Electrical activity in the heart
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What does the cardiac muscle control?
Regular beating of the heart
What does myogenic mean?
It can contract and relax without receiving signals from the neurons.
What is the cardiac muscle?
Myogenic
What does the electrical activity in the heart create?
The pattern of contractions which coordinates the regular heartbeat
Where does the process start?
Sino-atrial node (SAN)
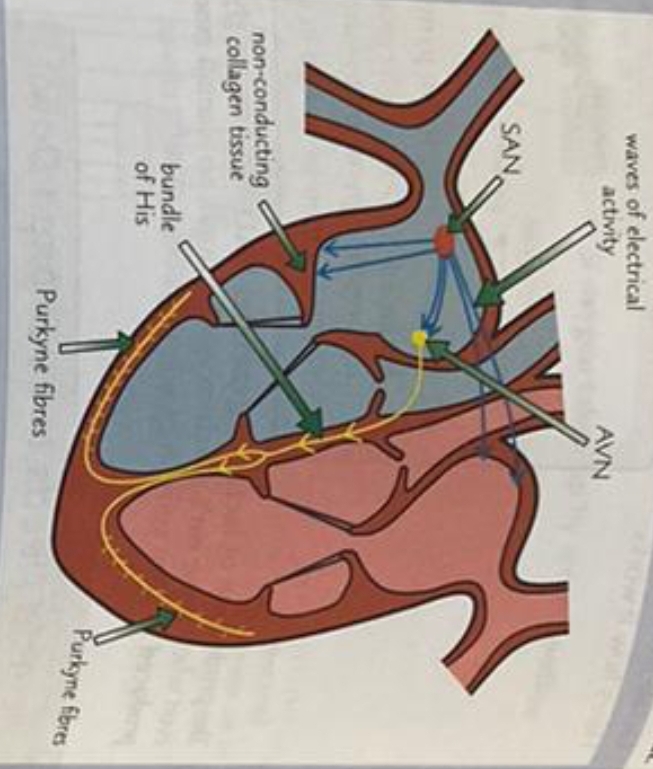
Where is it found?
In the wall of the right atrium
What is SAN like?
A pacemaker
What does SAN do?
It sets the rhythm of the heart beat by sending out regular waves of electrical activity to the atrial walls
What does that cause?
The right and left atria to contract at the same time
What does the band of non-conducting collagen tissue prevent ?
The waves of electrical activity from being passed directly from the atria to the ventricles
What does it do instead?
The waves of electrical activity are transferred from the SAN to the atrioventricular node (AVN)
What is the AVN responsible for?
Passing the waves of electrical activity on to the Bundle of His
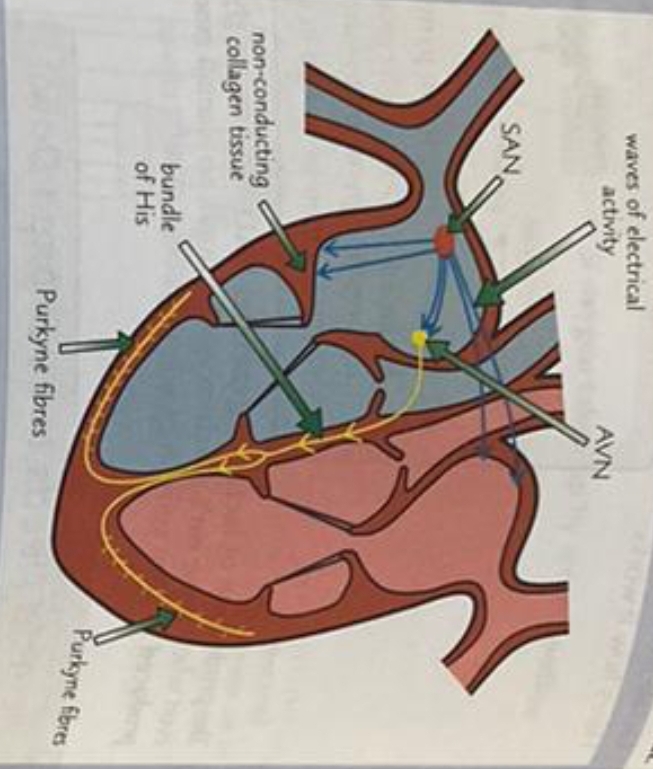
What is the Bundle of His?
A group of muscle fibres
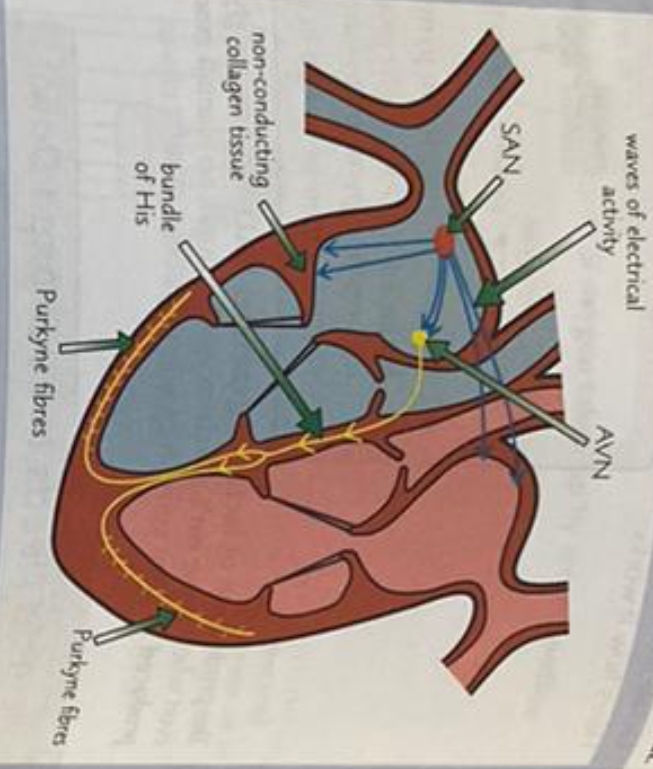
What is it responsible for?
responsible for conducting the waves of electrical activity to the finer muscle fibres in the right and left ventricle walls.
What is the name for the finer muscle fibres in the right and left ventricle walls?
Purkyne fibres
What happens after passing the waves of electrical activity on to the Bundle of His?
There is a slight delay before the AVN reacts, to make sure the ventricles contract after the atria have emptied
What do the Purkyne fibres carry?
Carry the waves of electrical activity into the muscular walls of the right and left ventricle
What does it cause?
Causes them to contract simultaneously, from the bottom up
What does an electrocardiograph record?
A machine that records the electrical activity of the heart
What is an electrocardiograph used for?
To check someone’s heart function
How does this happen?
The heart depolarises (loses electrical charge) when it contracts, and repolarises (regain charge) when it change using electrodes placed on the chest
What is the trace produced by the electrocardiograph called?
Electrocardiogram or ECG
What is the P wave caused by?
Contraction (depolarisation) of the atria
What is the QRS complex?
The main peak of the heartbeat, together with the dips at either side
What is the T wave due to?
Relaxation (repolarisation) of the ventricles
What does the height of the wave indicate?
How much electrical charge is passing through the heart
A bigger wave means?
More electrical charge, so (for the P and R waves) a bigger wave means a stronger contraction
What do doctors use ECGs for?
Diagnose heart problems
How do they use an ECG to detect heart problems?
They compare their patients ECGs with a normal trace
How does that help?
Helps them diagnose any problems with their heart rhythm
What does that indicate?
Indicates cardiovascular disease (heart or circulatory disease) other heart conditions (muscle damage or the AVN not conducting properly)
Tachycardia?
Heartbeat too fast
Bradycardia?
Heartbeat too slow
Fibrillation?
Irregular heartbeat