AP HUG Unit 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
1
New cards
Density
the frequency with which something occurs in a space → involves the numbers of a feature and the land area.
2
New cards
Sustainability
systems that provide people with what they want and need without impacting the future generations ability to get what they want and need.
3
New cards
Distribution
the arrangement of a feature in space.
4
New cards
Remote sensing
process of collecting information about the Earths surface from satellites orbiting the Earth-- data used in GIS.
5
New cards
Concentration
extent of a feature spread over space.
6
New cards
Spatial Perspective
Analyzing where things are located and why they are located there.
7
New cards
Possibilism
the environment has an impact on society but people have the ability to adjust the physical environment and set their own path in life.
8
New cards
Flow
________: the movement of people, ideas, goods, services → certain places may be located to increase /decrease ________.
9
New cards
Toponym
________: name given to a place on Earth.
10
New cards
Location
________: position that something occupies.
11
New cards
Environmental Determinism
________: Idea that the environment is the driver of societal development.
12
New cards
Field observations
________: geographer gives firsthand accounts (accurate and detailed but sometimes not possible to gather data)
13
New cards
Relative distance
________: qualitative (time, money, cardinal directions)
14
New cards
Photo analysis
________: use photos to understand type of culture, demographics, population density, and whats happening in a place.
15
New cards
Qualitative Data
________: Observations, interviews, and individual thoughts → up for discussion, will often change, hard to replicate.
16
New cards
Topographic
shows contour lines of elevation to show physical things on Earths surface (printed in 3D)
17
New cards
Isoline
information is connected through points of equal or very similar values (uses lines or color coding)
18
New cards
Dot Density
points show precise locations of data → more precise than choropleth
19
New cards
Graduated Symbol
shows percentage of amount of something and (imprecise) location using different sizes of the same symbol →
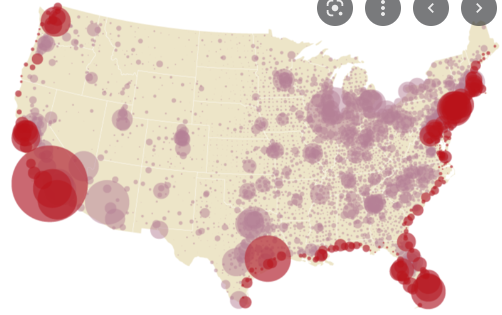
20
New cards
Cartogram
data is shown dynamically → the greater the value for country, the larger the area it is represented with on the map
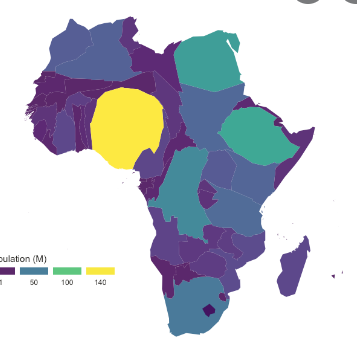
21
New cards
Flow Line
shows movement of goods, people, or ideas (must look at colors, items transported, and size) larger/thicker arrows to show higher volume of trade
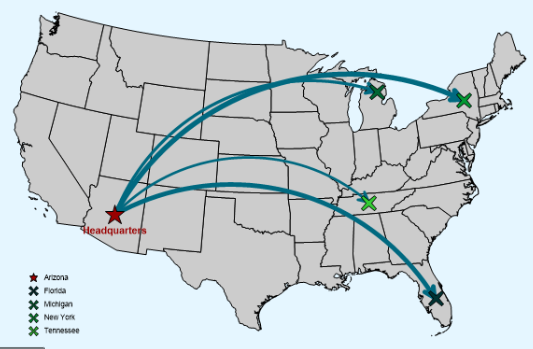
22
New cards
Thematic map
focus on a specific theme → chloroplast, flow line, cartogram, graduated symbol
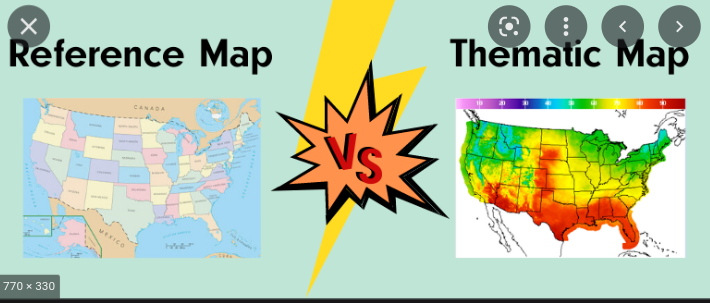
23
New cards
Reference map
to better understand what happens on earths surface → geographic area
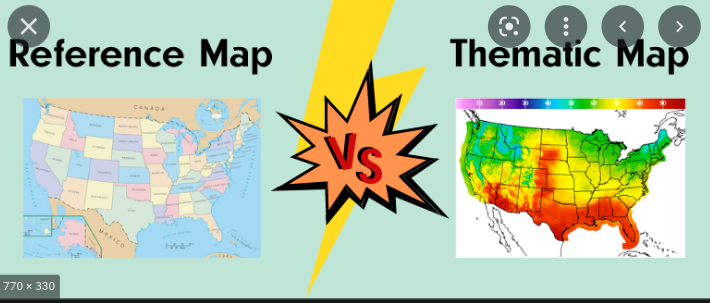
24
New cards
Absolute distance
quantitative (km, miles)
25
New cards
Relative distance
qualitative (time, money, cardinal directions)
26
New cards
Interrupted Map
pieces of the map are removed to try & remove distortion → not good for navigation or direction
27
New cards
Uninterrupted Map
no removed pieces or "break points" but maps have more distortion
28
New cards
Geographic Information System
computer system that layers maps by collecting, analyzing, and then displaying data
29
New cards
example uses
helps farmers know which parts of their field need what, gps
30
New cards
Field observations
geographer gives firsthand accounts (accurate and detailed but sometimes not possible to gather data)
31
New cards
Landscape analysis
studying wildlife, vegetation, or geography to see how a place has been impacted by people
32
New cards
Photo analysis
use photos to understand type of culture, demographics, population density, and whats happening in a place
33
New cards
Ways to collect data without being at the place
- media reports, travel narratives, government documents, personal interviews
34
New cards
Qualitative Data
Observations, interviews, and individual thoughts → up for discussion, will often change, hard to replicate
35
New cards
Quantitative Data
Information counted/measured → usually in number form, not up for debat
36
New cards
Individual
Look for employment opportunities, local schools, crime rates, public services, cost of living, etc
37
New cards
Waldo Tobler's first law of geography
while all things on Earth are related to all other things, the closer things are to one another, the more they are related
38
New cards
Distance Decay
Effect of distance on interactions → the farther away one thing is from the other, the less interaction the two will have
39
New cards
Space
physical distance between two places on Earth's surface
40
New cards
Distribution
the arrangement of a feature in space
41
New cards
Density
the frequency with which something occurs in a space → involves the numbers of a feature and the land area
42
New cards
Concentration
extent of a feature spread over space
43
New cards
Clustered
closely spaced together
44
New cards
Dispersed
relatively far apart
45
New cards
Place
specific point on Earth distinguished by particular characteristics
46
New cards
Location
position that something occupies
47
New cards
Toponym
name given to a place on Earth
48
New cards
"Sense of place"
individual's perception of a place
49
New cards
**Spatial Perspective
**Analyzing where things are located and why they are located there
50
New cards
Flow
the movement of people, ideas, goods, services → certain places may be located to increase/decrease flow
51
New cards
**Absolute Location
**GPS coordinates of the position of something on a map
52
New cards
**Relative Location
**position of a place in relation to other places or features (n, s, e, w) or (in between rivers or by an ocean, etc.)
53
New cards
Sustainability
systems that provide people with what they want and need without impacting the future generations ability to get what they want and need
54
New cards
Scale
the ratio of a distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground
55
New cards
Mercator Projection
Advantages: Shows true direction, Good for navigation purposes
Limitations: Massively distorts area, Size is distorted increasingly near the poles (greenland = africa in size) → creates bias against less-developed world
Limitations: Massively distorts area, Size is distorted increasingly near the poles (greenland = africa in size) → creates bias against less-developed world
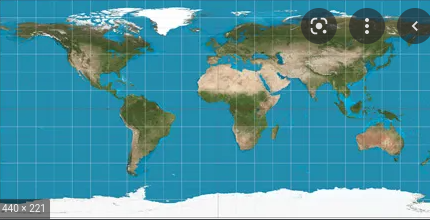
56
New cards
Gall - Peters
Advantages: Shows true direction, Area is relatively precise
Limitations: Distorts shape, Continents appear elongated
Limitations: Distorts shape, Continents appear elongated
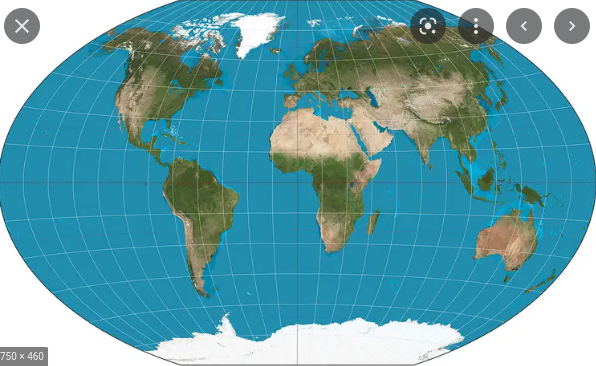
57
New cards
Robinson
Advantages: Globe-like appearance that looks ‘real’, Distorts size and shape, but not too much
Limitations: Imprecise measurements, Extreme distortion at the poles: flat at poles and compressed at equator
Limitations: Imprecise measurements, Extreme distortion at the poles: flat at poles and compressed at equator
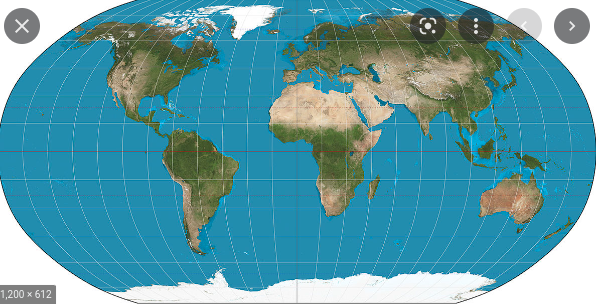
58
New cards
Azimuthal
Advantages: Preserves direction, When used from the point of the North Pole. no country is seen as the center
Limitations: Distorts shape and area, Only shows one half of area
Limitations: Distorts shape and area, Only shows one half of area
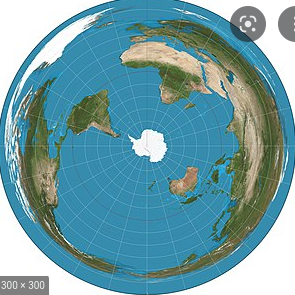
59
New cards
Goode - Homolsine
Advantages: Minimizes distortion in size and keeps land masses uninterrupted
Limitations: Doesn’t present info easily to the reader, Can’t be used for navigation in ocean
Limitations: Doesn’t present info easily to the reader, Can’t be used for navigation in ocean
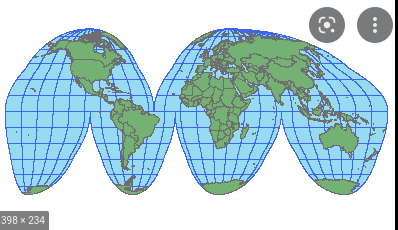
60
New cards
Fuller
Advantages: Good at keeping size and shape and not interrupting land masses
Limitations: Hard to interpret -- doesn’t use cardinal directions
Limitations: Hard to interpret -- doesn’t use cardinal directions

61
New cards
Winkel Tripel
Advantages: Shows minimum distortion in reference to land, distance, and direction
Limitations: Very distorted at poles, Lines of longitude and latitude are curved
Limitations: Very distorted at poles, Lines of longitude and latitude are curved
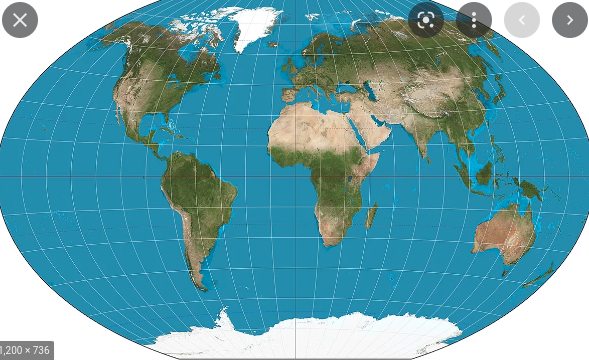
62
New cards
Region:
Geographic area with common characteristics and patterns → can be global, regional, or national
63
New cards
Formal (Uniform) Regions:
geographic area with common attributes, traditionally defined by economic, social, political, or environmental characteristics.
Examples: European Union (formal political region), Rocky Mountains (physical formal),
Examples: European Union (formal political region), Rocky Mountains (physical formal),
64
New cards
Functional (Nodal) Region:
Geographic area organized around a node, or center point → often around economic activity, travel, or communication
Examples: power plant (can only serve so many people), metro systems, airports, local pizza place delivery zones
Examples: power plant (can only serve so many people), metro systems, airports, local pizza place delivery zones
65
New cards
Perceptual Region:
geographic area that has no perfect definition → only exists because of people’s feelings, beliefs, or attitudes of the region. Differ from person to person because these exist in our minds
Examples: different ideas of what makes up the middle east,
Examples: different ideas of what makes up the middle east,
66
New cards
space time compression
opposite of distance decay. the set of processes that cause the relative distances between places (i.e., as measured in terms of travel time or cost) to contract, effectively making such places grow “closer" because of technological advancements.
67
New cards
How do Local governments use geographic data
use data to dictate land zones, where to build schools, etc.
68
New cards
How do Regional governments use geographic data
voting districts, which projects get state funding, allocate funding for infrastructure
69
New cards
How do National governments use geographic data
which laws should be passed, determine where federal funding should go, how to change tax policies
70
New cards
How do Local-scale businesses use geographic data
See where to build store-front, look at where people are living, medium income
71
New cards
How do Regional-scale businesses use geographic data
See which locations are outperforming others
72
New cards
How do National-scale businesses use geographic data
Countries tax rates, employment/labor laws, etc.
73
New cards
How do Individuals use geographic data
Look for employment opportunities, local schools, crime rates, public services, cost of living, etc.
74
New cards
chloropleth
uses colors to represent spatial data (referring to certain theme)