Biology A level OCR A; biodiversity
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
What is biodiversity?
Measure of variation between organisms in one or multiple species, usually worldwide but can include within an area
What is a habitat?
Where an organism or organisms lives
What is a species?
A group of organisms that can freely interbreed to produce fertile offspring
What is biodiversity about?
Structural and functional variety and stability in the world
What are the three levels of biodiversity?
- Habitat biodiversity
- Species biodiversity
- Genetic biodiversity
What is habitat biodiversity?
Variation of different habitats in a specific area, with species biodiversity relating to this
What is species biodiversity based on?
Range of different species found in their share habitat
How can the range of organisms found in a habitat presenting species biodiversity be measured?
- Species evenness
- Species richness
What is genetic biodiversity?
Variation of genes between individuals belonging to the same species. Creates breeds in a species
How should you measure the biodiversity of a habitat?
1. Observe all the species present
2. Identify all types of species
3. Count the individuals of each species
Due to impracticality, how should you alternatively measure the biodiversity of a species instead of counting each individual?
Sample the habitat.
How can you use a sample of a habitat to measure the number in the whole habitat?
1) Select a small portion, study carefully
2) Multiply up the number of individuals of each species found
3) This is now your estimate
What are types of sampling?
1. Random
2. Non-random
What are different types of non-random sampling?
1) Opportunistic
2) Stratified
3) Systematic
How do you perform random sampling?
Randomly select sites inside the habitat based on randomly generated numbers as coordinates
How do you perform non-random opportunistic sampling?
1. Use prior knowledge or knowledge during the process of collecting data
Deliberate sampling of an area
How do you perform non-random stratified sampling?
Divide a habitat into areas which appear different, sampling them each differently
How do you perform systematic sampling?
1. Take samples at fixed intervals across a habitat
2. This can be done through line transects and belt transects
What are the advantages of random sampling?
Data is not biased by selective sampling
What are the disadvantages of random sampling?
- May not cover all areas of habitat(s) equally
- Species with a low presence could be missed; improper measurement of biodiversity
What are the advantages of non random opportunistic sampling?
Easier and quicker than random sampling
What are the disadvantages of non random opportunistic sampling?
- Data may be biased
- Overestimate of species importance based on their looks; improper measurement of biodiversity
What are the advantages of stratified sampling?
- Ensures that all different areas of a habitat are sampled
- Species are not under represented
What are the disadvantages of stratified sampling?
Possibility of over-representation of some areas in the sample
What is the advantage of systematic sampling?
This sample will represent if a habitat shows a clear gradient in some environment factor
What is the disadvantage of systematic sampling?
Only species on the line or within a belt can be recorded
What precautions and preparation should be done before sampling a habitat?
- Suitable clothing
- Suitable footwear
- Apparatus to carry out sampling
- Clipboard, pen and paper
- Appropriate keys to identify plants
- Camera or smartphone to record specimens and grid locations
What may be a best approach to sampling techniques?
Combining sampling techniques
What should you avoid when sampling in an environment?
Disturbance
What are the methods for sampling plants? (Includes the equipment being used)
1. Random quadrants
2. Transect
What must you identify inside a quadrant?
Percentage cover of the species of plants; abundance
What can make quadrants more accurate?
Grids of squared numbers;
- 9
- 25
- 64
- 100
How can you measure the percentage cover?
Use a point frame at regular intervals across a quadrant
How do you use a transect? (Organisms touching)
1. Mark out a line in the area you want to study with a tape measure
2. Collect data along the line
3. Count the organisms that touch the line
What are the two types of belt transects?
1. Interrupted belt transect
2. Continuous belt transect
How does interrupted belt transect work?
Quadrants placed at intervals along the belt
This is a form of a combined technique for quantitative data
How does a continuous belt transect work?
Quadrants are placed beside the line, moved along the line to study each band in detail. More time and detail than interrupted belt transect
What does a belt transect actually allow to measure?
The calculation of density
Why is obtaining quantitative data of animals difficult?
Large animals will hide away at the presence of humans
Small animals will run away too quickly to count and/or hide
How can certain animals be identified if they cannot be seen?
Signs they have left behind i.e. footprints
How can you catch invertebrates?
- Sweep netting
- White sheet under a branch + Knock the branch
- Pitfall trap
- Tullgren funnel
- Light trap
How can you catch invertebrates with a sweep net?
1) walk through the habitat with a stout net
2) Sweep the net through vegetation in wide arcs
3) Empty contents on a white sheet
4) Additional pooter can be used to collect the animals
Can all methods be used to measure both species richness and species evenness?
Yes, all methods, including;
- Frame quadrant
- Pooter
- Point quadrant
- Sweep net
Can be used to measure species evenness and species richnes
How do you use a pitfall trap?
1) Dig a hole in the soil below the soil surface level
2) Place a container in the hole
3) Animals will fall in the container
4) Shelter the trap to cover from rain
How does a light trap attract flying insects? What happens after they come close into contact?
- Consists of ultraviolet light that attracts the insects
- Flying insects eventually fall into alcohol placed below
What form of legality might you need to trap an animal?
A licence
What must be made sure if you are capturing the animal?
You do not harm the animal in any way
How can most small animals be captured?
Longworth trap (humane trap)
How can the Longworth trap be applied for good quality data?
Mark-and-recapture technique
How do you perform a mark-and-recapture technique?
1) Capture a sample of animals
2) Mark each individual in some way that causes it no harm or disadvantage. Call it C1
3) Release all marked animals
4) Capture a sample of animals again. Number of captured animals again will be C2.
5) Any animals captured that have been recaptured with a marker are now C3
What is the total population formula for mark-and-recapture technique?
Total population = (C1 * C2)/C3
What can manipulate the results of the mark-and-recapture method?
1. Animals that learn the trap is harmless or contains food
2. Animals that became trapped the first time do not like the experience and stay away from the trap
Flip if you like jurassic park
CLEVER GIRL

What qualities and legality do you need to perform a tag on animals with rings?
- Skill
- Experience
- A permit
What is an allele?
Different versions of a gene in the same gene loci
What is the gene locus?
Position/location of a gene on a chromosome
What is polymorphic gene locus?
Locus with more than two alleles
What is Simpsons index of diversity?
A measure of habitat biodiversity
What is species evenness?
A measure of how evenly represented the species are in a habitat/area
What is species richness?
A measure of how many different species are present in the habitat/area
What is the species evenness of a habitat which there are an even number of individuals in each species?
High species evenness
What is a high species evenness likely to have?
A high species richness
How can you measure species richness?
Count all the species present in the habitat
How do you calculate species evenness?
1. Carry out a quantitative survey
2. Observe and calculate species evenness
When carrying out a survey/sample, what are some conditions that must be controlled?
- If across a number of years; same time of year/time of day
- Same size of sample area/length of transect
- Same sampling technique used
- Exactly the same place that samples are taken in each habitat
How do you measure the number of tiny animals living in the soil?
1. Take a sample of the soil and sift though it to find all individuals
2. Count all the individuals
How do you measure tiny animals in water?
1. Use a net to sample in the body of water and sift through the mud
2. Estimate population size and density though counting
How to calculate Simpson index of diversity?
First find;
- Number of individuals of a certain species
- Number of total individuals of all species combined
What does a high value of Simpsons index of diversity indicate?
- High species biodiversity; good species evenness and species richness
- Therefore a stable habitat/ecosystem
What happens if you change a small factor of the habitat in a high Simpsons index of diversity?
Effect on the whole habitat is small
What does a small value of Simpsons index of diversity suggest?
- Low species evenness and low species richness
- Habitat is dominated by one or a few specific species
- Ecosystem is not very stable
What happens if you change a small factor of the habitat in a small Simpsons index of diversity
Affects the whole habitat.
How can genetic diversity be assessed?
- Look at the observable features
- Variation of appearance represents more genetic differences between gametes
What is a measure of genetic diversity?
Having more than one allele for a particular locus in a species.
How can you calculate genetic diversity?
- Calculate the number of loci in one individual that are heterozygous
OR
- Calculate percentage of loci in the population with more than one allele for the same trait and compare
What does polymorphic gene loci increase?
Gives a higher probability for a higher genetic biodiversity
What are loci with more than two alleles known as?
Polymorphic gene loci
What is the equation for Simpsons index of diversity?
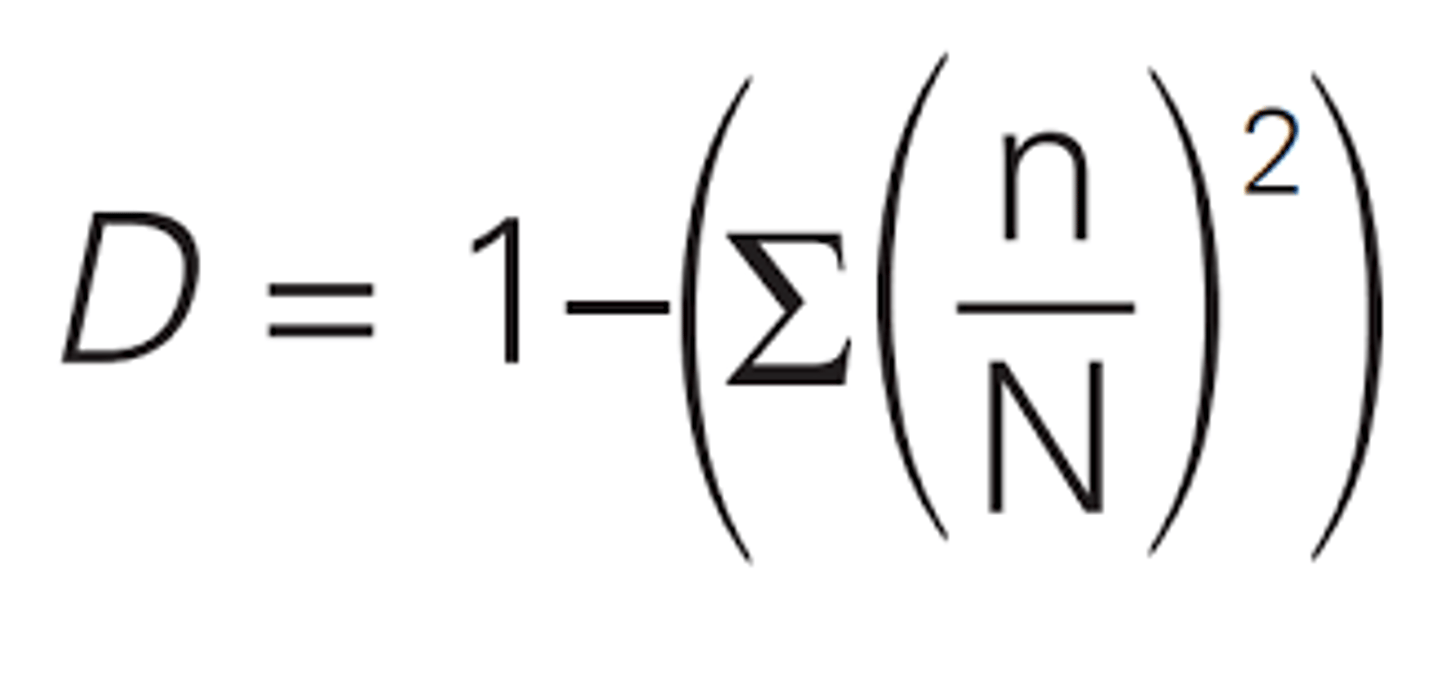
What is climate change?
Significant, long lasting changes in weather patterns
What is monoculture?
A crop consisting of one strain of one species
Why is genetic diversity declining?
As a result of human activities
As humans what have we begun doing as part of our activities?
- Learned to use the environment to our advantage
- Alter ecosystems to provide ourselves with food
- We destroy and fragment habitats
- We are using more and more of the earths resources
- We pollute the atmosphere
What occurs as we clear natural vegetation for agricultural purposes?
We reduce the size of habitats and the population size of any species living in those habitats
What does it mean if the population size of a wild species decreases?
Genetic diversity becomes reduced
Why is genetic diversity important in species'?
As it means species has a greater capacity to adapt to changing conditions through evolution, preventing extinction
What two specific human activities increases the efficiency of modern agriculture and are against genetic diversity?
- Monoculture
- Selective breeding
Why is monoculture very limited in genetic diversity?
It consist on only one species
Why is monoculture only consisting of one species?
As it makes product easier to harvest
How does selective breeding affect genetic diversity?
- Farmers select traits that allow efficient profit
- Concentrating on specific characteristics means other characteristics have been ignored
- Genetic diversity of the species declines
What is genetic erosion?
It is the irreversible loss of genetic diversity though monoculture and selective breeding
What steps will climate change cause less genetically diverse species to do?
1. Less genetically diverse species to only follow habitats with which they are most suited
2. Species move to poles in slow migration
What obstructions could block migration of less genetically diverse species?
- Major human developments
- Agricultural land
- Large bodies of water
- Mountain ranges
Who is particularly at risk of specific migration due to changes in climate change?
Domesticated;
- Plants
- Animals
What will happen with non-genetically diverse crops if significant climate change occurs or a sudden disease
1. Vulnerability to disease and climate change will cause death of many crops
2. Efficiency of agriculture will decline and less food will become available
3. Farmers will need to change the crops they grow and variety of animals they keep
What is extinction?
Last living member of a species dies and the species ceases to exist
What is certain about extinction?
- Over 800 recorded extinctions since 1500
- 20% of species could be gone by 2030
- One third of primate species could be extinct
- Half of the species alive today could be extinct by 2100
Why is our great mass extinction event different to other mass extinction events?
Extinction is caused by human activity rather than natural climate change or natural disaster
What is a keystone species?
A species that has absolute significance to its environment despite a low abundance
What is soil depletion?
Loss of soil fertility
What causes low soil fertility?
Removal of mineral ions due to continuous cropping