Chapter 22 - Lymphatic System & Immunity
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Pathogen
disease producing microbe
Immunity
ability to ward off damage or disease
Innate Immunity
protections present at birth
Adaptive Immunity
introduction of pathogens that creates specific recognition
Lymphatic System - Components
lymph
lymphatic vessels
red bone marrow
lymphatic tissue
lymph nodes
lymphatic organs
Interstitial Fluid
components filtered from blood plasma through capillary tissue
most is reabsorbed into capillaries
Lymph
interstitial fluid that enters lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic Tissue - Structure
reticular connective tissue that contains large amounts of lymphocytes
Lymphatic System - Function (3)
1) drains excess interstitial fluid
2) transports dietary lipids (vitamins)
3) carry out immune responses
Lymphatic Capillaries
ends as lymphatic vessels
closed on one end
between cells of tissues
Lymphatic Vessels
start as lymphatic capillaries
has thin walls and valves
Lymph Trunks
start as lymphatic vessels
named after the regions of body they drain
Lymphatic Ducts - Function
start as lymphatic trunks
two collecting cuts that drain lymph into subclavian veins
lymphatic Ducts - Types (2)
1) right lymphatic duct
2) thoracic duct
Right Lymphatic Duct
drains the following into the right subclavian vein
right side of head
neck
thorax
right upper limb
Thoracic Duct
drains the following into the left subclavian vein
lower limbs
abdominal region
left upper limb
left side of thorax
left side of head
left side of neck
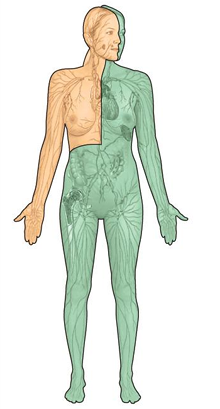
Orange lymph drains into the…
right lymphatic duct → right subclavian vein
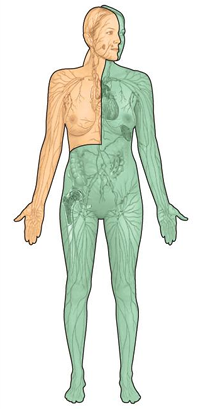
Green lymph drains into the…
thoracic duct → left subclavian vein
Lymph - Cycle
blood plasma → blood capillaries → lymph capillaries → lymph node → lymph vessels → lymph trunk → lymph duct → subclavian vein → blood plasma
Skeletal Muscle Pump
muscle contraction compress lymphatic vessels and force lymph towards subclavian veins
Primary Lymphatic Organs
sites where stem cells divide
red bone marrow
thymus
Secondary Lymphatic Organs
lymph nodes
spleen
lymphatic nodules
Thymus - Location
behind the sternum
Thymus - Structure
a soft organ that contains lobules of lymphocytes and macrophages
surrounded by connective tissue that extends inside
Thymus - Function
thymosin produces lymphocytes that will mature into T-cells to provide immunity
Lymph Nodes - Location
along lymphatic pathways
Lymph Nodes - Structure
encapsulated by connective tissue
lymphocytes and macrophages
Lymph Nodes - Function
filter and cleans lymph as it flows through the node
Breast Cancer
development of malignant tumor within the breast
Breast Drainage
75% of lymph fluid of the breasts drains into lymphatics in the lateral quadrants
drains into the 20-40 axillary lymph nodes
Spleen - Location
upper left quadrant of the abdomen
Spleen - Structure
largest lymphatic organ
wrapped in connective tissue and contains blood
Spleen - Function
filters blood by removing damaged blood cells and bacteria
Lymphatic Nodules - Structure
masses of lymphatic tissue surrounded by a capsule
Lymphatic Nodules - Location
mucous membranes lining GI, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
also appendix and tonsils
Mucosa-Associated Lymphatic Tissue (MALT)
locations in mucous membranes where lymph nodules are located
First Line of Defense
skin and mucous membranes
Second Line of Defense
antimicrobial substances, phagocytes, inflammation, fever
Phagocytosis - Phases (5)
1) chemotaxis
2) adherence
3) ingestion
4) digestion
5) killing
Chemotaxis (1)
chemicals that attract phagocytosis are released from microbes, WBC, damaged tissue, or complimentary proteins
Adherence (2)
phagocyte attaches to microbe
Ingestion (3)
plasma membrane of phagocyte send out pseudopods to engulf microbe, becomes phagosome
Digestion (4)
phagosome enters cytoplasm and merges with lysosomes and becomes a phagolysosome, digestive enzymes break down substances
Killing (5)
microbe is killed and materials that cannot be degraded become residual bodies
Phagocytosis - Cycle
phagocyte → phagosome → phagolysosome → residual bodies
Inflammation - Conditions
pathogens
abrasions
chemical irritations
distortion
cell disturbance
extreme temperatures
Inflammation - Symptoms (PRISH)
P - pain
R - redness
I - immobility
S - swelling
H - heat
Vasodilation
increase diameter of arterioles
promotes fluidity, brings more plasma and immune cells
Increased Capillary Permeability
substances normally retained in the blood are permitted to pass from blood vessels
promoted defensive proteins such as antibodies and clotting factors to injured area
Antigens
large molecules that the body does not recognize as itself
lymphatic system will identify specific antigens, remember them, and destroy them
apart of an adaptive immune response
Lymphocyte Origin
red bone marrow releases premature lymphocytes to later mature
Lymphocyte Development
T-lymphocytes become T-cells in the Thymus
B-lymphocytes become B-cells in the bone marrow
T-Cells - Function
interacts directly with non-self antigens to kill
provides a cellular immune response
B-Cells - Function
interacts indirectly by producing antibodies to kill antigens
provides a humoral immune response
Adaptive Immunity - Types (2)
1) cell-mediated immunity
2) antibody-mediated immunity
Cell-Mediated Immunity
cytotoxic T-cells directly attack invading antigens such as…
intracellular pathogens
cancer cells
foreign tissue transplants
Antibody-Mediated Immunity
B cells transform into plasma cells and synthesize specific proteins called antibodies or immunoglobins
effective against extracellular pathogens
Antibodies - Definition
specialized plasma proteins created by B-cells that provide immune reactions
also called immunoglobins
Immunoglobins - Types (5)
1) IgG
2) IgA
3) IgM
4) IgD
5) IgE
IgG - Antibody
tissue fluid and plasma that defends against bacterial cells, viruses, and toxins
only antibody that can cross the placenta
IgA - Antibody
exocrine gland secretions that provides protection of mucous membranes
tears
saliva
gastric juices
etc
IgM - Antibody
in blood plasma and reacts with blood cells during transfusions
IgD - Antibody
found in the surface of B-lymphocytes and functions of B cell activation
IgE - Antibody
found in mast cells and basophils for allergic reaction
Primary Immune Response
when B-cells or T-cells become activated for the first time
Secondary Immune Response
B-cells and T-cells use their memory and reactivate against a specific antigen
Natural Acquired Active Immunity
after exposure to an antigen for the first time
Artificially Acquired Active Immunity
use of vaccines to artificially produce antibodies
Naturally Acquire Passive Immunity
antibodies passed from mother to fetus
Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity
injection of antibodies
Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI)
field that deals with common pathways that link nervous, endocrine and immune systems
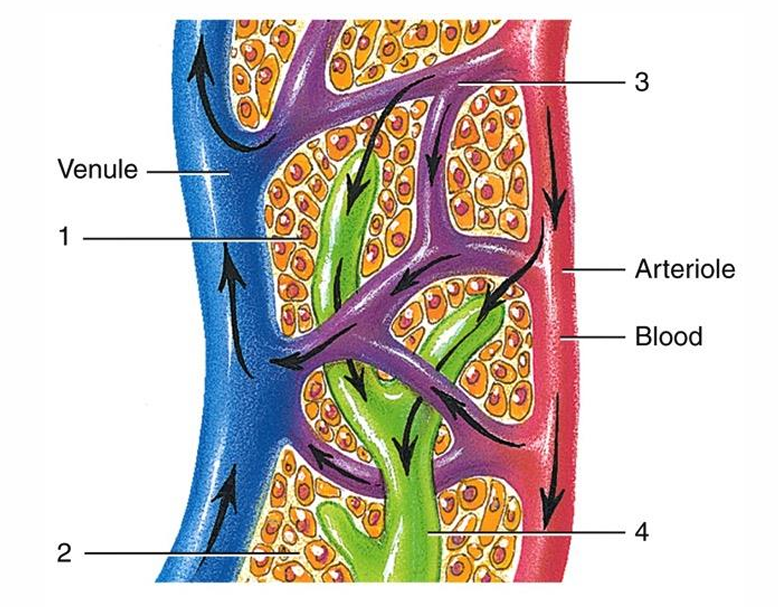
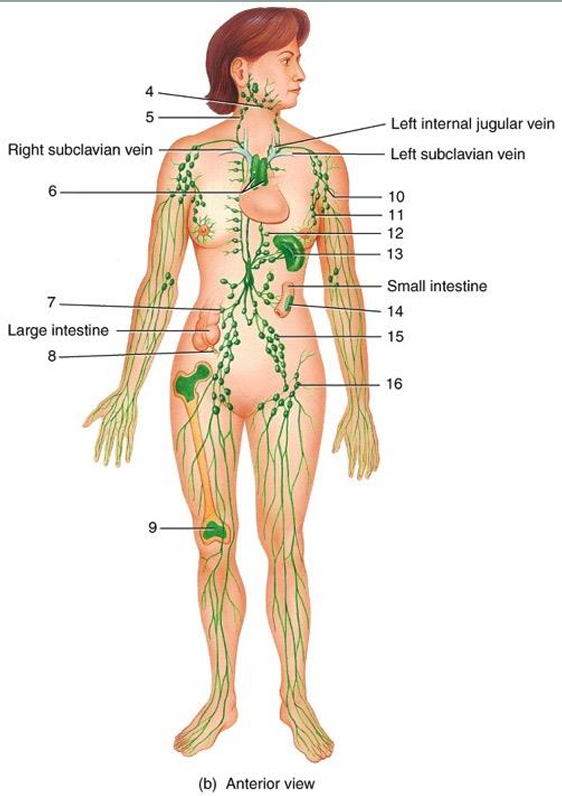
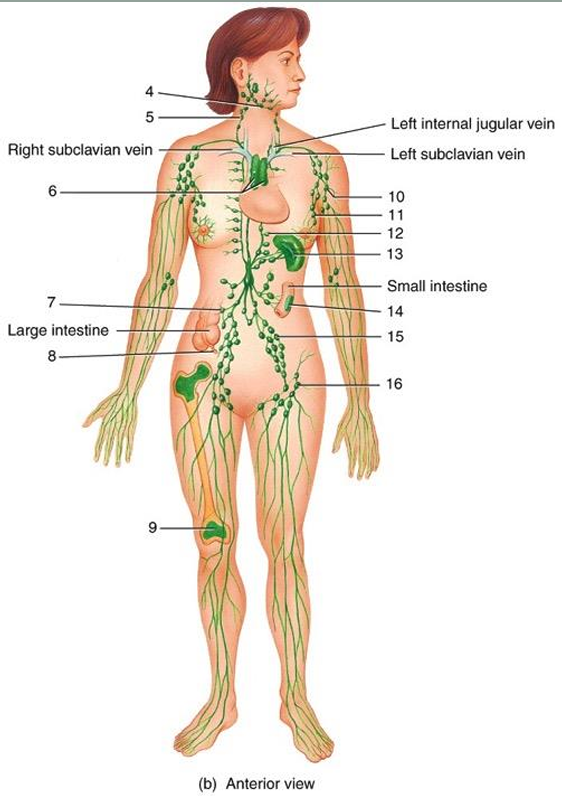
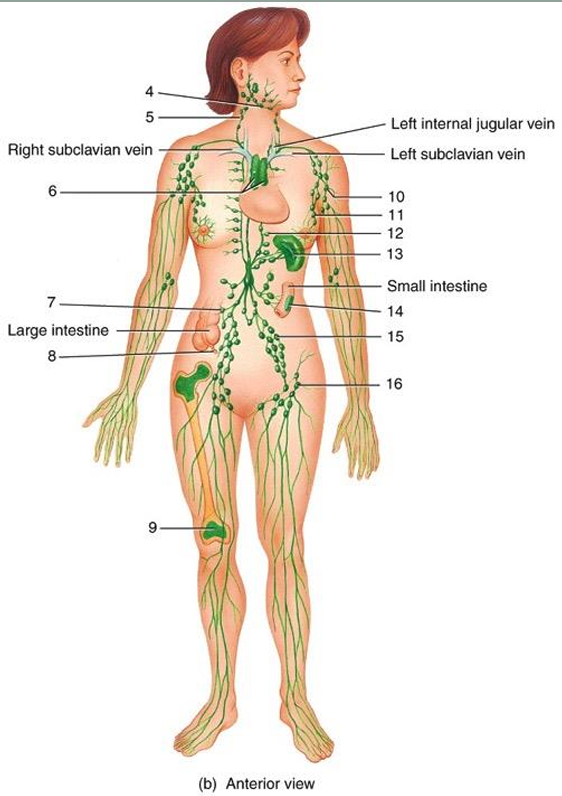
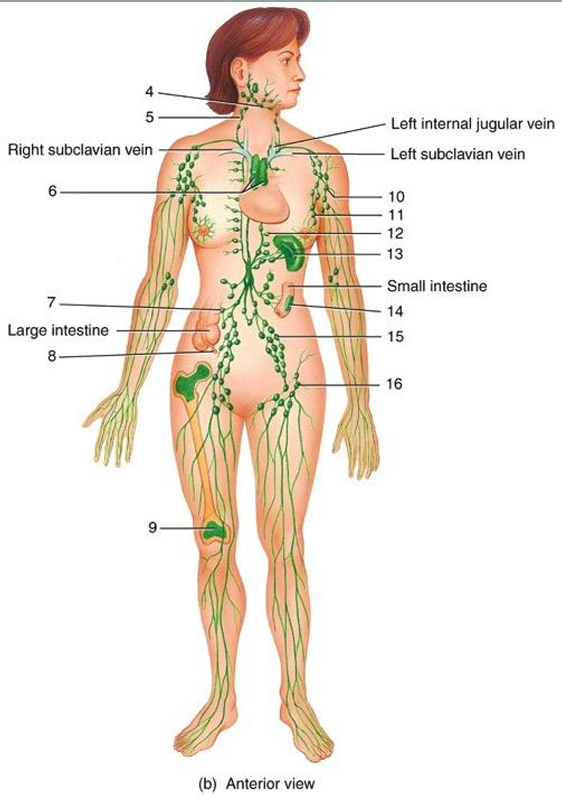
1
tissue cell
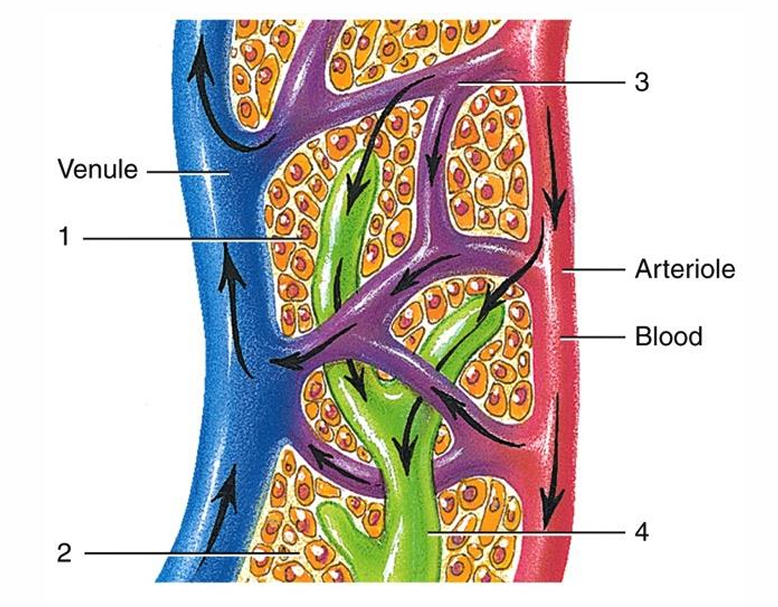
2
interstitial fluid
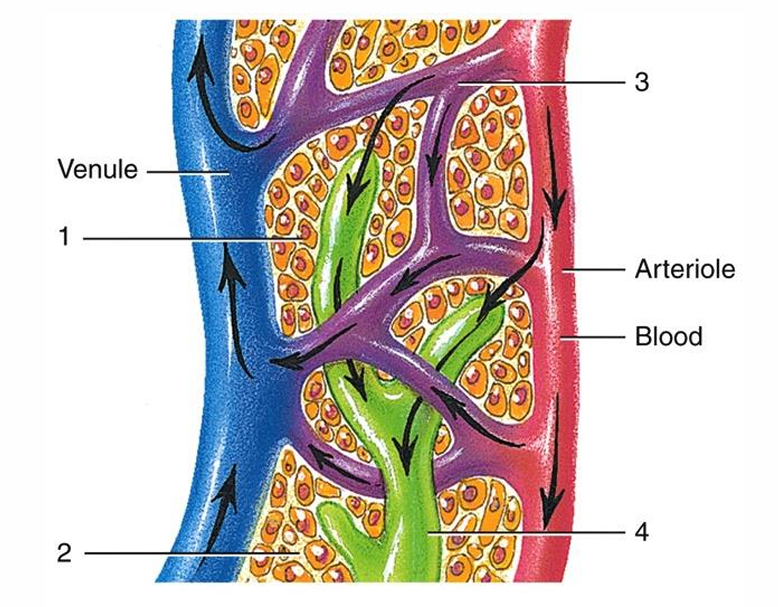
3
blood capillary
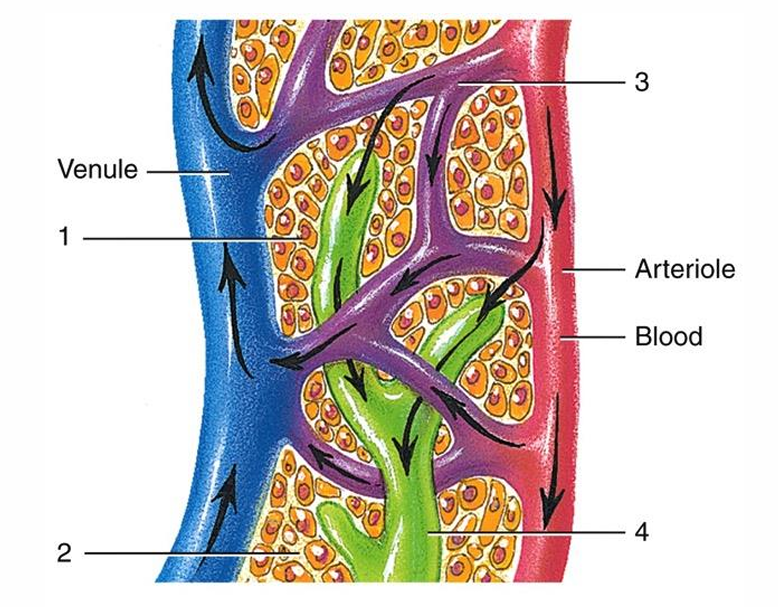
4
lymph capillary
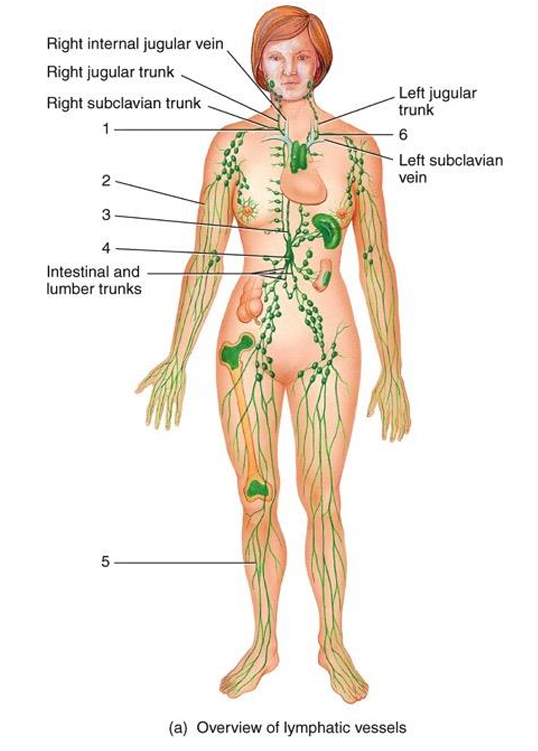
1
right lymphatic duct
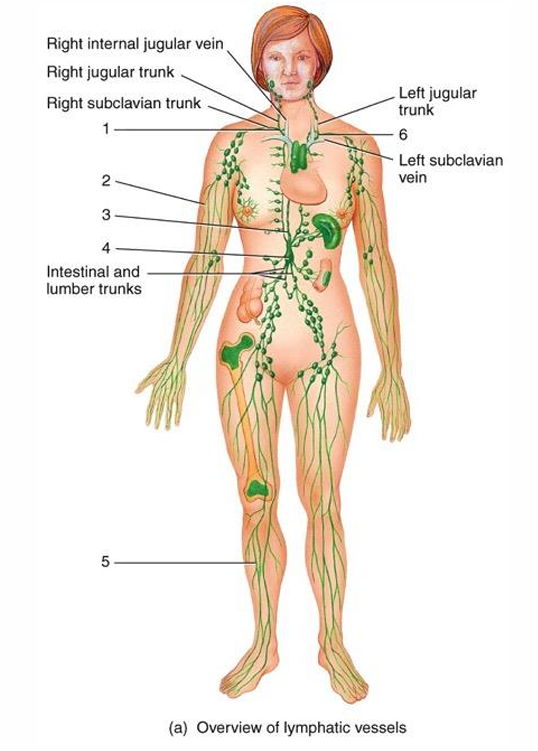
2
lymphatic vessel
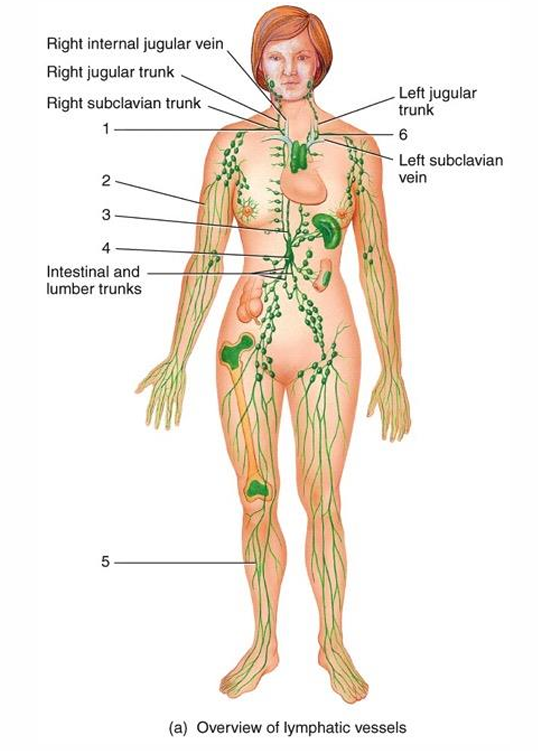
3
thoracic duct
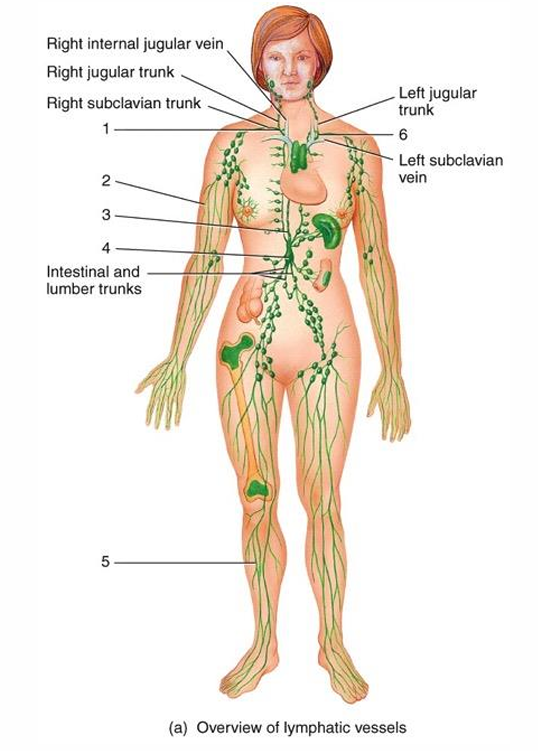
cisterna chyli
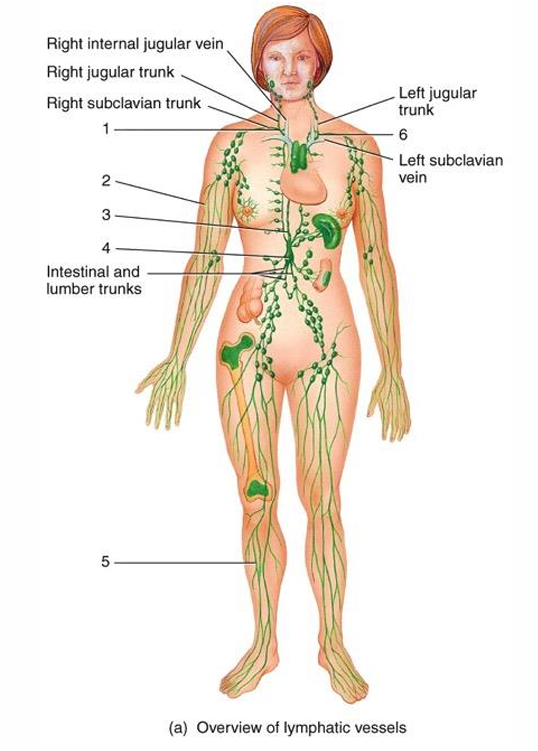
5
lymphatic vessel
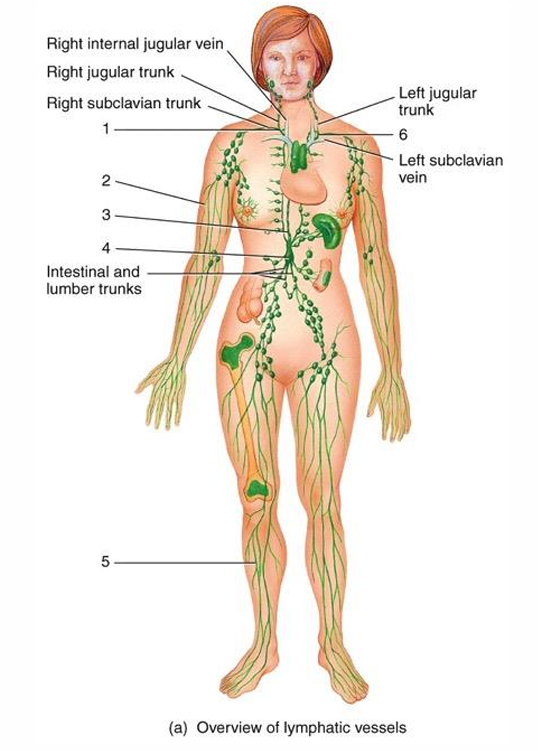
6
thoracic duct
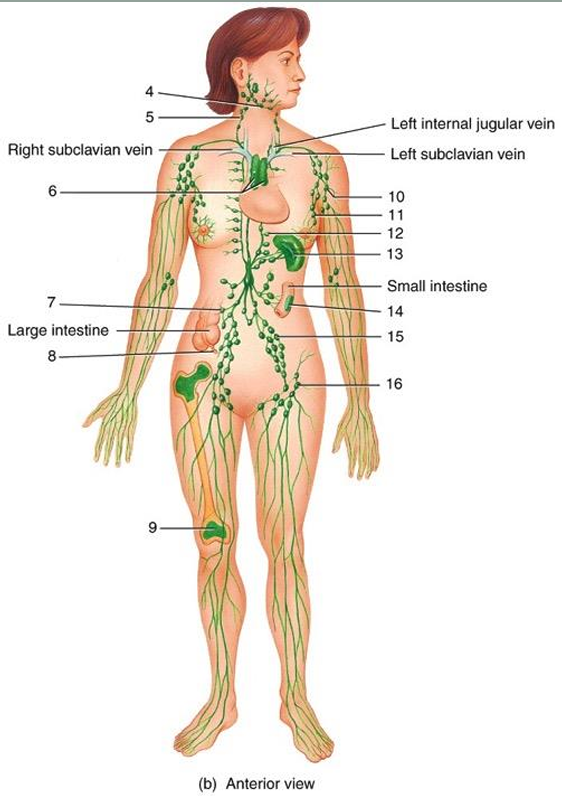
4
submandibular node
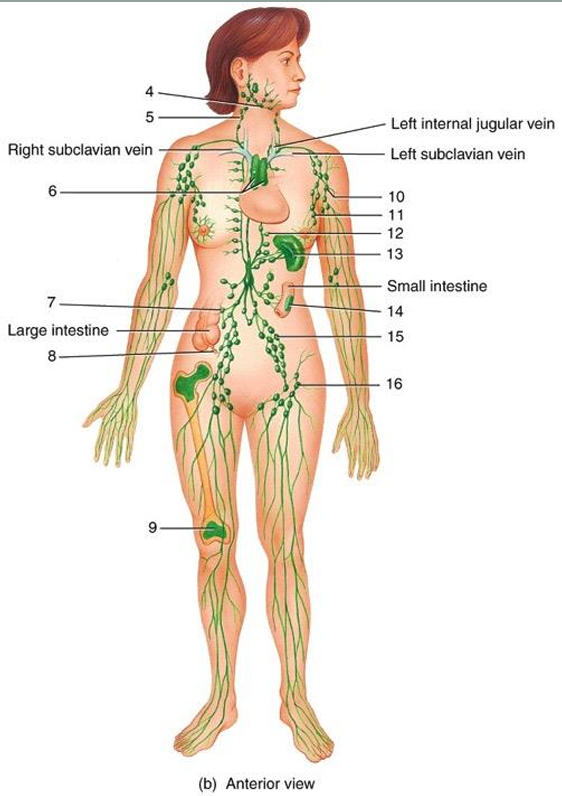
5
cervical node
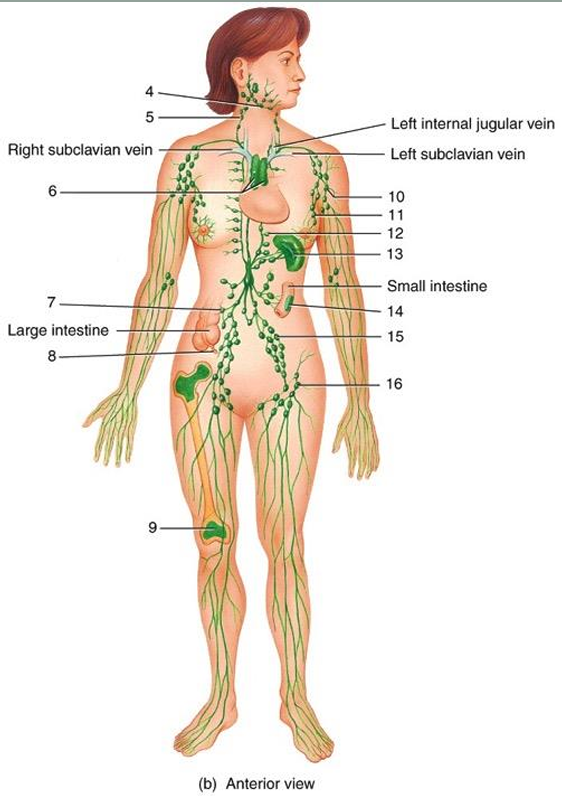
6
thymus
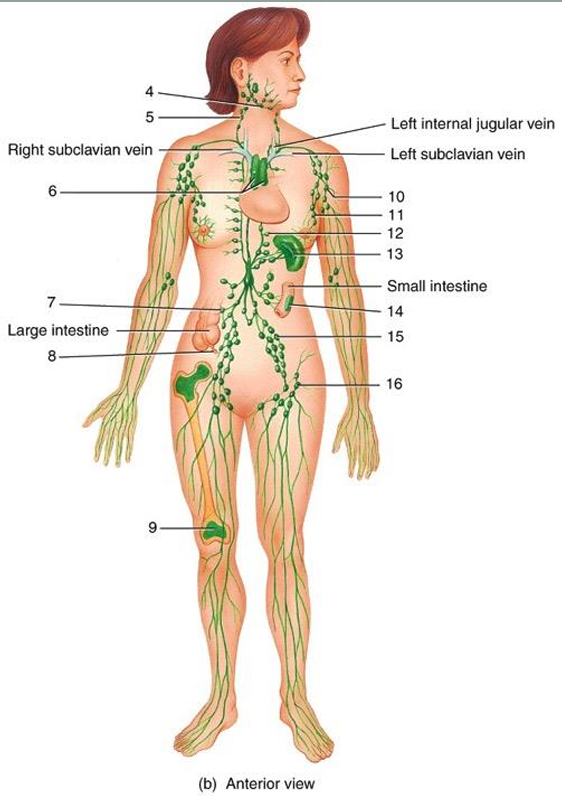
7
intestinal node
8
appendix
9
red bone marrow
10
axillary node
11
mammary node
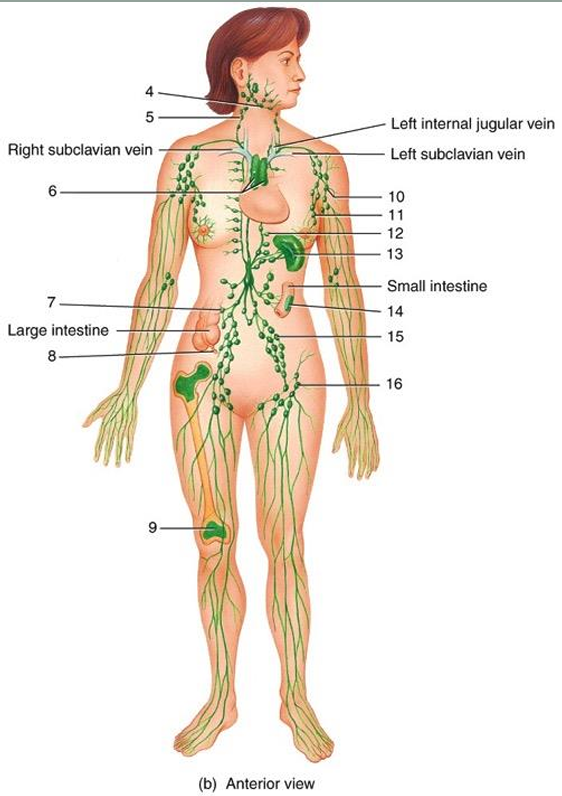
12
thoracic node
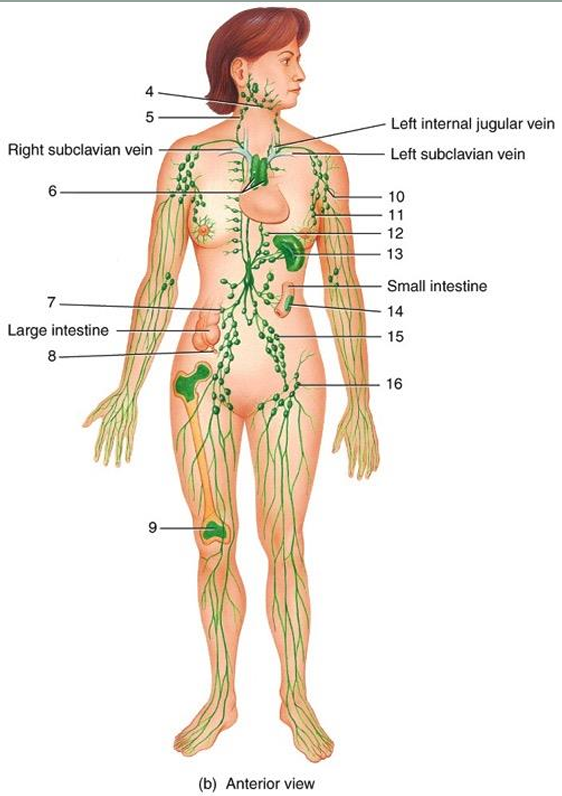
13
spleen
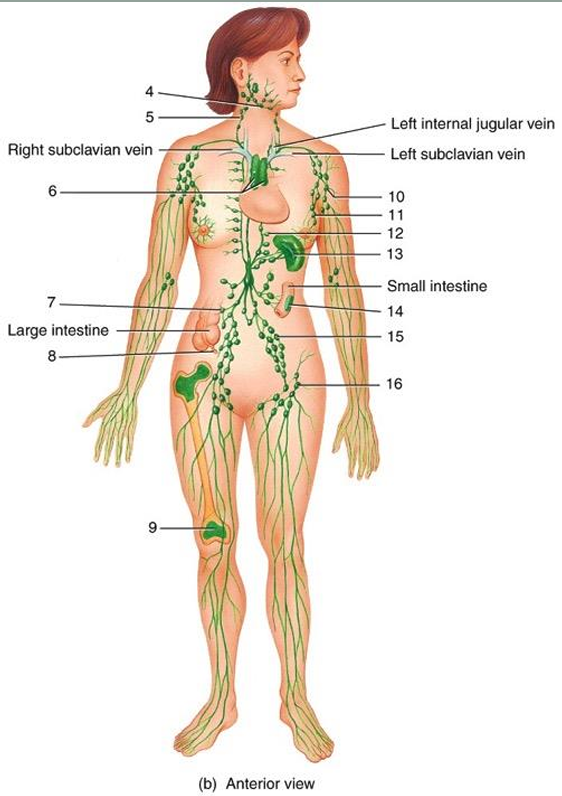
14
peyer’s patches
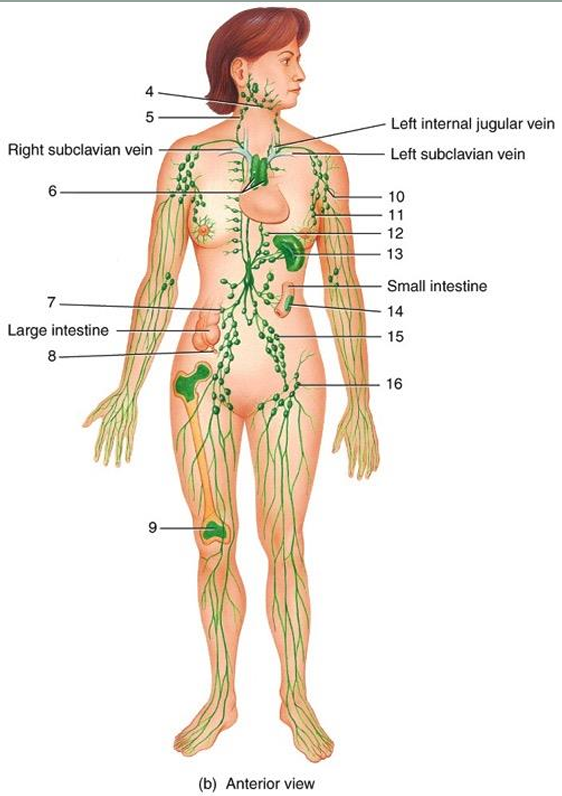
15
iliac node
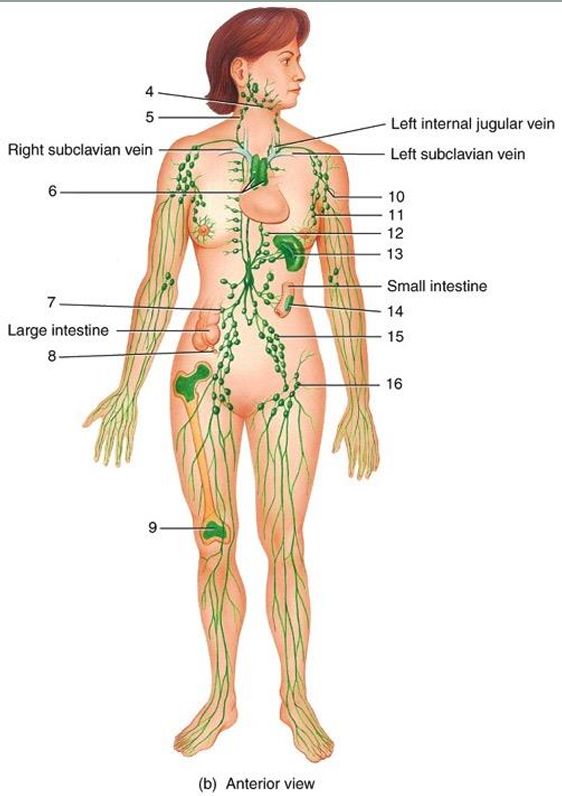
16
inguinal node
Afferent Lymph Vessel
lymph capillary → lymph node
towards lymph node
Efferent Lymph Vessel
lymph node → lymph trunk
away from lymph node