MEDRADSC 3Y03 - Substitute Decision Maker
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
According to the Health Care Consent Act, what is the time limit on consent?
None
T/F: Consent does not need to be in writing
True
T/F: Consent can be implied from pt actions and behaviours
True
T/F: Obtaining consent may not be delegated to other health practitioners
False
Who is still responsible legally if consent is delegated to other health practitioners?
Main provider
In an event of an emergency, is consent required?
No, if the wishes of the pt are unknown
When can a dr override SDM?
Emergency
SDM not honouring pt’s wishes
SDM not acting in best interest of pt
T/F: Consent can be withdrawn anytime by pt or SDM
True
Who is responsible for determining capacity/decision-making skills of pt?
Responsible physician
Who else may help a physician assess capacity/decision-making skills?
Other practitioners that have skill and judgement while remaining responsible legally
Who can pt appeal their decision to?
Consent and Capacity Board (CCB)
SDM
Substitute decision maker
SDM definition
Someone entitled by law to make healthcare decision on behalf of pt w/o capacity to make decisions for themselves regarding tx, admission to long term care and personal assistance services
3 types of SDM
Family members
Persons appointed legally by pt prior to being incapacitated
Ontario Public Guardian and Trustee
SDM of last resort
Ontario Public Guardian and Trustee
Requirements to be an SDM
Capable of making decision that’s required
16 y/o or older
Not requiring care of their own
Willing to take responsibility
Available, be reachable by phone within time frame, distance not an impediment
If there are more than 1 SDM of equal ranking (e.g siblings), how can they decide?
Must be able to reach consensus regarding healthcare decisions
Who cannot be an SDM?
Someone paid to provide you w personal care unless they’re your spouse, partner or relative (e.g nurse, PSW)
Mentally incapable
under 16 y/o
Requires care of their own
SDM Hierarchy
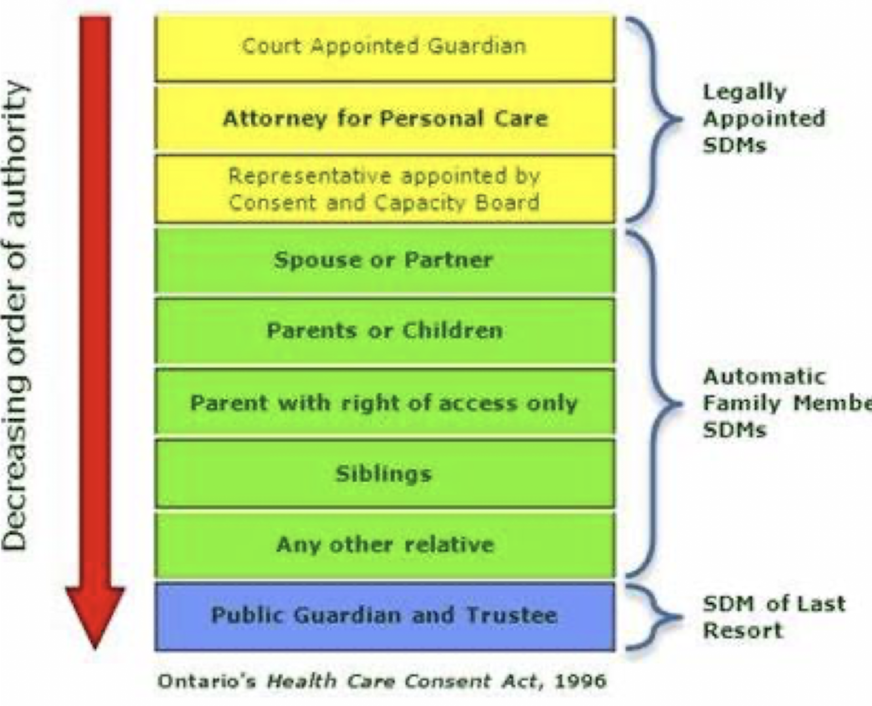
Spouse
Married
Lived in common law relationship for 1 year
Parents of a child together
Entered into cohabitation agreement under Family Law Act
Partner
Lived together for at least 1 year
Close personal r/s that is of primary importance in both lives
May be non-sexual
Child
Child of their birth or adoptive parents/step-parents
Any other relative
People related by blood, marriage or adoption
What happens when no one meets the requirements or willing to be the SDM?
Ontario Public Guardian and Trustee becomes the SDM
T/F: Ontario Public Guardian and Trustee (OPGT) is not a govt agency
False
What happens when 2 SDMs of equal ranking cannot agree on decisions?
OPGT steps in
T/F: OPGT has less duties and responsibilities as other SDMs
False
Advance Care Planning (ACP)
Process of preparing a person and their SDM abt making decisions in future if necessary
What is discussed in ACP while the pt is capable?
Pt’s healthcare wishes, values and beliefs about future care
ACP wishes are not
Informed consent to care
Directions to healthcare practitioners
Role of ACP
Guide SDM in providing informed consent
ACP may be provided in written or oral form. What takes precedence?
Neither
If neither written or oral form takes precedence, what other factor does?
Whichever is more recent
T/F: Advance directives, living wills are part of the Health Care Act
False
Is ACP voluntary or mandatory?
Voluntary
T/F: Health care facilities must require pts to use forms to write down their wishes
False
T/F: ACP is not only focused on end-of-life care
True