Modern World History Vocab 1.1-1.4
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Last updated 4:54 PM on 9/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
Mesopotamia
A region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers that developed the first urban societies.
2
New cards
Monotheistic
Belief in one God (Greek roots. Mono - one. Theo - God.)
3
New cards
Covenant
a contract or promise
4
New cards
Prophets
Religious teachers God uses to speak to people.
5
New cards
Indus River
a large river surrounded by fertile land in modern India/Pakistan.
6
New cards
Dynasty
A line of rulers from the same family
7
New cards
Mandate of Heaven
a political theory from ancient China that kings had the divine right to rule
8
New cards
Oligarchy
A government ruled by a few powerful people (Oligoi - few. Arkhein - to rule)
9
New cards
Democratic
A government in which the people either have political power indirectly or directly.
10
New cards
The Hellenistic Era
the time period following the death of Alexander during which Greek culture spread through the known world. A Hellenisitic society means to "imitate Greeks"
11
New cards
Socrates
(470-399 BCE) An Athenian philosopher who thought that human beings could lead honest lives and that honor was far more important than wealth, fame, or other superficial attributes. He questioned everything, including authority, leading to him being sentenced to death by drinking hemlock.
12
New cards
Socratic Method
way of teaching developed by Socrates that used a question-and-answer format to force students to use their reason to see things for themselves
13
New cards
Plato
(430-347 BCE) Was a disciple of Socrates whose cornerstone of thought was his theory of Forms, in which there was another world of perfection. He thought an ideal society would be divided into 3 groups: philosopher-kings, warriors, and the common people.
14
New cards
Aristotle
Greek philosopher. A pupil of Plato and the author of works on logic, metaphysics, ethics, natural sciences, politics, and poetics, he profoundly influenced Western thought. He focused on observation and investigation. He observed other governments and concluded that monarchy, aristocracy, and constitutional governments were the best.
15
New cards
Republic
A form of government in which citizens choose their leaders by voting (In Rome, only high-class people were in the government)
16
New cards
Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.
17
New cards
Nero
(54 CE-68 CE) First Roman emperor to persecute Christians
18
New cards
Constantine
Roman Emperor. He issued the Edict of Milan which outlawed the persecution of Christians. The first emperor to become Christian
19
New cards
Theocracy
A state ruled by religious figures
20
New cards
Caliph
Muslim spiritual and civil rulers, Muhammad’s successors.
21
New cards
Mohammad
The founder of Islam (570 CE - 632 CE)
22
New cards
Islam
A monotheistic religion. Name means “peace through submission to the will of Allah.” Originated in the Middle East.
23
New cards
Lineage groups
Groups of people with a common ancestor. Commonly 5-10 generations back. (Africa)
24
New cards
Ghana, Mali
Trade state in West Africa. Their king was Mansa Musa (1317-1337)
25
New cards
Songhai
Trade state in West Africa. It surpassed Mali in the 15 century. It was at the height of its power during the reign of Muhammad Ture. They mostly traded salt and gold. The lasted until the 16th century.
26
New cards
Landed aristocrat
A member of the noble class with the inherent right to own land.
27
New cards
Sultanate
A state or country ruled by a sultan
28
New cards
Mesoameria
Southern North America through Central America. It contains modern day Costa Rice, Honduras, Guatemala, Mexico, etc.
29
New cards
Inca
(c. 1400 - 1533 CE) Southern American civilization along the Andes. Thrived during the 15th century. They had networks of roads throughout their empire. They fell to Spanish invaders due to lack of advanced weapons.
30
New cards
Maya
(abt 2000 BCE - 16th century CE) Mesoamerican civilization. They had pyramids, temples, and palaces. They were a polytheistic civilization and had an advanced writing system of hieroglyphs and invented the concept of 0 in math.
31
New cards
Aztec
An advanced Mesoamerican civilization. They were polytheistic and fell to Spanish invaders in the 16th century. They were known for their warriors, agriculture, land, art, and architecture.
32
New cards
Charlemagne
800 CE. King of Germanic people (Franks). The first Roman Emperor since 476 CE. It was a sign of a new civilization, not a rebirth of an old one.
33
New cards
Feudalism
Medieval social system based on the exchange of land for loyalty and military service. Lords granted fiefs to vassals, who in turn provided military support and other services. Serfs worked the land and owed labor and taxes to lords.
34
New cards
Middle ages
A time period that was a transition from the ancient to modern worlds.
35
New cards
Common Law
Laws that applied to the whole kingdom
36
New cards
Magna Carta
An English legal document signed in 1215 that limited the power of the monarchy and protected the rights of the nobility. It established the principle that even the king is subject to the law. Considered a foundation for constitutional rights and influenced later legal systems.
37
New cards
Parliament
A representative body of advisors to a king or other leader.
38
New cards
Renaissance
(1350-1550) A period based on the rebirth of Roman & Greek culture. Began in Italy. Encouraged a high regard for the individual.
39
New cards
Protestant Reformation
the “religious renaissance.” It started when people started questioning (protesting) Catholicism and the Catholic Church. Martin Luther had a big impact on it.
40
New cards
Martin Luther
A monk who stood up against the Catholic Church (1530). His ideas started the Protestant Reformation.
41
New cards
Gunpowder empires
Empire whose success was mostly based on the mastery of firearms. They tended to have autocratic governments where the leader has absolute control and a large bureaucracy to help them. They had large growth in military and financial control over spice routes.
42
New cards
Ottoman Empire
(Gunpowder empire) Late 13th century. Made up of Turks. Lead by Osman and centered on the Anatolian Peninsula.
43
New cards
Sultan
Head of the Ottoman system. They are the supreme power in political and military matters. This system isolated the them from their people.
44
New cards
Safavid Persia
(Gunpowder empire). Founded by Shah Esma’il in 1501. They seized a lot of Iran & Iraq. The held power over that region until 1629 when the fell into anarchy.
45
New cards
Mongul India
(Gunpowder empire). 1500. They weren’t native to India and descended from the Mongols. They brought unity to Hindu and Muslim kingdoms. They had smaller, but more advanced armies, letting them capture Dehli. During their reign, there was peace, political stability, and more trade and manufacturing. They eventually got to large, and many wars improvished the people, leading to the empire declining.
46
New cards
Shah
“King” of Persian state
47
New cards
Anarchy
When a state has no ruler and/or is in disorder.
48
New cards
Qing China
(Gunpowder empire). It started with a peasant revolt (led by Li Zicheng) against the Ming dynasty. The Manchus conquered Beijing + Li Zicheng’s armies and created a new dynasty: the Qing dynasty. Qing means “pure.” They lost power in the 18th century due to corruption and unrest.
49
New cards
Absolute monarchy
A form of government in which the ruler has absolute power and is not subject to the law.
50
New cards
Divine right of kings
The belief that a king’s right to rule is given to them by God, and not their people.
51
New cards
Aristocrat
A person given privileges and/or status based on inherited lands, titles, or wealth.
52
New cards
Subsistence farmer
A person who works the land for just enough to feel their families.
53
New cards
Serfdom
Laws which tired peasants to the land they worked
54
New cards
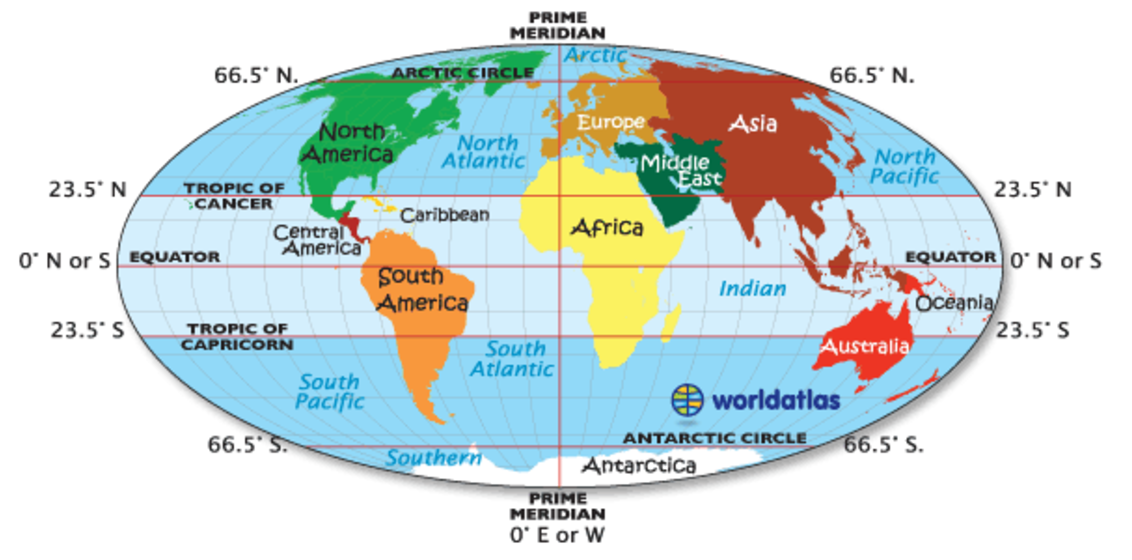
7 Continents, 5 oceans, prime meridian, equator
Things for map of world