Brain and Behaviour (8): Pain
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Pain
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage.
Why is pain important?
It promotes avoidance of situations that may decrease biological fitness and encourages resting behavior that enhances recovery following injury.
Nociceptors
Specialised neurons that detect painful stimuli and send signals to the spinal cord and brain.
What fibres are involved in pain?
Aδ fibres (first initial fast pain):
lightly myelinated
medium diameter
C fibres (second pain - dull ache) :
unmyelinated
small diameter
A⍺ and Aβ fibres (normal Proprioceptors for motor control):
myelinated
large diameter
Process of Pain
Pain detected → Activation of receptors and nociceptors
Spinal Reflex → removing body part from pain
Signals in the brain → conscious of sharp pain in area
Paths to other brain areas → slower throbbing pain
Distraction away from pain
What are the 2 pathways of pain into the brain?
To Somatosensory Cortex (via thalamus): encodes sensory experience
To emotional cortex (via thalamus): encodes emotional experience
“Inflammatory Soup”
A combination of immune mediators that sensitise nociceptors
What is Peripheral Sensitisation?
Where nociceptors become more responsive due to inflammation and damage.
What is Central Sensitisation?
Where nociceptors become more responsive due to repeated stimulation (pain), leading to “wind-up pain.”
Why is increased pain sensitivity beneficial?
Reminds you that you have hurt yourself
Protects injured area from further damage
What are hyperalgesia and allodynia?
Hyperalgesia: increased response to painful stimuli
Allodynia: pain from non-painful stimuli
What treatments are used on burn patients?
Changing dressings, physiotherapy (painful)
Opioid treatments (but issues with dosing/tolerance)
Virtual reality environment (e.g. “snow world”) → reduces:
Activity in pain processing brain areas (e.g. somatosensory cortex) & pain by 30-50%
What is the Gate Control Theory of Pain?
A theory suggesting that a 'gate' in the spinal cord can modulate or block pain signals from reaching the brain; Pain signals can be inhibited by activating non-painful sensory input (e.g. rubbing the skin).
What is Stress-Induced Analgesia?
Pain reduction triggered by stress, involving the endogenous opioid system.
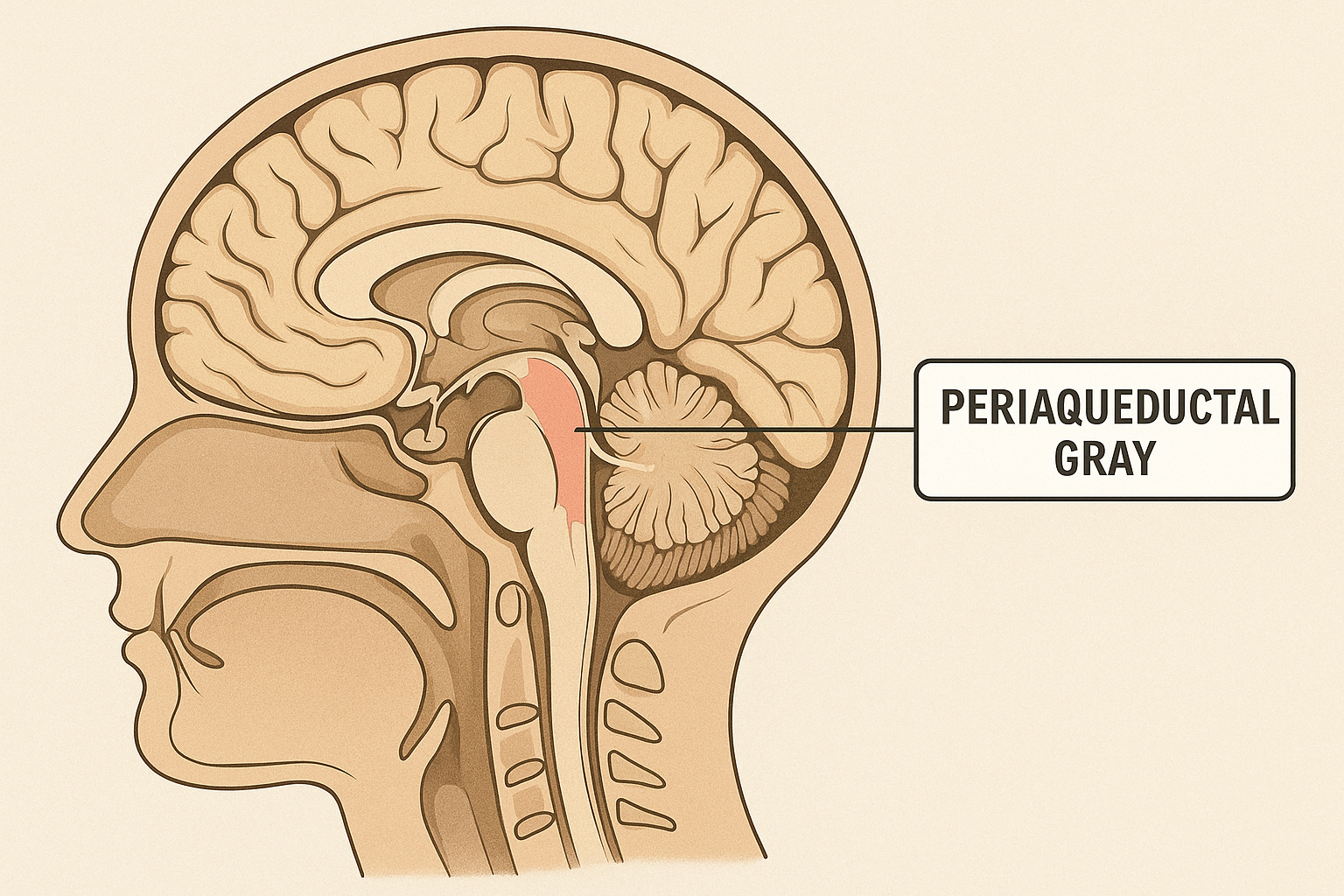
What brain areas are involved in (descending) Pain inhibition?
Periaqueductal gray (PAG)
Rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM)
Dorsal horn
What are some common analgesic drugs and their effects?
NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen): Inhibit prostaglandin synthesis → less nerve sensitivity
Opioids (e.g., morphine): Activate opioid receptors in brain and spinal cord → blocking pain signals from being sent to brain.
Lidocaine: Sodium channel blocker → stops nerves firing → blocking pain signals from being sent to brain.
Capsaicin: "exhausts" the pain system by desensitising TRP channels and depletes Substance P
What is the role of Cannabinoids in Pain Relief?
Endocannabinoids act at CB1 receptors in PAG to reduce pain.
What differentiates chronic pain from acute pain?
Chronic pain lasts >12 weeks, often associated with underlying nerve or central changes.
What are causes of neurogenic (neuropathic) pain?
Nerve damage
Lack of inhibition
Abnormal sprouting (e.g., phantom limb pain, shingles)
How is chronic pain managed?
Multimodal approach including:
Antidepressants
Anticonvulsants
NMDA antagonists
Therapy for comorbidities.
What factors influence individual pain perception?
Biological (genetics, sex hormones)
Psychological
Cultural
Situational factors
How do sex differences affect pain?
Women report more frequent and intense pain → may need different treatments.
What are Mc1r gene implications for pain sensitivity?
Women with the redhead-associated Mc1r-2 allele show increased analgesia (pain reduction) to kappa-opioids (pain killers)