Chapter 4 - Tissue: The Living Fabric
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Define Tissue
→ Groups of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common or related function
Individual body cells are specialized
Each type performs specific functions that maintain homeostasis
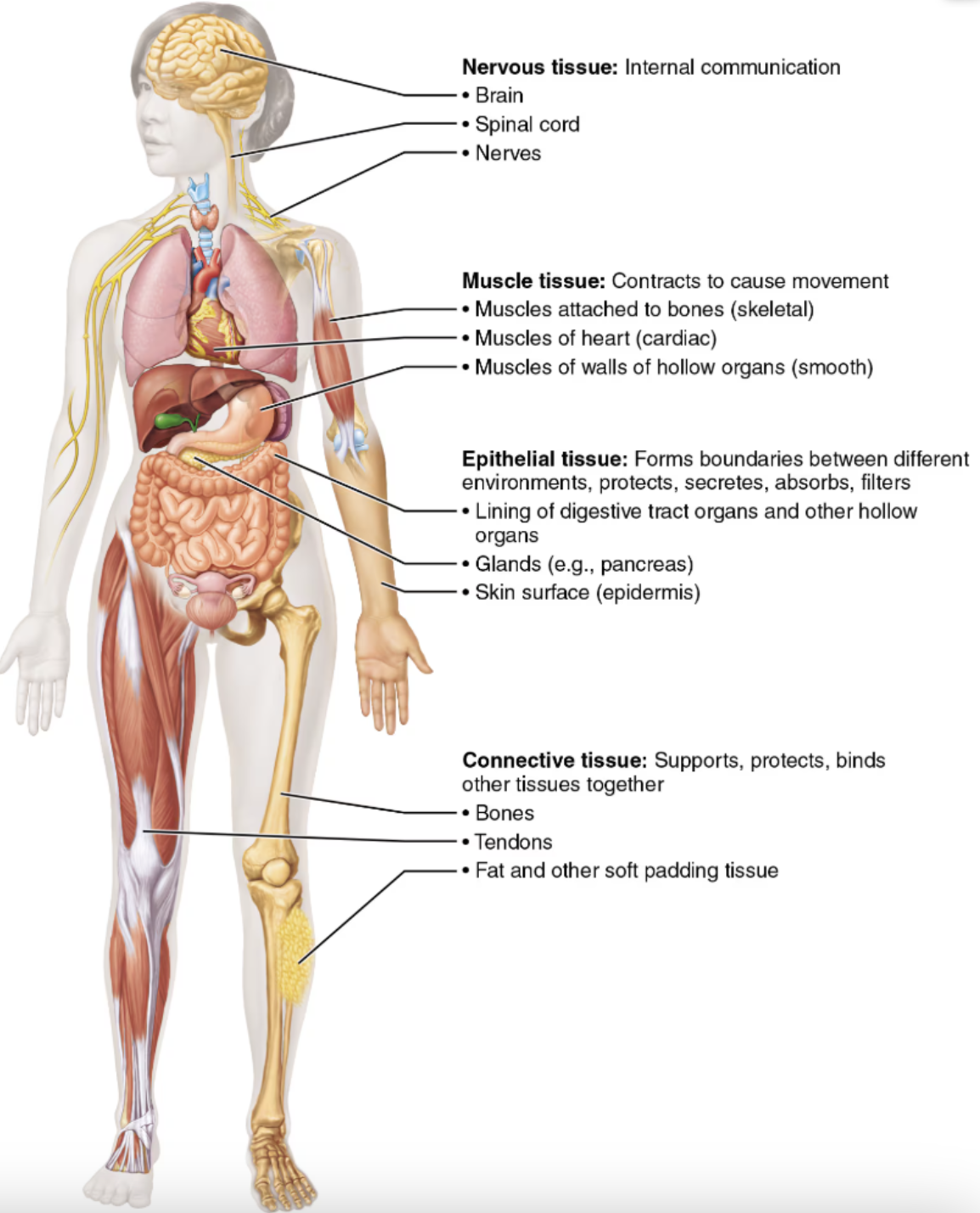
List the four basic tissue types
Epithelial tissue⇒ Forms boundaries between different environments, protects, secretes, absorbs, filtersConnective tissue⇒ Supports protects, binds other tissues togetherMuscle tissue⇒ Contracts to cause movementNervous tissue⇒ Internal communication
Examples of the four basic tissue types
Epithelial tissueLining of digestive tract organs and other hollow organs
Glands (EX: pancreas)
Skin surface( epidermis)
Connective tissueBones
Tendons
Fat and other soft padding tissue
Muscle tissueSkeletal → Muscles attached to the bones
Cardiac → Muscles of heart
Smooth → Muscles of walls of hallow
Nervous tissueBrain
Spinal cord
Nerves
Define Epithelial Tissue
A a layer of cells that covers body surfaces or cavities
Forms boundaries between different environments, protects, secretes, absorbs, and filters
List the functions of Epithelial Tissue
Protection
Absorption
Filtration
Excretion
Secretion
Sensory reception
List the special distinguishing characteristics epithelial tissue
Protective/secretory/absorptive lining
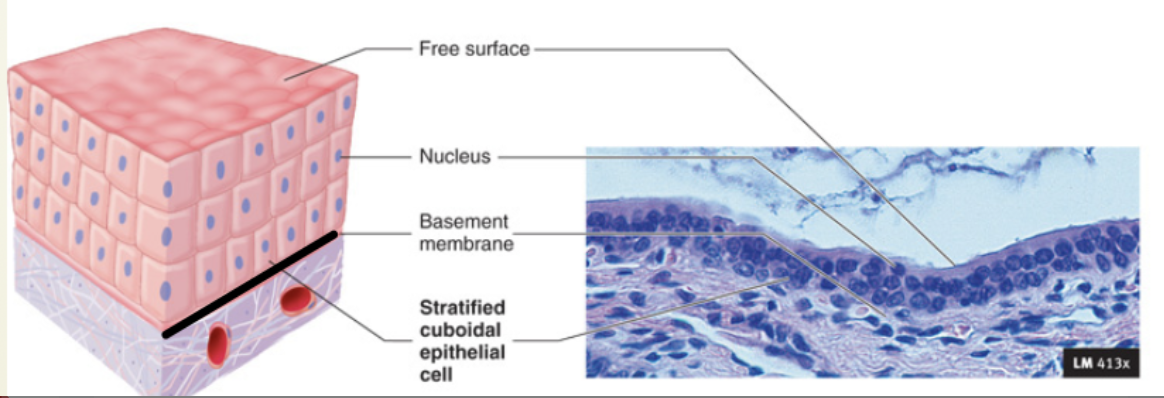
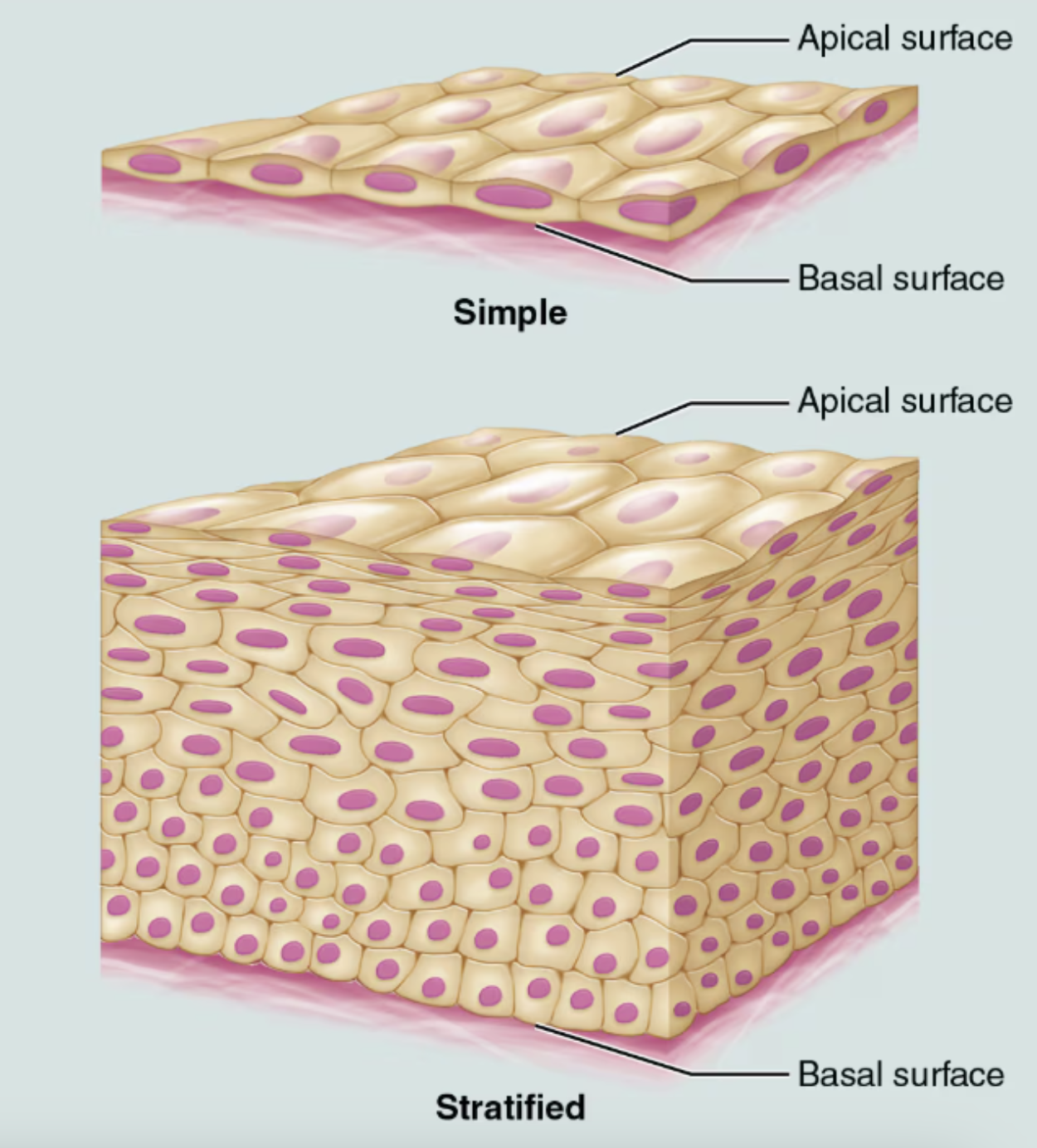
Apical surface - “Free surface”
Polarity
Basement membrane
Support from connective tissue
Tightly packed
Specialized contacts
Avascular
Avascularity
Basal cells readily divide
High regenerative capacity
Explain what it means that Epithelial tissue has is Protective/secretory/absorptive lining
Protective → Basal surface ⇒ the surface near the base or interior of a structure; nearest the lower side or bottom of a structure
Basal lamina → Noncellular, adhesive supporting sheet consisting largely of glycoproteins secreted by epithelial cells; acts as a selective filter that determines which molecules diffusing from the underlying connective tissue are allowed to enter the epithelium & also acts as scaffolding along which epithelial cells can migrate to repair a wound
Absorptive lining → Apical surface ⇒ the surface that faces the outside of the body or the inner cavity of an organ
Microvilli → tiny projections on the free surfaces of some epithelial cells; increase surface area for absorption
Cilia → Tiny, hairlike projections of a cell; may move in a wavelike manner to propel substances across the exposed cell surface
Explain what it means that Epithelial tissue has an Apical Surface
Polarity → epithelia have two surfaces that differ in structure and function:
Apical surface ⇒ the surface that faces the outside of the body or the inner cavity of an organ
Microvilli → tiny projections on the free surfaces of some epithelial cells; increase surface area for absorption
Cilia → Tiny, hairlike projections of a cell; may move in a wavelike manner to propel substances across the exposed cell surface
Basal surface ⇒ the surface near the base or interior of a structure; nearest the lower side or bottom of a structure
Basal lamina → Noncellular, adhesive supporting sheet consisting largely of glycoproteins secreted by epithelial cells; acts as a selective filter that determines which molecules diffusing from the underlying connective tissue are allowed to enter the epithelium & also acts as scaffolding along which epithelial cells can migrate to repair a wound
Explain what it means that Epithelial tissue has a Basement membrane
Support from connective tissue → In between the epithelial and connective tissues is a basement membrane that reinforces the epithelial sheet; helps it resist stretching and tearing, and defines the epithelial boundary; consists of two layers:
Basal lamina ⇒ Noncellular, adhesive supporting sheet consisting largely of glycoproteins secreted by epithelial cells; acts as a selective filter that determines which molecules diffusing from the underlying connective tissue are allowed to enter the epithelium & also acts as scaffolding along which epithelial cells can migrate to repair a wound
Retricular lamina ⇒ A layer of extracellular material containing a fine network of collagen fibers; together with the basal lamina, it is a major component of the basement membrane
Explain what it means that Epithelial tissue is Tightly packed
Specialized contacts → epithelial cells fit closely together to form continuous sheets; adjacent cells are tied together by:
Tight junctions ⇒ Prevent substances from leaking through spaces between cells
Desmosomes ⇒ Keep cells from pulling apart
Explain what it means that Epithelial tissue is Avascular
Avascularity → Contains no blood vessels; It is innervated → supplied by nerve fibers
Epithelial cells are nourished by substances diffusing from blood vessels in the underlying connective tissue
Explain what it means that Epithelial tissue has Basal cells readily divide
Epithelium has a high regenerative capacity
If and when their apical-basal polarity and lateral contacts are destroyed, epithelial cells begin to reproduce themselves rapidly
As long as epithelial cells receive adequate nutrition, they can replace lost cells by cell division
List two forms of Epithelial tissue that occur in the body
Covering and lining epithelium
Which forms the outer layer of the skin; dips into and lines the open cavities of the urogenital, digestive, and respiratory systems; and covers the walls and organs of the closed ventral body cavity
Glandular epithelium
Which forms the glands of the body
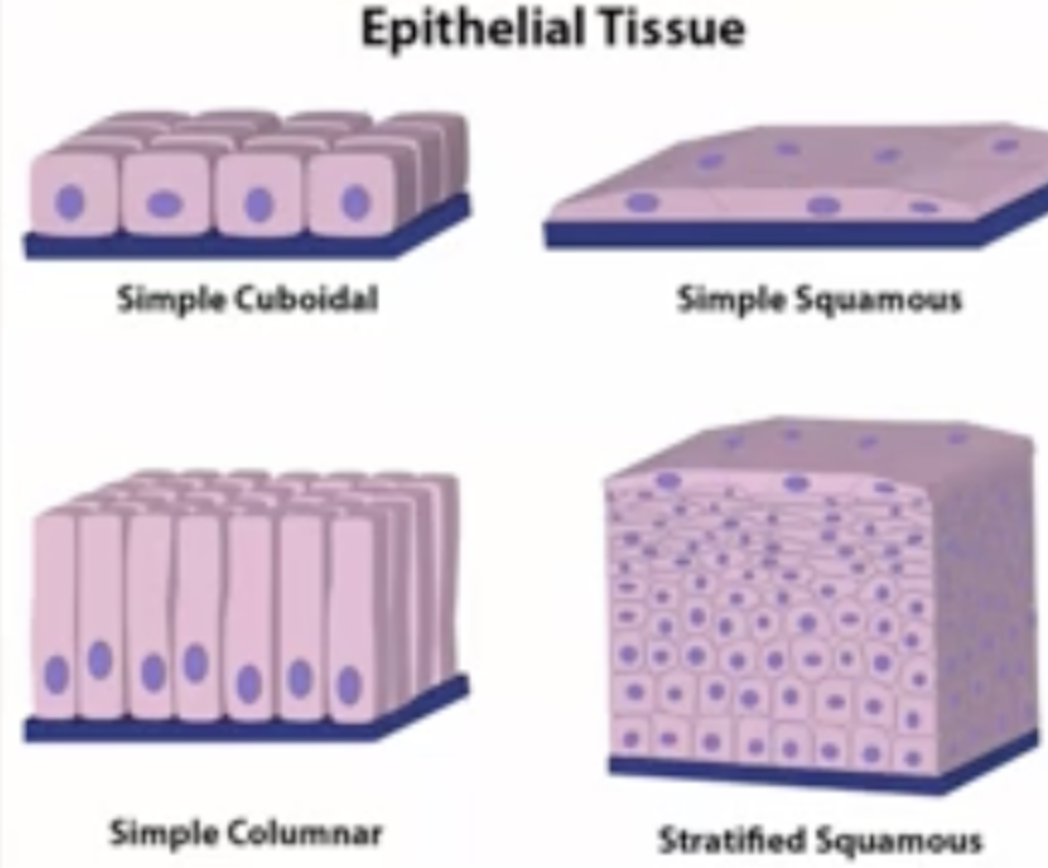
Classification of Epithelia based on number of cell layers
Simple epithelia
Consists of a single cell layer
They are typically found where a thin epithelial barrier is desirable
Stratified epithelia
Composed of two or more cell layers stacked on top of each other
Are common in high-abrasion areas where protection is important,
EX: skin surface and the lining of the mouth
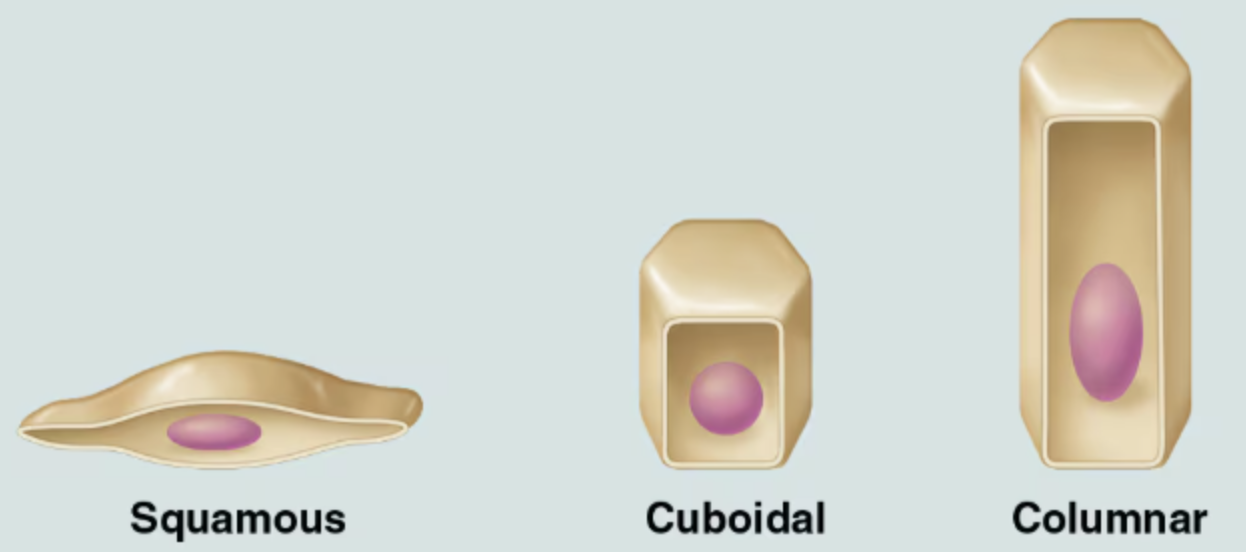
Classification of Epithelia based on cell shape
Squamous cells
Flattened and scale-like
Cuboidal cells
Boxlike, approximately as tall as they are wide.
Columar cells
Tall and column shaped
Name, classify, and describe the various type of epithelia, and indicate their chief function(s) and location(s)
Simple Squamous
Simple Cuboidal
Simple Columnar
Pseudo-stratified Columnar
Stratified Squamous
Transitional
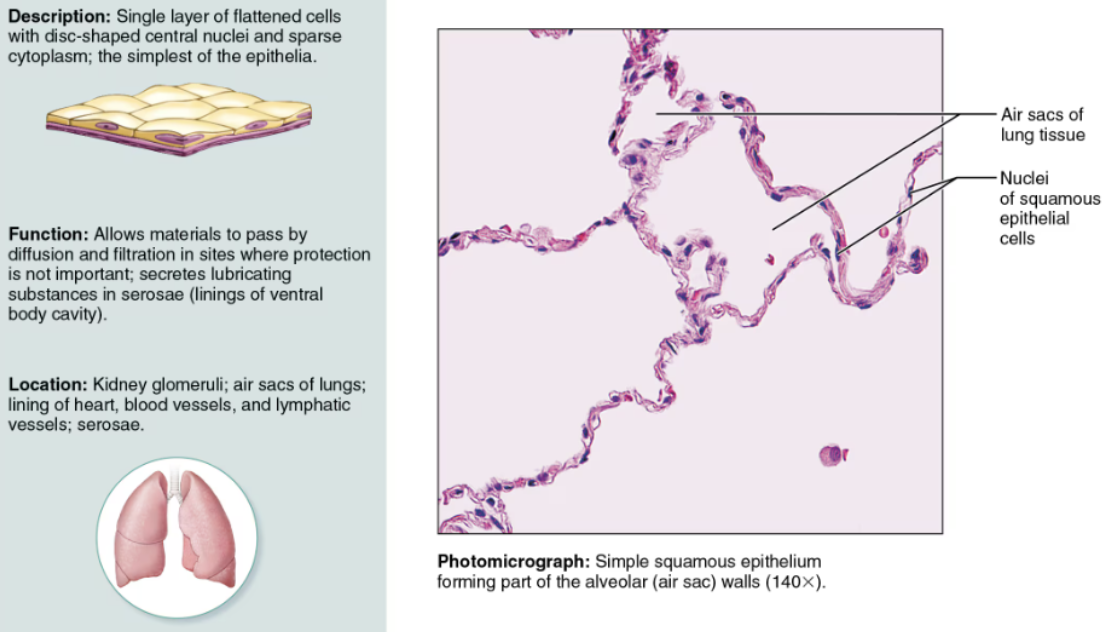
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Simple Squamous
DESCRIPTION: A single layer of squamous cells
FUNCTION: Highly adapted for filtration and exchange of substances, it forms walls of air sacs of the lungs and lines blood vessels
LOCATION: It contributes to serosae as mesothelium and lines all hollow circulatory system organs as endothelium
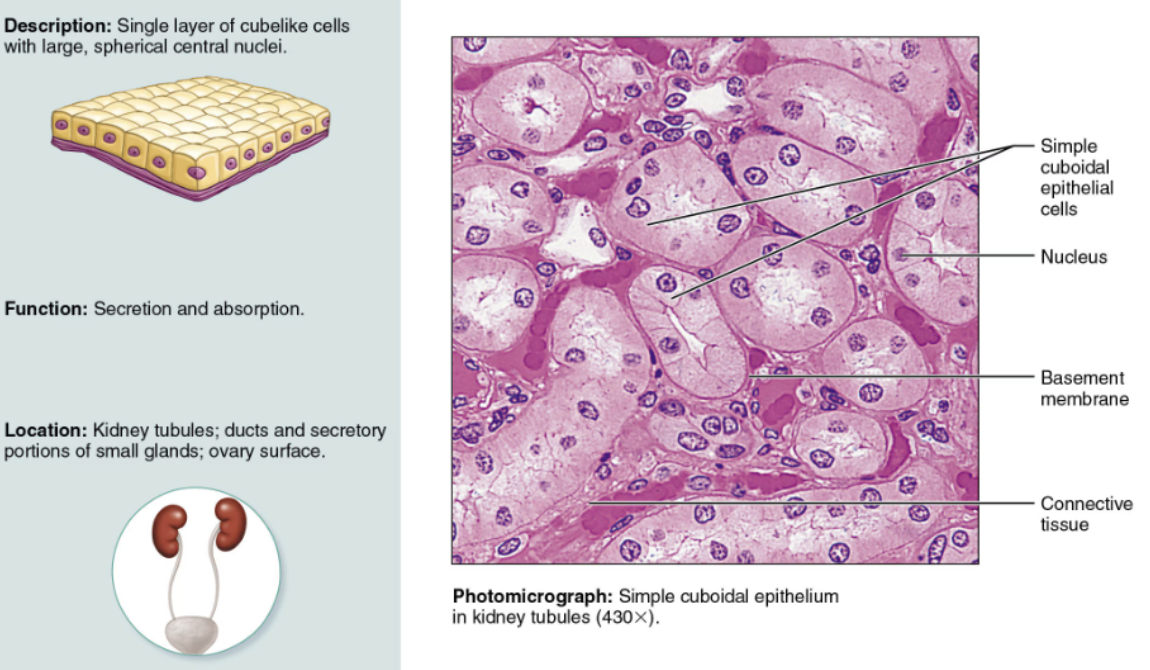
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Simple Cuboidal
FUNCTION & LOCATION: Commonly active in secretion and absorption, is found in glands and in kidney tubules
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Simple Columnar
DESCRIPTION: Consists of a single layer of tall columnar cells that exhibit microvilli and often mucus-producing cells
FUNCTION: Specialized for secretion and absorption
LOCATION: It lines most of the digestive tract
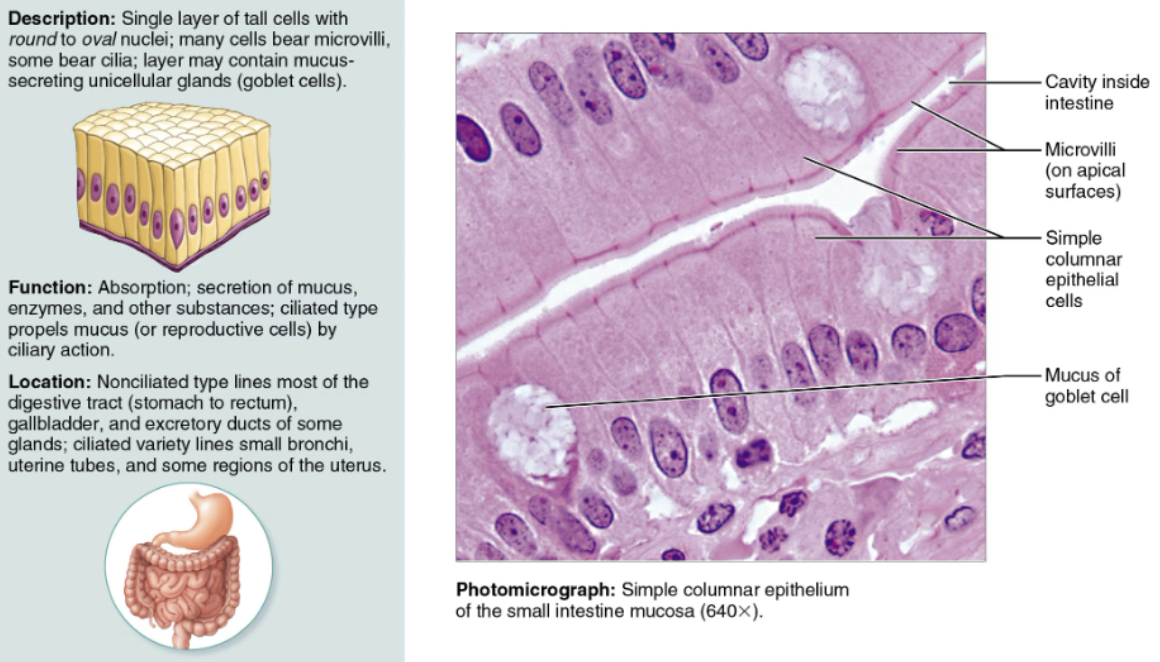
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Pseudo-stratified Columnar
DESCRIPTION: A simple columnar epithelium that appears stratified
FUNCTION & LOCATION: Its ciliated variety, rich in mucus-secreting cells, lines most of the upper respiratory passage
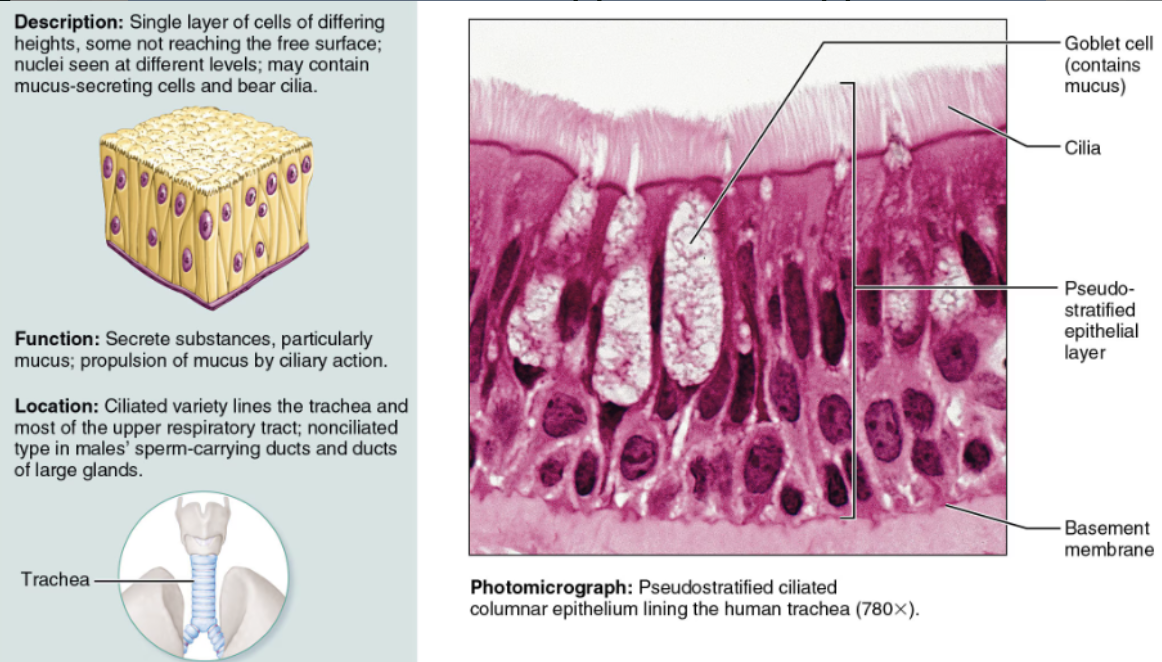
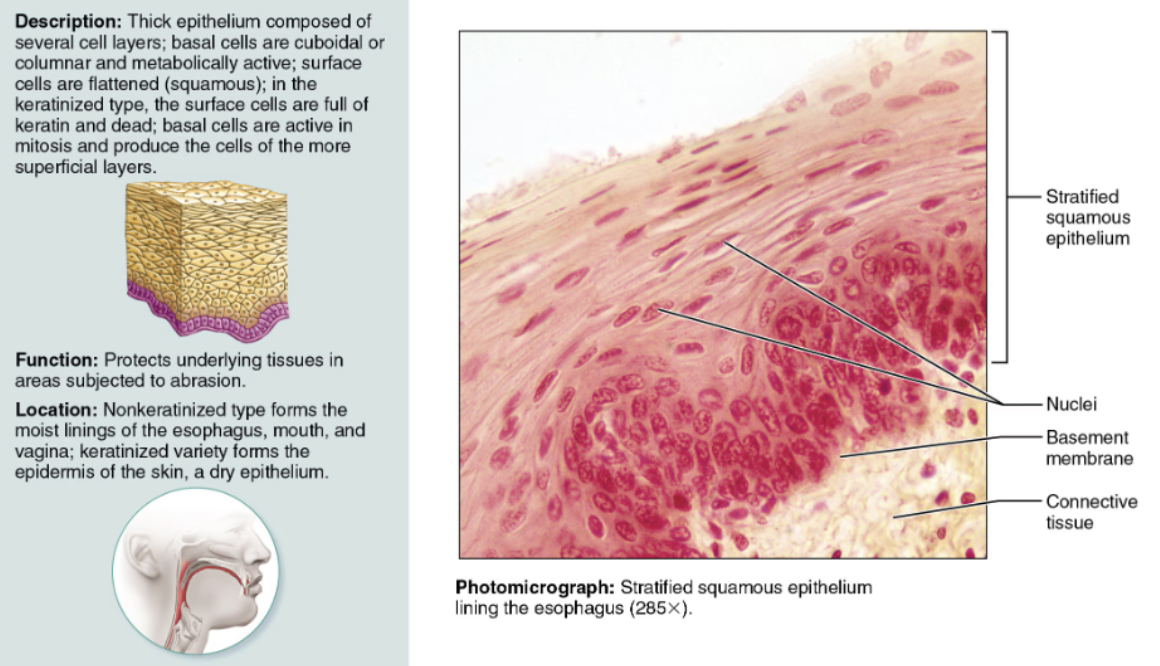
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Stratified Squamous
DESCRIPTION: Multilayered; cells at the free surface are squamous
FUNCTION: It is adapted to resist abrasion
LOCATION: It lines the esophagus and vagina; its keratinized variety forms the skin epidermis
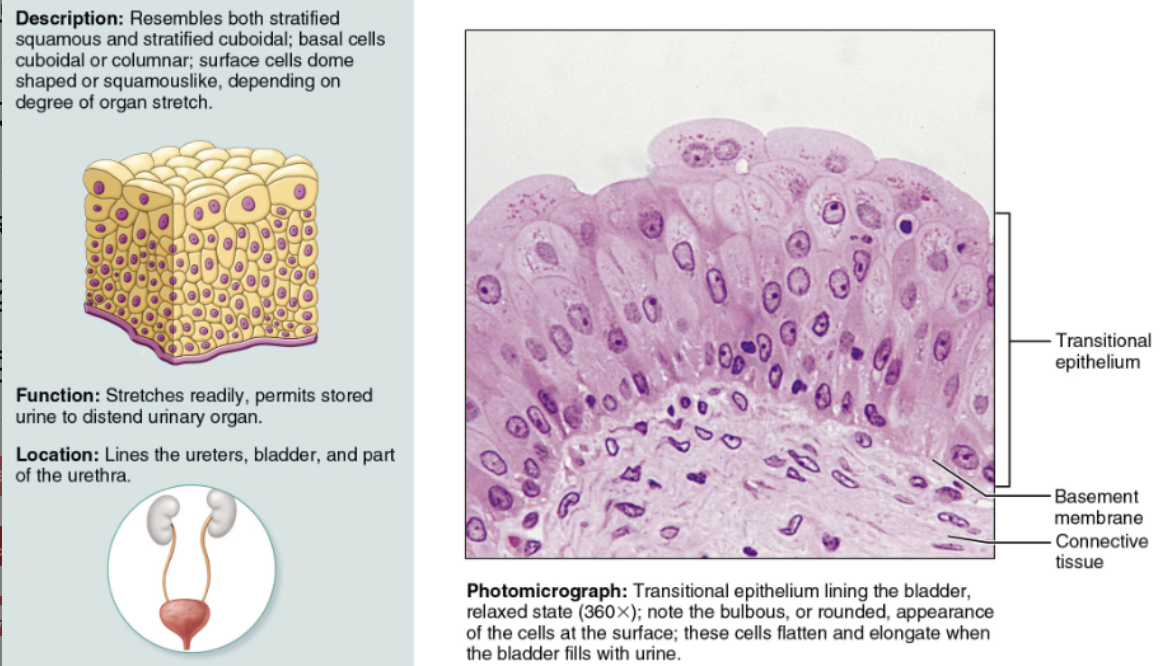
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Transitional
DESCRIPTION: A modified stratified squamous epithelium
FUNCTION: Adapted for responding to stretch
LOCATION: It lines hollow urinary system organs
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Stratified Cuboidal
DESCRIPTION: Typically has two layers of cuboidal cells
LOCATION: Quite rare in the body, mostly found in the ducts of some of the larger glands (sweat glands, mammary glands)
Indicate their chief function(s) and location(s) of Stratified Columnar
DESCRIPTION: Only its apical layer of cells is columnar
FUNCTION: Occurs at transition areas or junctions between two other types of epithelia
LOCATION: Small amounts are found in the pharynx (throat), the male urethra, and lining some glandular ducts
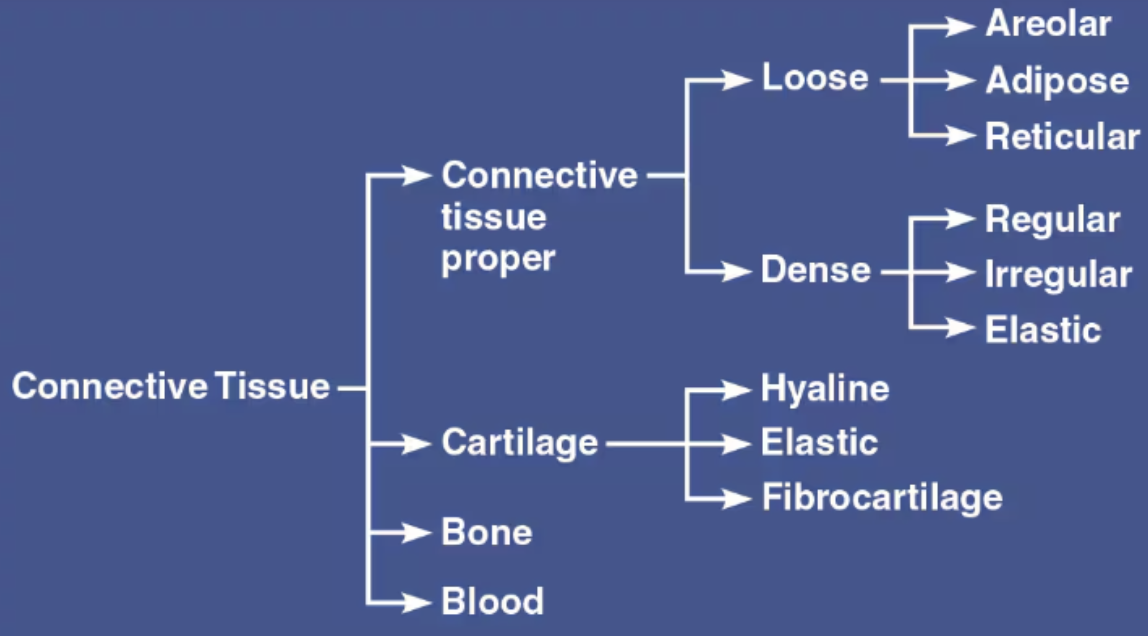
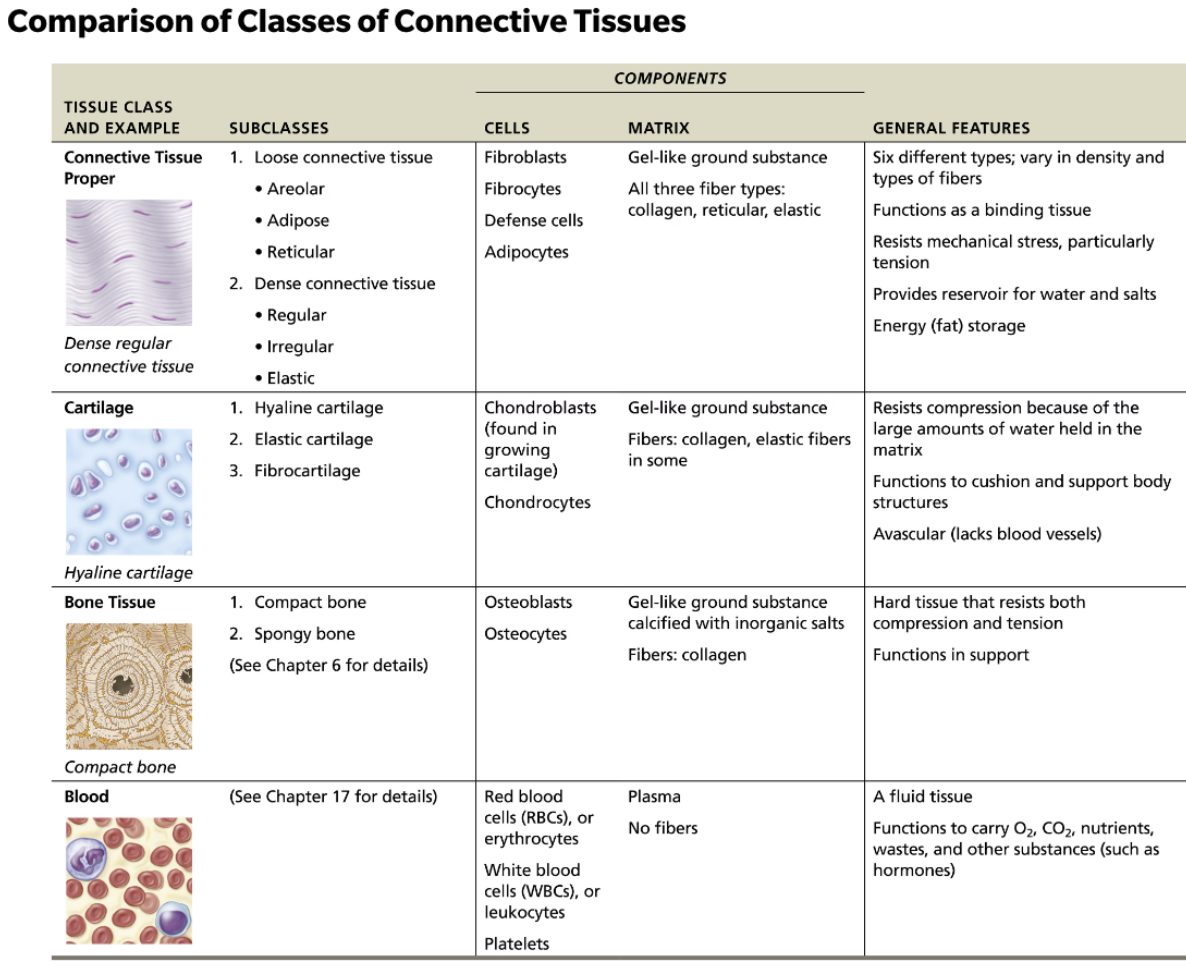
Define Connective Tissue
A primary tissue
Form and function vary extensively
Functions include binding and support, protection, insulation, fat storage, and transportation (blood)
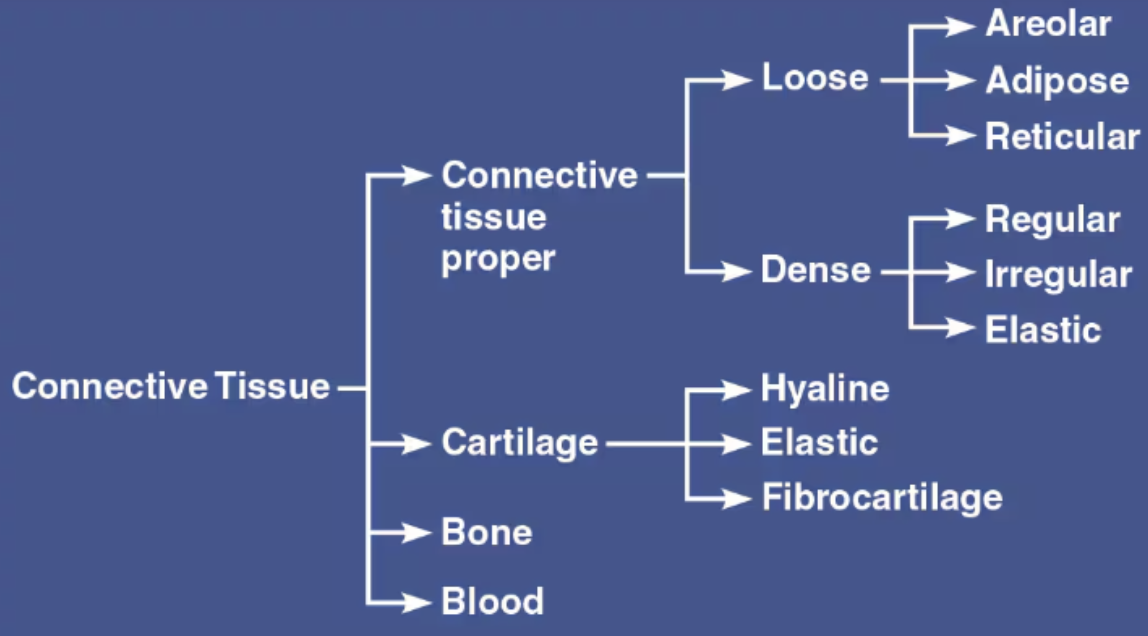
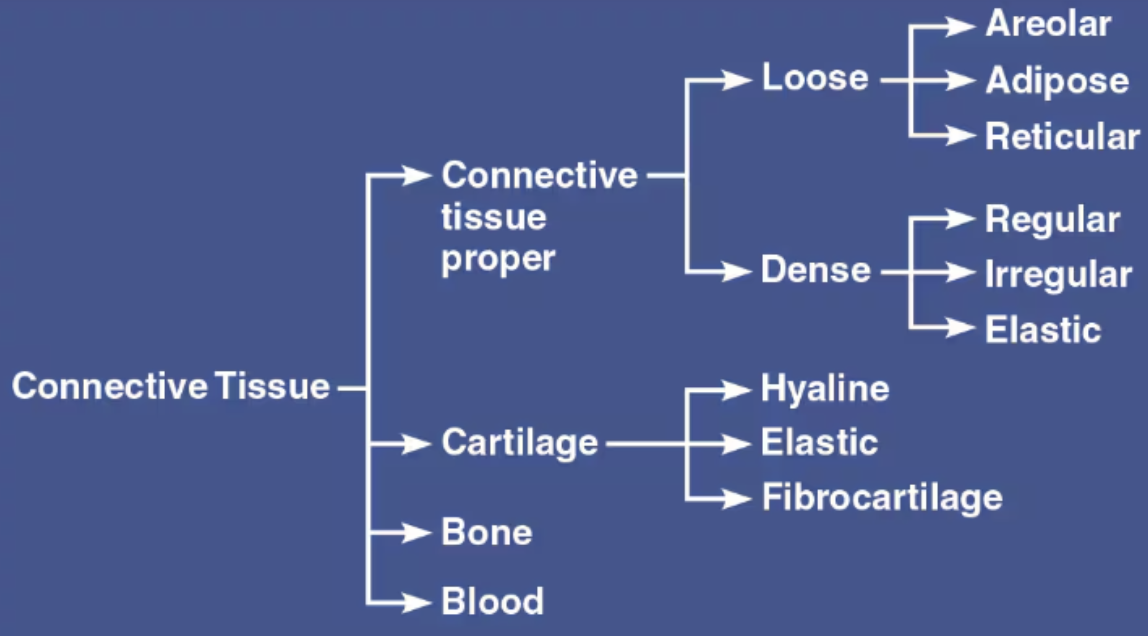
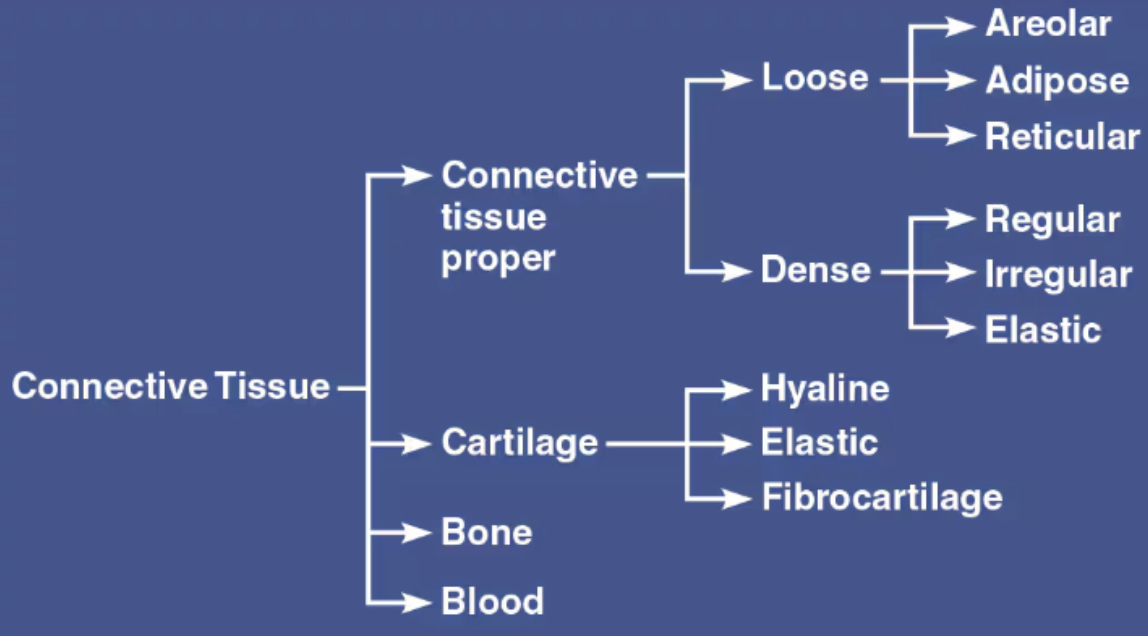
List the four main classes of Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue proper
Cartilage
Bone
Blood
List the Proper Connective Tissues
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
Dense
List the Specialized Connective Tissues
Cartilage (supportive connective tissue)
Bone (supportive connective tissue)
Blood (Fluid CT)
Indicate differences between Connective Tissue
Depending on type, connective tissue may be well vascularized (most), poorly vascularized (dense connective tissue), or avascular (cartilage)
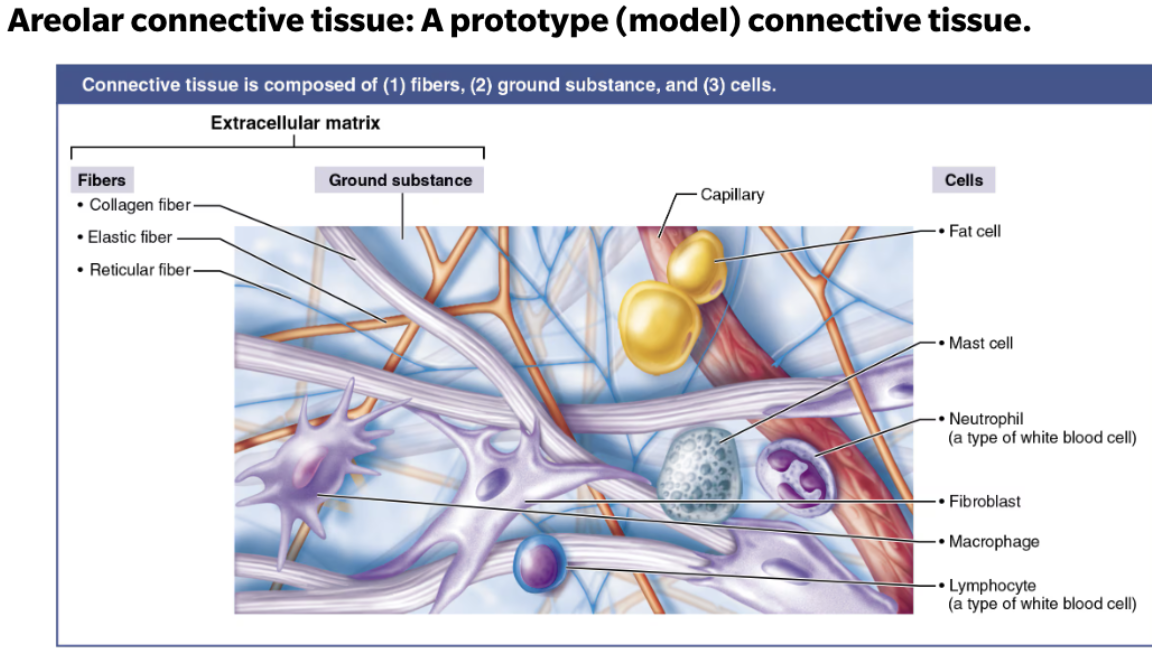
List and describe connective tissue its structural elements
Ground substance
The unstructured material that fills the space between the cells and surrounds the fibers
Gel-like
Firm
Fibers
Proteins that provide support
Collagen
Elastic
Reticular
Cells
Each major class of connective tissue has a resident cell type that exists in immature (-blast) and mature (-cyte) forms
Matrix-secreting cell (-blast)
Mature cell (-cyte)
Undifferentiated cell type
Ground substance + Fibers = Extracellular matrix
List and describe the three components of Ground Substance
Hyaluronic Acid
Lubricant
Functions as a molecular sieve through which nutrients and other dissolved substances can diffuse between the blood capillaries and the cells
Proteoglycans
Trap water
Consist of a protein core to which large polysaccharides called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are attached
Tend to form huge aggregates in which the GAGs intertwine and trap water, forming a substance that varies from a fluid to a viscous gel → higher the GAG content, the more viscous the ground substance
Adhesive molecules
Glue molecules
Serve mainly as a connective tissue glue that allows connective tissue cells to attach to the extracellular matrix
List and describe the three types of Connective Tissue Fibers
Collage Fibers
Fibrous protein → collagen
“White fibers” → Assemble spontaneously into cross-linked fibrils
Tensile strength
Elastic Fibers
Rubbery protein → elastin
“Yellow fibers” → Long, thin, elastic fibers form branching networks in the extracellular matrix
Elasticity
EX: skin, lungs, and blood vessel walls
Reticular Fibers
Short, fine fibers are made of a different type of collagen than the more common, thicker collagen fibers
They connect to the coarser collagen fibers, but they branch extensively, forming delicate networks
Abundant where connective tissue is next to other tissue types
EX: basement membrane of epithelial tissues and around capillaries
List the types of Cells in Connective Tissues
-blast ⇒ form new matrix
Immature
-cytes ⇒ maintain matrix
Mature
-clasts ⇒ break down matrix
List the two subclasses of Connective Tissue Proper
Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
Dense Connective Tissue
Regular
Irregular
Elastic
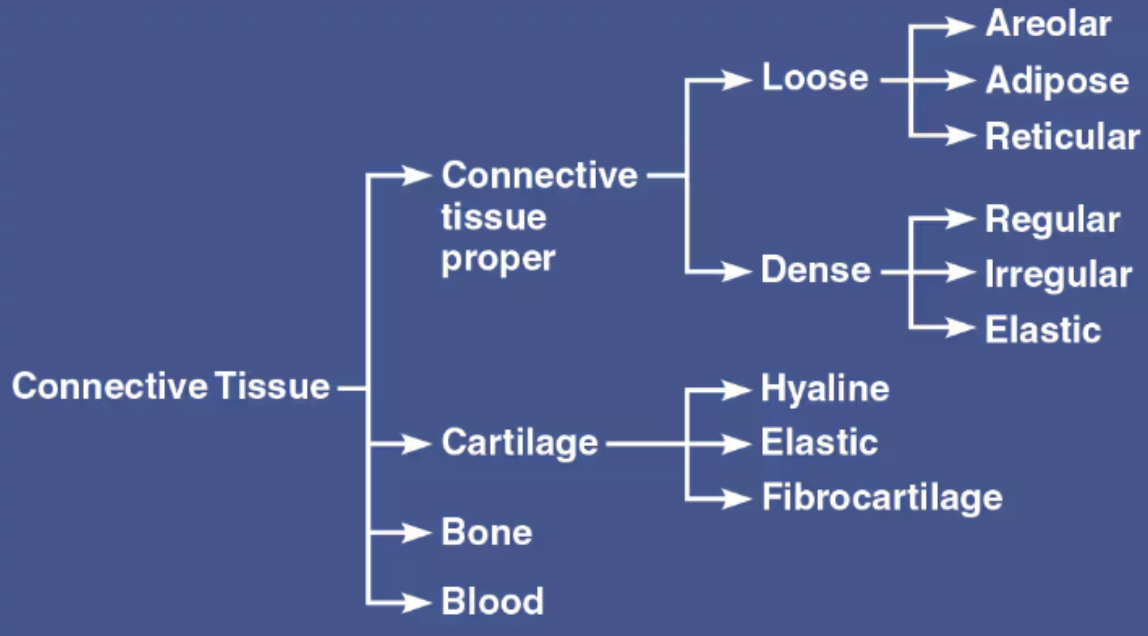
Describe Areolar Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
Cells
Fibroblasts/cytes
Fibers
Loose network of mixed fibers
Gel-like ground substance
Function
Binds epithelial tissue to underlying structure, binds muscles together
Supporting and binding other tissues (the job of the fibers)
Holding body fluids (the ground substance’s role)
Defending against infection (via the activity of white blood cells and macrophages)
Storing nutrients as fat in adipocytes (fat cells)
Location
Beneath epithelial tissues
Between muscles
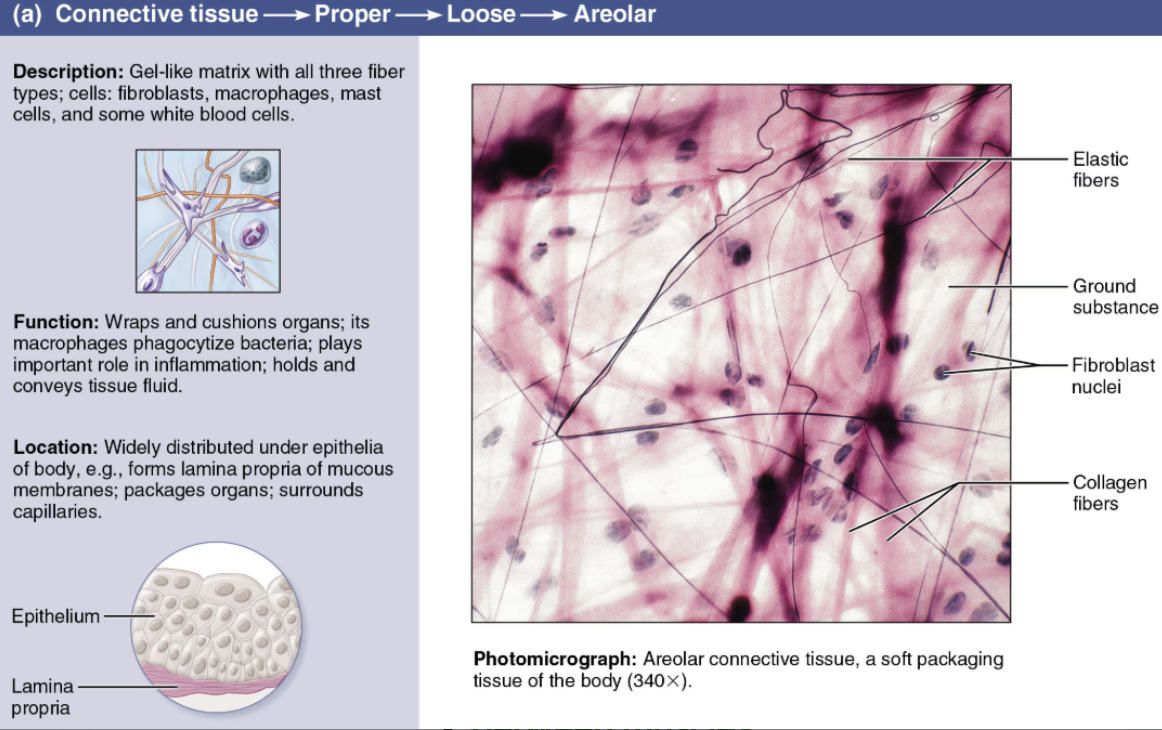
Describe Adipose Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
Cells
Adipocytes
Fibers
Few collagenous
Scant matrix
Function
Cushing
Insulation
Energy storage
Location
Under skin
Around vital organs
Behind eyes
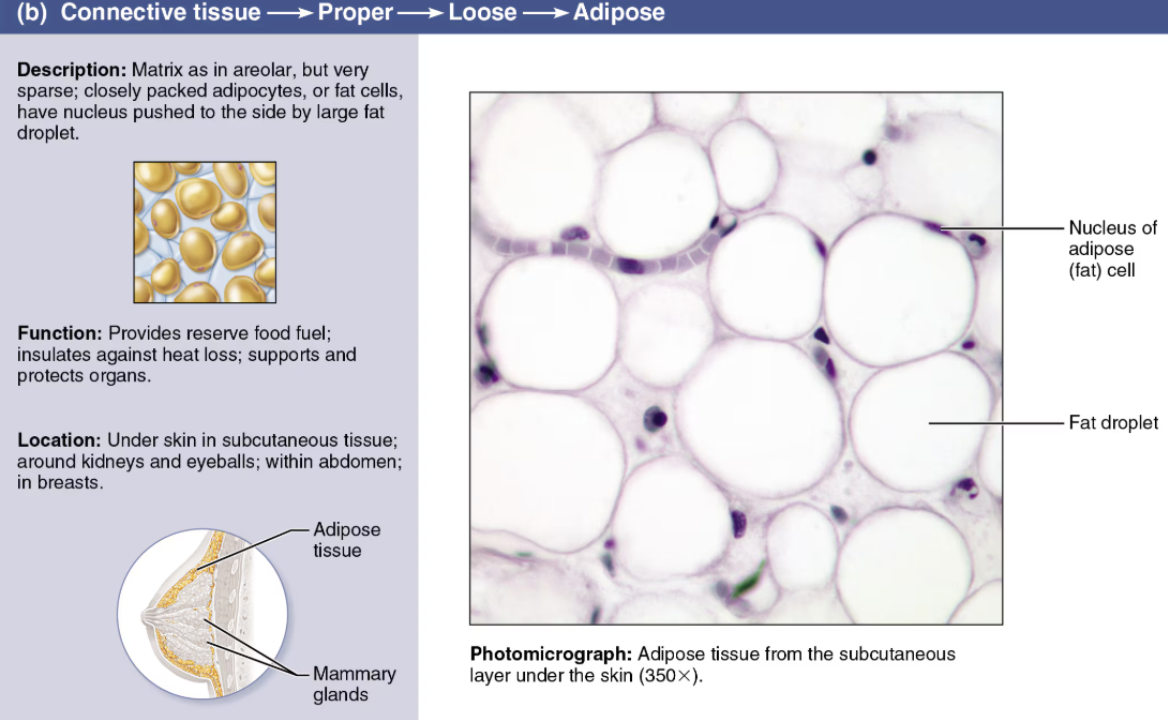
Describe Reticular
Loose Connective Tissue
Cells
Fibroblasts/cytes
Fibers
Reticular → Collagen-based, but much thinner and not as strong
Soft ground substance
Function
Framework for lymphatic structures
Location
Liver
Spleen
Lymph nodes
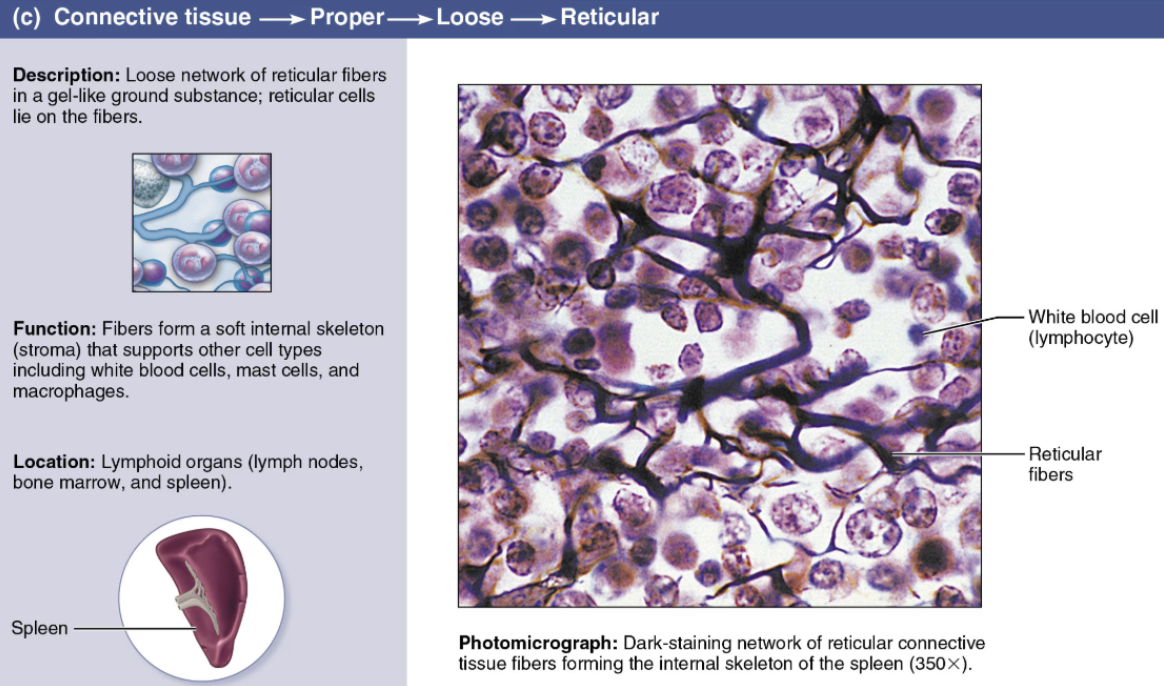
Describe Dense Connective Tissue
Cells
Fibroblasts/cytes
Fibers
Both, but one predominates
Function
Binds body parts together
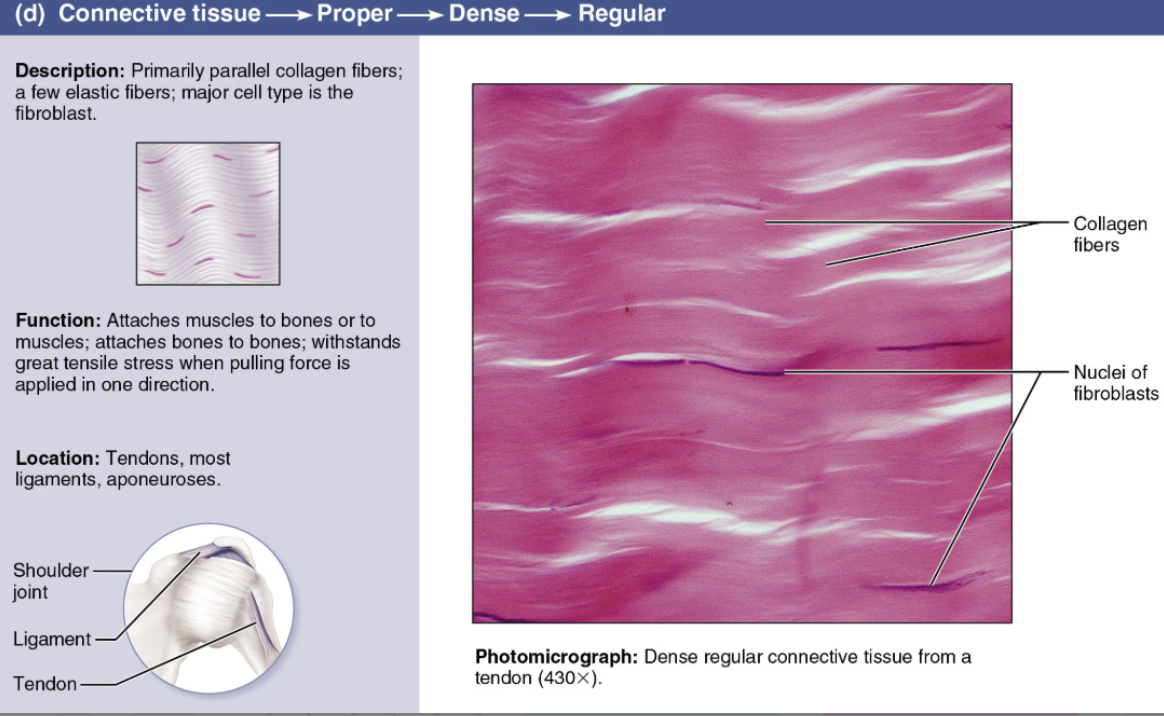
Describe Regular
Dense Connective Tissue
DESCRIPTION: dense parallel bundles of collagen fibers; few cells, little ground substance
FUNCTION: high tensile strength
LOCATION: forms tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses; in cases where this tissue also contains numerous elastic fibers it is called elastic connective tissue
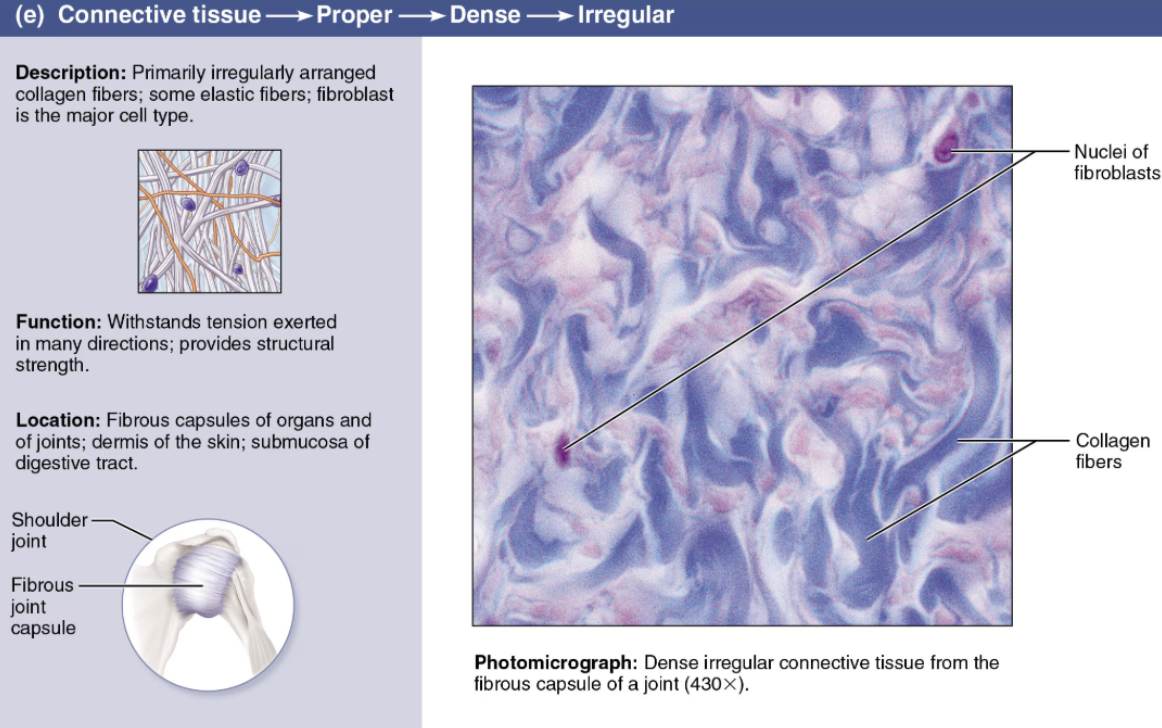
Describe Irregular
Dense Connective Tissue
DESCRIPTION: Like regular variety, but fibers are arranged in different planes
FUNCTION: Resists tension exerted from many different directions
LOCATION: Forms the dermis of the skin and organ capsules
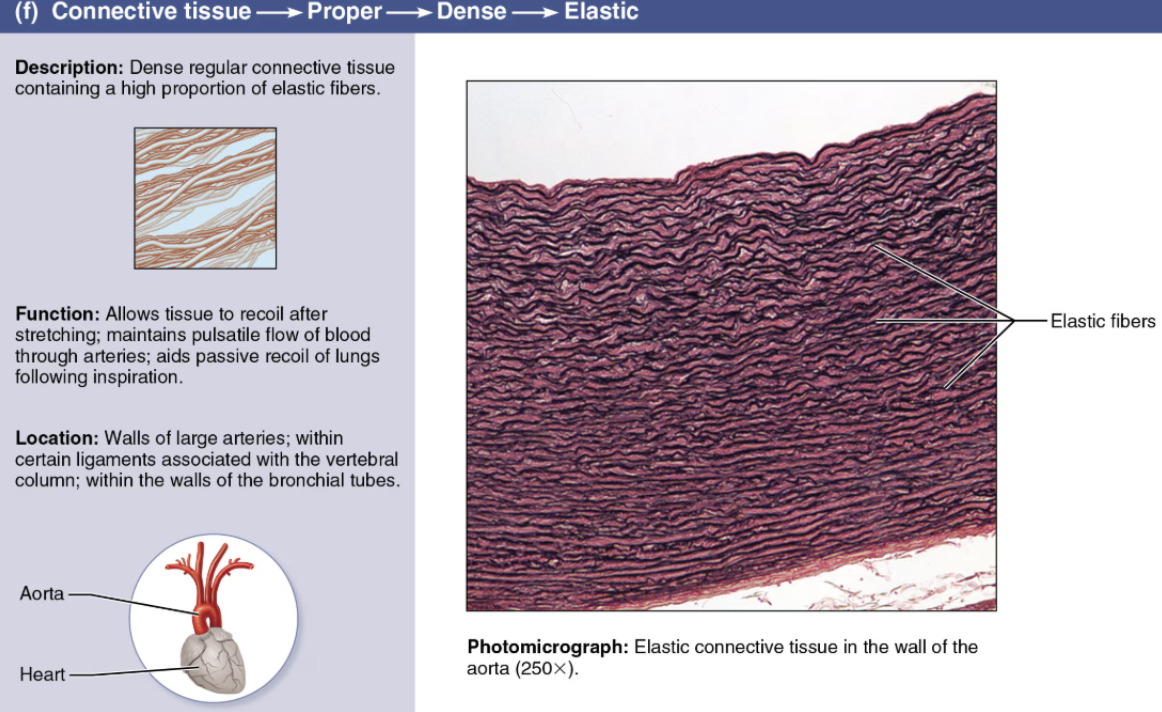
Describe Elastic
Dense Connective Tissue
Describe Cartilage
Connective Tissue
Cells
Chondrocytes (-blast, clasts)
Matrix
Fibers → Collagenous or elastic
ground substances → Chondromucoprotein (rigid…semisolid)
List the 3 types of Cartilage
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
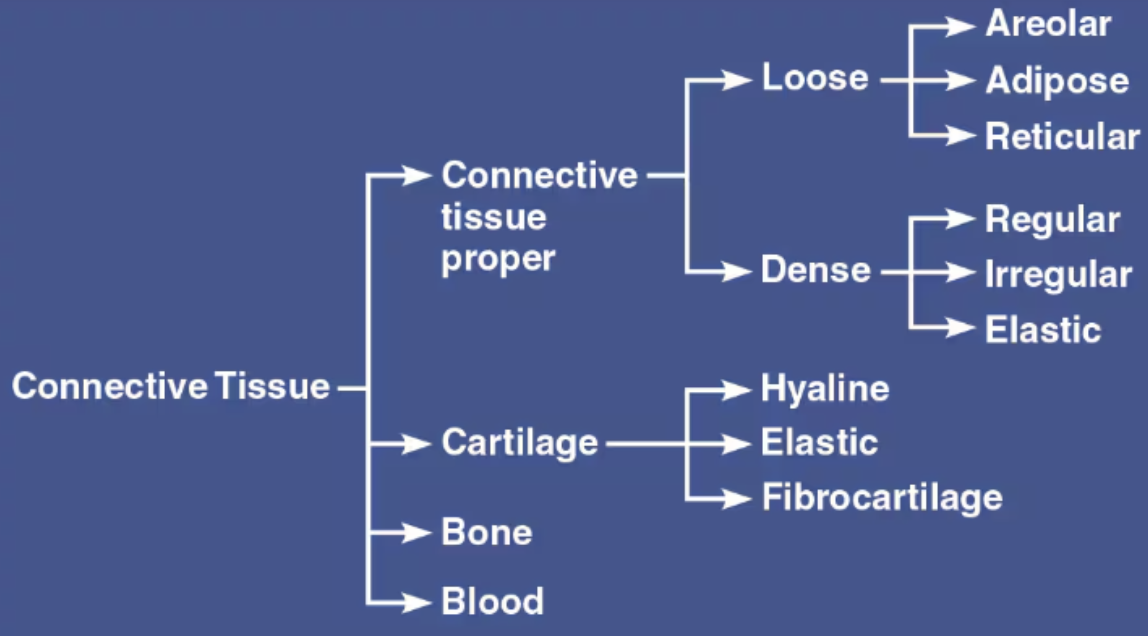
Describe Hyaline Cartilage
Cartilage
DESCRIPTION: Firm ground substance containing collagen fibers
FUNCTION: Resists compression well
LOCATION: Found in embryonic skeleton, at articulating surfaces of bones, costal cartilages, and in the trachea; most abundant type
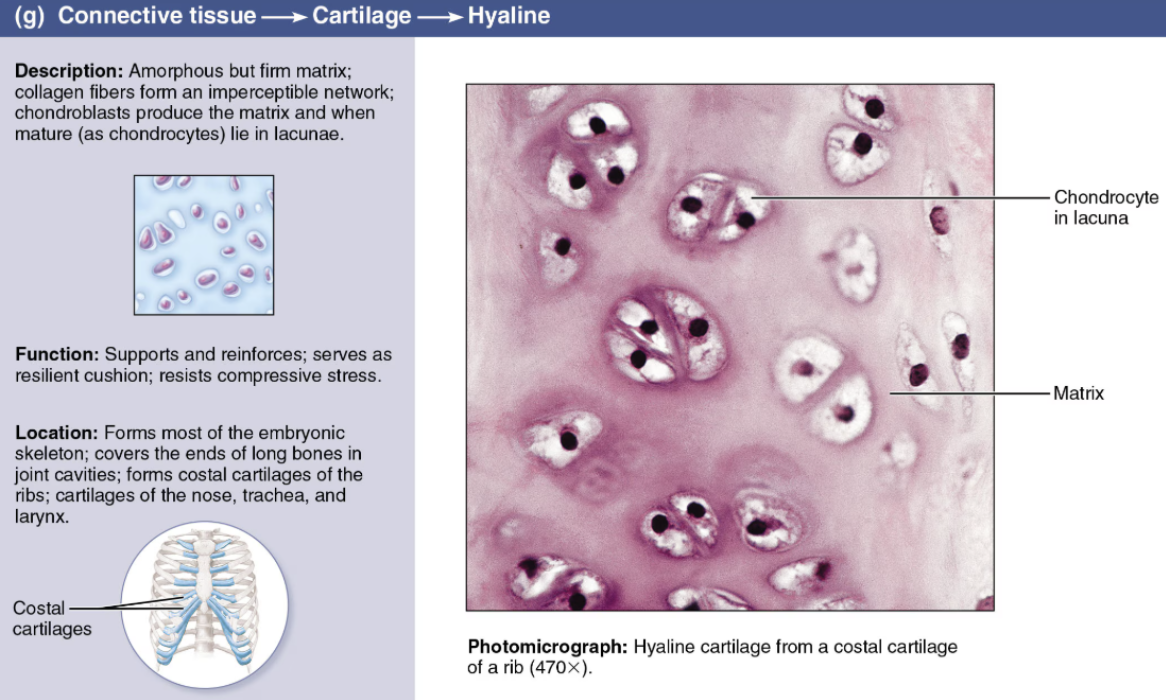
Describe Elastic Cartilage
Cartilage
DESCRIPTION: Elastic fibers predominate
FUNCTION: Framework for ears; provides flexible support of the external ear and epiglottis
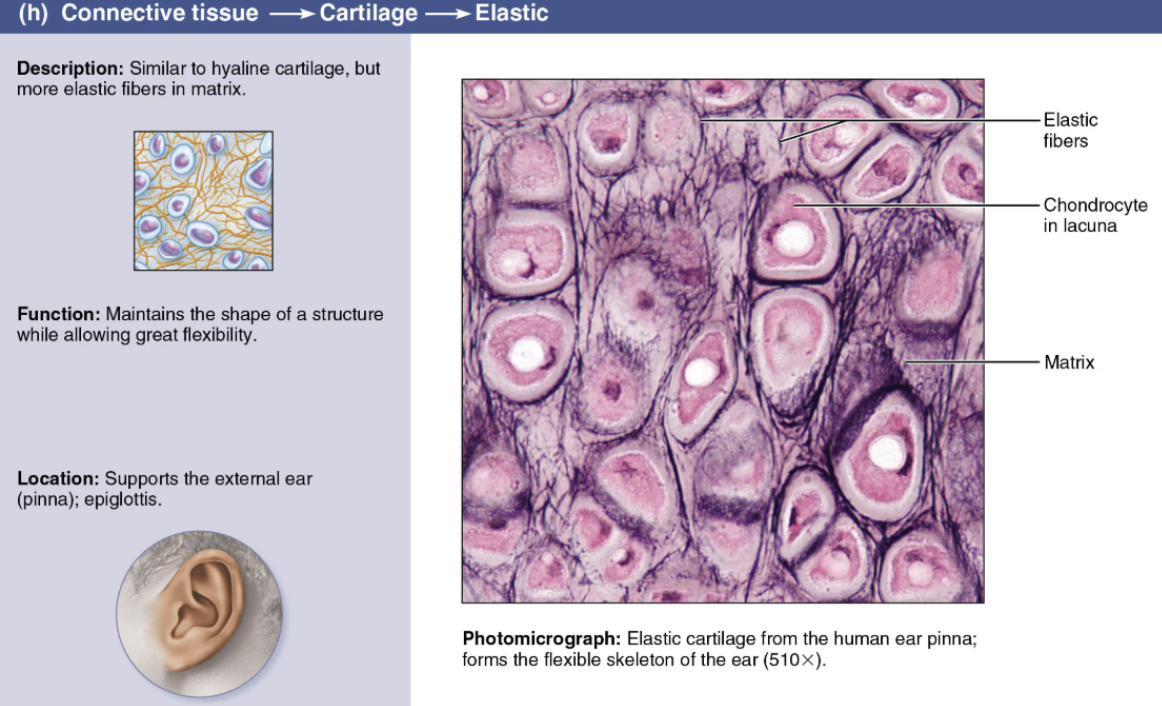
Describe Fibrocartilage
Cartilage
DESCRIPTION: parallel collagen fibers
FUNCTION: resists both tension and compression well
LOCATION: forms intervertebral discs and knee cartilages
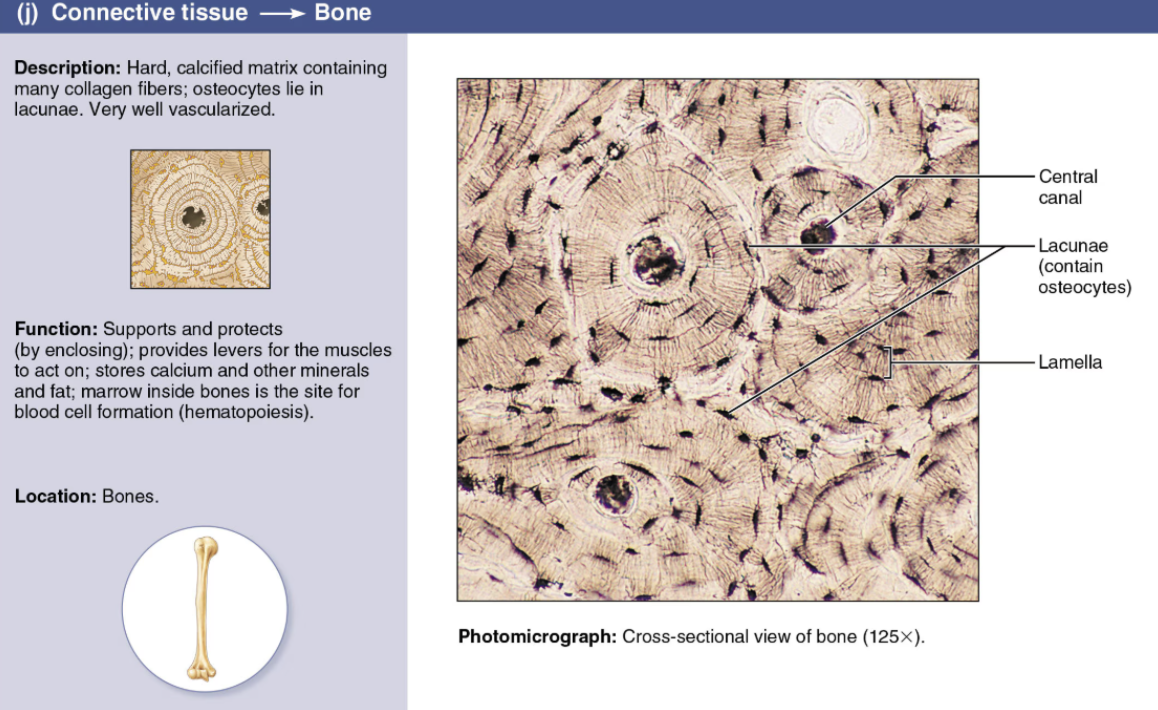
Describe Bone
Connective Tissue
Cells
Osteo-
Matrix
Hydroxyapatite
Consists of a hard, collagen-containing matrix embedded with calcium salts
LOCATION: Forms the bony skeleton
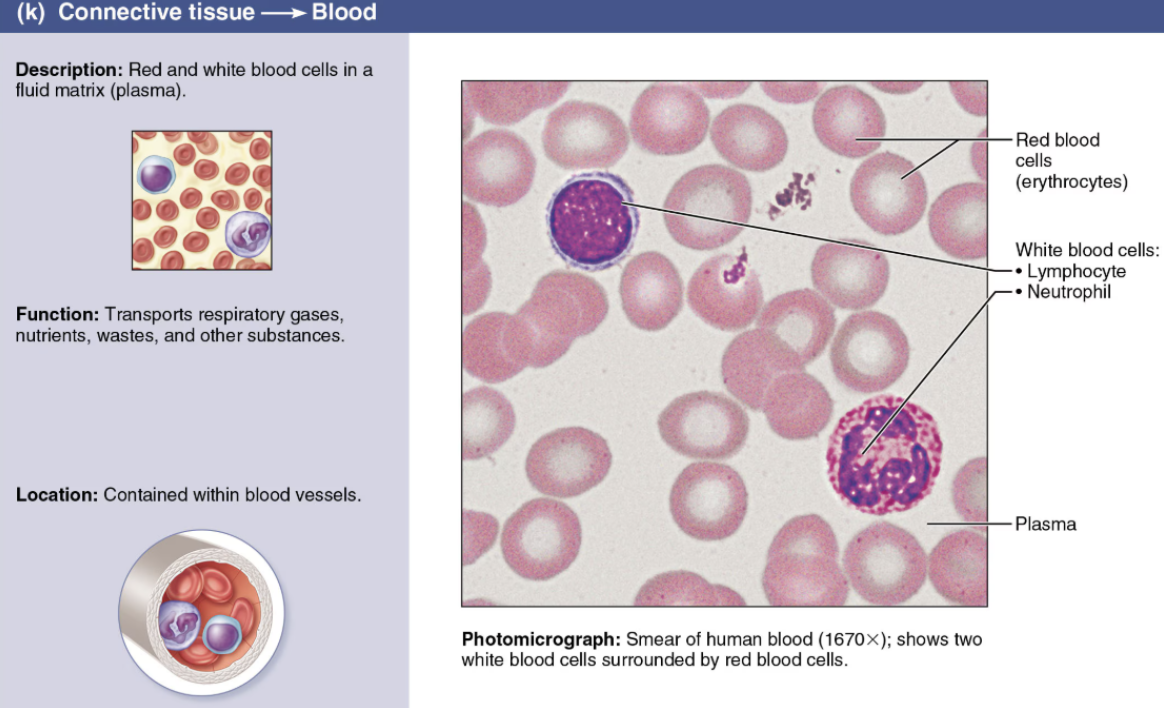
Describe Blood
Connective Tissue
Cells
RBC
WBS
PLTS
Matrix
Fluid (plasma)
Describe the types of connective tissue found in the body and indicate their characteristic functions
Define Muscle tissues
Group of body tissues that contract (shorten) to produce local movements or the movement of an entire organism
Muscle cells possess myofilaments
Actin filaments
Myosin filaments
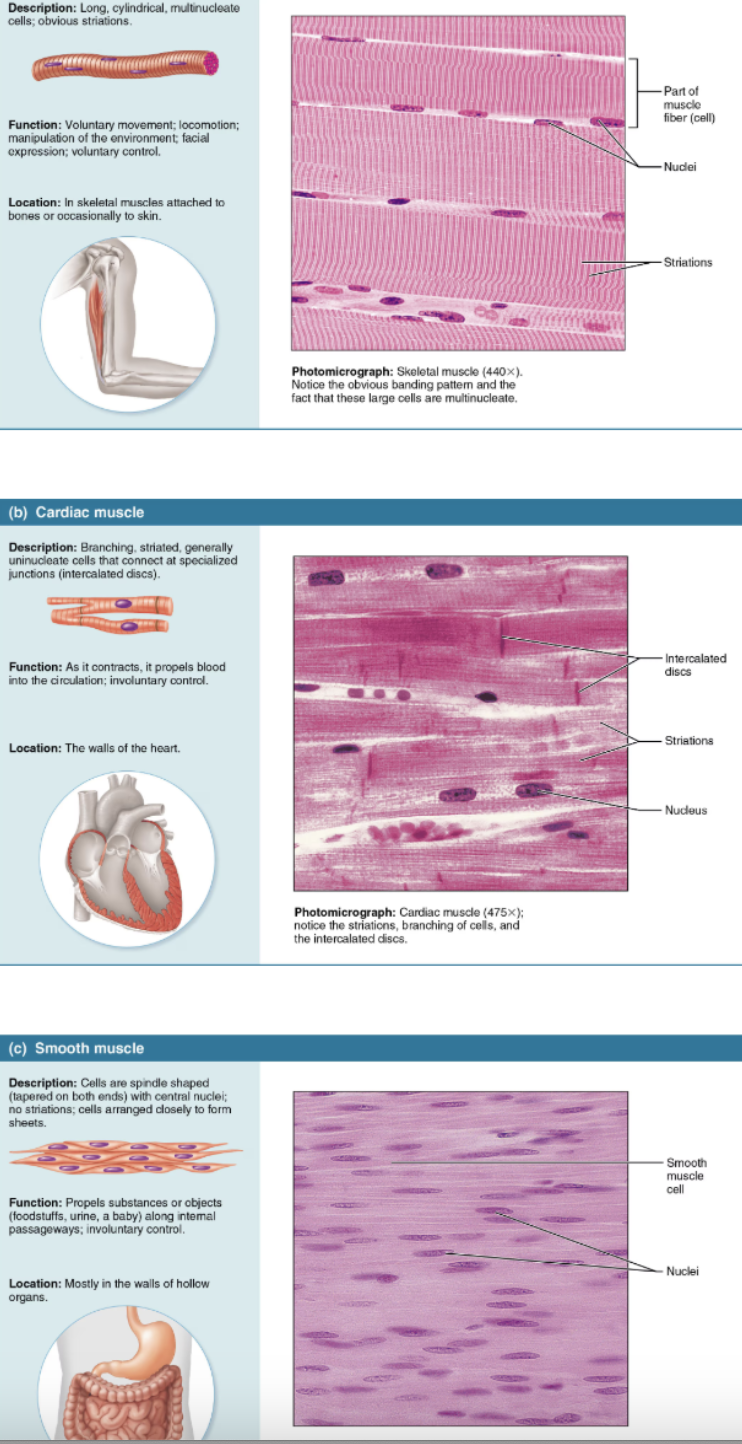
List the 3 classes of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Compare and contrast the structures and body locations of the three types of muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle
long, cylindrical cells that contain many peripherally located nuclei; obvious striations
Attached to the bones of the skeleton
VOLUNTARY
Cardiac muscle
striations
Specialized muscle of the heart
INVOLUNTARY
Smooth muscle
Spindle-shaped cells with one centrally located nucleus and no externally visible striations (bands)
Found mainly in the walls of hallow organs
INVOLUNTARY
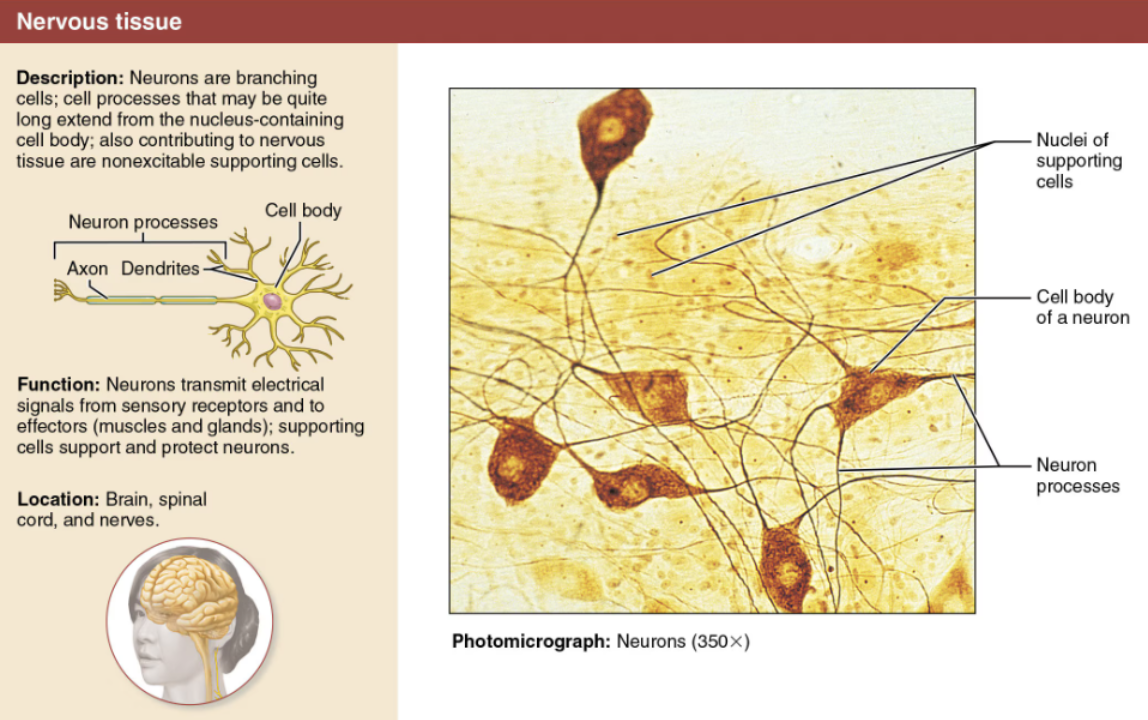
Define Nervous Tissue
Main component of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and nerves), which regulates and controls body functions
Describe Neurons
DESCRIPTION: Branching cells
FUNCTION: Highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses
Respond to stimuli (via processes called dendrites)
Transmit electrical impulses over substantial distances within the body (via processes called axons)
Indicate the general characteristics of Nervous Tissue