Pulmonary Exam 2: Acid Base Balance (Dr. Baleja)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
any chemical substance that can donate a hydrogen ion is called a __________
acid

any chemical substance that can accept a hydrogen ion is called a __________
base (alkali)

pH =
- log [H+]
![<p>- log [H+]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/082d4092-5bff-435d-baa8-a0c4620ce560.jpg)
A pH shift of 1 unit corresponds to a ___-fold shift in [H+]
10

Why is pH balance important?
A shift in pH can change biologically important compound's electrical charge which, in turn, can alter their conformation and consequently their biological activity
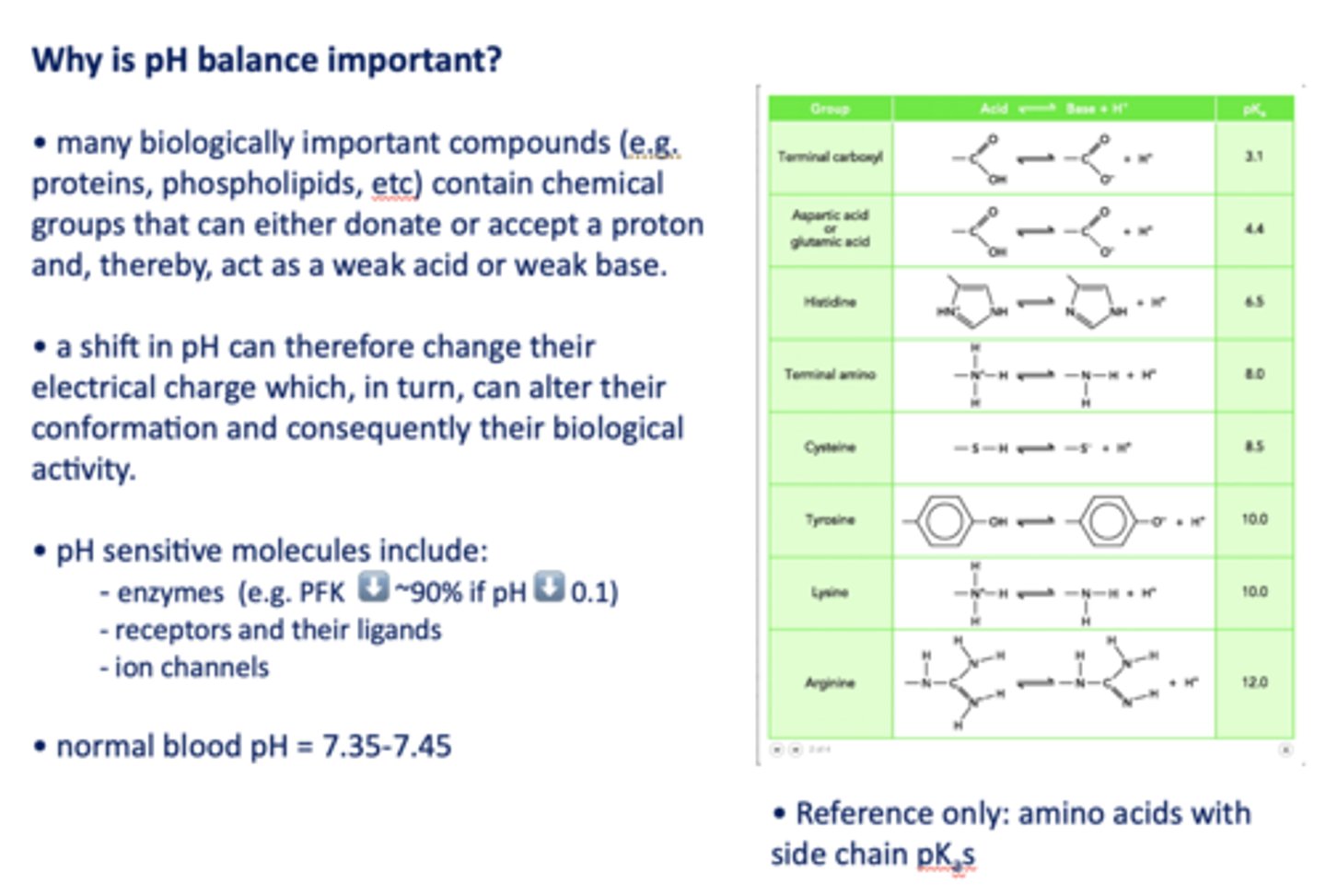
pH sensitive molecules include what three things?
- Enzymes (e.g. PFK ⬇️ ~90% if pH ⬇️ 0.1)
- Receptors and their ligands
- Ion channels
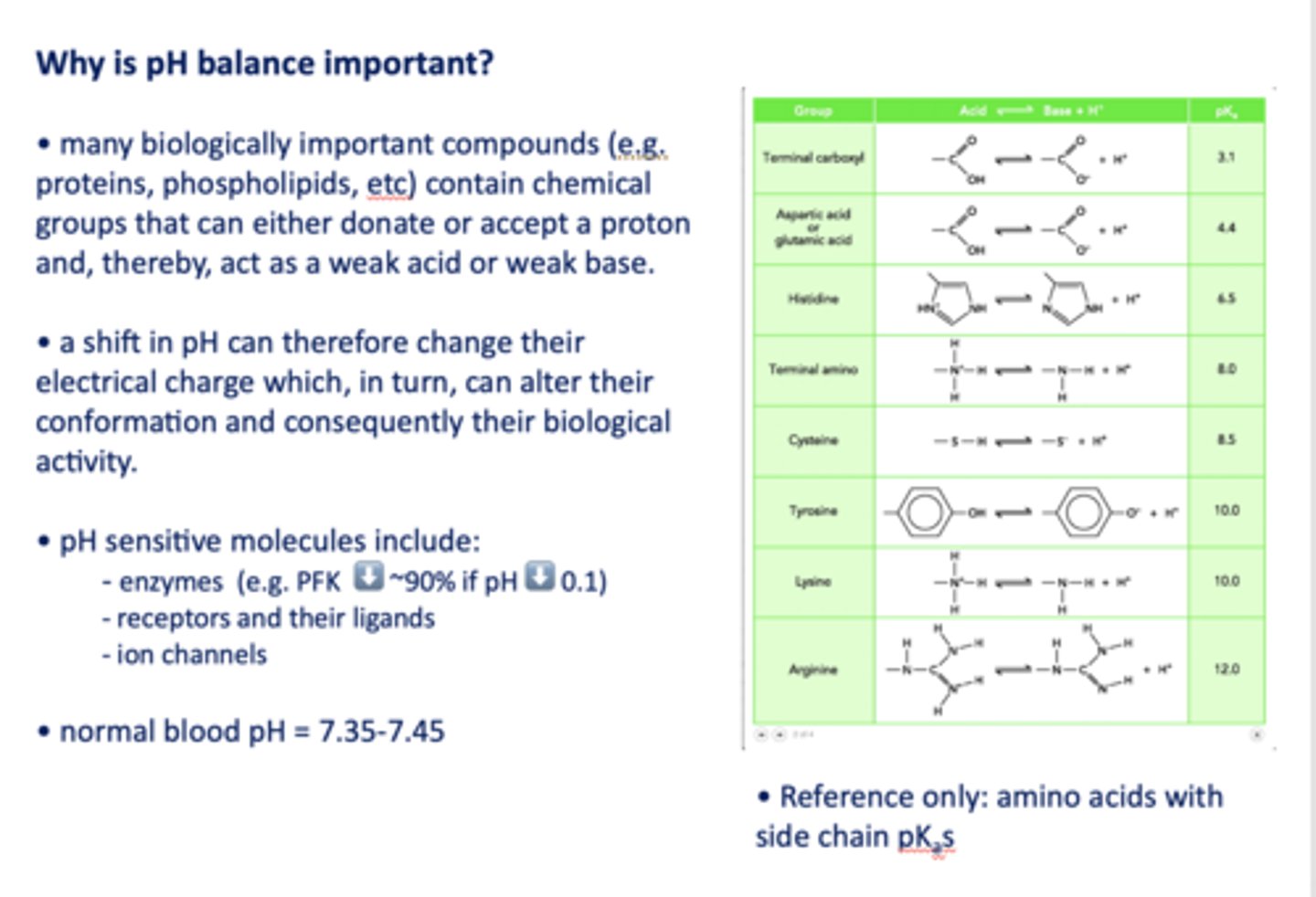
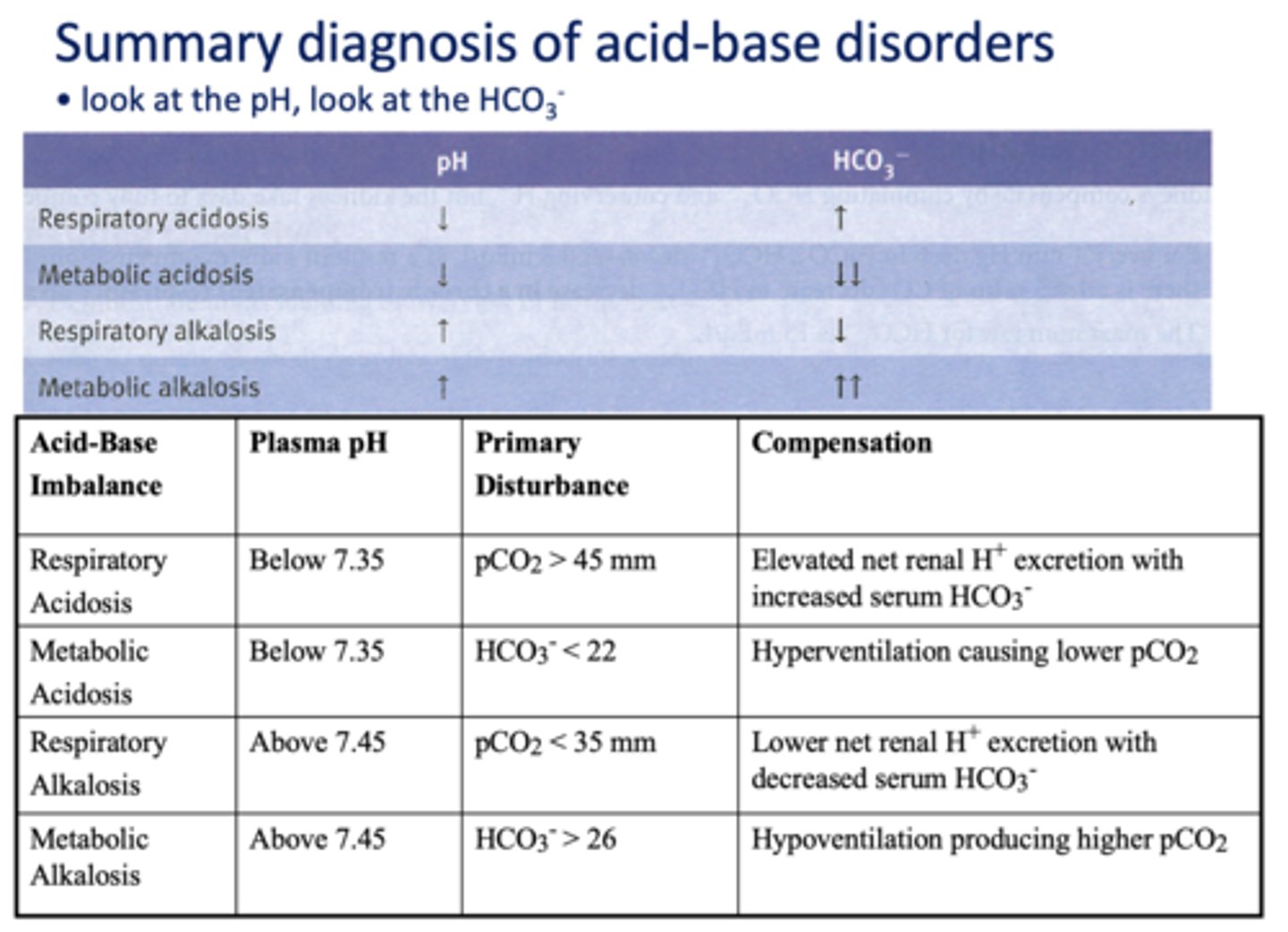
normal blood pH range:
7.35-7.45
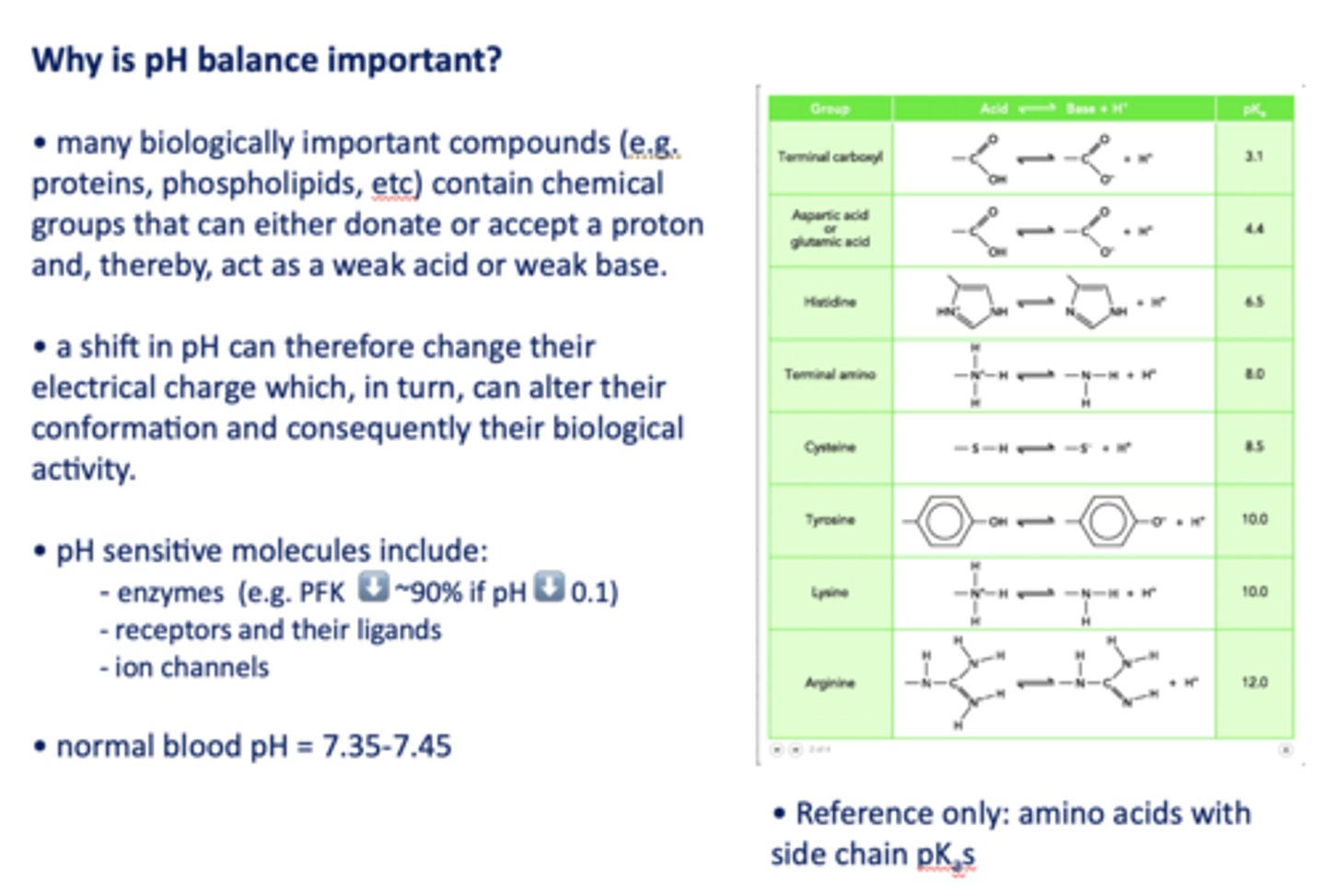
___________ are buffered by chemical buffer bases, such as HCO3− in the extracellular fluid (ECF)
Strong acids
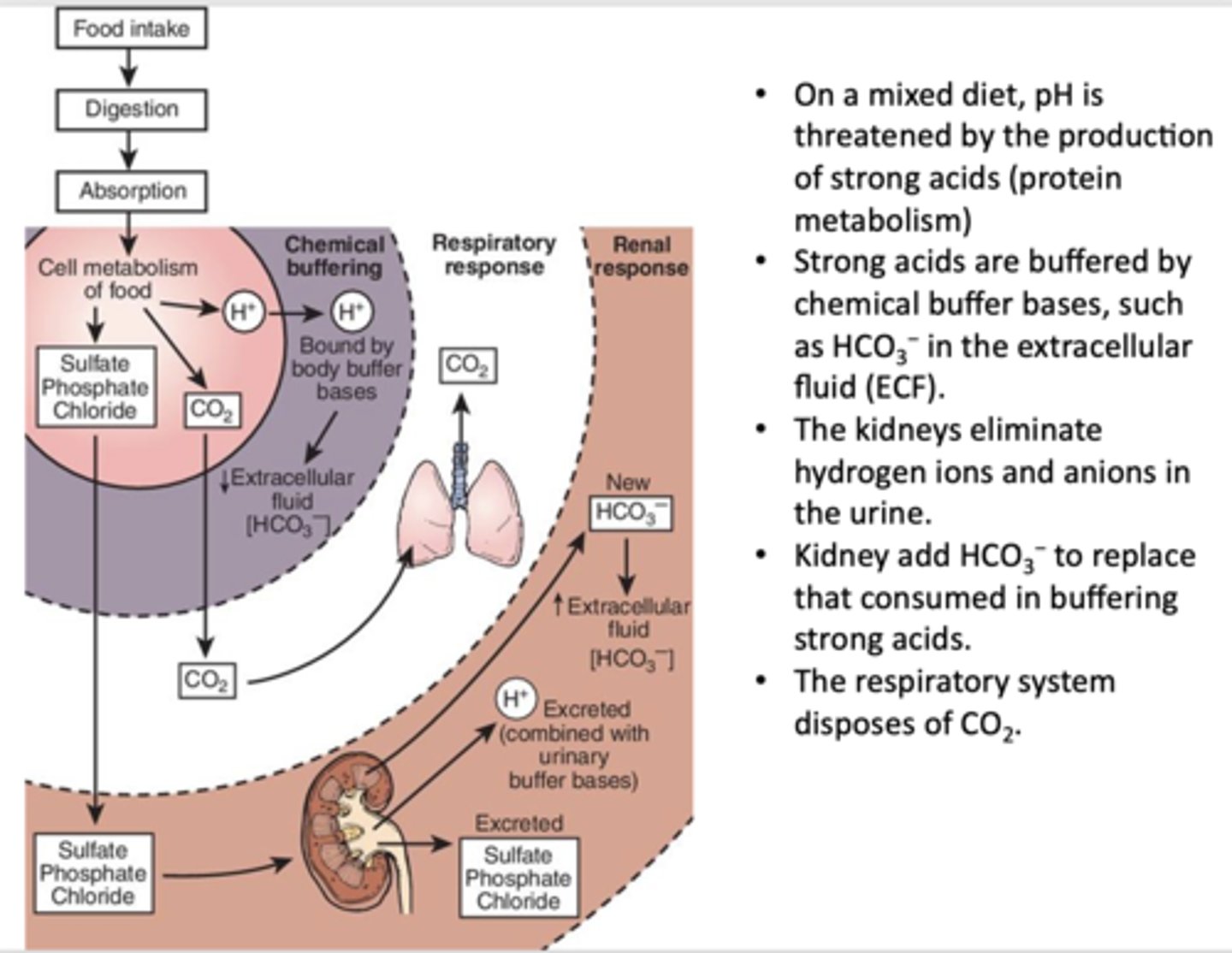
_____________ eliminate hydrogen ions and anions in the urine and add HCO3− to replace that consumed in buffering strong acids
Kidneys
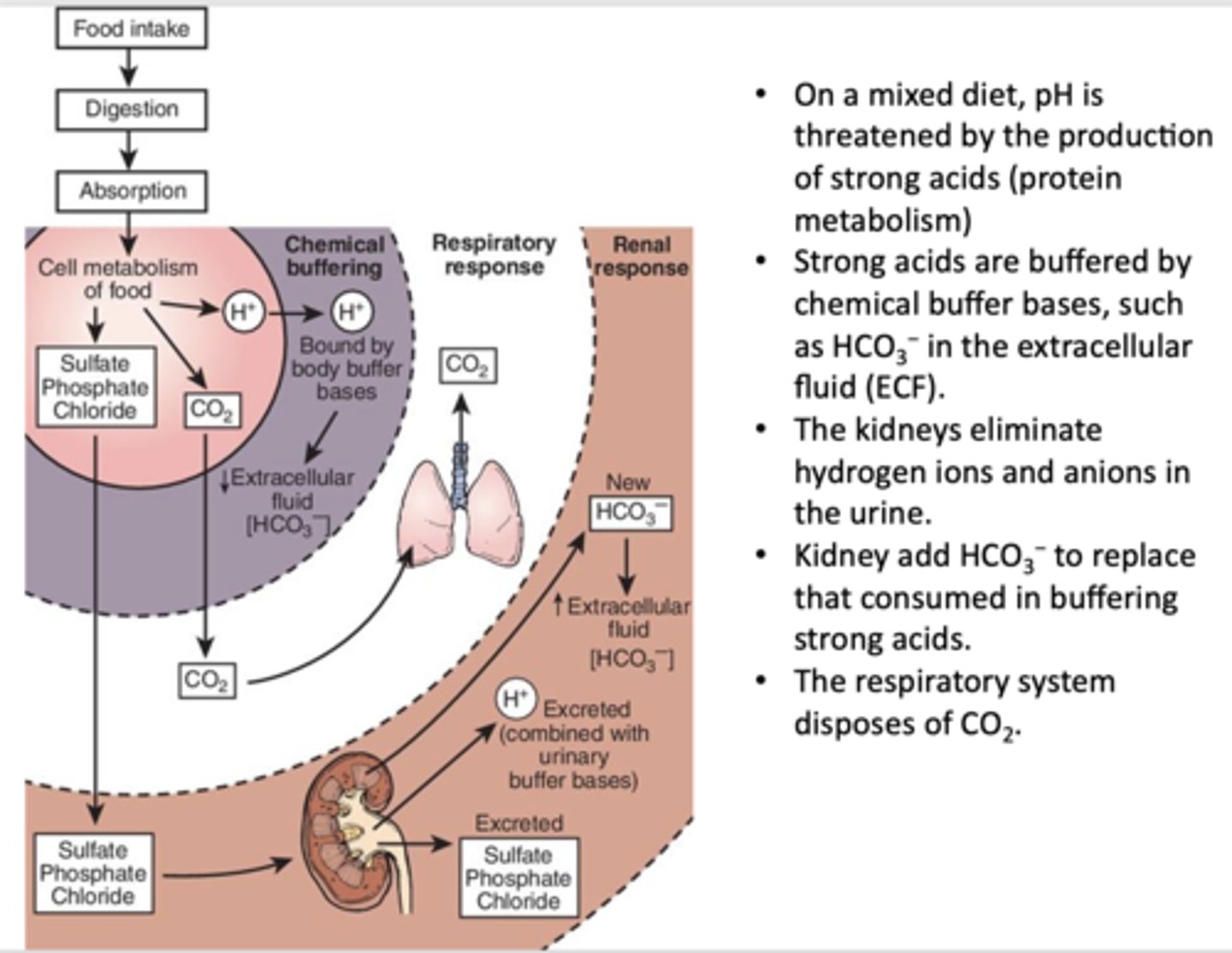
What has the following characteristics?
- Produced by the normal metabolism of dietary carbohydrates, lipids and some amino acids as part of aerobic respiration (~ 15,000 mmols per day, about 1.5 lbs)
- Acidifies blood because most of it is hydrated to carbonic acid which dissociates into bicarbonate and a proton.
CO2

CO2 is what type of acid?
volatile acid

most _____ is eliminated from the body by the lungs
CO2

What has the following characteristics?
- From catabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids to yield H2SO4
- From catabolism of purine to yield uric acid
- From phosphoproteins and phospholipids to yield H3PO4
- From incomplete oxidation of carbohydrates and fats to yield lactic acid and keto acids
Nonvolatile acids

Nonvolatile acids cannot be expelled directly by the lungs and generate a net acid load of ~______ mmoles per day
40

assuming the lungs are working, there are still ~___ mmoles of acid per day that must be neutralized to avoid a decreasing pH.
70

There are four major components of the acid-base homeostatic mechanism:
- Body fluid buffers
- The lungs
- Chemosensors in the circulation and brain
- The kidney
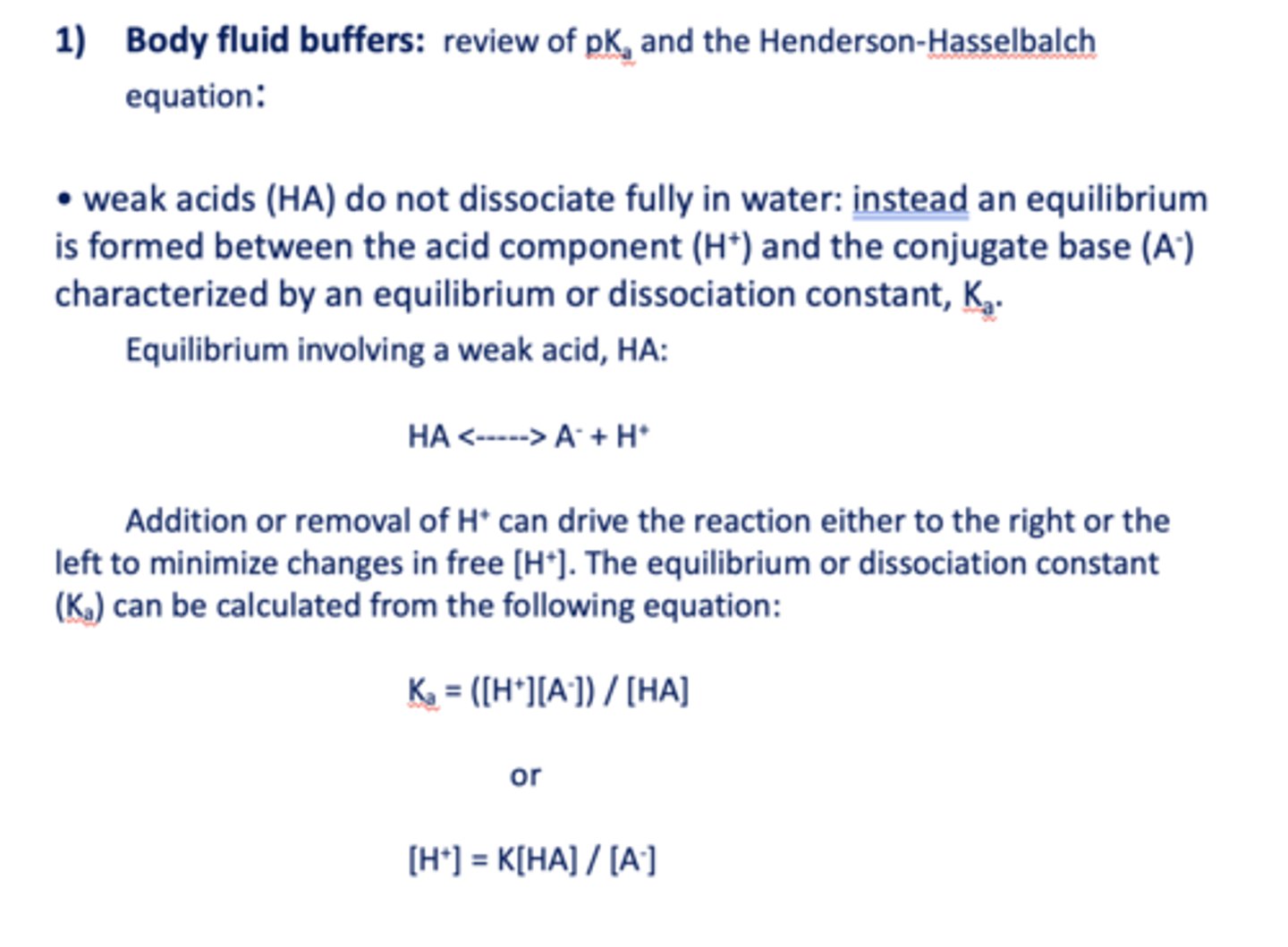
____________ do not dissociate fully in water: instead an equilibrium is formed between the acid component (H+) and the conjugate base (A-) characterized by an equilibrium or dissociation constant, Ka.
Weak acids (HA)
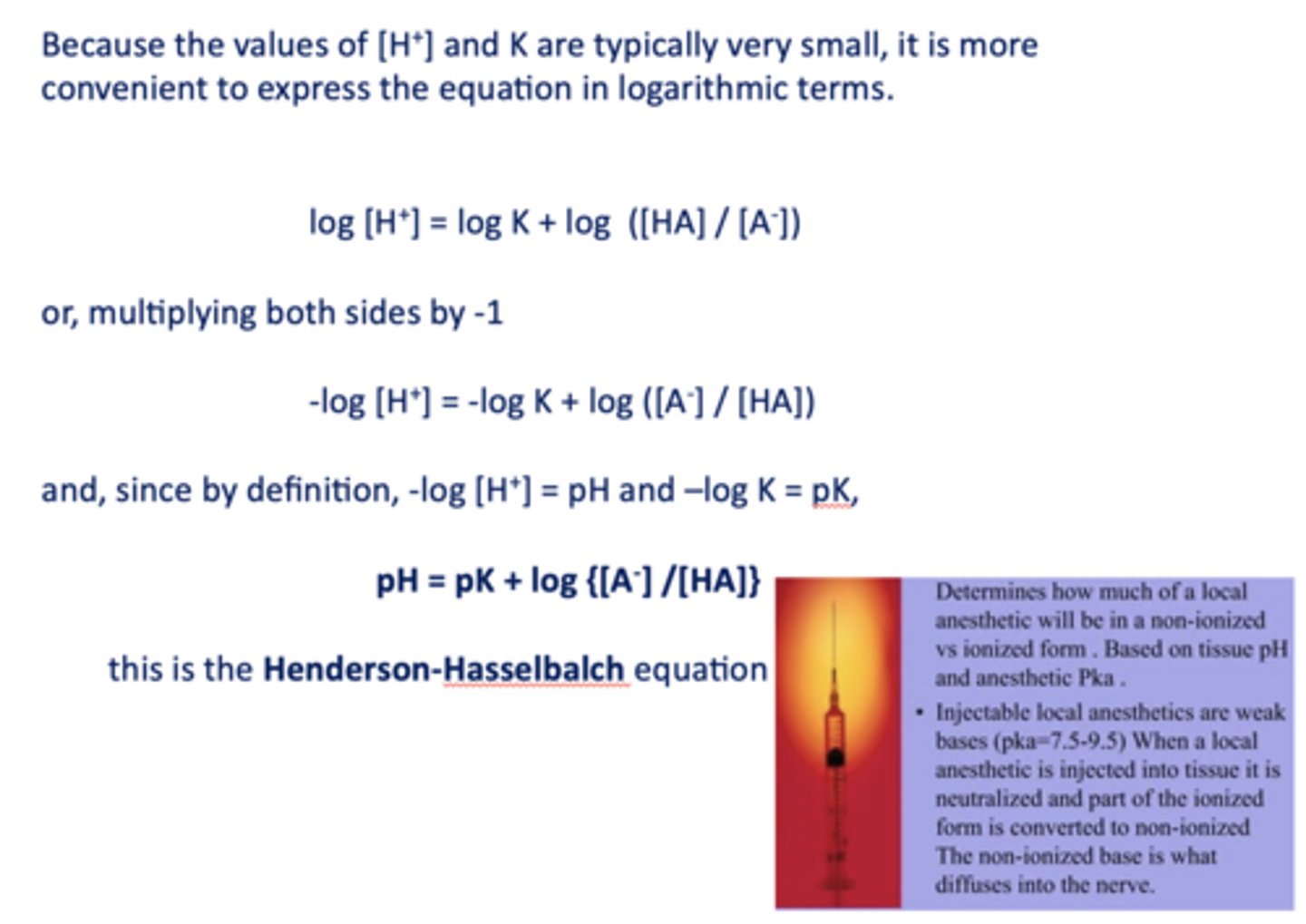
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pK + log {[A-] /[HA]}
![<p>pH = pK + log {[A-] /[HA]}</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4469cdd2-8e32-4b91-9a8d-148a3deb38ad.jpg)
Local anesthetics are ____________
Weak bases
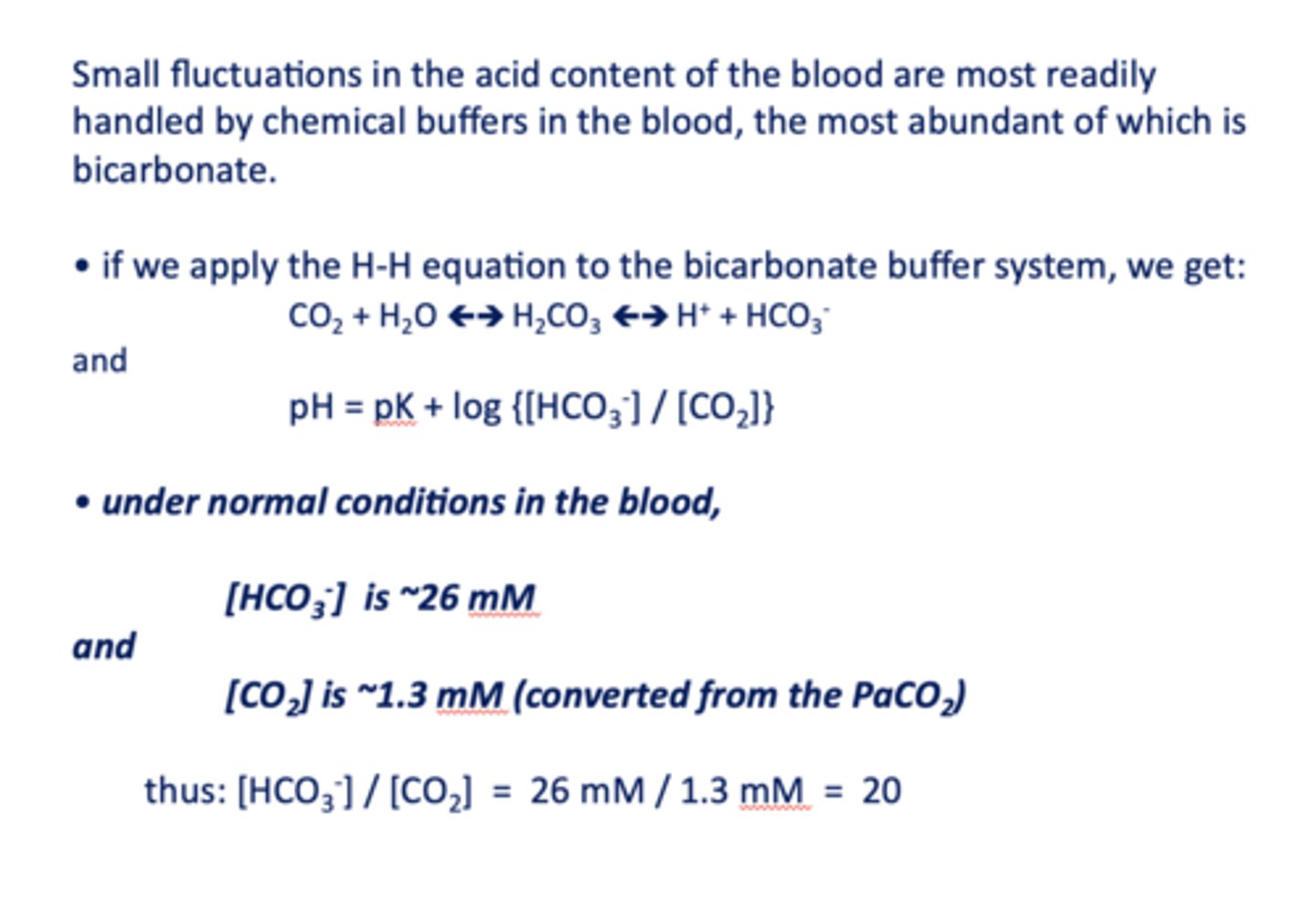
Small fluctuations in the acid content of the blood are most readily handled by chemical buffers in the blood, the most abundant of which is ____________
bicarbonate
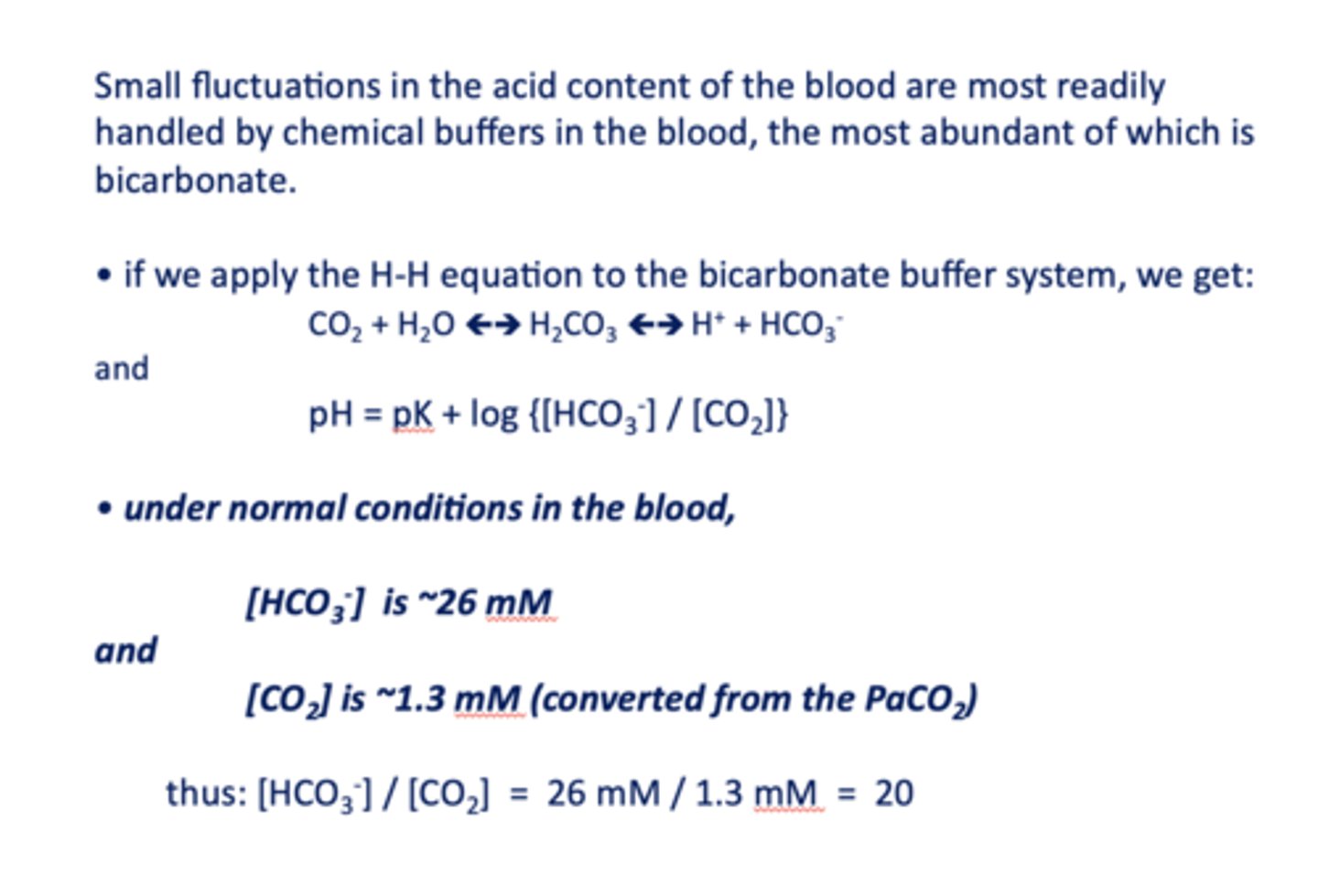
the ratio of [HCO3-]/ [CO2] in normal conditions in the blood is equal to =
20
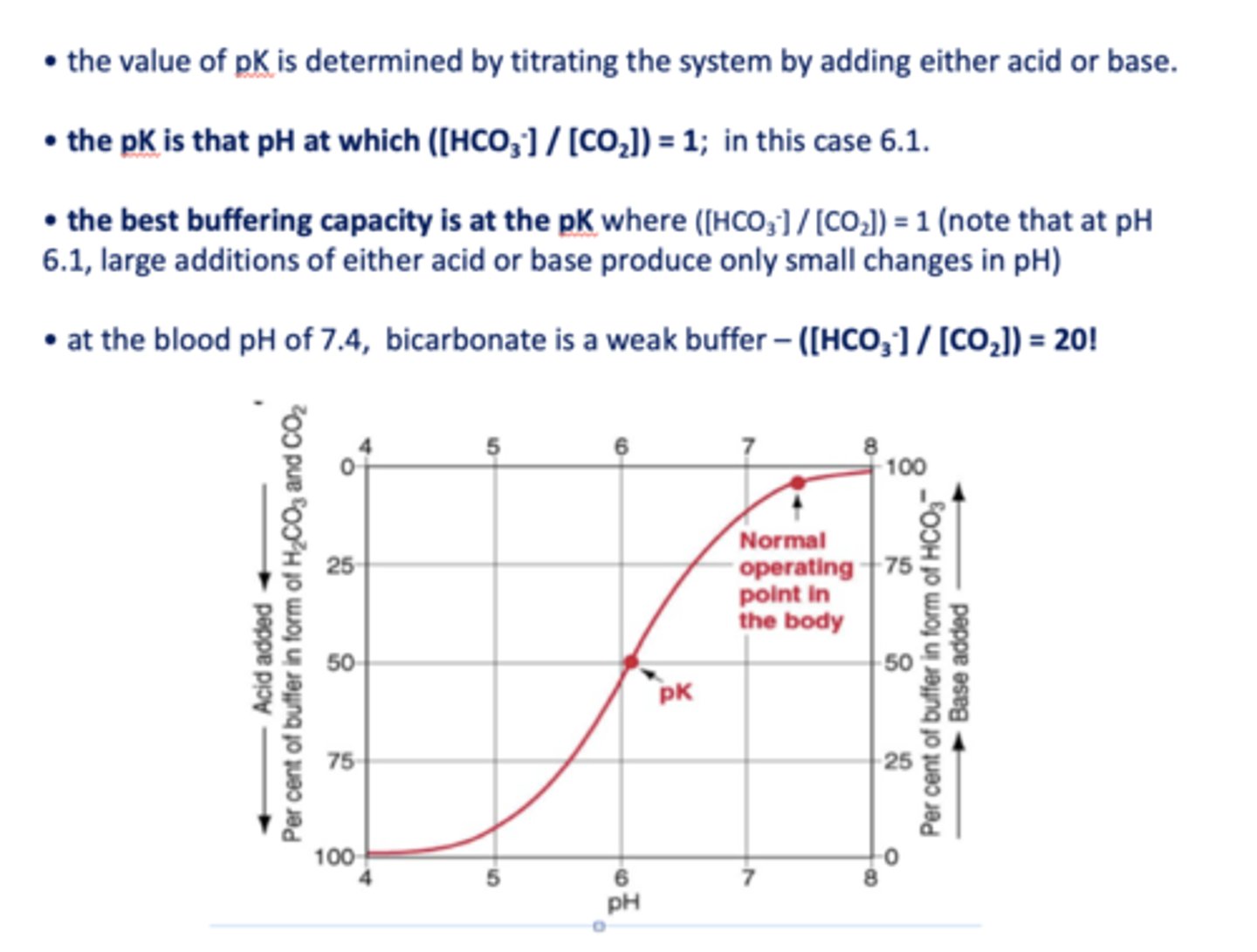
what is the pKa of bicarbonate?
6.1
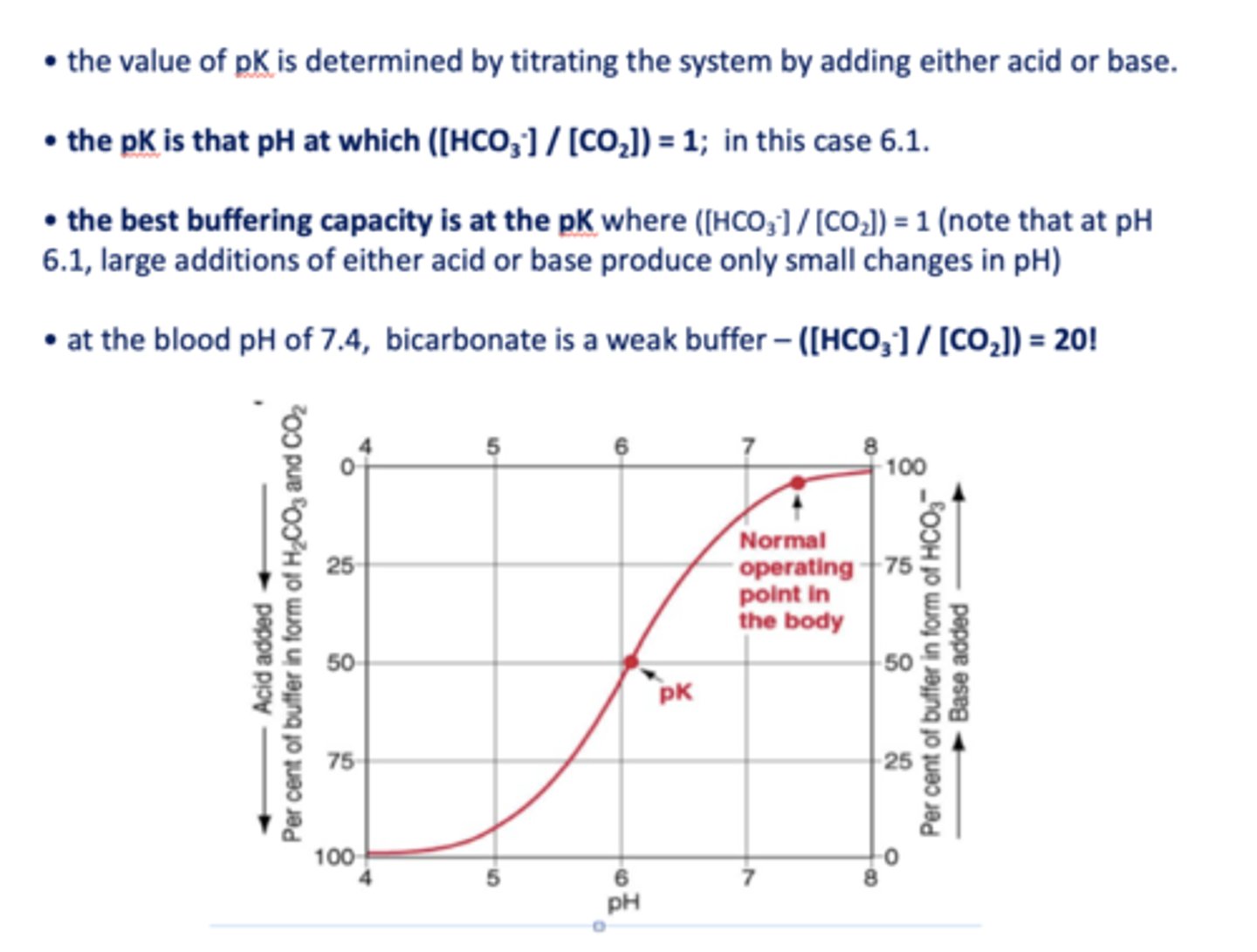
at the blood pH of 7.4, bicarbonate is a _________
weak buffer
inspection of the equation shows that the pH of the blood (and ECF) varies when either the ________ change.
[HCO3-] or PaCO2
![<p>[HCO3-] or PaCO2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b1ec212b-81af-46b5-9ffb-e6811c7f5145.jpg)
under normal conditions in the blood, [HCO3-] is about ______
26 mM/l
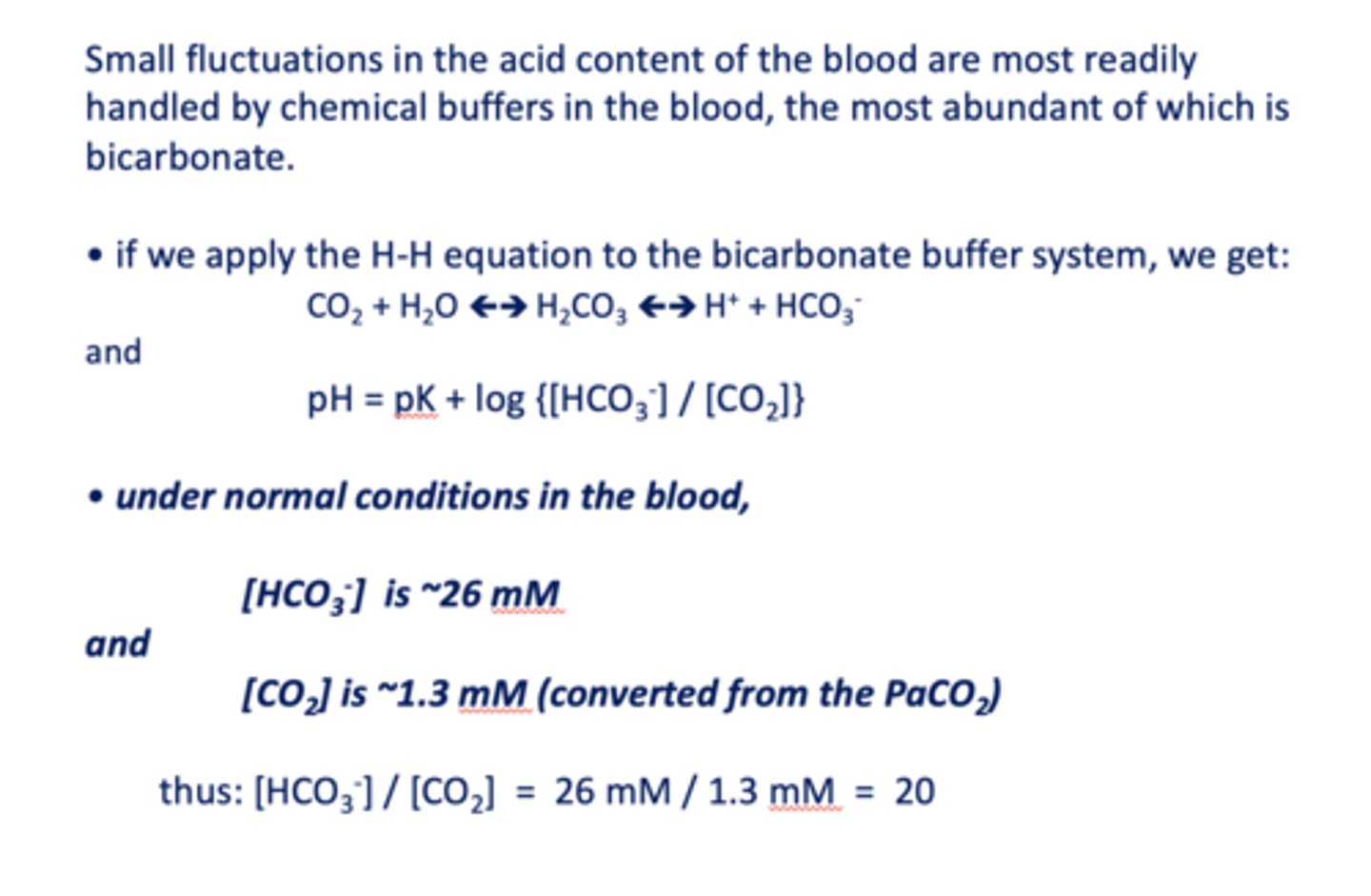
under normal conditions in the blood, [CO2] is about ______
1.3 mM/l
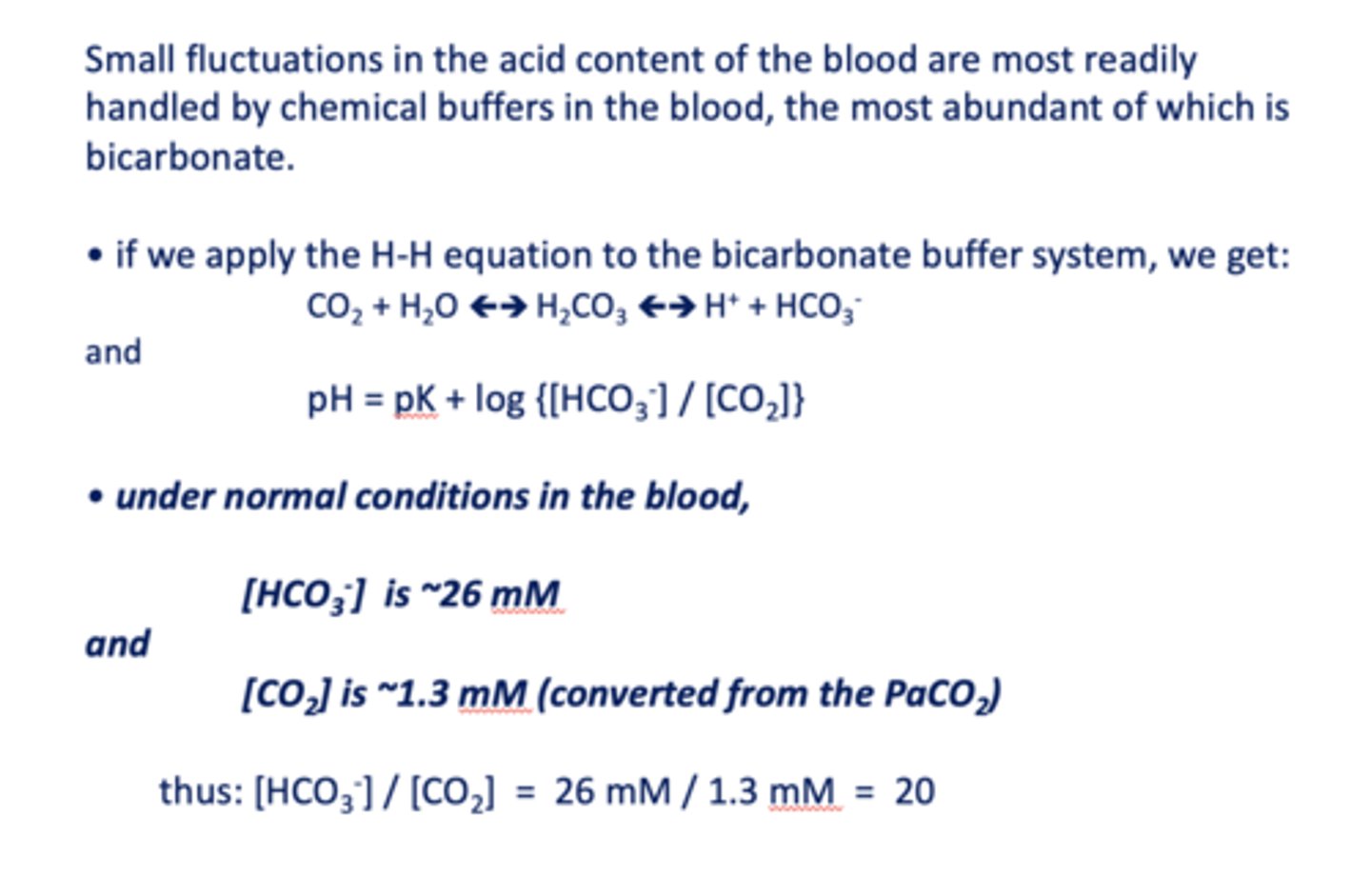
the best buffering capacity is at the pK where [HCO3-]/[CO2] is equal to
1
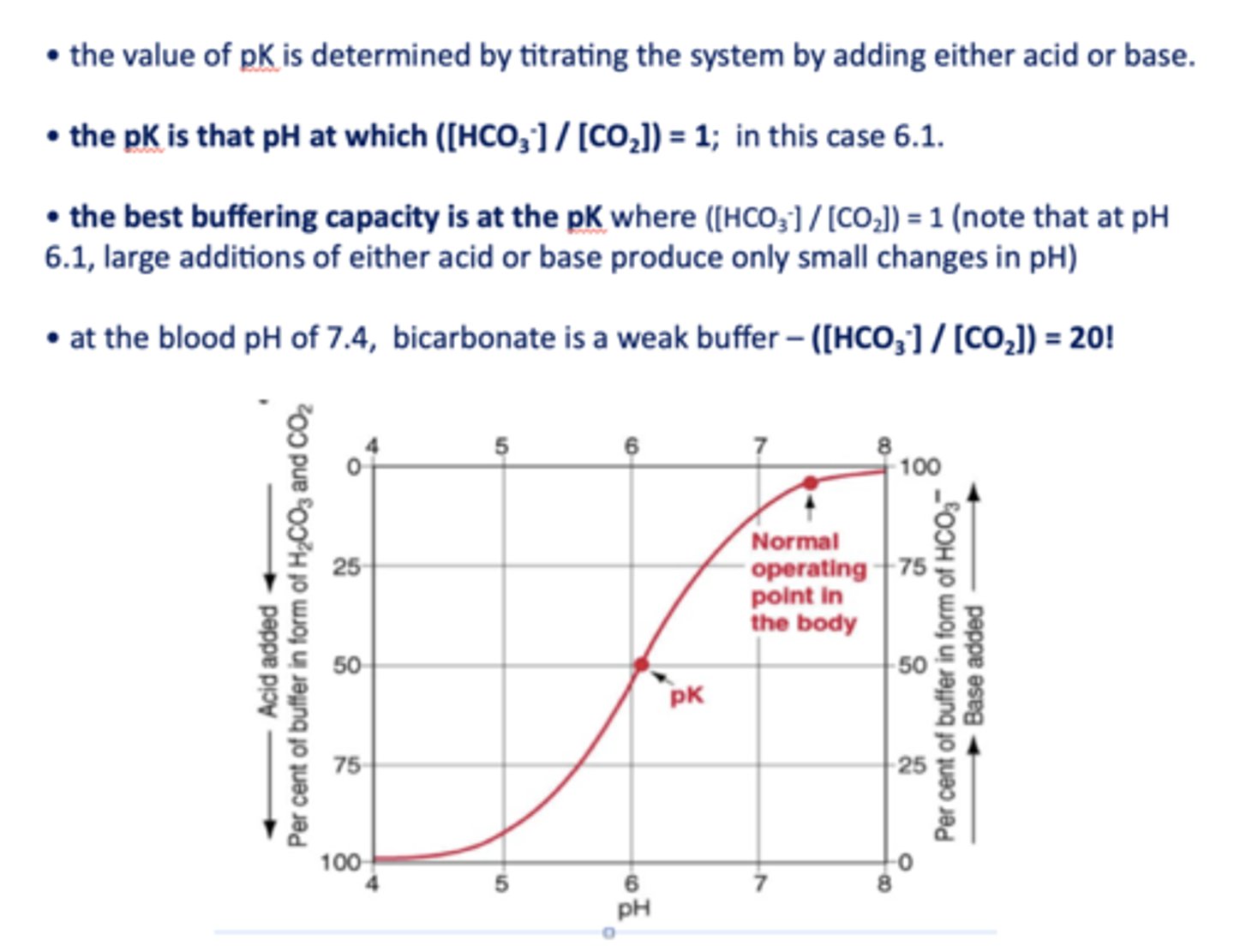
two ways to restore to normal pH when pH decreases
- Increase bicarbonate
- Decrease CO2
a key relationship between the pulmonary system and the CO2 levels in the blood is given in the equation...
PaCO2 ∞ VCO2 / VA
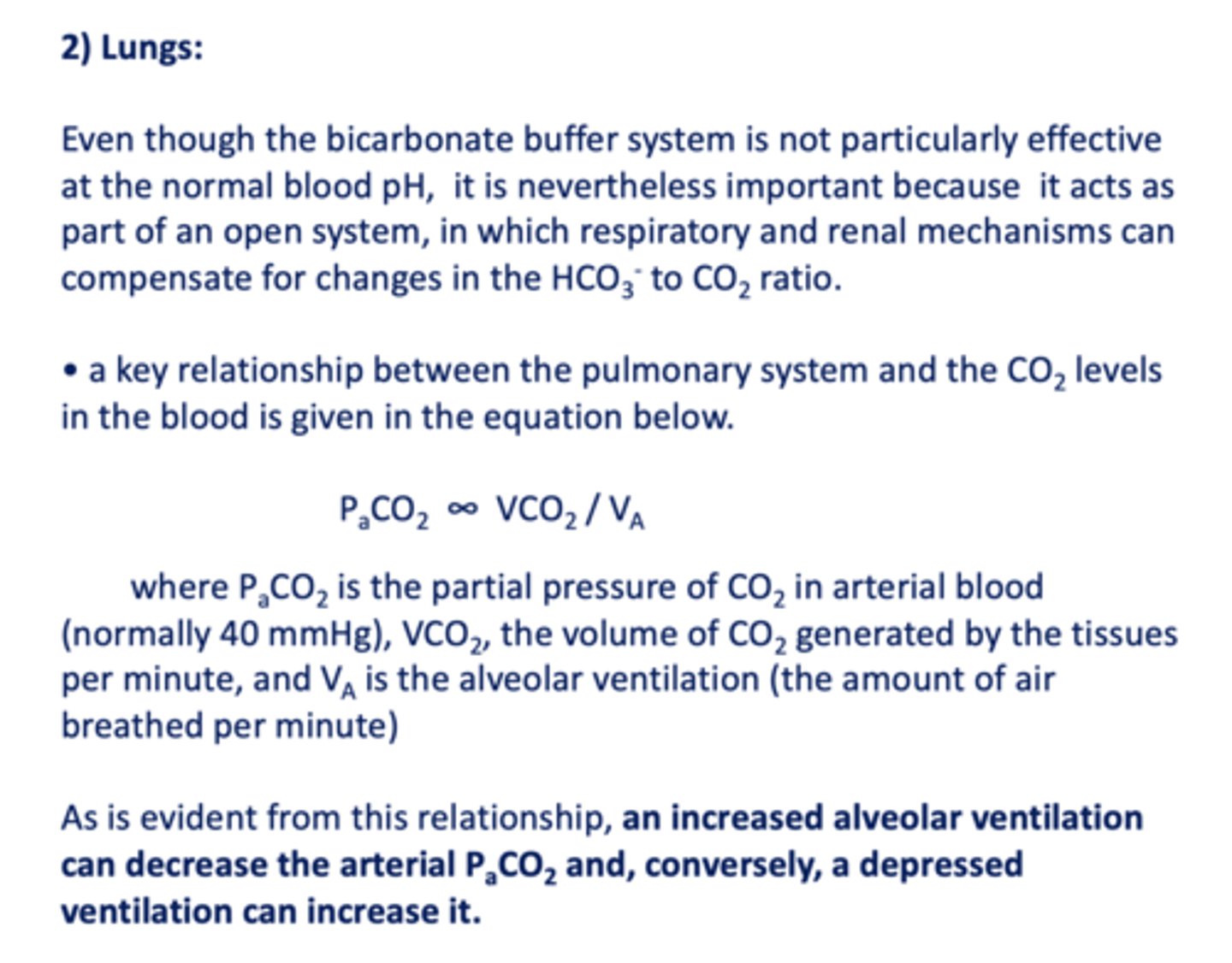
an increased alveolar ventilation can ______ the arterial PCO2
decrease

an decrease in alveolar ventilation can ______ the arterial PCO2
increase

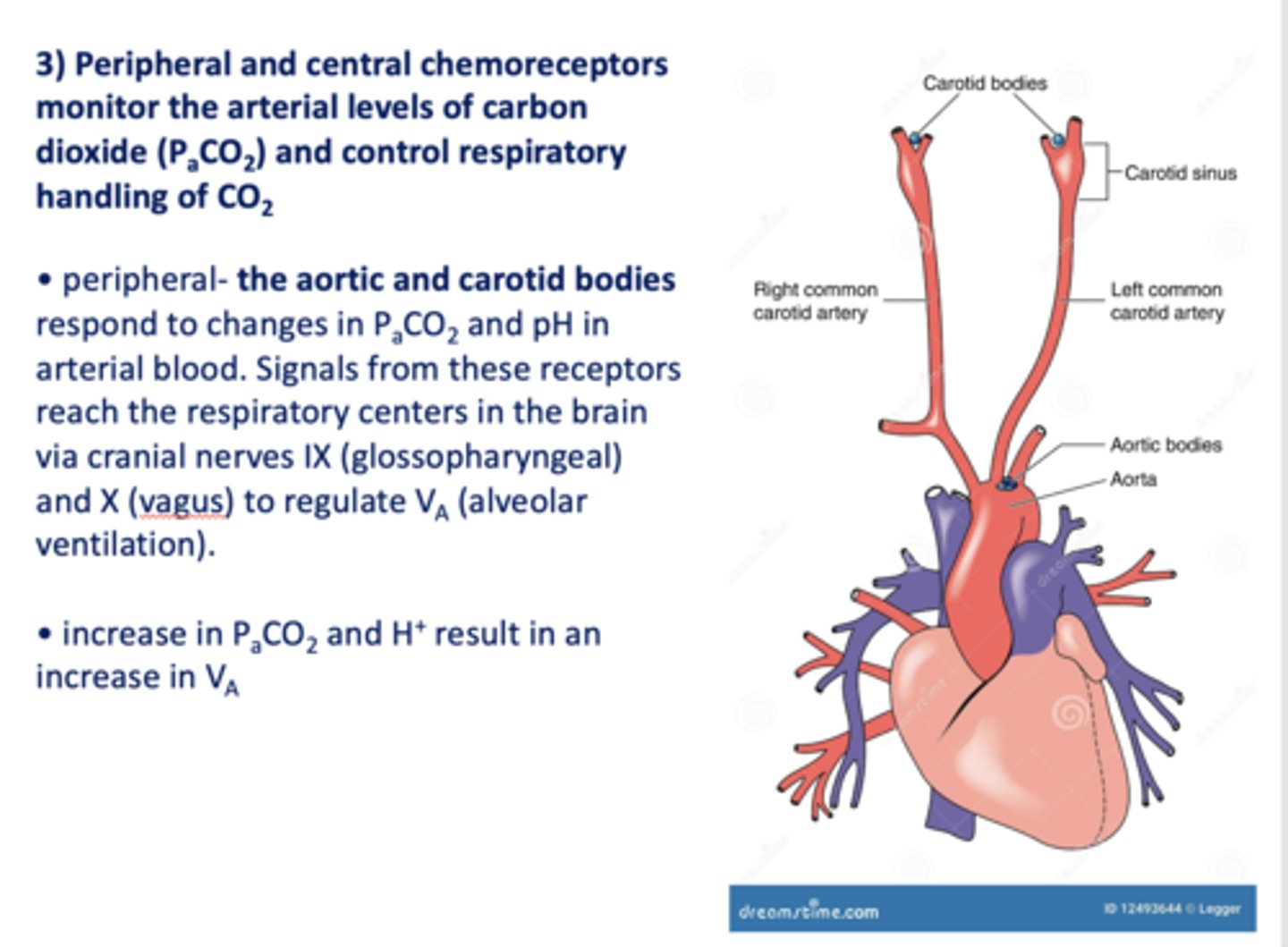
Peripheral and central chemoreceptors monitor the arterial levels of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) and control respiratory handling of _________
CO2
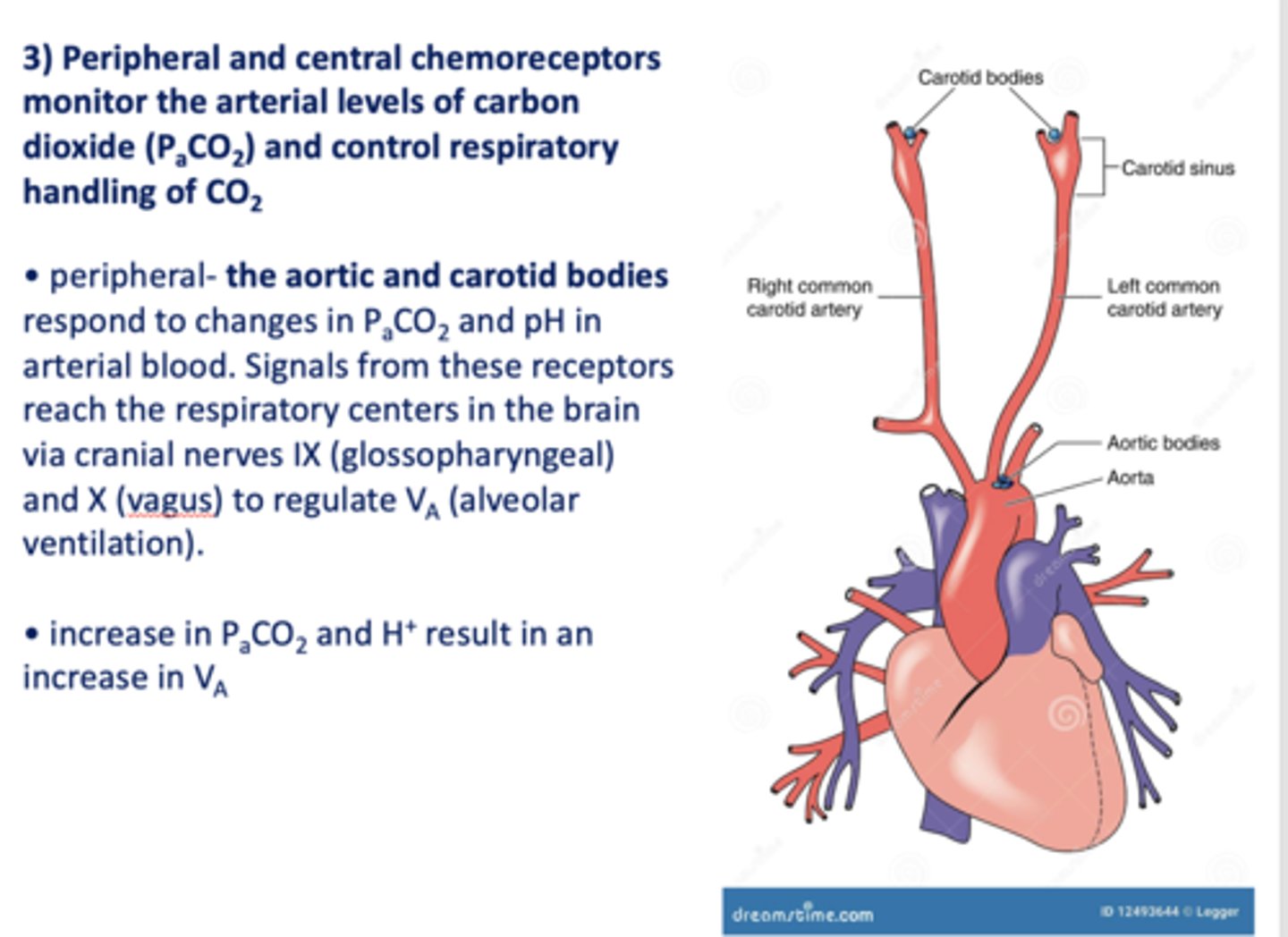
Peripheral ____________ and ____________ respond to changes in PaCO2 and pH in arterial blood. Signals from these receptors reach the respiratory centers in the brain via cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal) and X (vagus) to regulate VA (alveolar ventilation).
Aortic and carotid bodies
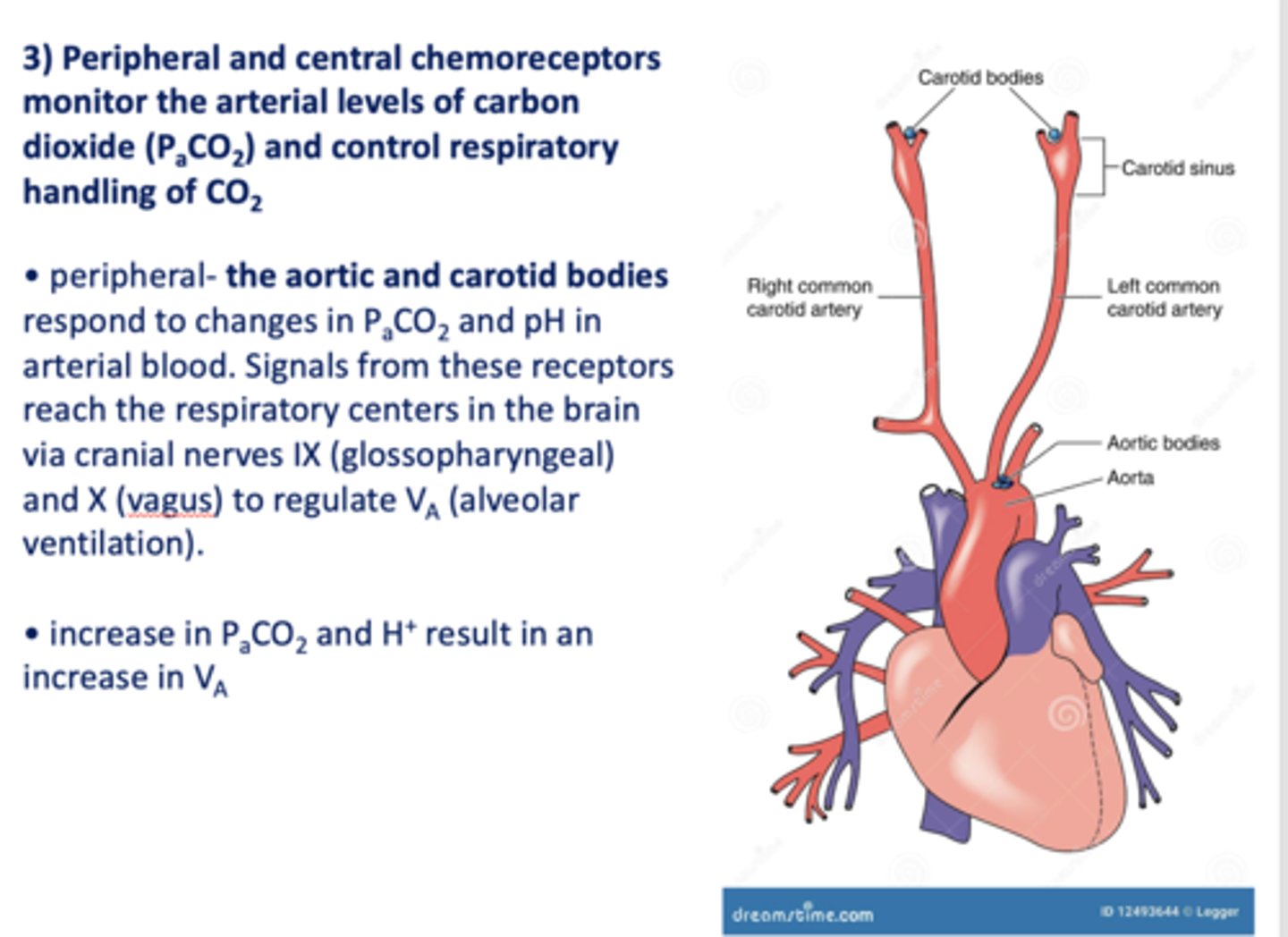
increase in PaCO2 and increase in pH will result in ____________ alveolar ventilation (Va)
increase
this organ's role in acid-base balance is to reabsorb bicarbonate and excrete H+ into the urine:
kidneys
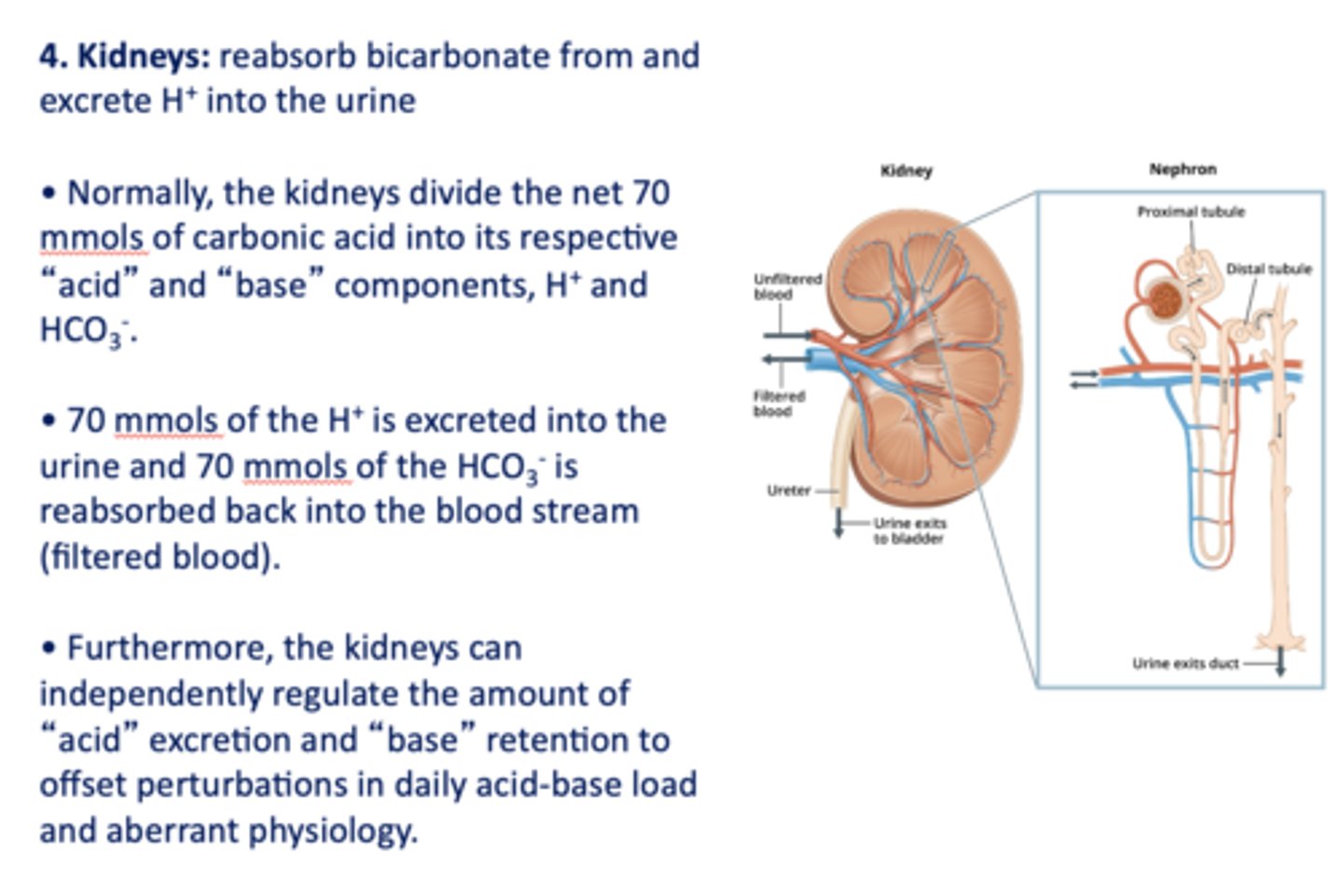
Within the kidneys 70 mmols of the ___________ is excreted into the urine and 70 mmols of the ___________ is reabsorbed back into the blood stream (filtered blood).
H+, HCO3-
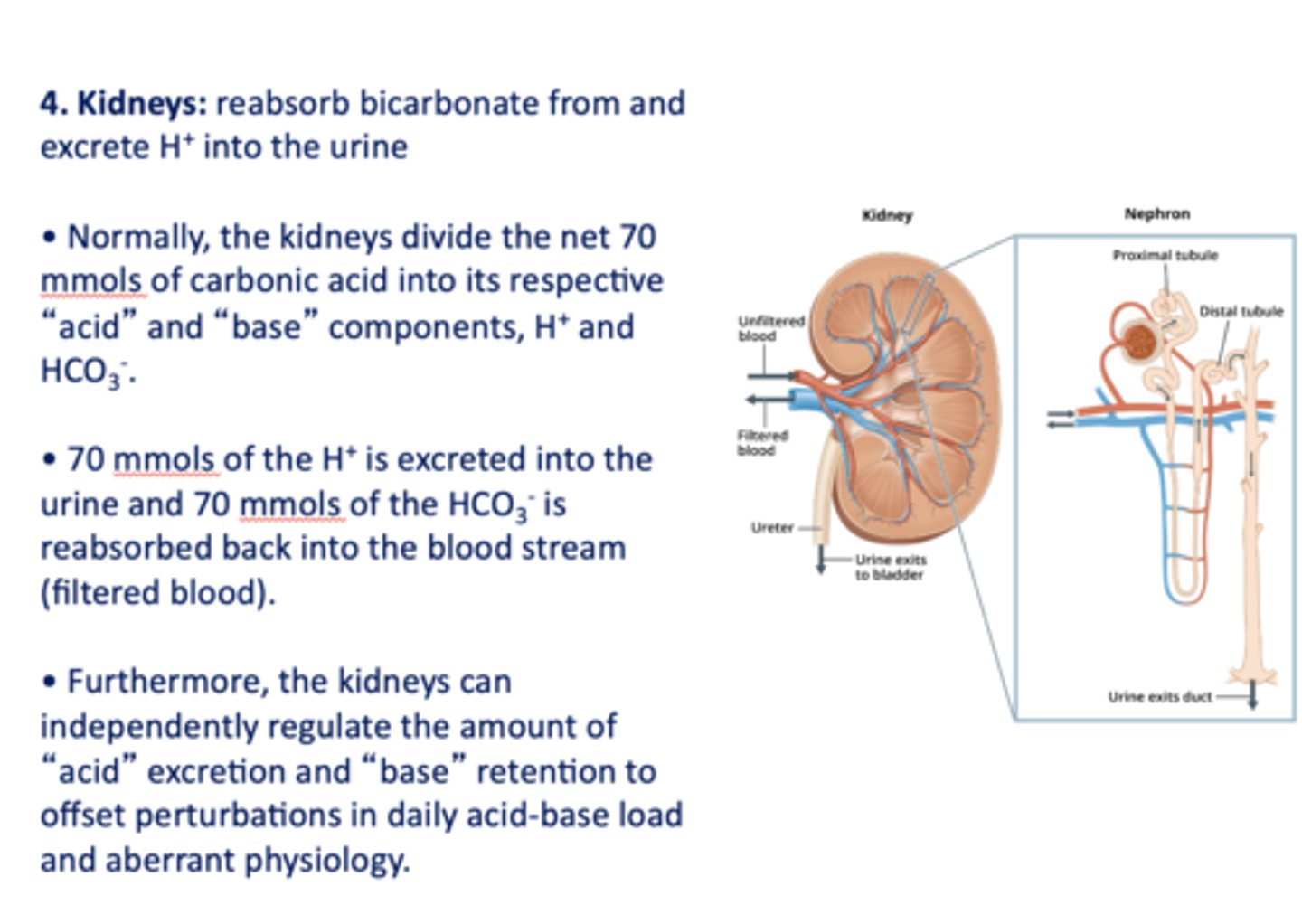
the _____________ can independently regulate the amount of "acid" excretion and "base" retention to offset perturbations in daily acid-base load and aberrant physiology
kidneys
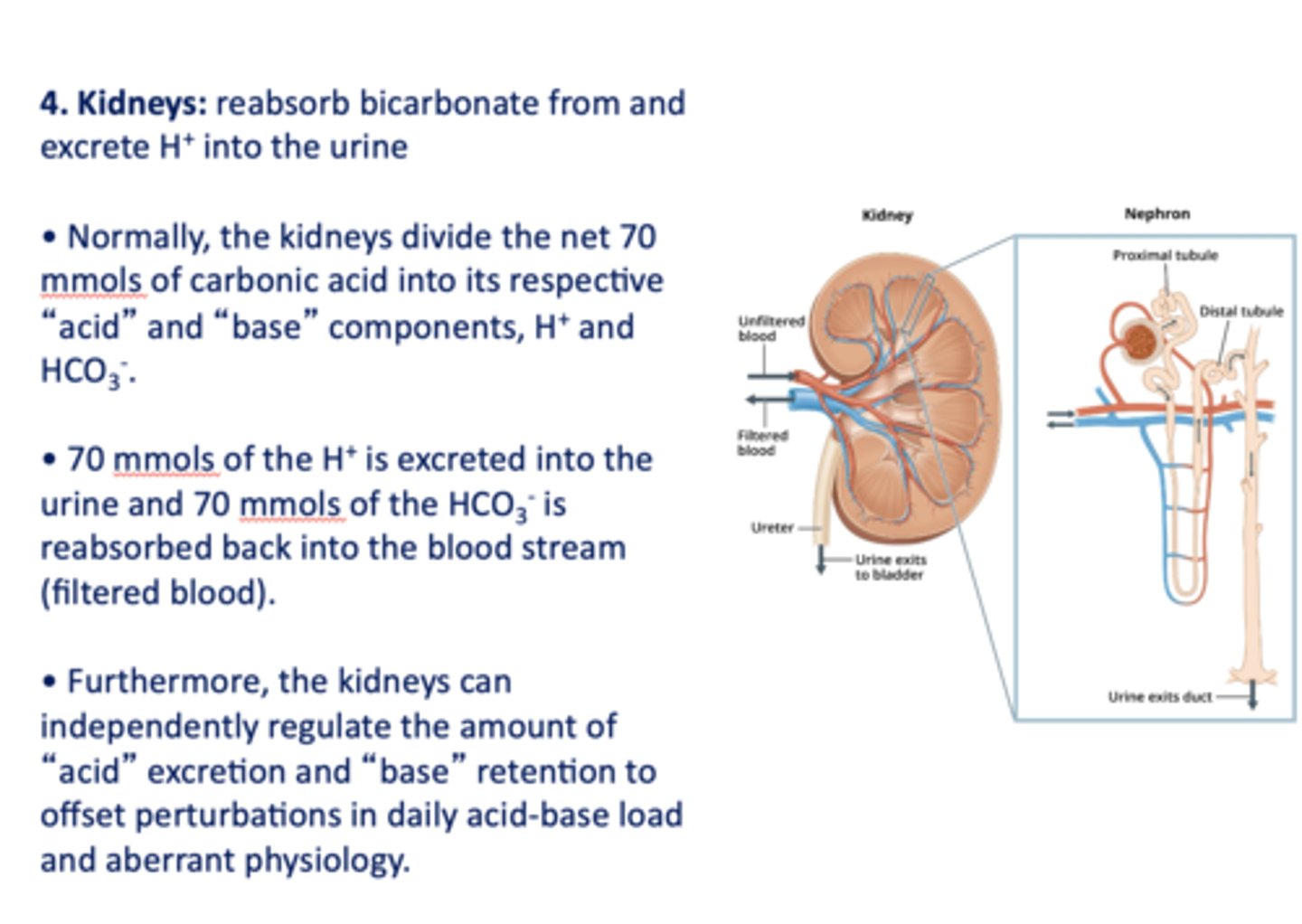
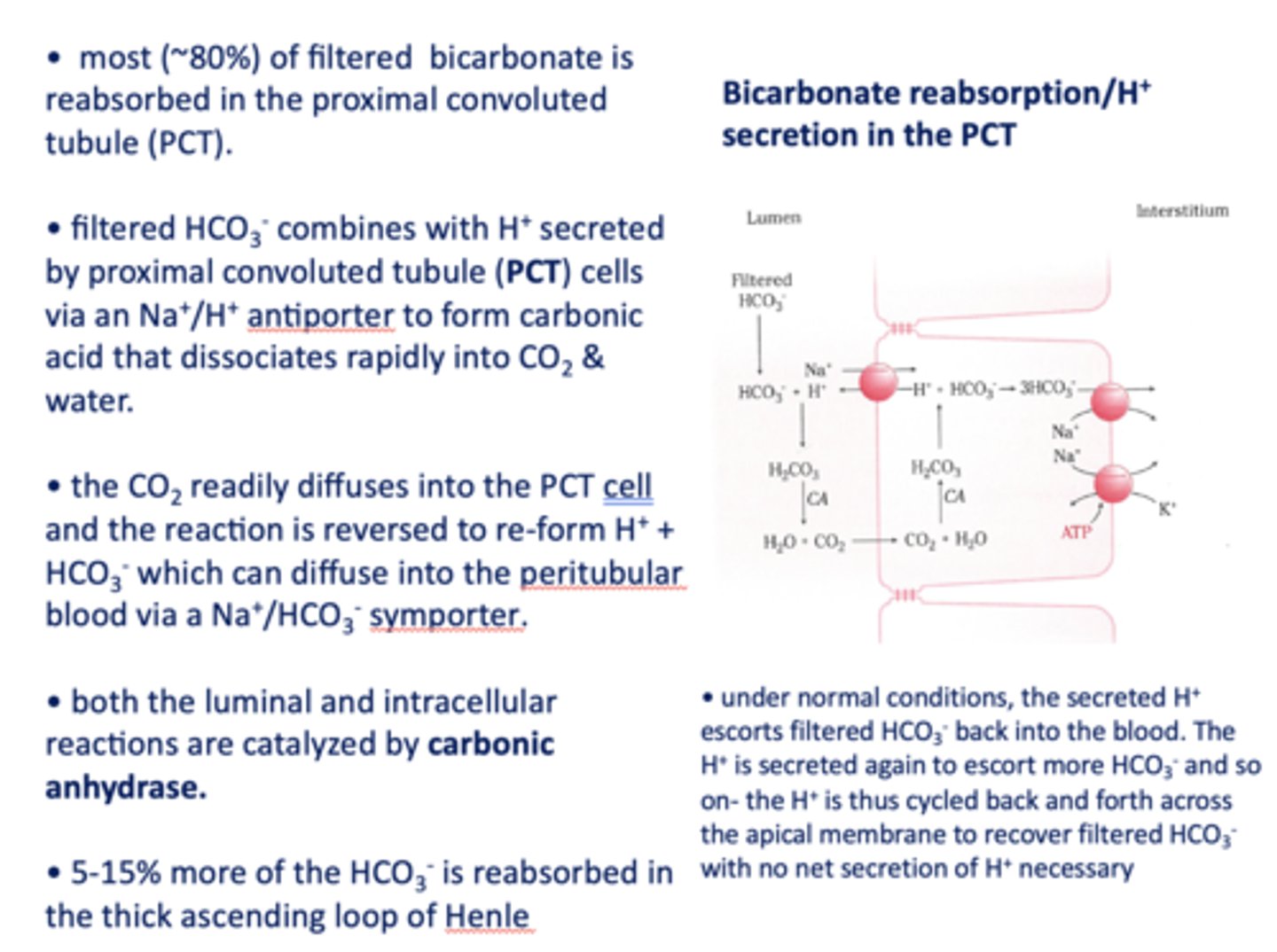
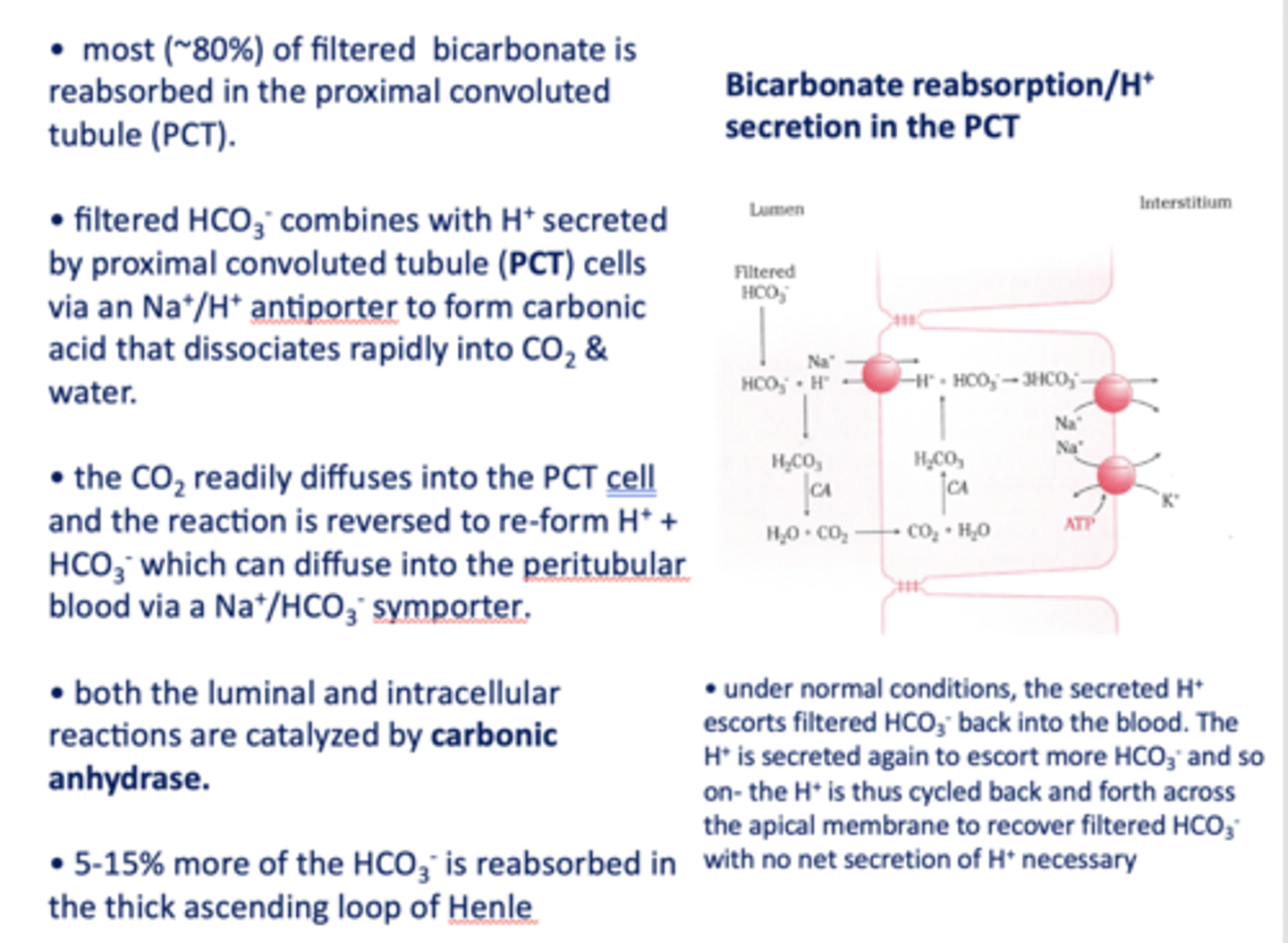
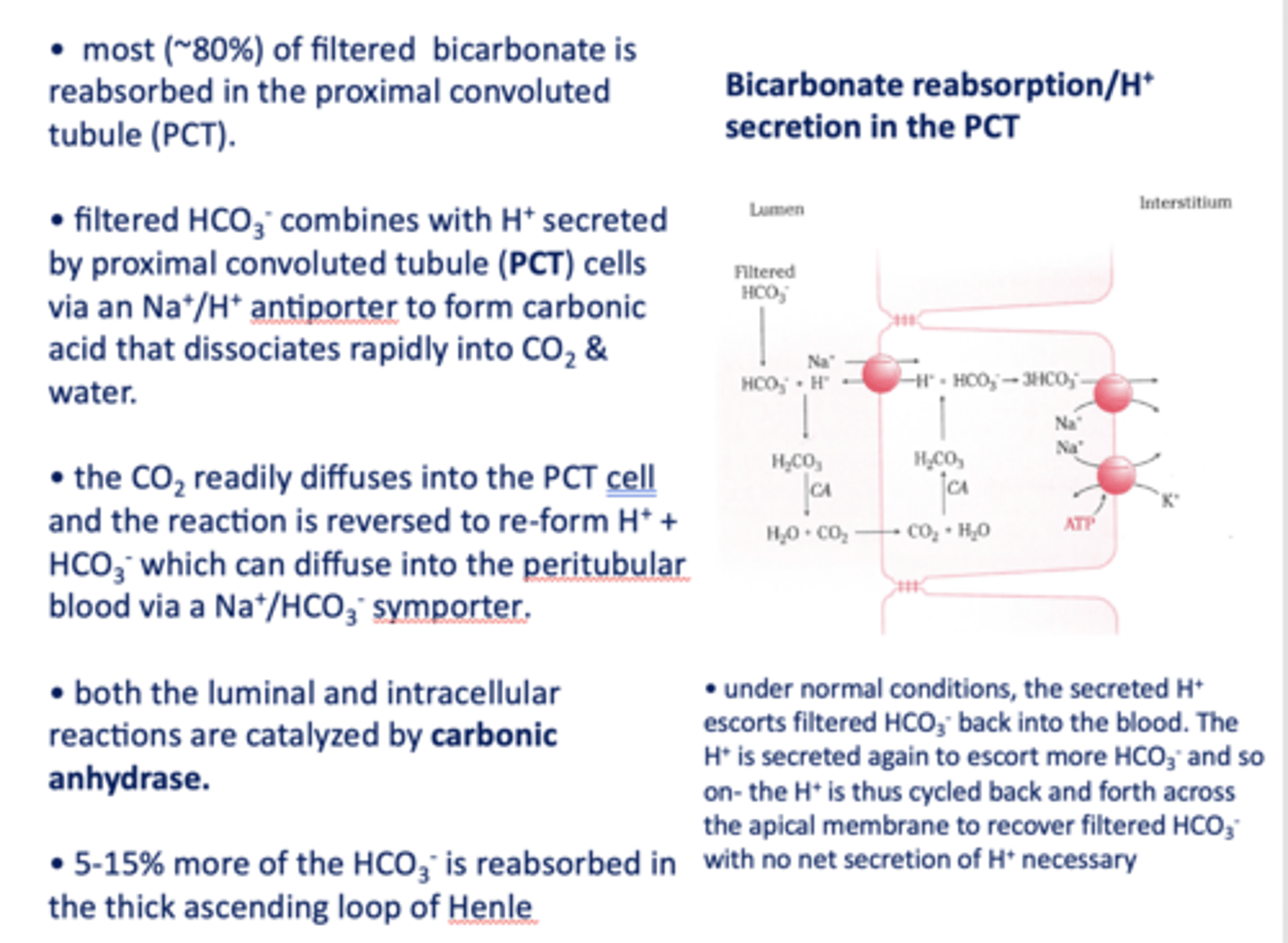
in the kidneys, most (~80%) of filtered bicarbonate is reabsorbed in the _________
proximal convoluted tubule
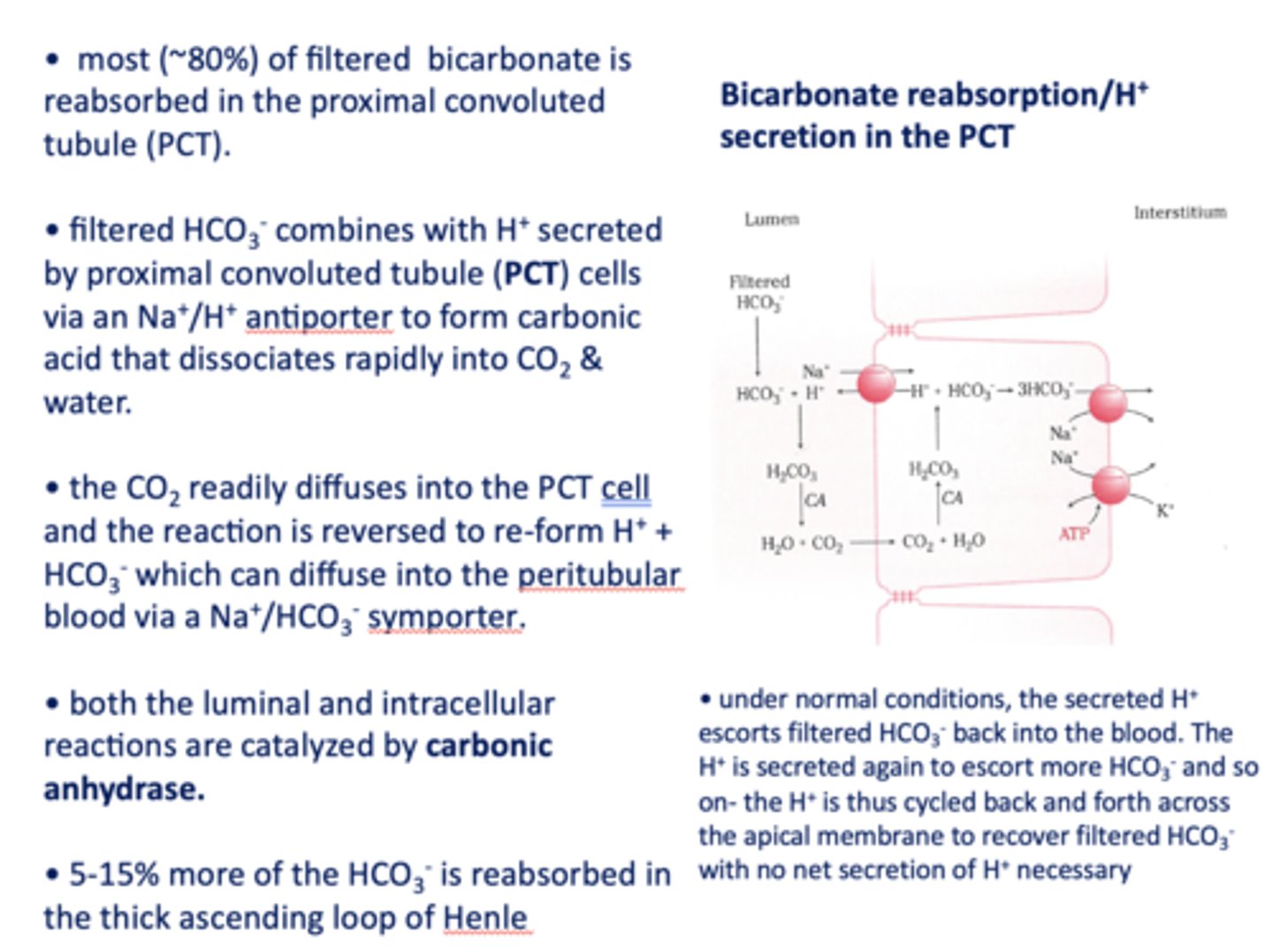
filtered HCO3- combines with H+ secreted by proximal tubule cells via a ______ antiporter to form carbonic acid that dissociates rapidly into CO2 and water
Na+/H+
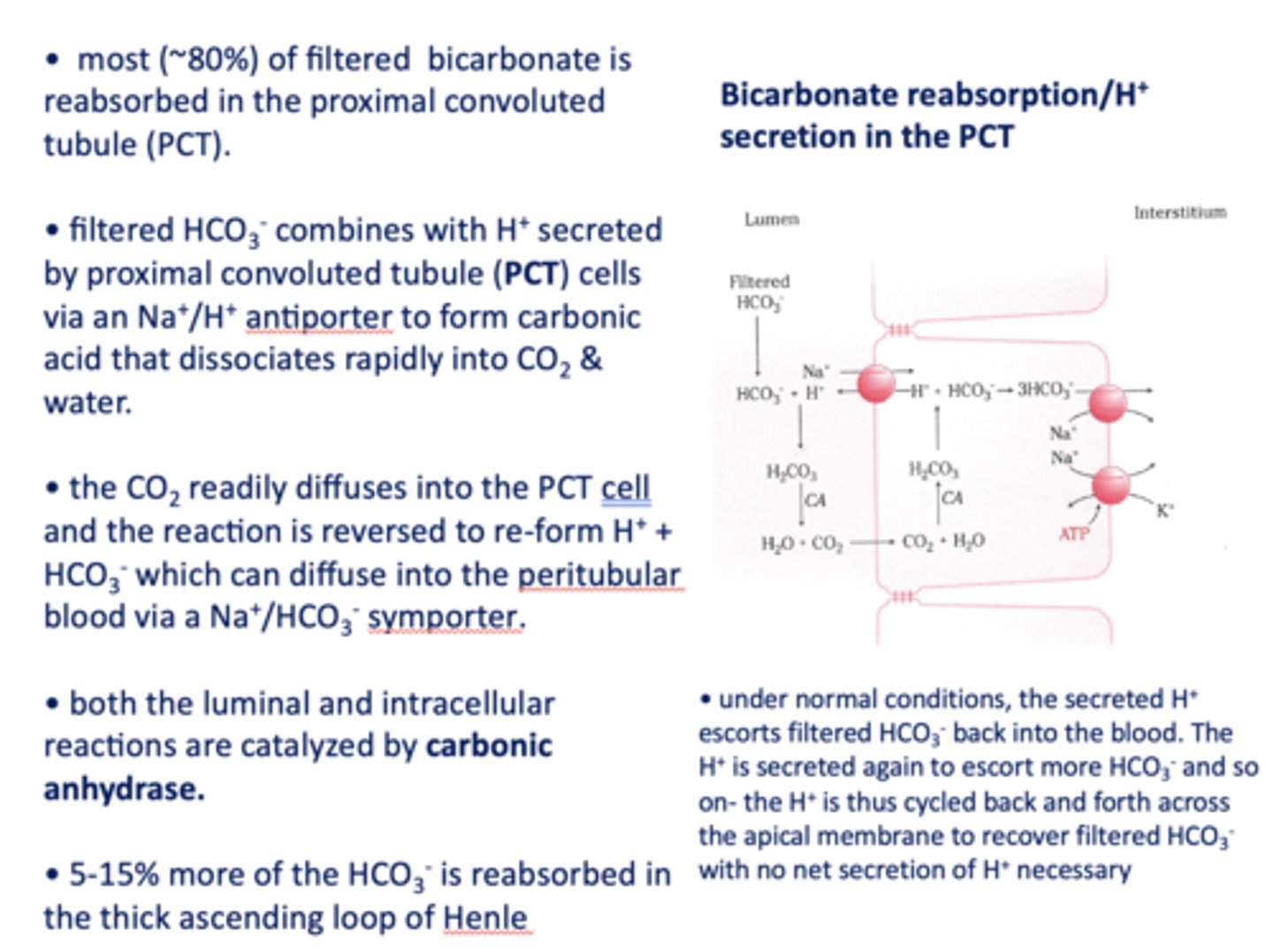
the CO2 readily diffuses into the PCT cell and the reaction is reversed to re-form _______ and _______
H+, HCO3-
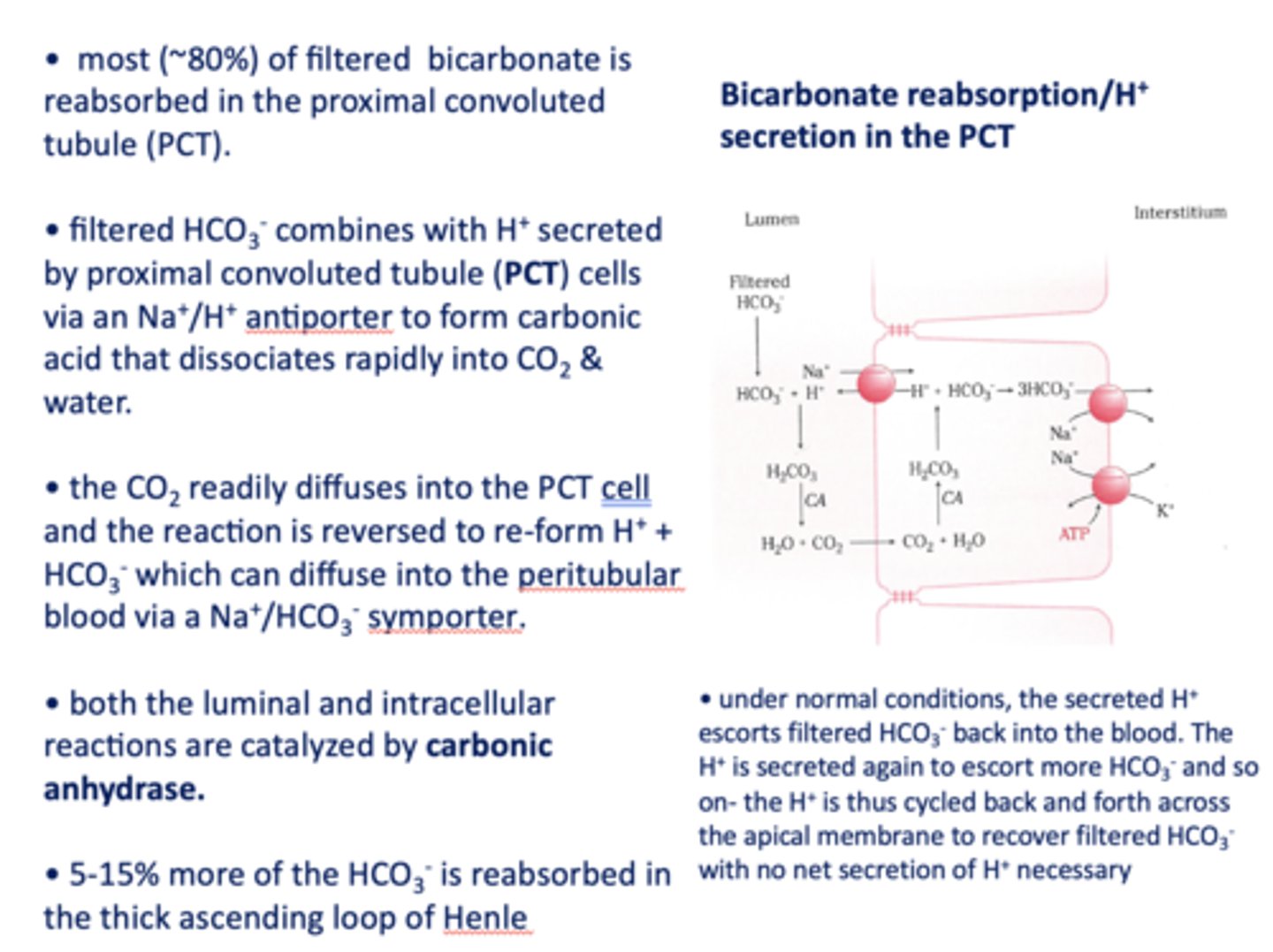
HCO3- formed in the PCT cell can diffuse to the peritubular blood via a ___________
Na+/HCO3- symporter
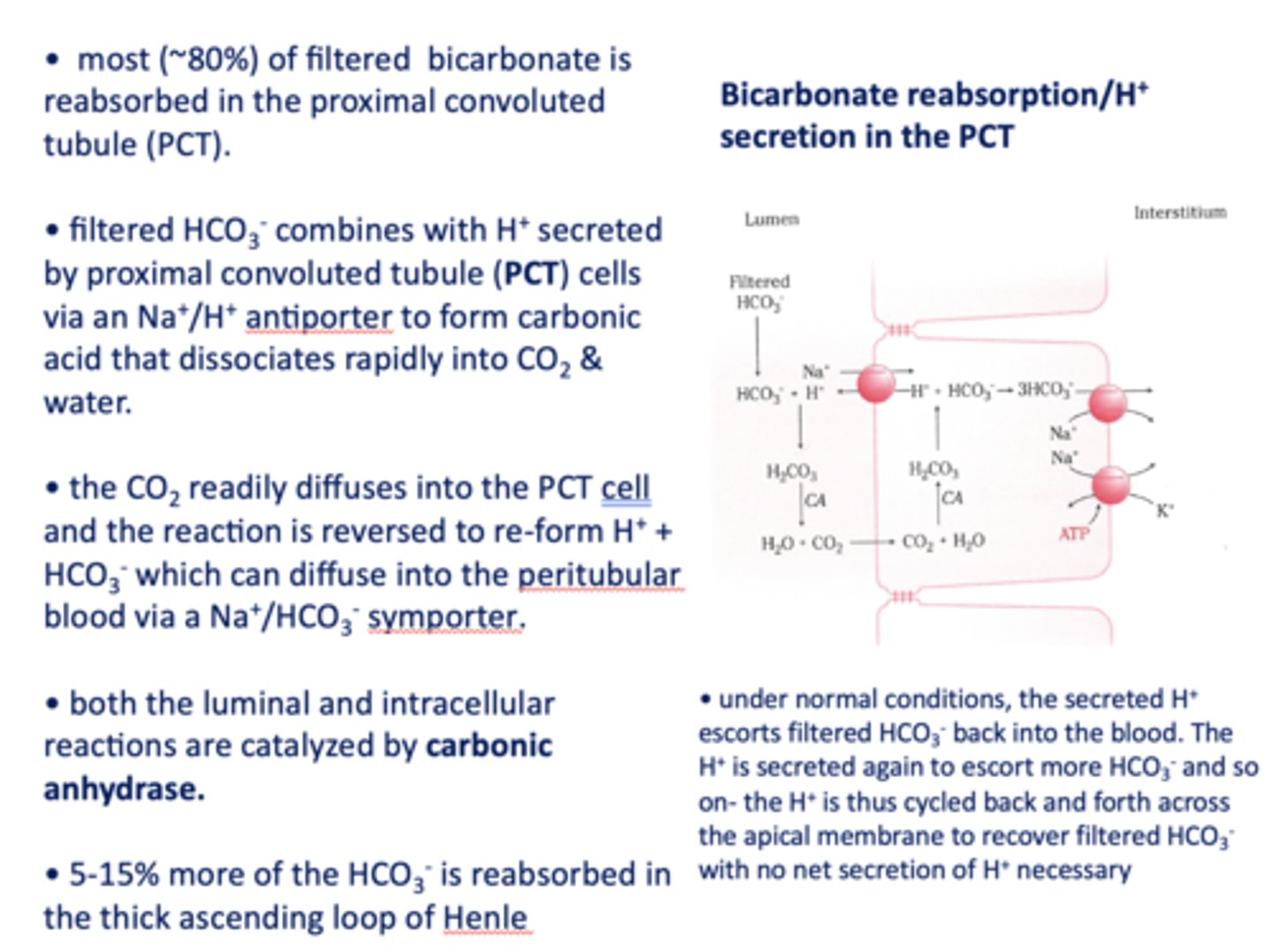
both the luminal and intracellular reactions are catalyzed by _________
carbonic anhydrase
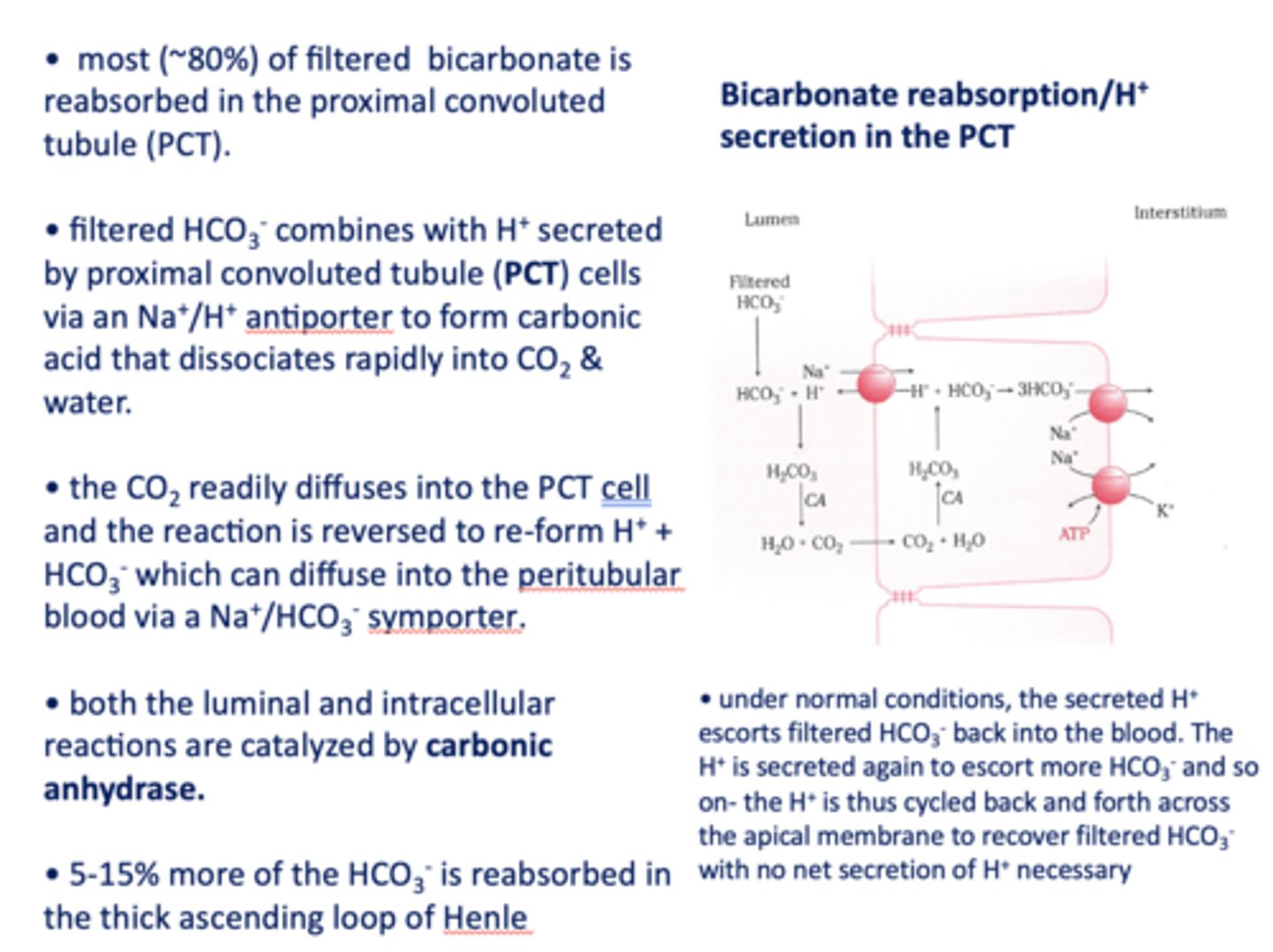
5-15% of the HCO3- is absorbed in the ____________
thick ascending loop of henle
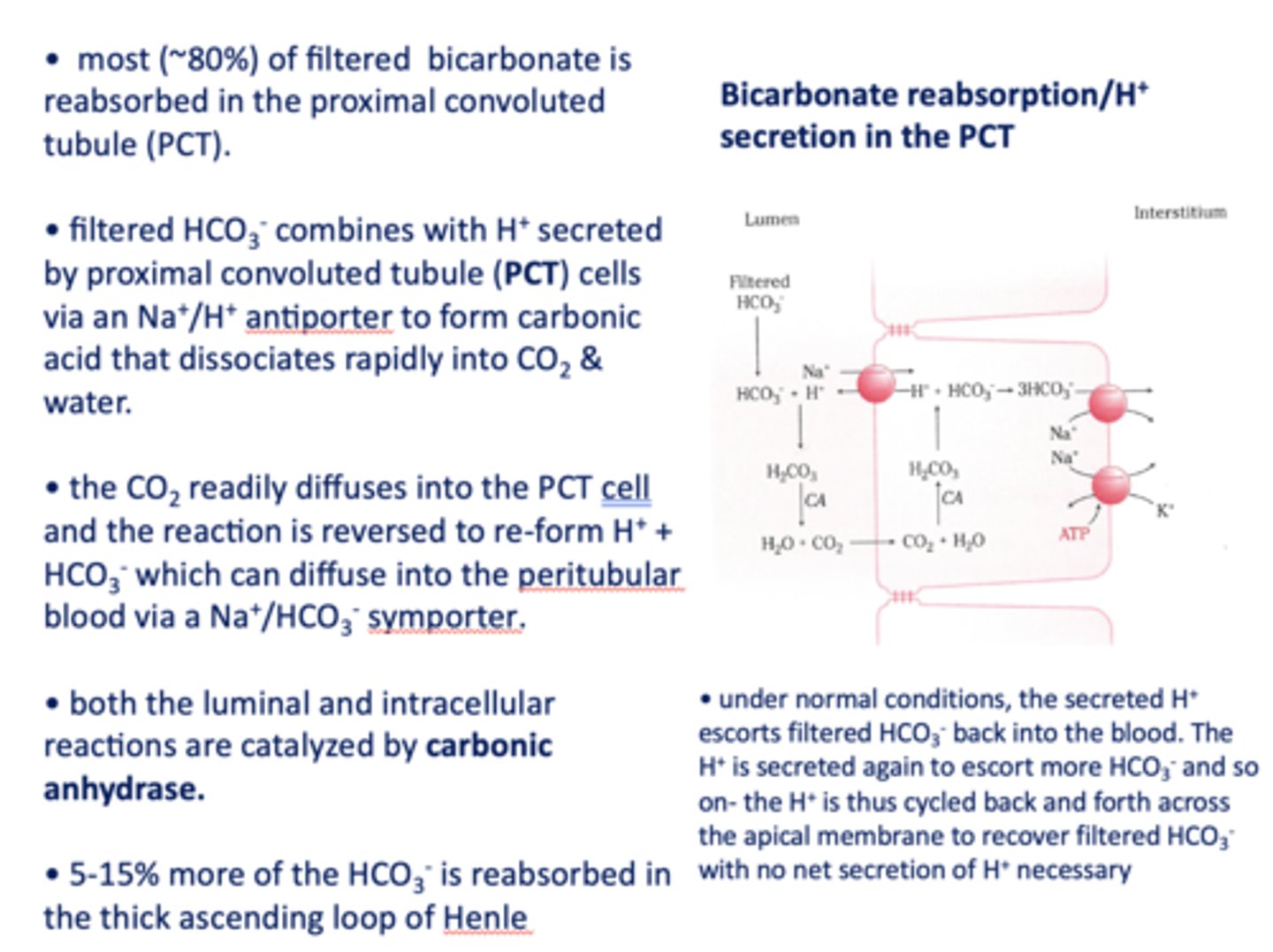
T/F: There is no net secretion of H+ necessary in the bicarbonate reabsorption section in the PCT?
True
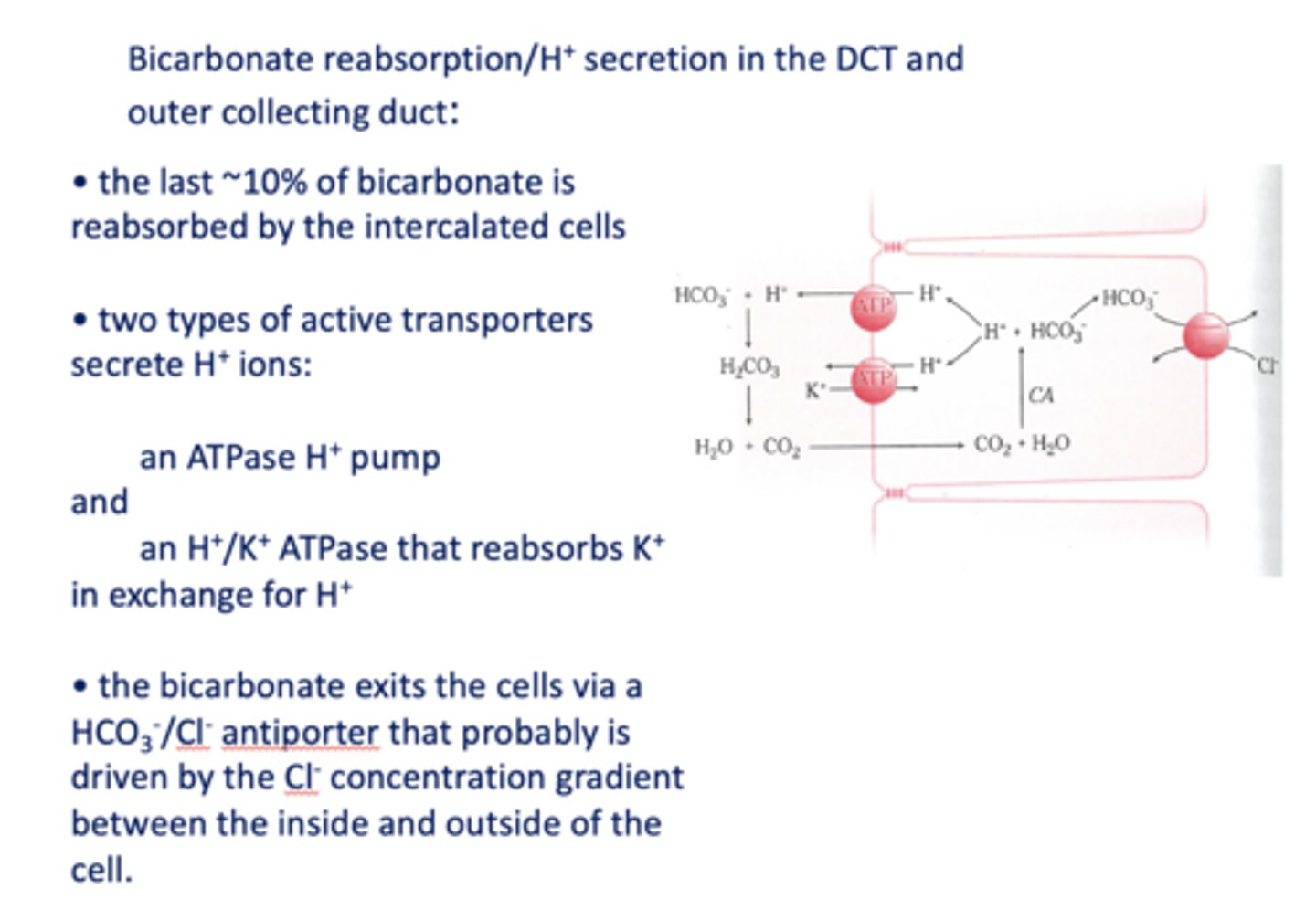
the last ~10% of bicarbonate is reabsorbed by the intercalated cells in the _____
distal convoluted tubule
in the kidneys, the Na+/H+ antiporter is located on the _____ side
lumenal
in the kindeys, the Na+/HCO3- symporter is located on the _____ side
interstitial
What are the two types of active transporters that secrete H+ ions in the DCT/Outer collecting duct?
H+ ATPase pump & K+/H+ ATPase
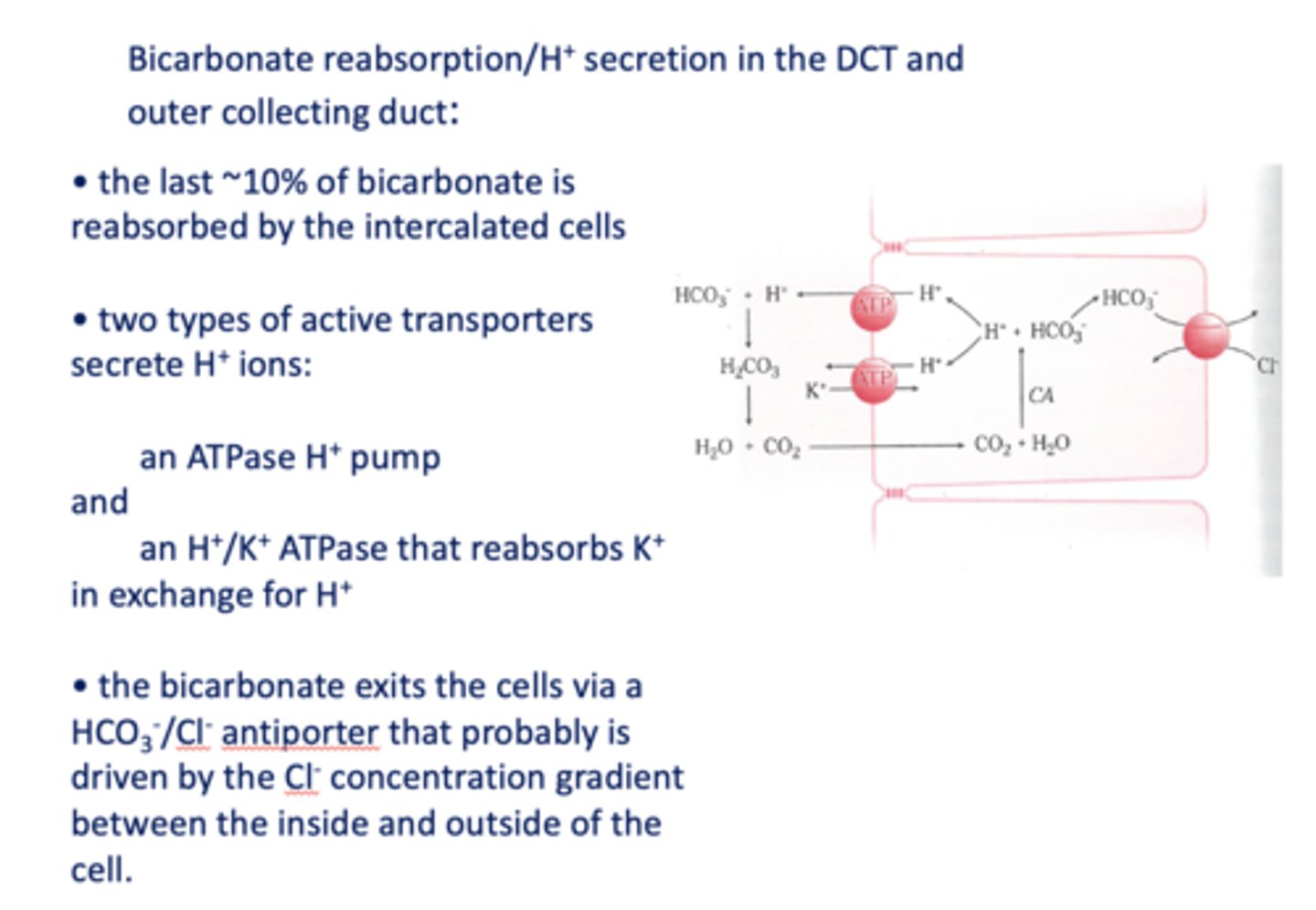
In DCT, bicarbonate exits the cell via a _______ that is likely driven by the Cl- concentration gradient
HCO3-/Cl- antiporter
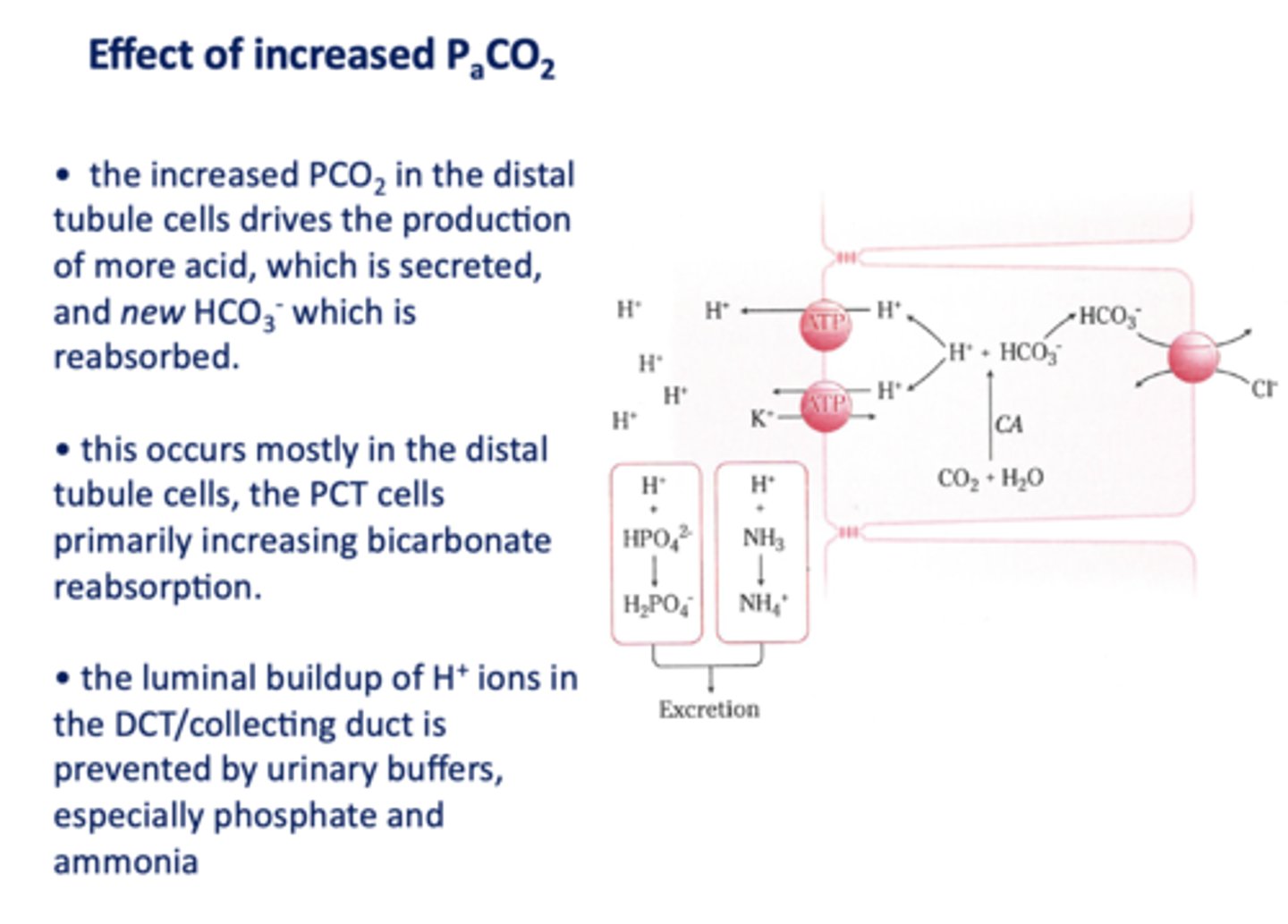
an increase in PCO2 in the DCT will result in more H+ secreted into the lumen, causing more ______ to be reabsorbed
HCO3-
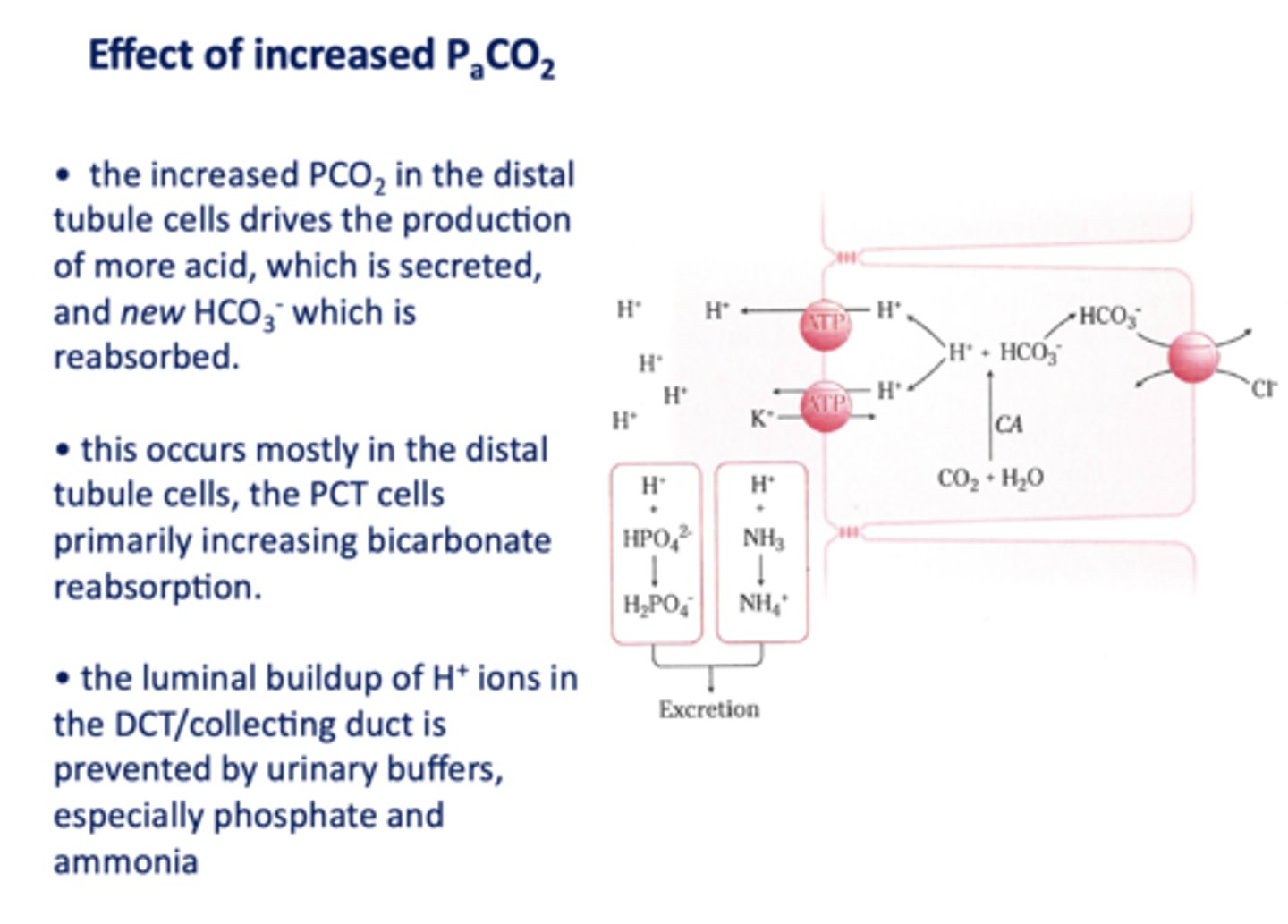
the luminal buildup of H+ ions in the DCT/collecting duct is prevented by urinary buffers, especially ____________ and ____________
phosphate and ammonia
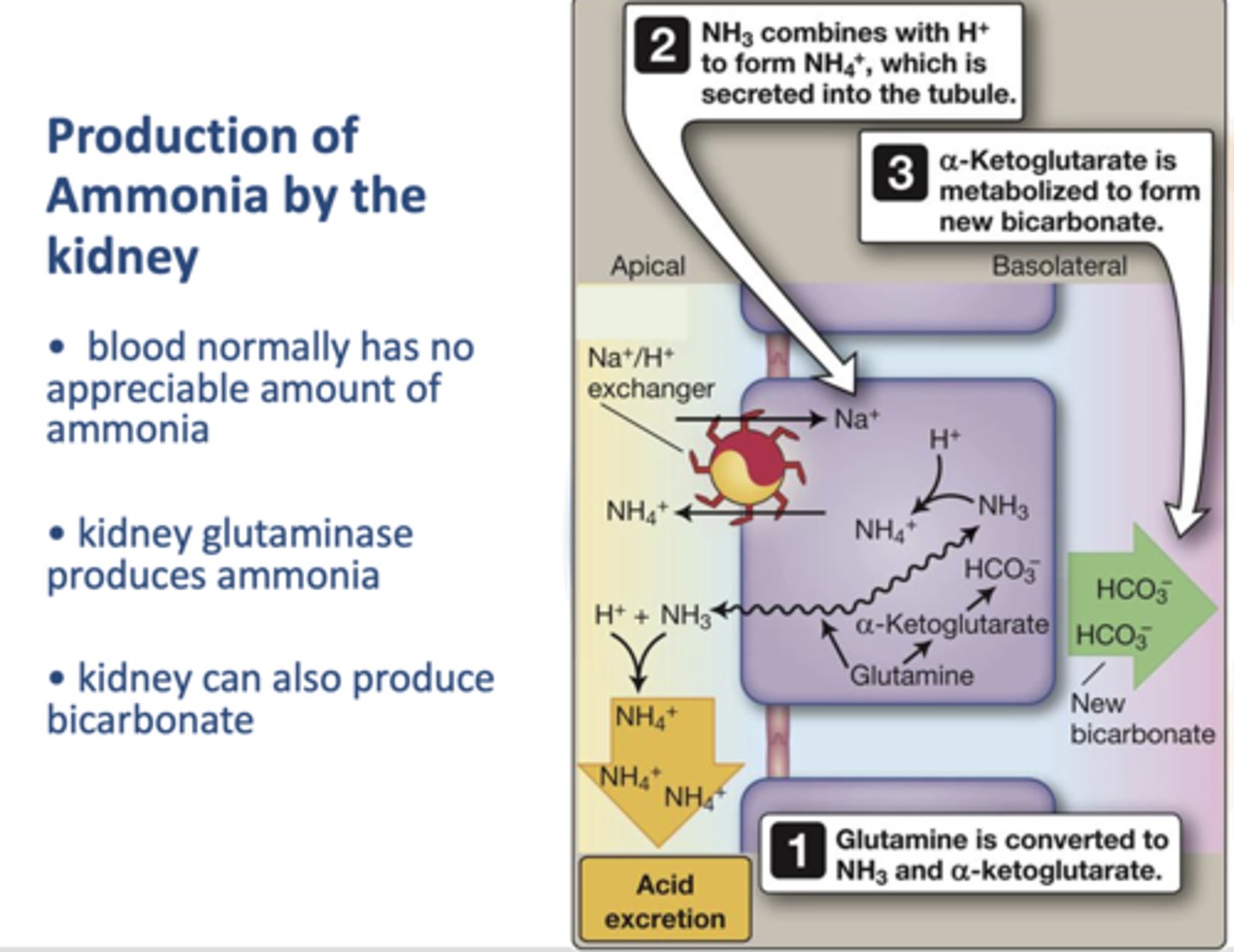
What enzyme in the kidney produces amonia?
Glutaminase
Define the following:
A condition or process that lowers the pH level
acidosis
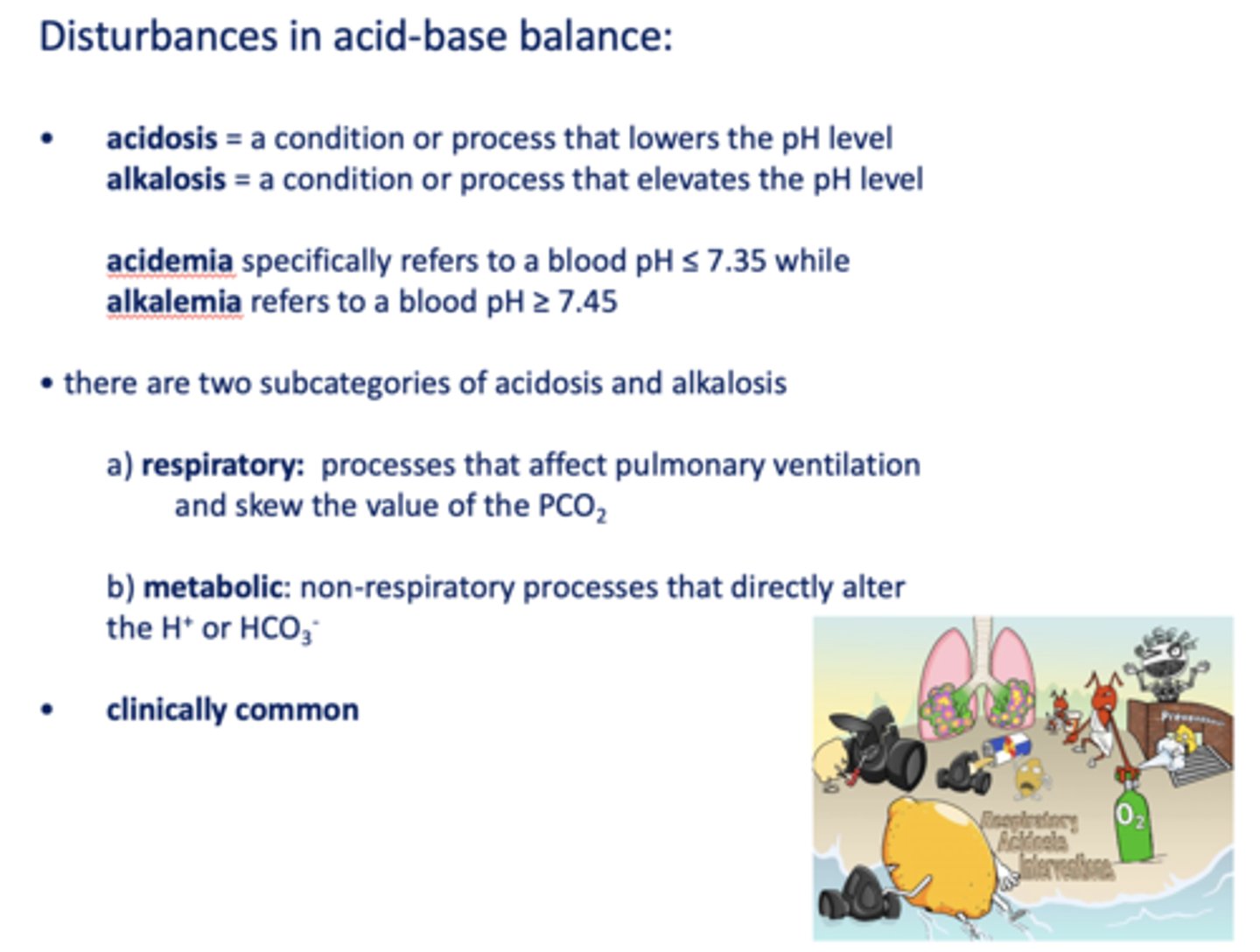
Define the following:
A condition or process that elevates the pH level
alkalosis
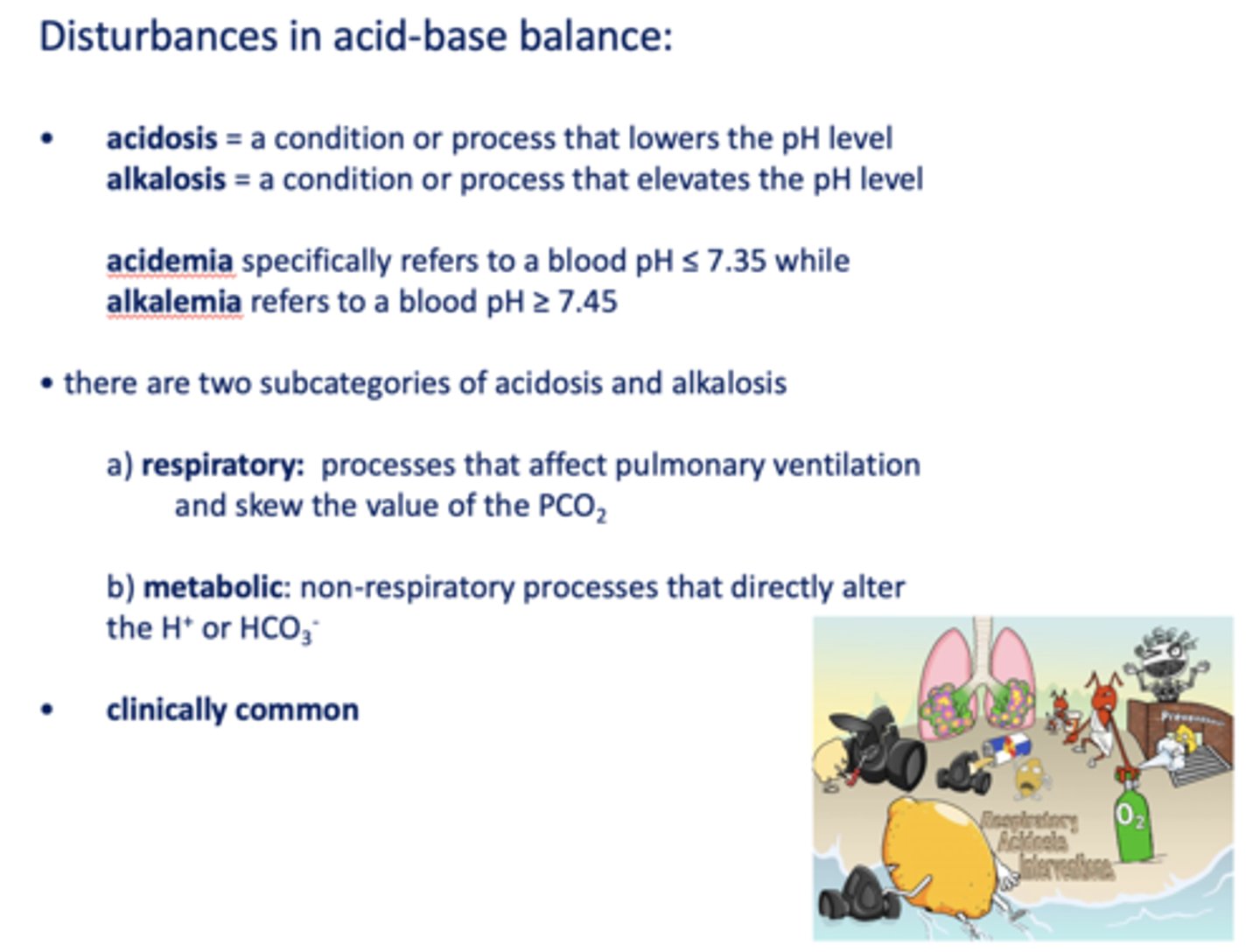
Define the following:
Specifically refers to a blood pH ≤ 7.35 while
acidemia
Define the following:
Refers to a blood pH ≥ 7.45
alkalemia
Define the following:
Processes that affect pulmonary ventilation and skew the value of the PCO
respiratory
Define the following:
Non-respiratory processes that directly alter the H+ or HCO3-
metabolic
What has the following characteristics?
- Decreased pulmonary ventilation
- Raises the PCO2
- Drives the reaction to the right
- Thereby increasing H+ and HCO3-:
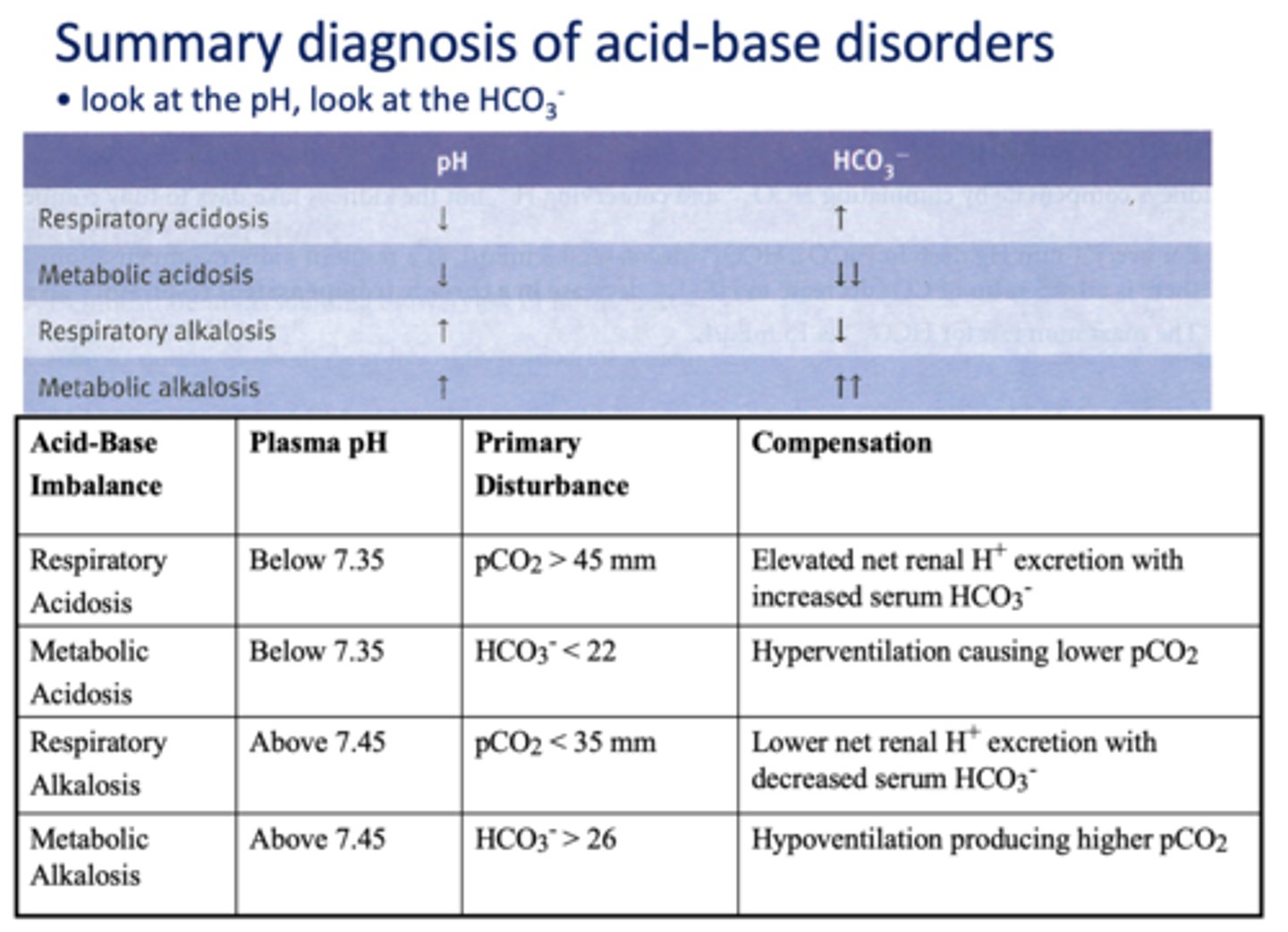
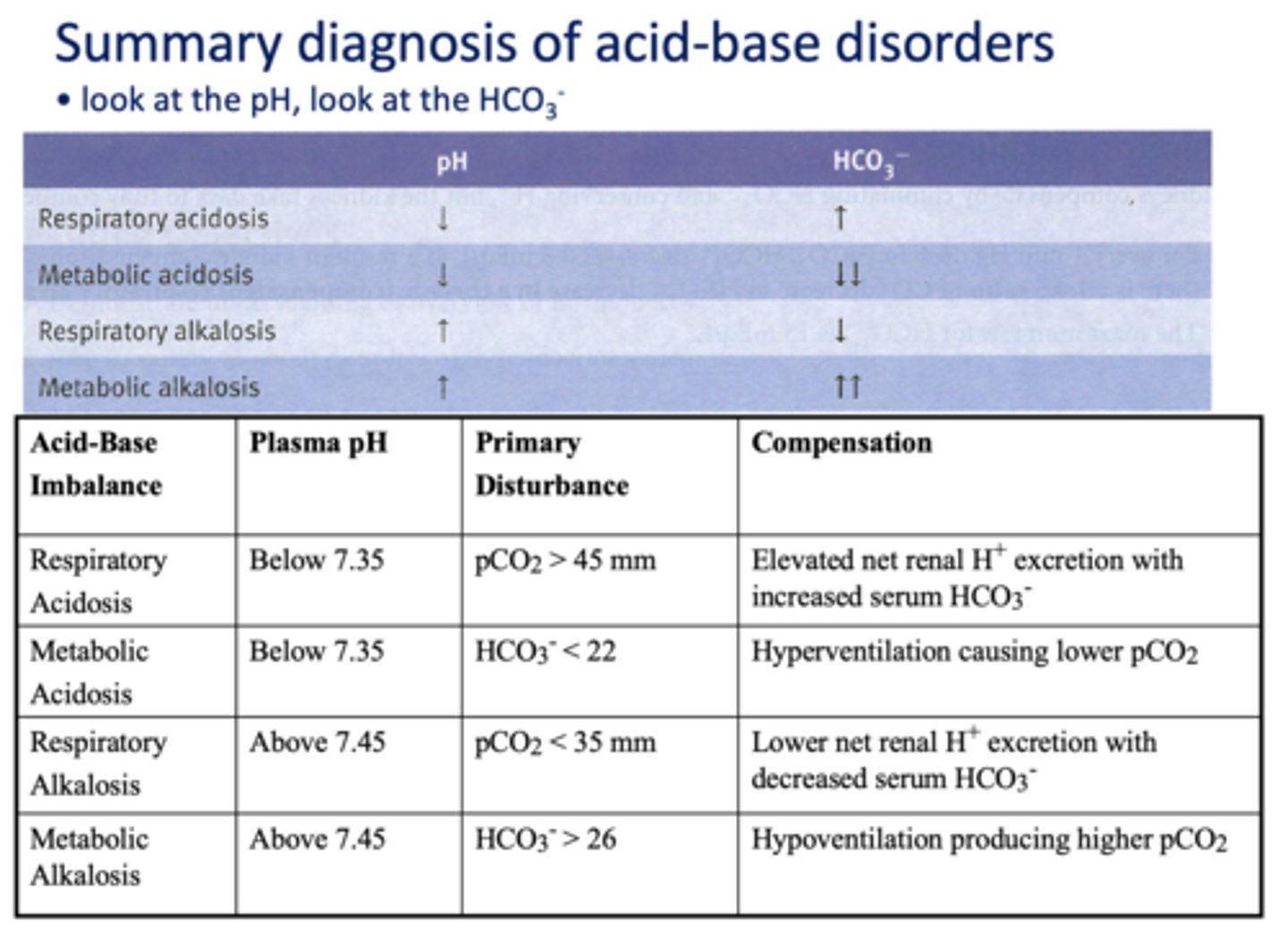
respiratory acidosis
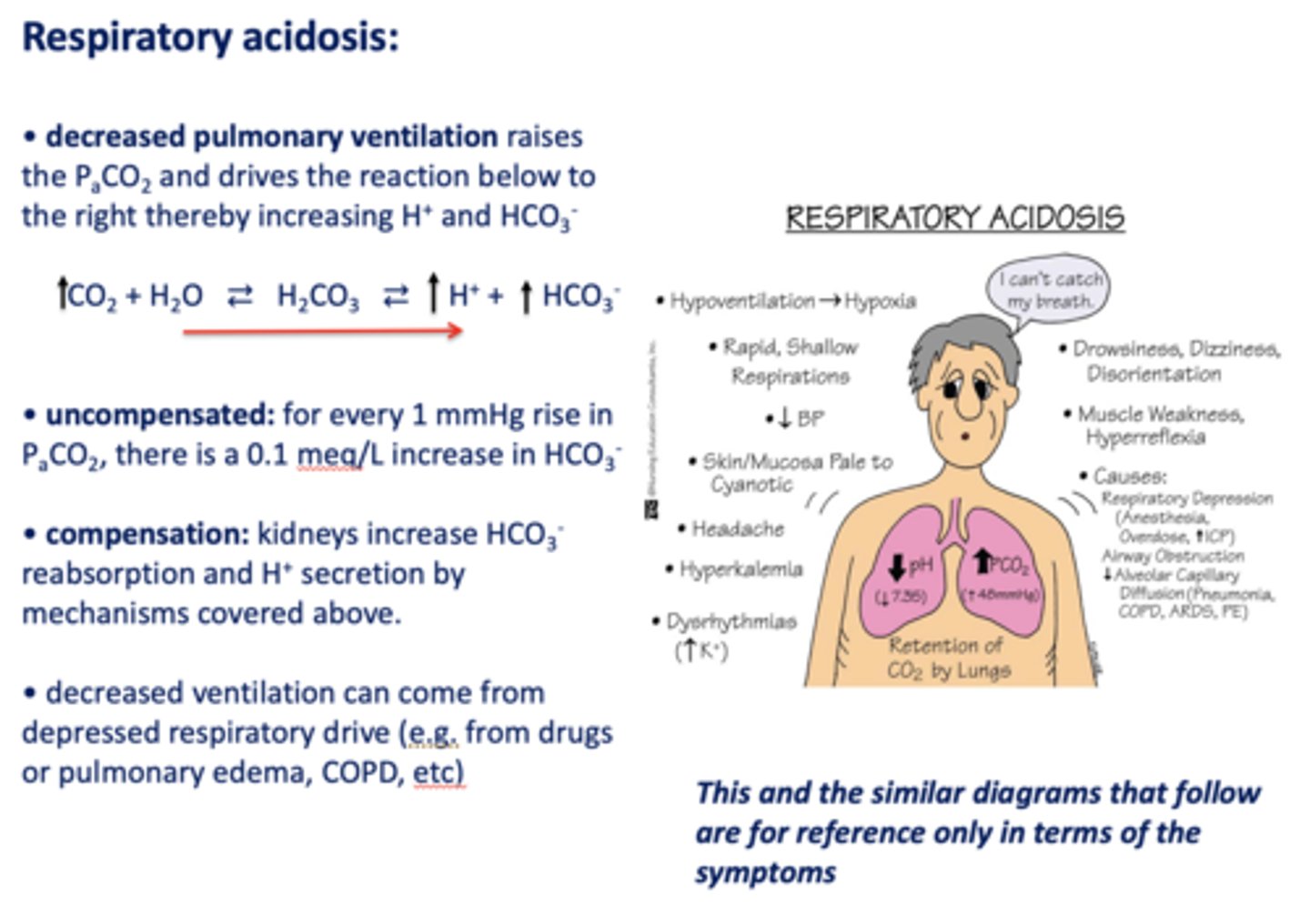
Acid/base disturbance characterized by:
- High H+
- High HCO3-
respiratory acidosis
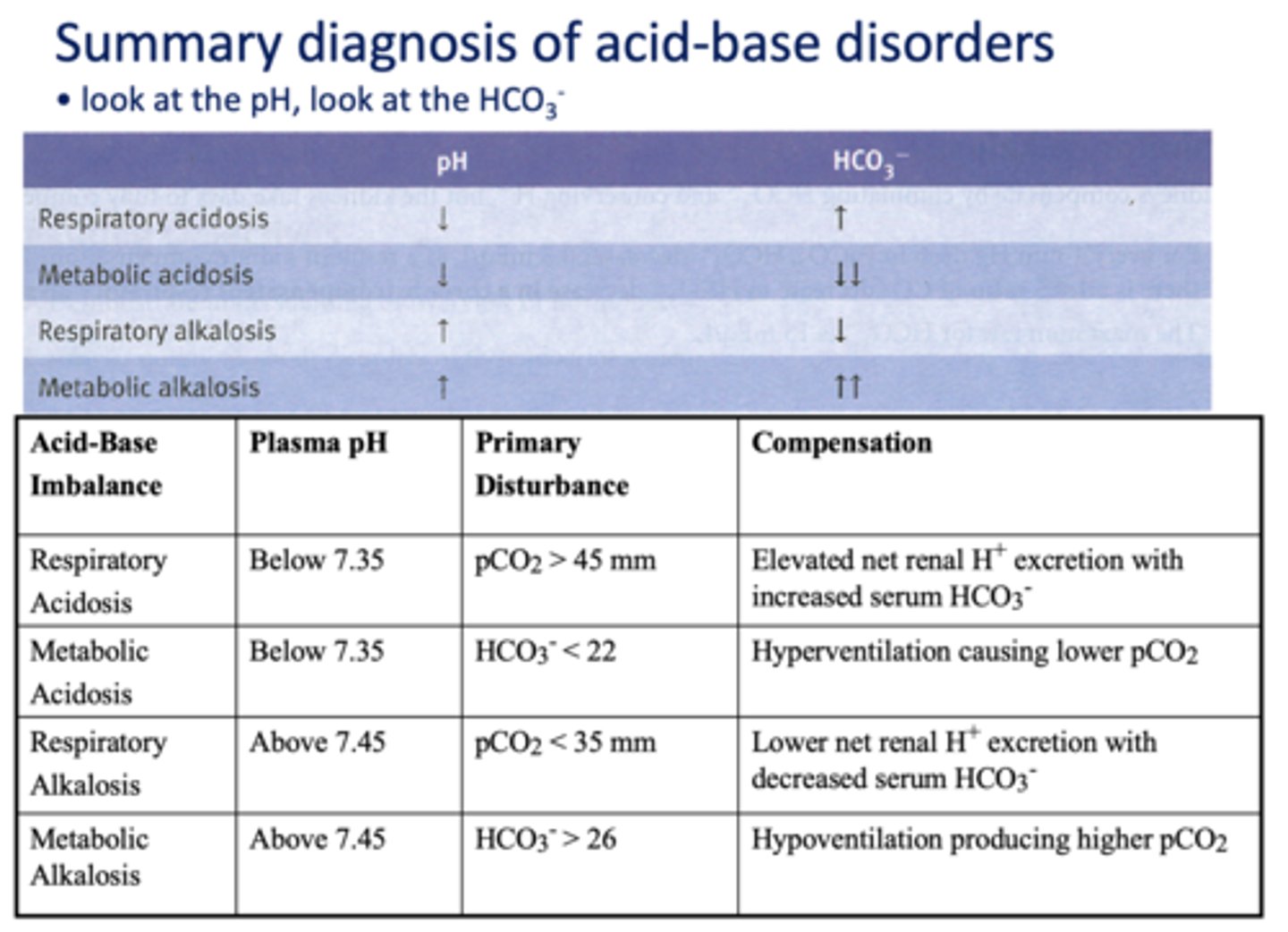
how is respiratory acidosis compensated for?
- Kidney increase HCO3- reabsorption
- H+ secretion
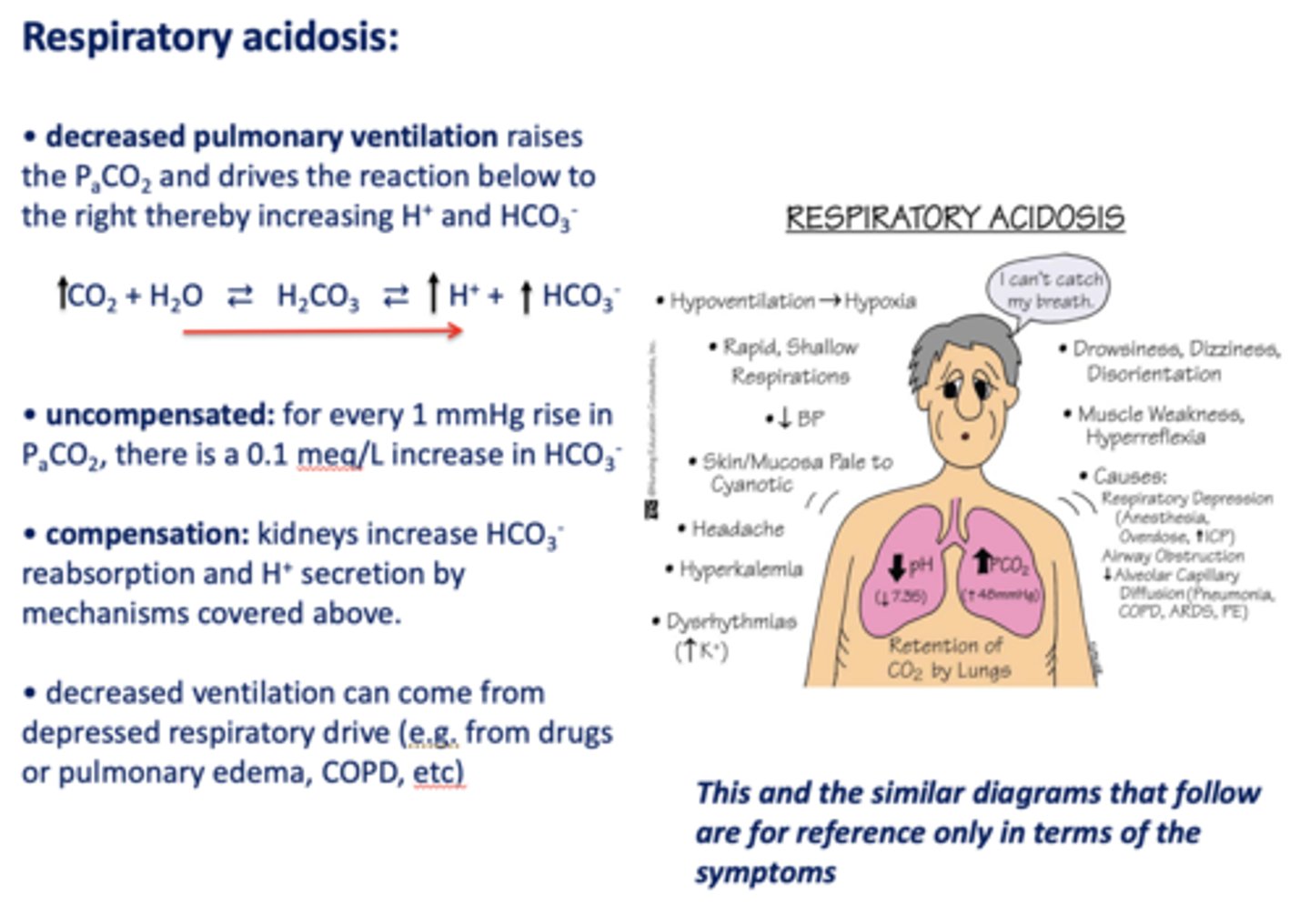
t/f: decreased ventilation can occur from depressed respiratory drive i.e. drugs, pulmonary edema, asthma, COPD etc
True
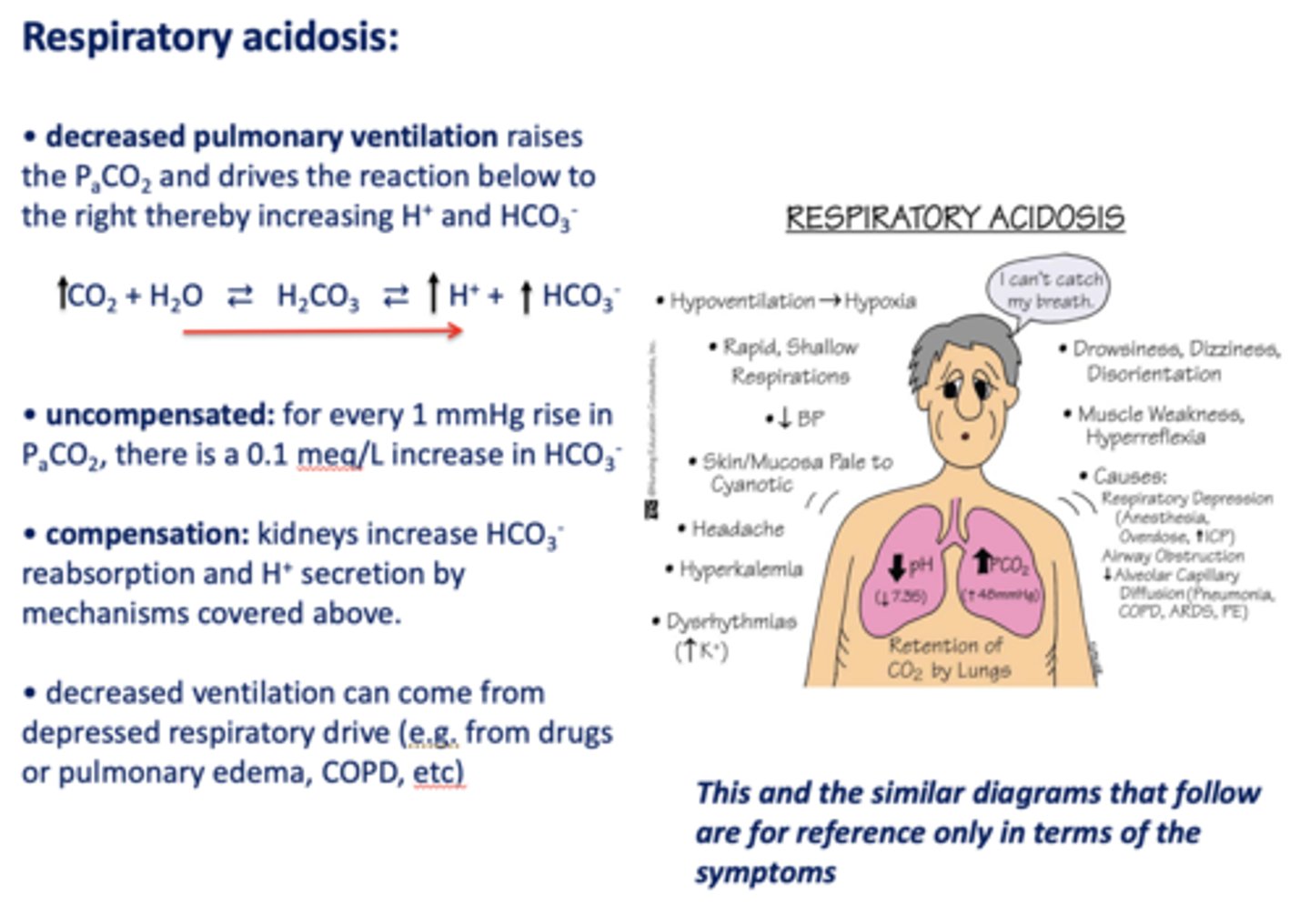
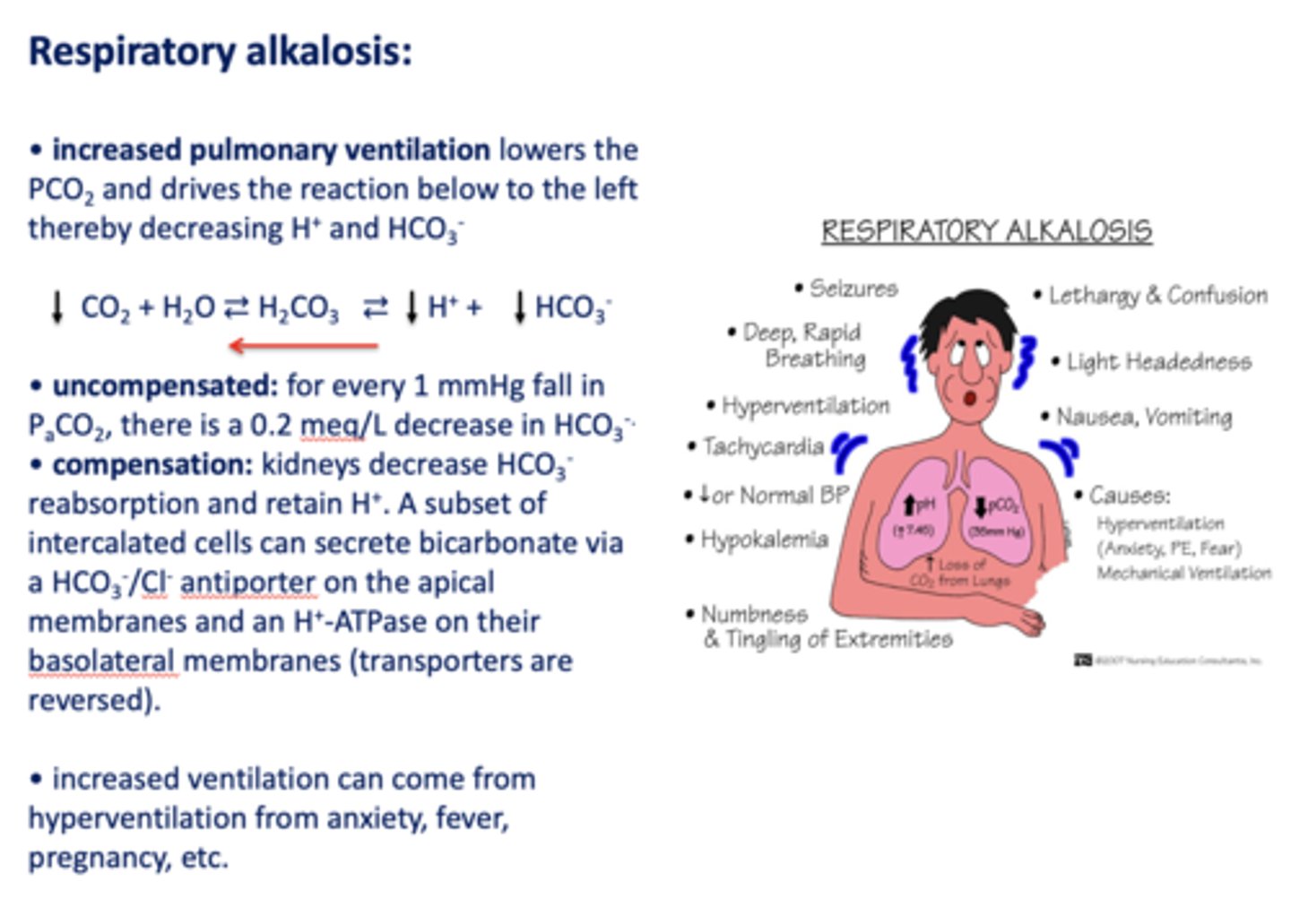
Define the following:
Increased pulmonary ventilation lowers the PCO2 and drives the reaction below to the left thereby decreasing H+ and HCO3-
respiratory alkalosis
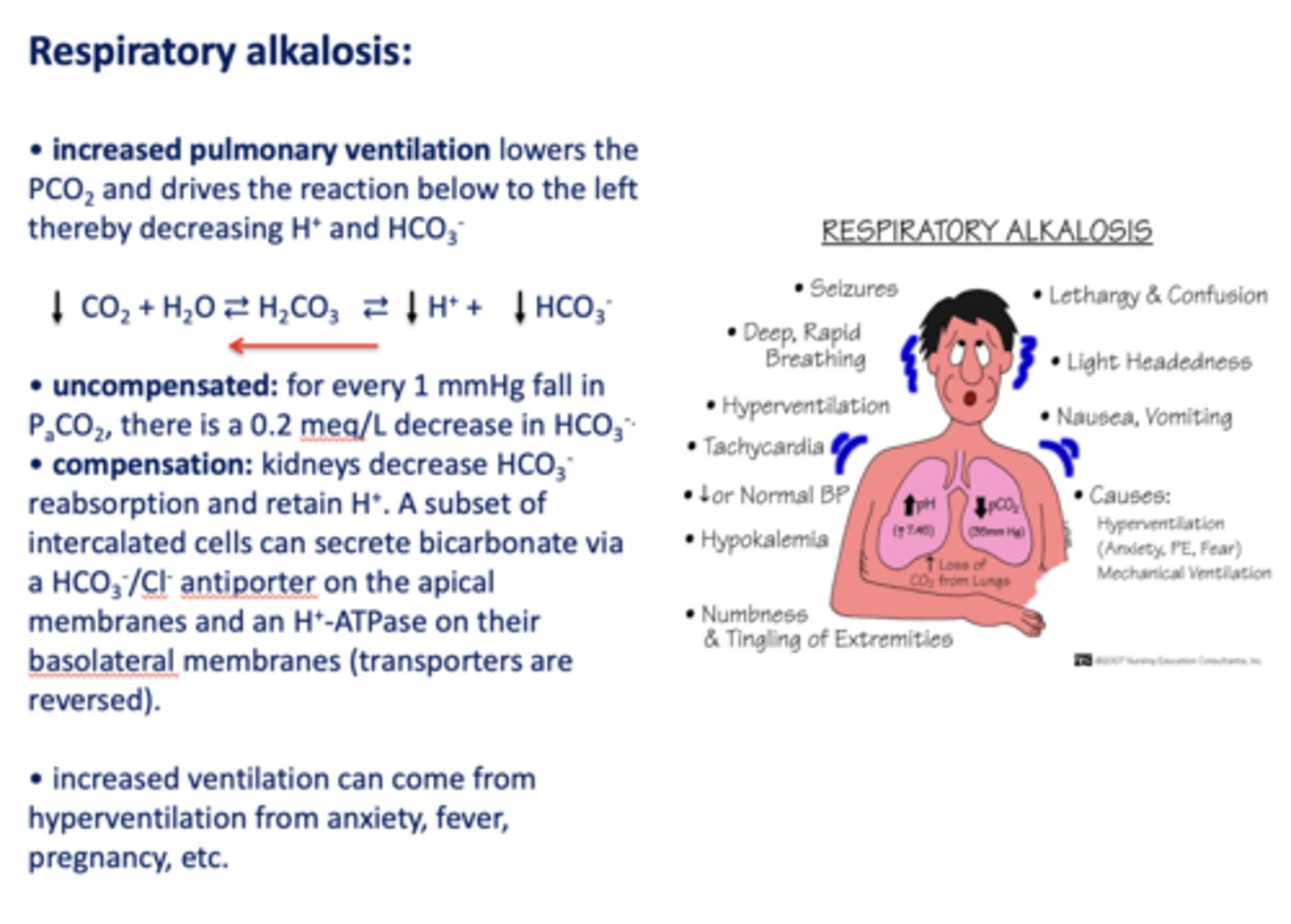
Acid/base disturbance characterized by:
- Low H+
- Low HCO3-
respiratory alkalosis
how is respiratory alkalosis compensated for?
- Kidneys decrease HCO3- reabsorption
- Retain H+
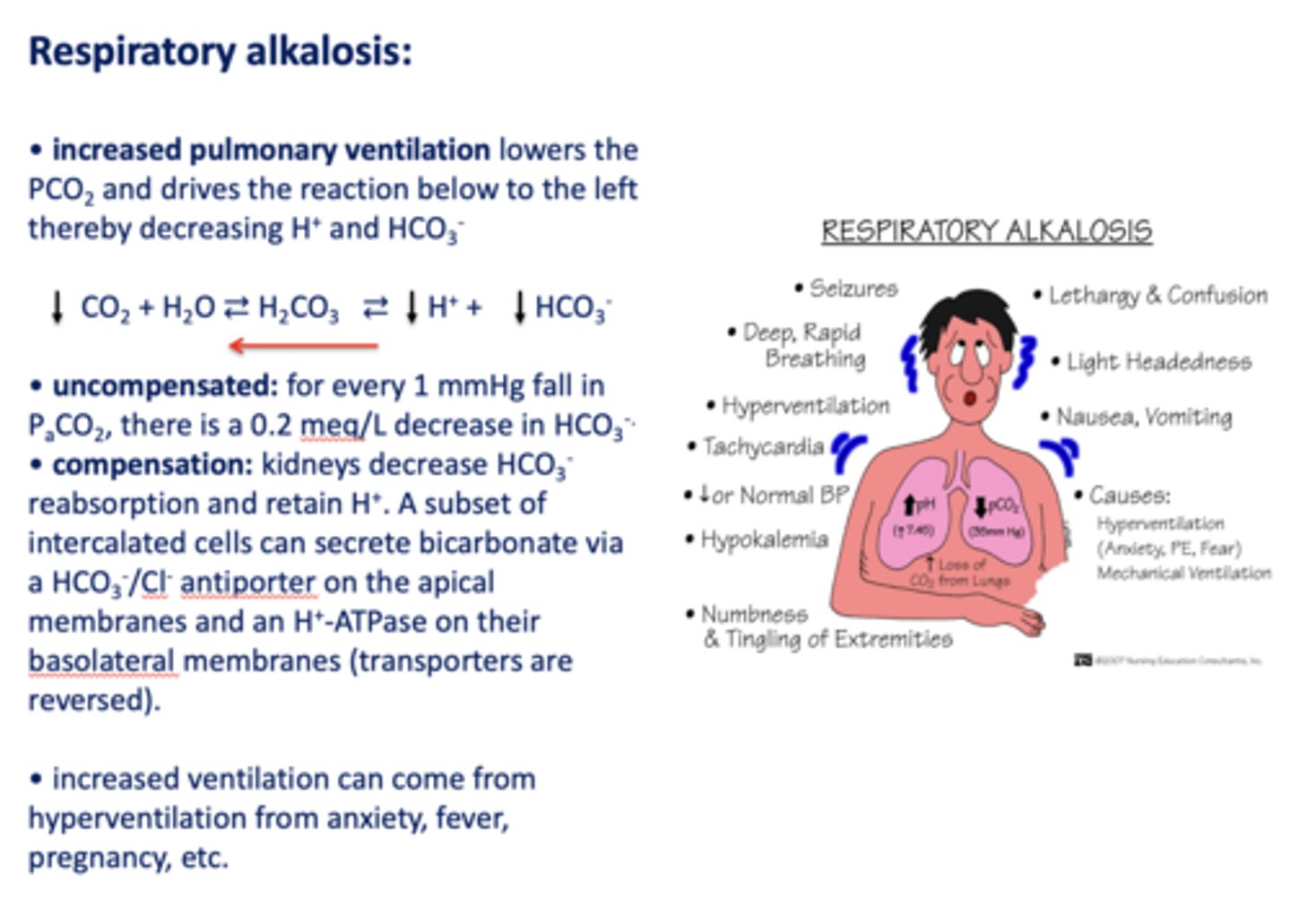
What has the following characteristics?
Compensation: kidneys decrease HCO3-reabsorption and retain H+. A subset of intercalated cells can secrete bicarbonate via a HCO3-/Cl- antiporter on the apical membranes and an H+-ATPase on their basolateral membranes (transporters are reversed)
respiratory alkalosis
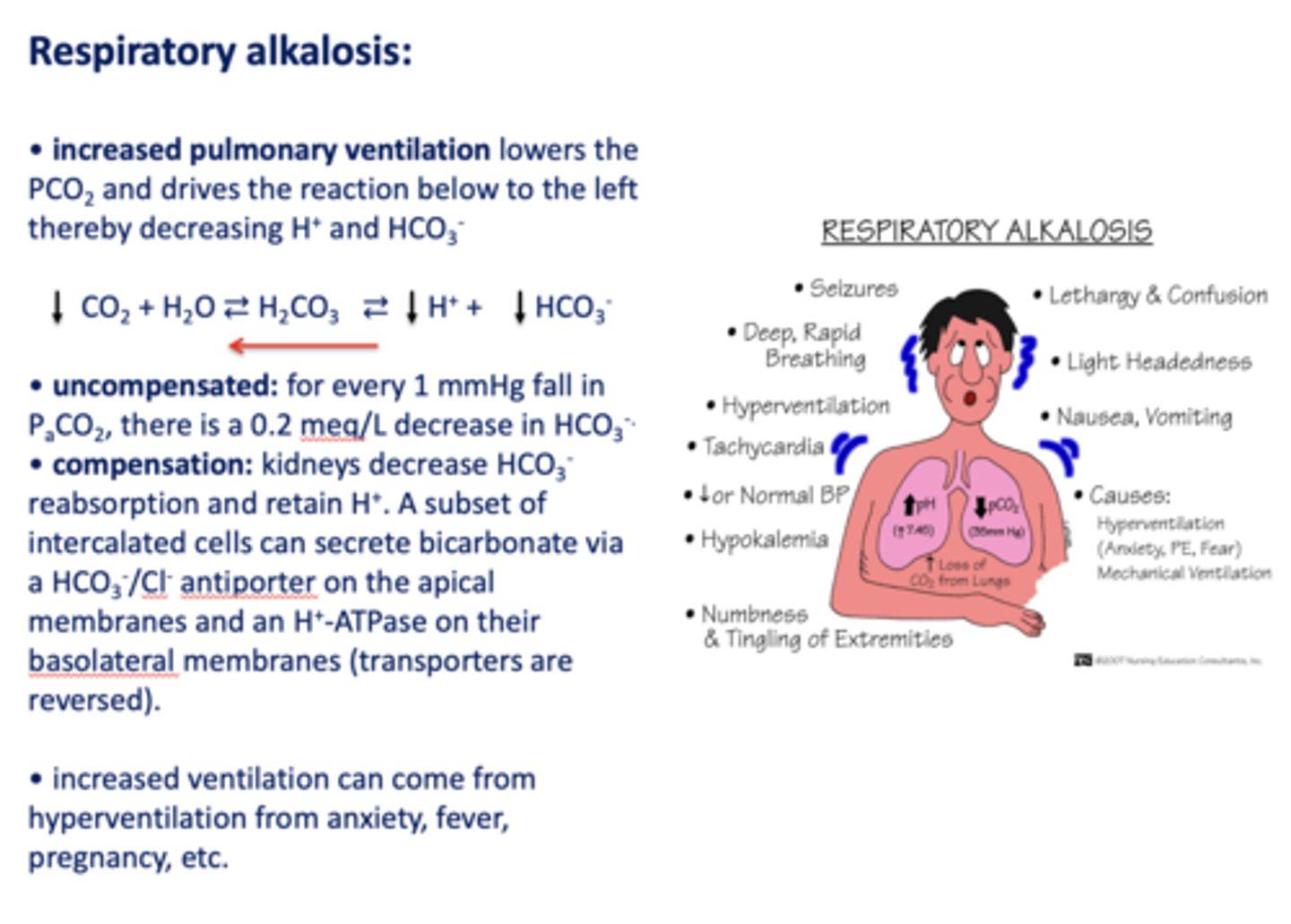
t/f: increased ventilation can come from hyperventilation from anxiety, fever, pregnancy etc.
true
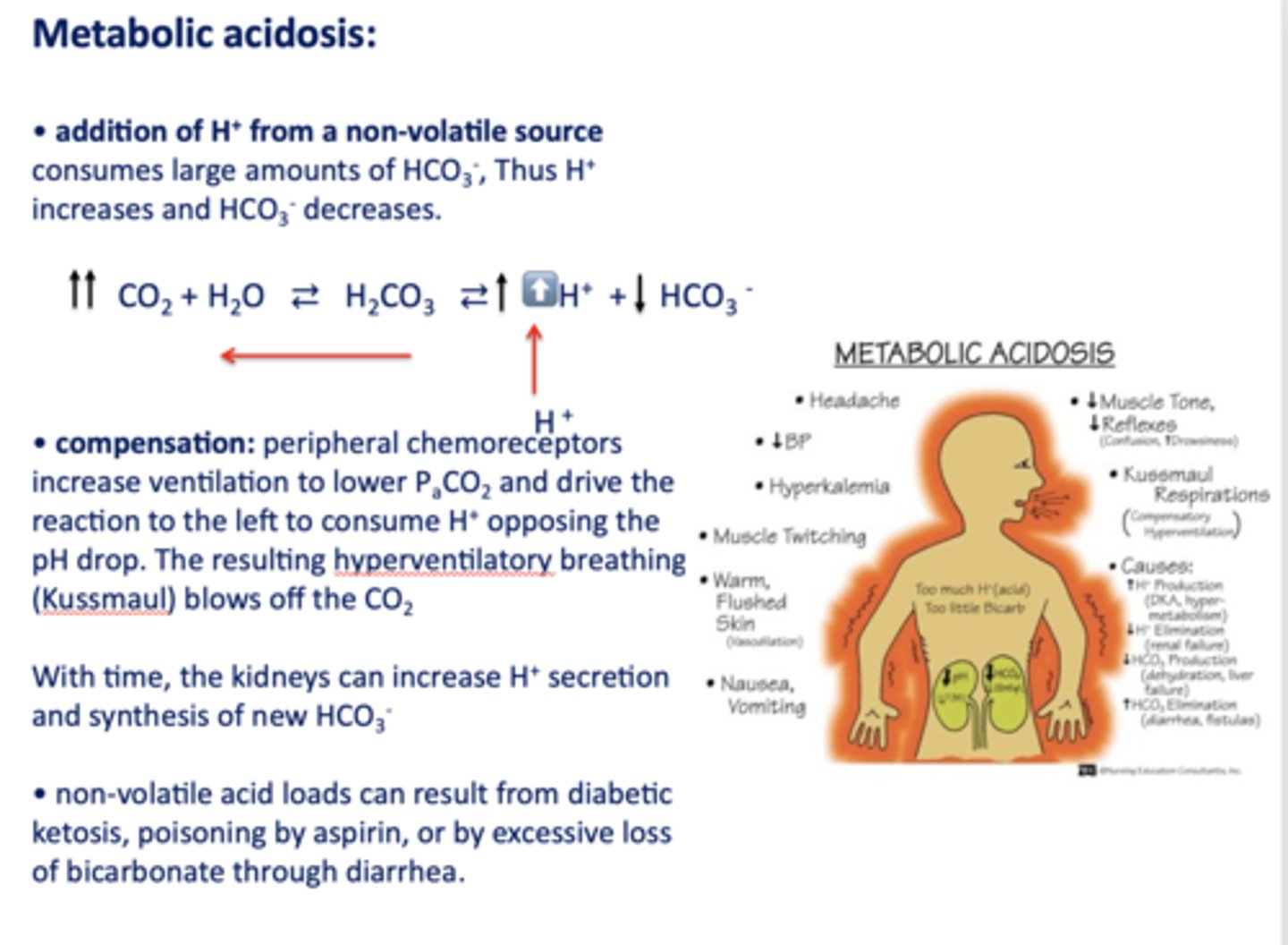
Define the following:
Addition of H+ from a non-volatile source consumes large amounts of HCO3-, Thus H+ increases and HCO3- decreases
metabolic acidosis
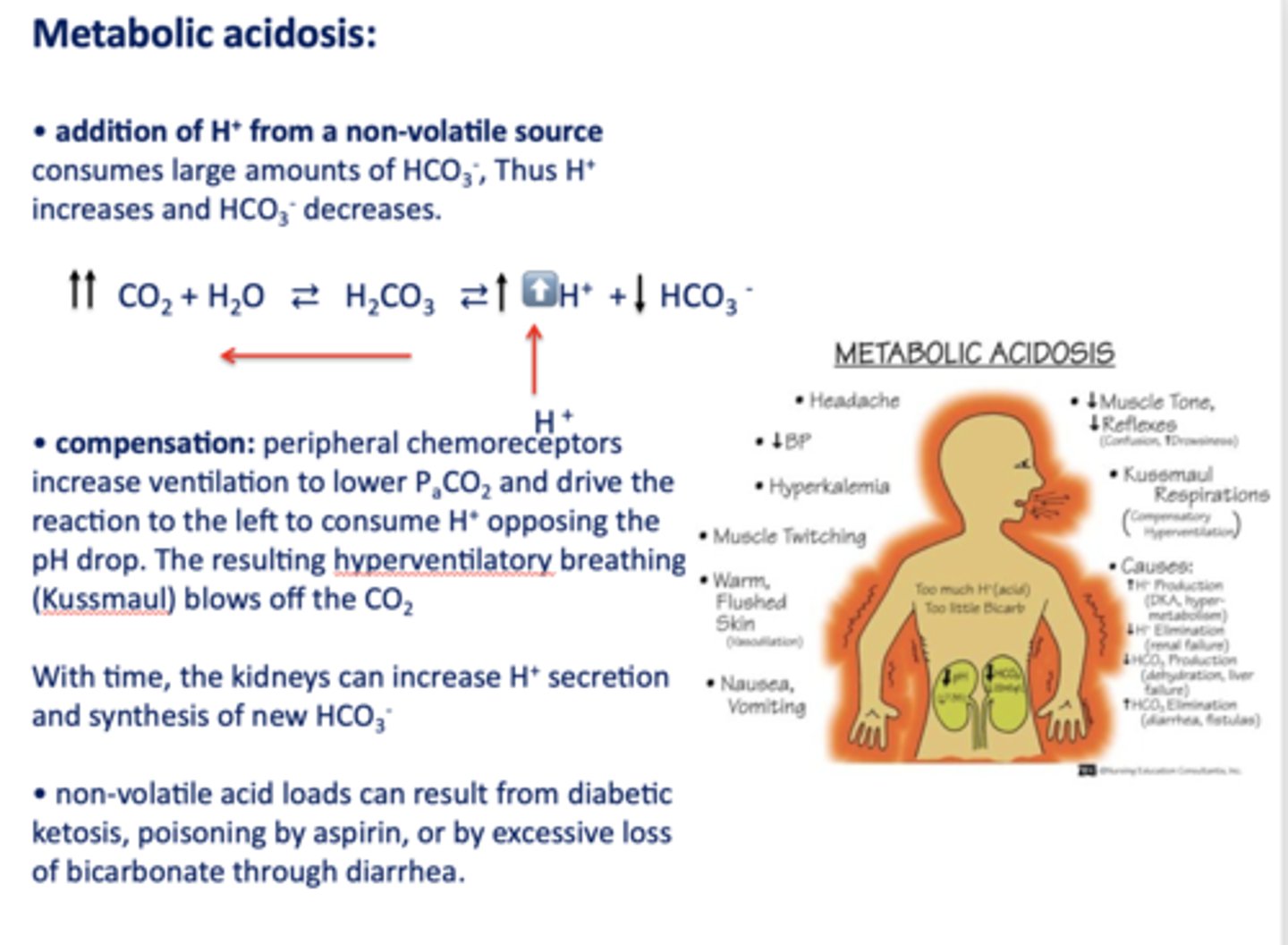
Acid/base disturbance characterized by:
- High H+
- Low HCO3-
metabolic acidosis
What has the following characteristics?
Compensation: peripheral chemoreceptors increase ventilation to lower PaCO2 and drive the reaction to the left to consume H+ opposing the pH drop. (hyperventilatory breathing (Kussmaul))
metabolic acidosis
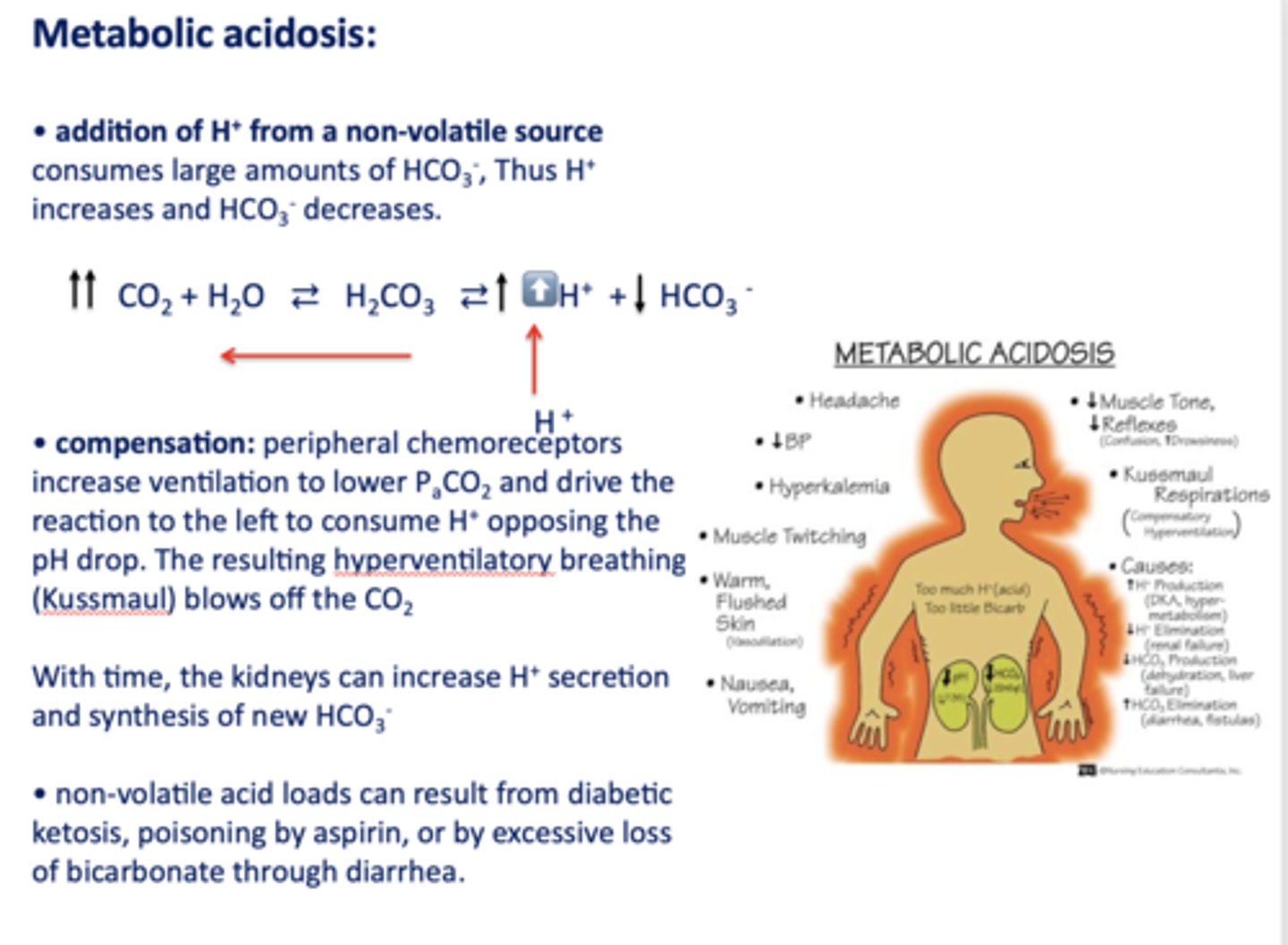
t/f: non-volatile acid loads can result from diabetic ketosis, lactic acid, poisoning by aspirin, ethylene glycol, renal failure or by excessive loss of bicarbonate through diarrhea or urinary excretion
true
when calculating the anion gap, what ions are measured?
- Na+
- Cl-
- HCO3-

the anion gap normally is about _____ meq/liter
6-10

if the anion gap is larger than 6-10 meq/L, this means that _______ is occurring and bicarbonate being used to buffer
metabolic acidosis

acidosis due to bicarbonate loss in diarrhea would _____ the anion gap
decrease
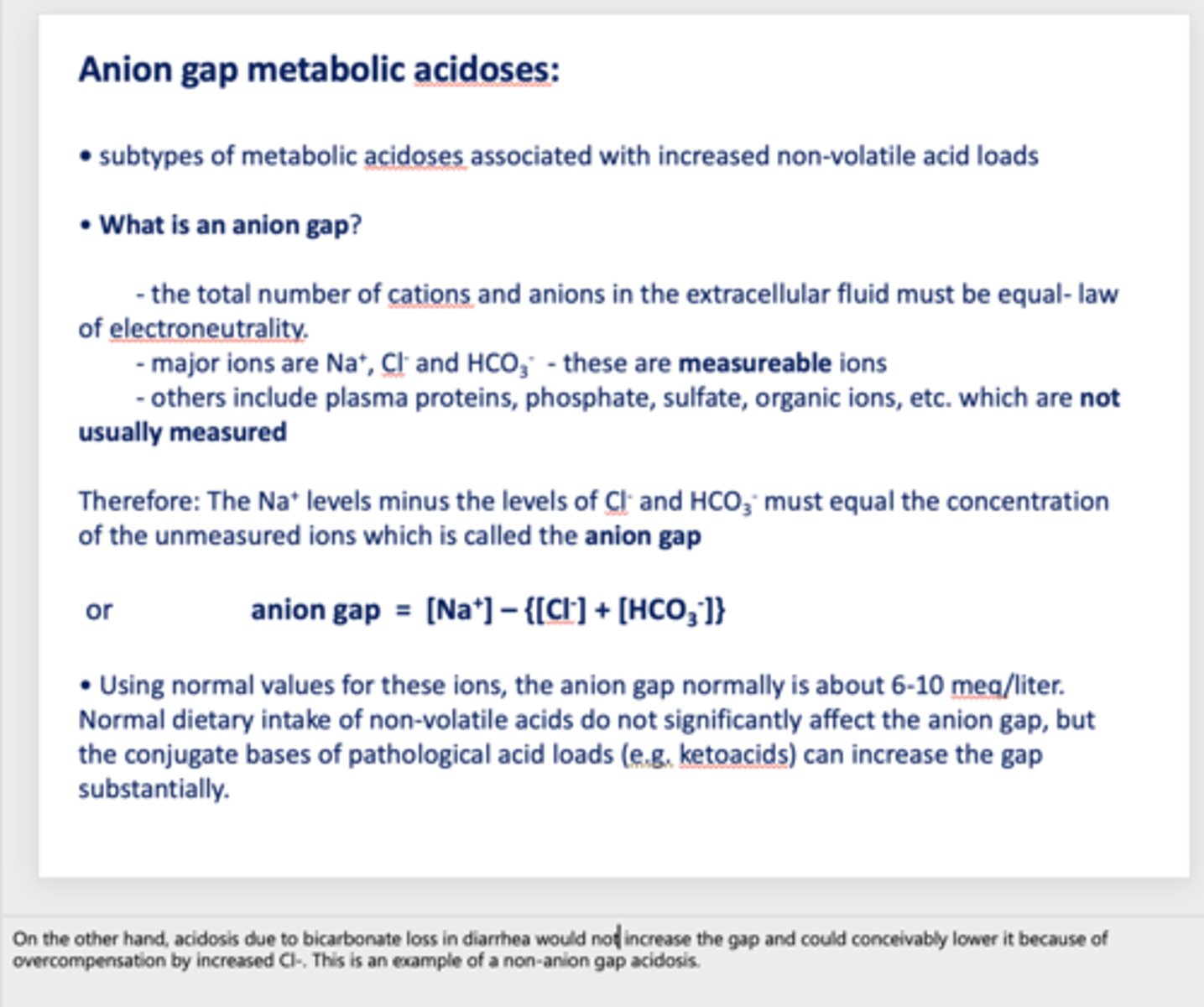
What has the following characteristics?
- The total number of cations and anions in the extracellular fluid must be equal- law of electroneutrality.
- The Na+ levels minus the levels of Cl- and HCO3- must equal the concentration of the unmeasured ions
anion gap

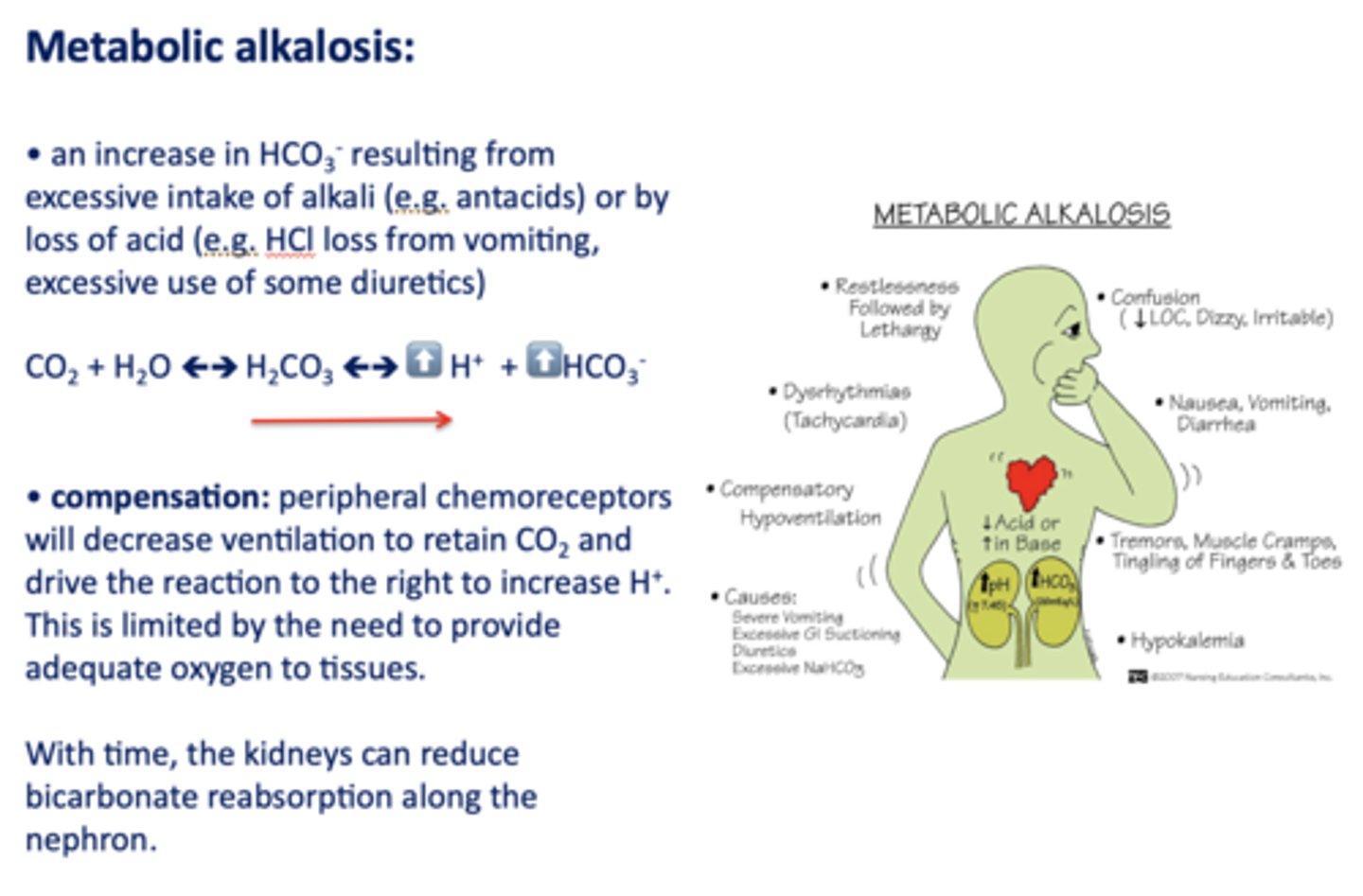
Define the following:
An increase in HCO3- resulting from excessive intake of alkali (e.g. antacids) or by loss of acid
metabolic alkalosis
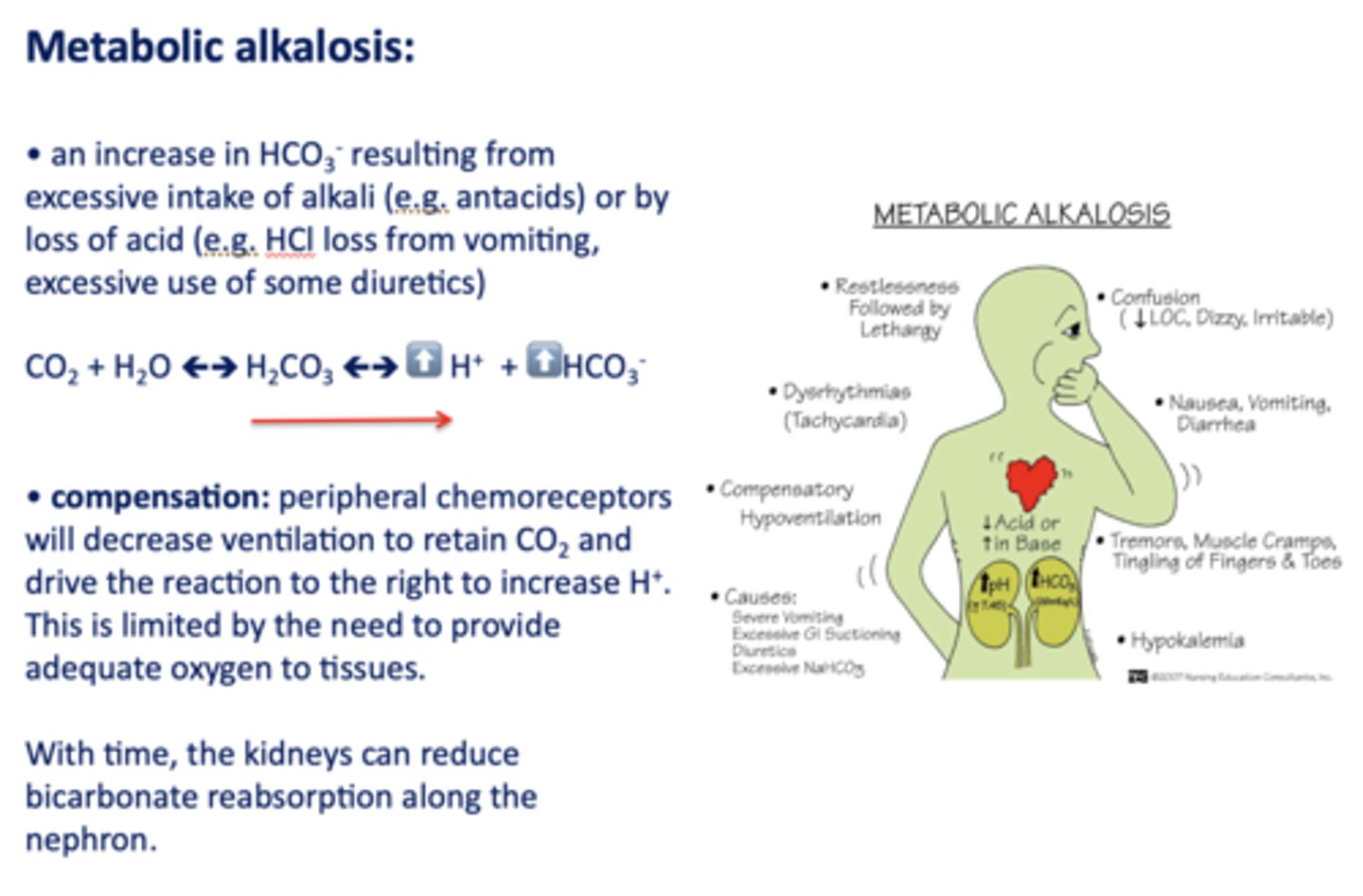
Acid/base disturbance characterized by:
- Low H+
- High HCO3-
metabolic alkalosis
What has the following characteristics?
Compensation: peripheral chemoreceptors will decrease ventilation to retain CO2 and drive the reaction to the right to increase H+.
metabolic alkalosis
in order for the pH to be 7.4, the HCO3-/CO2 ratio must be __
20

Compensation of the HCO3-/CO2 ratio strives to:
A. Recover [HCO3-] back to normal
B. Recover [PCO2] back
C. Bring ratio back to 20
C. Bring ratio back to 20

A deep exhalation will effectively expel which substance from the human body?
A. CO2
B. keto acids
C. hydrated H+
D. lactic acid
A. CO2

If the VCO2 (the volume of CO2 generated by the tissues per minute) increases, and VA (the alveolar ventilation) is unchanged, what will happen to the partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood?
A. decrease
B. increase
C. stay the same
D. cannot be predicted
B. increase

Which organ of the human body is used to most regulate bicarbonate and H+ levels in the blood on a time scale of hours to days?
A. kidney
B. heart
C. lung
D. colon
A. kidney

Which organ of the human body is used to most regulate CO2 levels in the blood on a time scale of minutes?
A. kidney
B. heart
C. lung
D. colon
C. lung

Excretion of H+ in the DCT cells of the kidney requires?
A. ATP
B. K+ symport
C. Na+ symport
D. passive transport of H+ through a pore
A. ATP

Which of the following best represents the lab values in an individual who is hyperventilating?
A. decreased pH, elevated bicarbonate (HCO3-)
B. decreased pH, decreased bicarbonate (HCO3-)
C. increased pH, decreased bicarbonate (HCO3-)
D. increased pH, elevated bicarbonate (HCO3-)
C. increased pH, decreased bicarbonate (HCO3-)

An individual who has diabetes has run out of insulin. Furthermore, the individual ate something that caused diarrhea. The most likely lab values would show
A. decreased pH, elevated bicarbonate (HCO3-)
B. decreased pH, decreased bicarbonate (HCO3-)
C. increased pH, decreased bicarbonate (HCO3-)
D. increased pH, elevated bicarbonate (HCO3-)
B. decreased pH, decreased bicarbonate (HCO3-)
