L2 The eye and retina
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
What form of energy is light
electromagnetic energy
2
New cards
What are the two main properties of light?
Wavelength and intensity
3
New cards
Psychological property of wavelength
colour
4
New cards
Psychological property of intensity
brightness
5
New cards
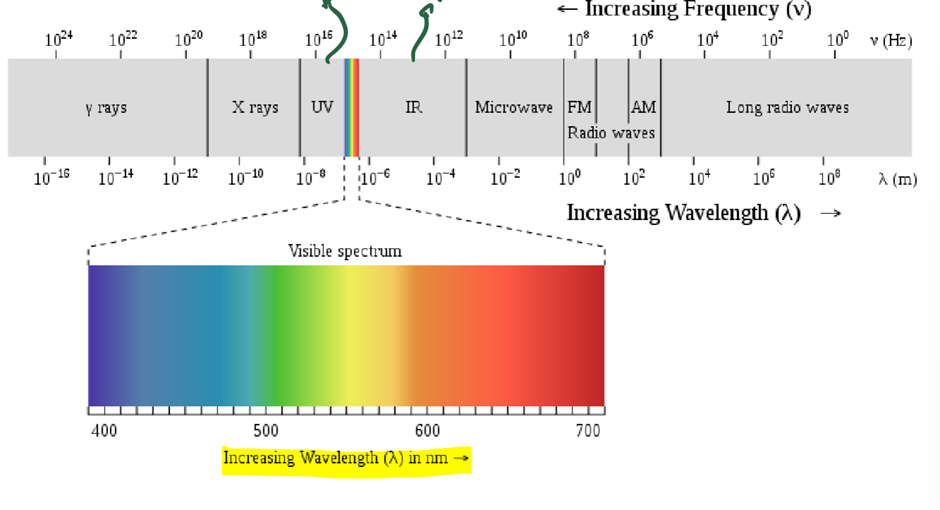
Name this diagram
the electromagnetic spectrum
6
New cards
How does light enter the eye
light is reflected from objects and into the eye
7
New cards
What is the function of the eye in perception?
The eye focuses an image on the retina for perceptual processing.
8
New cards
Where are receptors located in the eye
in the retina
9
New cards
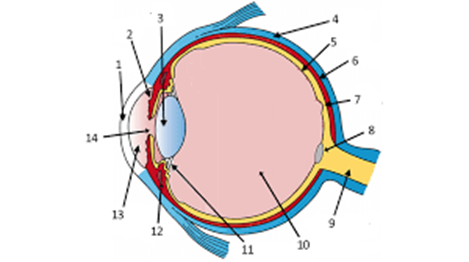
label the pupil and iris
14 and 2
10
New cards
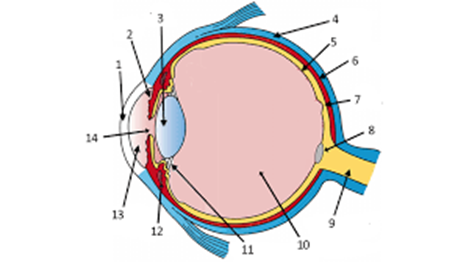
label the cornea and lens
1 and 3
11
New cards
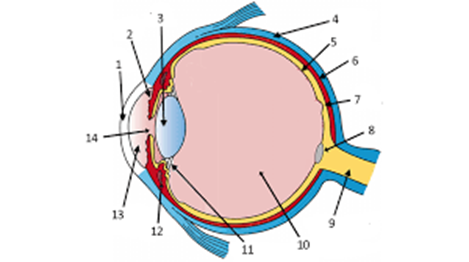
what is label 7
the fovea
12
New cards
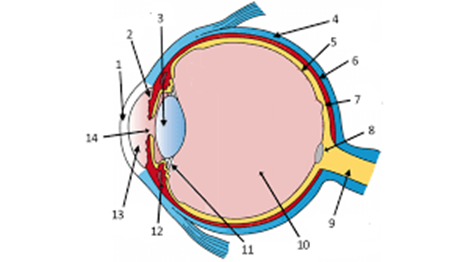
what is label 5
the retina
13
New cards
Role of iris in receiving light
adjustable aperture to limit or extend the amount of light passing through
14
New cards
Diameter range of the pupil
2mm – 9mm
15
New cards
What is the role of the cornea and lens?
to focus light on the retina
16
New cards
% of focusing power provided by the cornea
80%
17
New cards
% of adjusting power provided by the lens
20% (but can change)
18
New cards
Why can the shape of the lens change
due to the action of ciliary muscles
19
New cards
What is accommodation in the eye?
The lens changes shape to focus on near or distant objects.
20
New cards
Explain how lens accommodates for nearer vs further objects
becomes fatter vs becomes thinner
21
New cards
What are refractive errors
when the lens does not operate correctly, do not focus correctly on the retina
22
New cards
What are two common refractive errors?
Myopia and hyperopia
23
New cards
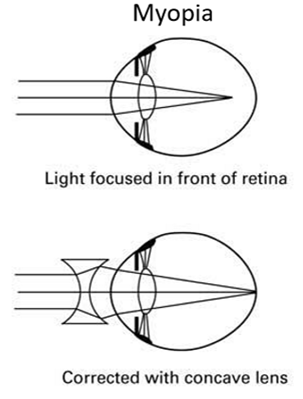
What is myopia
nearsightedness, when near objects are clear but far objects are blurry
24
New cards
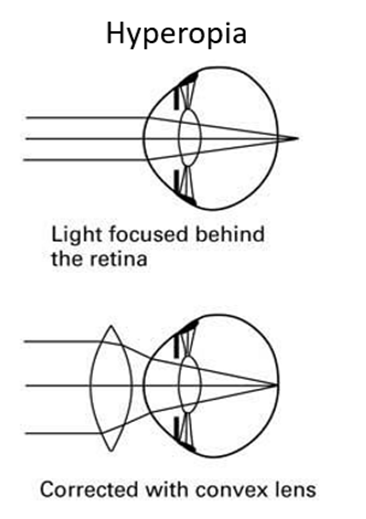
What is hyperopia
farsightedness, when near objects are blurry but far objects are clear
25
New cards
What is the retina?
A light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that contains photoreceptors
26
New cards
What part of the eye is associated with the receptor processes
retina, and rods and cones
27
New cards
Role of photoreceptors
carry out transduction
28
New cards
What are photoreceptors
light sensitive cells
29
New cards
What are the two types of photoreceptors?
Rods and cones
30
New cards
What is transduction?
The process where photoreceptors convert light into electrical impulses
31
New cards
What is the role of visual photopigments in transduction
to react to light and trigger electrical signals
32
New cards
How many rods and cones are there in the human eye?
About 120 million rods and 6 million cones.
33
New cards
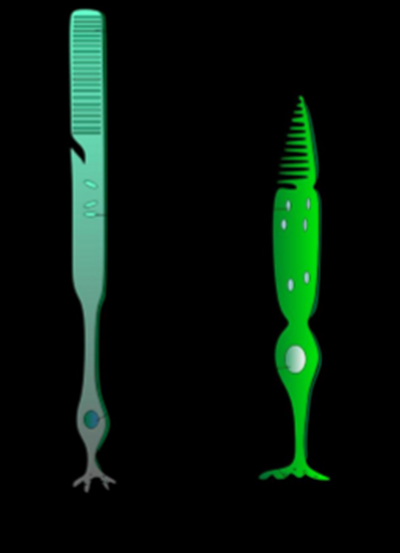
which is rod and cone
1st is rod, 2nd is cone (note different lengths/shapes)
34
New cards
6 ways in which rods and cones differ
number, sensitivity, involvement in colour perception, retinal distribution, acuity and neural convergence
35
New cards
Are rods or cones more sensitive to light (work better in dim lights)
rods
36
New cards
Are rods or cones more useful in daylight
cones
37
New cards
3 ranges of lighting levels
scotopic, photopic and mesopic
38
New cards
Which lighting levels are rods active
scotopic and mesopic
39
New cards
Which lighting levels are cones active
photopic and mesopic
40
New cards
Why do photoreceptors stop responding in bright light
because bright light bleaches photopigments, need to recover / regain sensitivity
41
New cards
What is dark adaptation
increase in eye’s sensitivity in the dark
42
New cards
Where are rods mostly located?
Rods are mostly located in the peripheral retina.
43
New cards
Where are cones mostly located?
Cones are mostly located in the fovea (central retina).
44
New cards
Are rods or cones responsible for colour vision
cones
45
New cards
Why can’t we see colour at night?
Cones, which detect colour, do not function well in low light
46
New cards
What are the three types of cones (and their wavelengths)?
Red (long wavelengths), Green (medium wavelengths), and Blue (short wavelengths).
47
New cards
What colour perception do rods produce
monochromatic vision (black and white)
48
New cards
Which type of wavelengths are rods more sensitive to
medium wavelengths (green light)
49
New cards
Number of types of cones vs rods
3 vs 1
50
New cards
What is the Purkinje shift?
At night, red looks darker than green
51
New cards
Nature of retinal distribution of photoreceptors
not evenly distributed
52
New cards
What is the fovea (location + consists of?)
small central area of the retina that contains only cones
53
New cards
Explain blindspot
area of the retina with no photoreceptors
54
New cards
where does an image of an object fall when looking directly at it
on the fovea
55
New cards
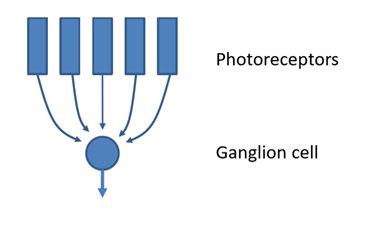
What is neural convergence?
when one neuron receives signals from many other neurons
56
New cards
Which photoreceptors have greater convergence?
Rods have greater convergence than cones
57
New cards
What determines acuity
neural convergence
58
New cards
What is acuity
the ability to detect fine details of a stimulus
59
New cards
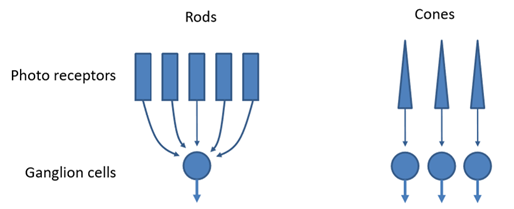
Which photoreceptors have higher acuity
cones
60
New cards
Why does less convergence lead to higher acuity
because it allows for more precise spatial representation of visual info (each individual photoreceptor sends signal to dedicated pathway)
61
New cards
Why is vision sharpest in the fovea?
Each cone in the fovea connects to a single ganglion cell, enhancing detail perception.
62
New cards
Why do we move our eyes to look directly at objects of interest?
To position the image on the fovea for maximum acuity.
63
New cards
What is mesopic vision?
Vision in intermediate light levels when both rods and cones are active.
64
New cards
Why does acuity decrease in low lighting conditions
because rods, which dominate night vision, have low acuity due to high neural convergence