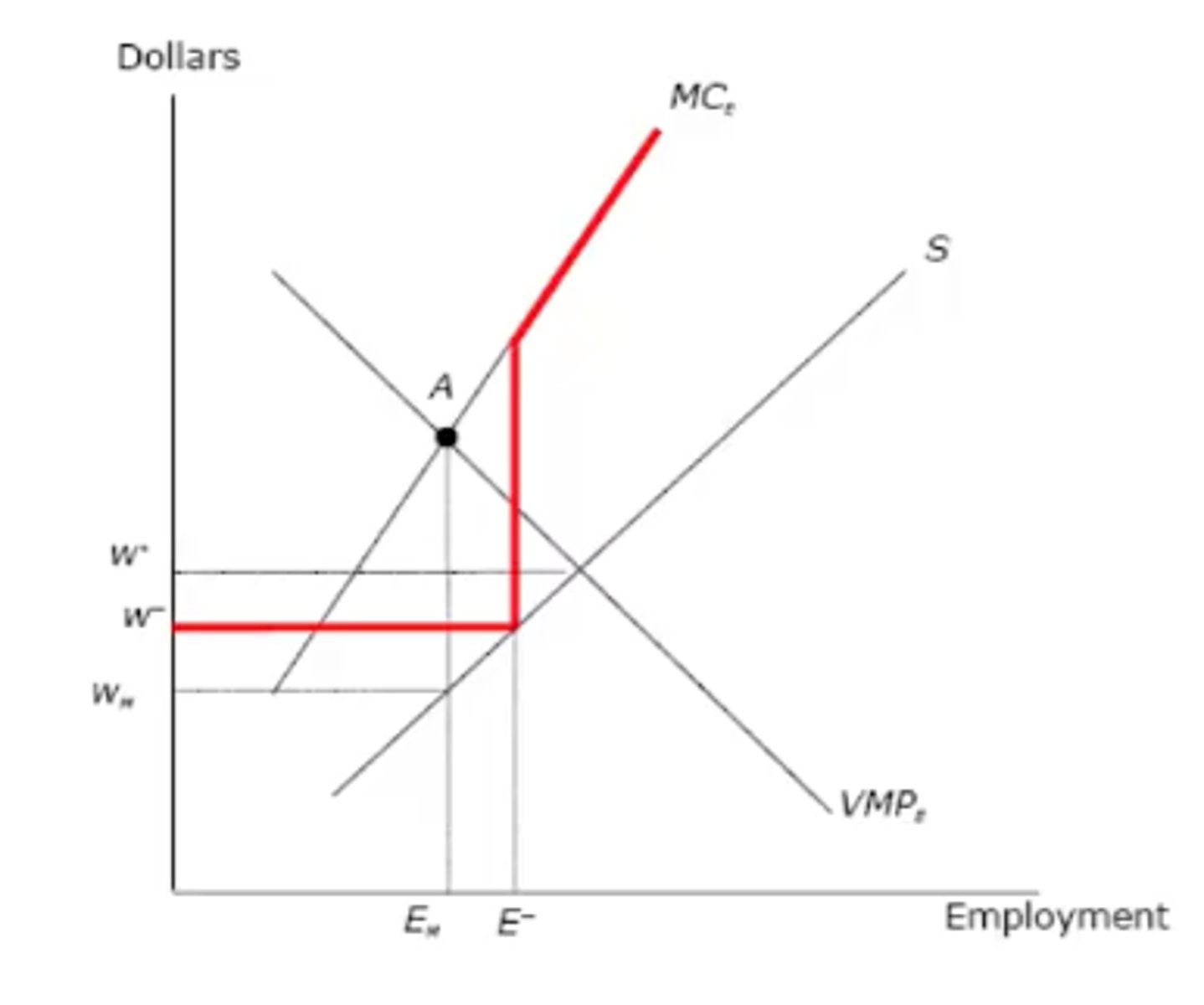
MRC
Minimum wage makes _________ horizontal until it hits supply