Uniformly Accelerated Linear Motion: Model Development & Motion 1
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 1: Sections 3.1 & 3.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the assumptions of the uniformly accelerated linear motion model?
Particle, 1D motion, constant acceleration
What does uniformly accelerated linear motion mean?
Uniformly = constant
Accelerated = change in velocity
Linear = 1D
Motion = position is changing
What is average acceleration?
The change in velocity divided by the elapsed time
What is the average acceleration equation?
ax (uppercase bar) = Δvx / Δt
What is the symbol and SI unit of average acceleration?
Ax (uppercase bar) and meter per second squared
What is instantaneous acceleration?
The acceleration at an instant time
What is the equation for instantaneous acceleration?
ax = limit Δvx / Δt
What is the symbol and SI unit for instantaneous acceleration?
ax and meter per second squared
Assume that a velocity vs. time graph is a straight line as shown. What is known about the instantaneous acceleration? Why?
Positive because the slope is positive
Constant because the slope is constant
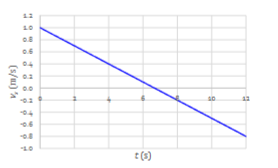
Describe the change in (instantaneous) velocity.
The velocity is always becoming more negative
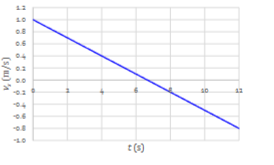
Describe the change in (instantaneous) speed.
The speed is becoming smaller until 6.5 s when it is becoming larger
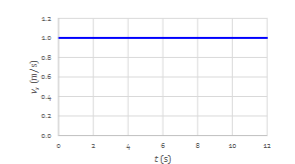
Describe the velocity and acceleration.
Velocity is positive and constant
Acceleration is zero and constant
What are the four equations of motion for constant acceleration?
Vx = V0x + axt
x= x0 + ½ (v0x + vx)t
x= x0 + v0xt + ½ axt²
vx² = v0x² + 2ax(x-x0)
What are the units of instantaneous acceleration?
m/s²
When we say "acceleration," which acceleration do we mean?
Instantaneous acceleration
In a motion diagram, why would the acceleration be labeled in the middle instead of labeled twice?
The acceleration is constant
Why is the velocity labeled twice when it is only labeled once (in the middle) in the uniform linear motion model?
The velocity is changing in the uniformly accelerated linear motion model
How many independent equations of motion do we have for the uniformly accelerated linear motion model?
Independents: 2
How many unknowns should we generally have for the uniformly accelerated linear motion model?
Unknowns: 2
If the two unknowns in a uniformly accelerated linear motion problem are x and vx, what are the two best equations of motion to apply?
vx = v0x + axt
x = x0 + v0xt + ½ axt2