BIO220: Identifying Muscle Microanatomy
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Nuclei
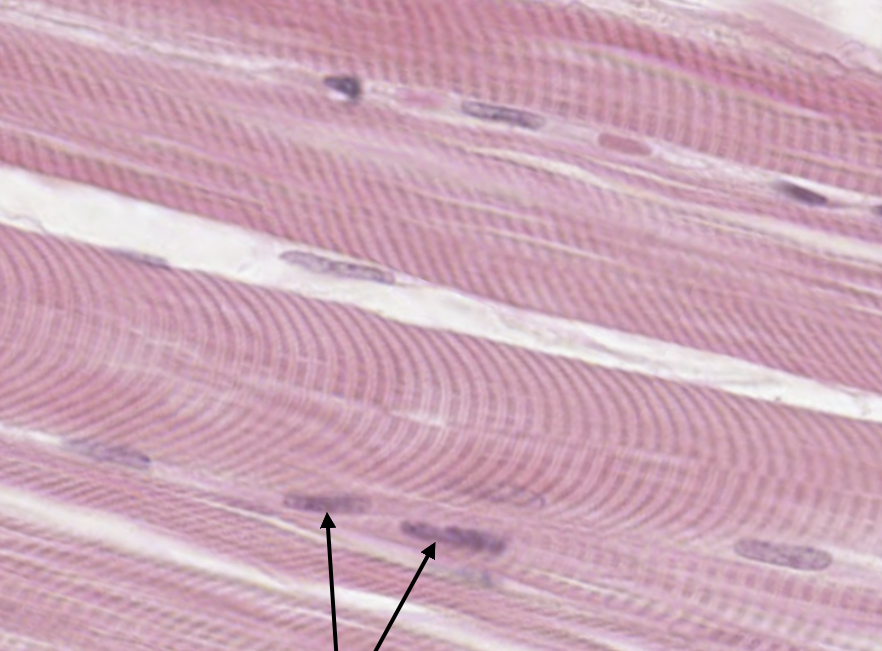
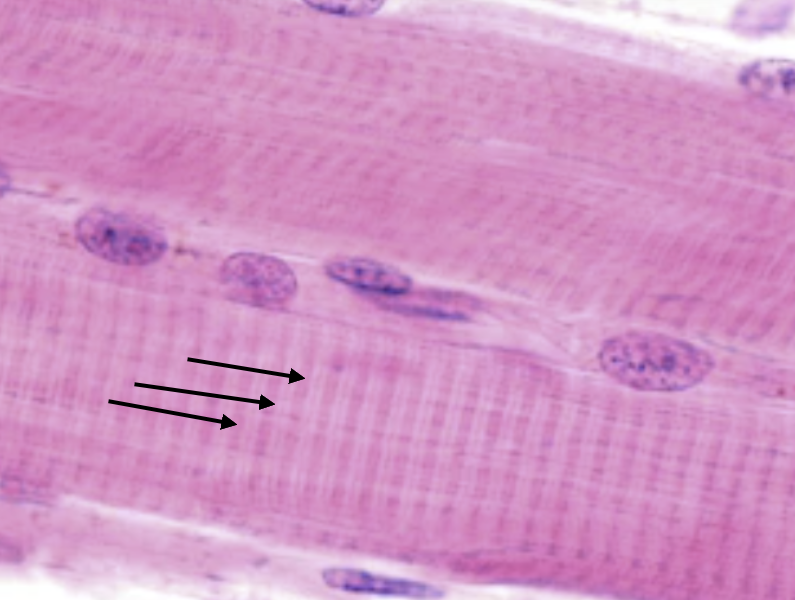
Striations
Sacromere
1?
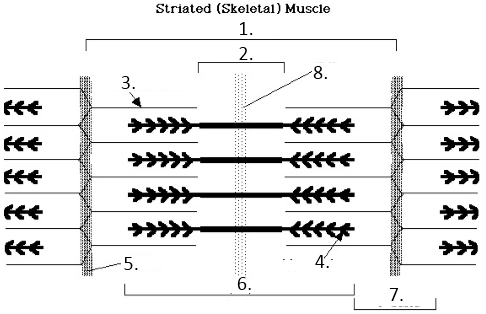
H-Band
2?
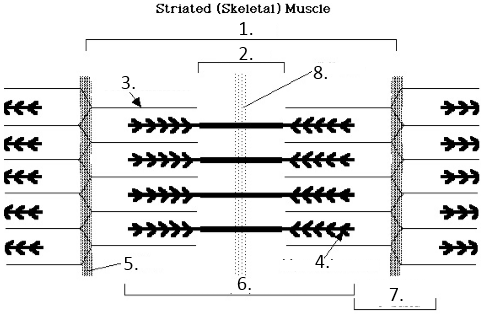
Actin
3?
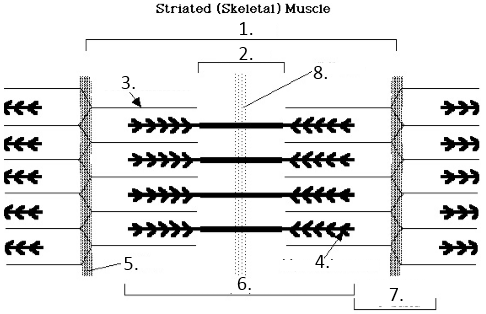
Myosin
4?
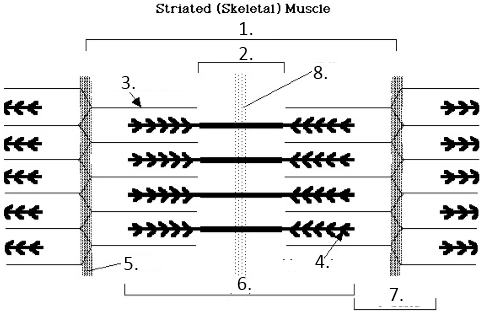
Z line
5?
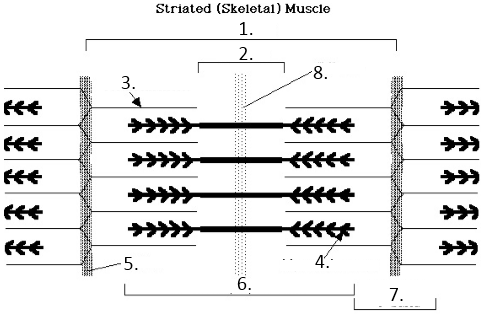
A Band
6?
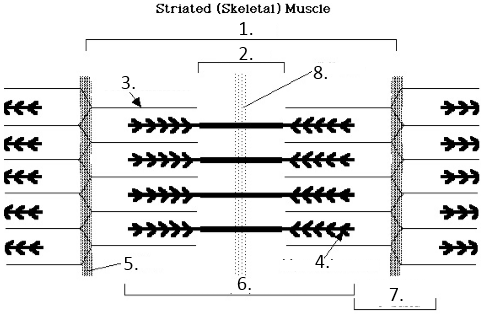
I band
7?
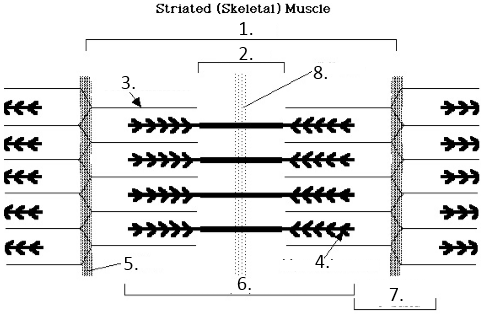
M Line
8?
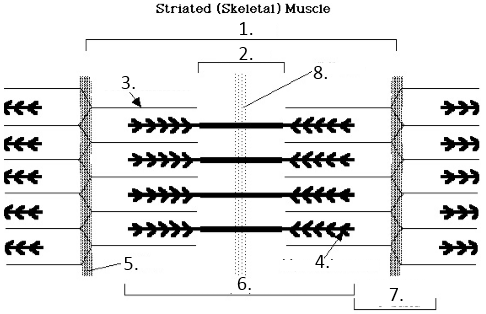
T-Tubules
Terminal Cisternae
Sacroplasmic Reticulum
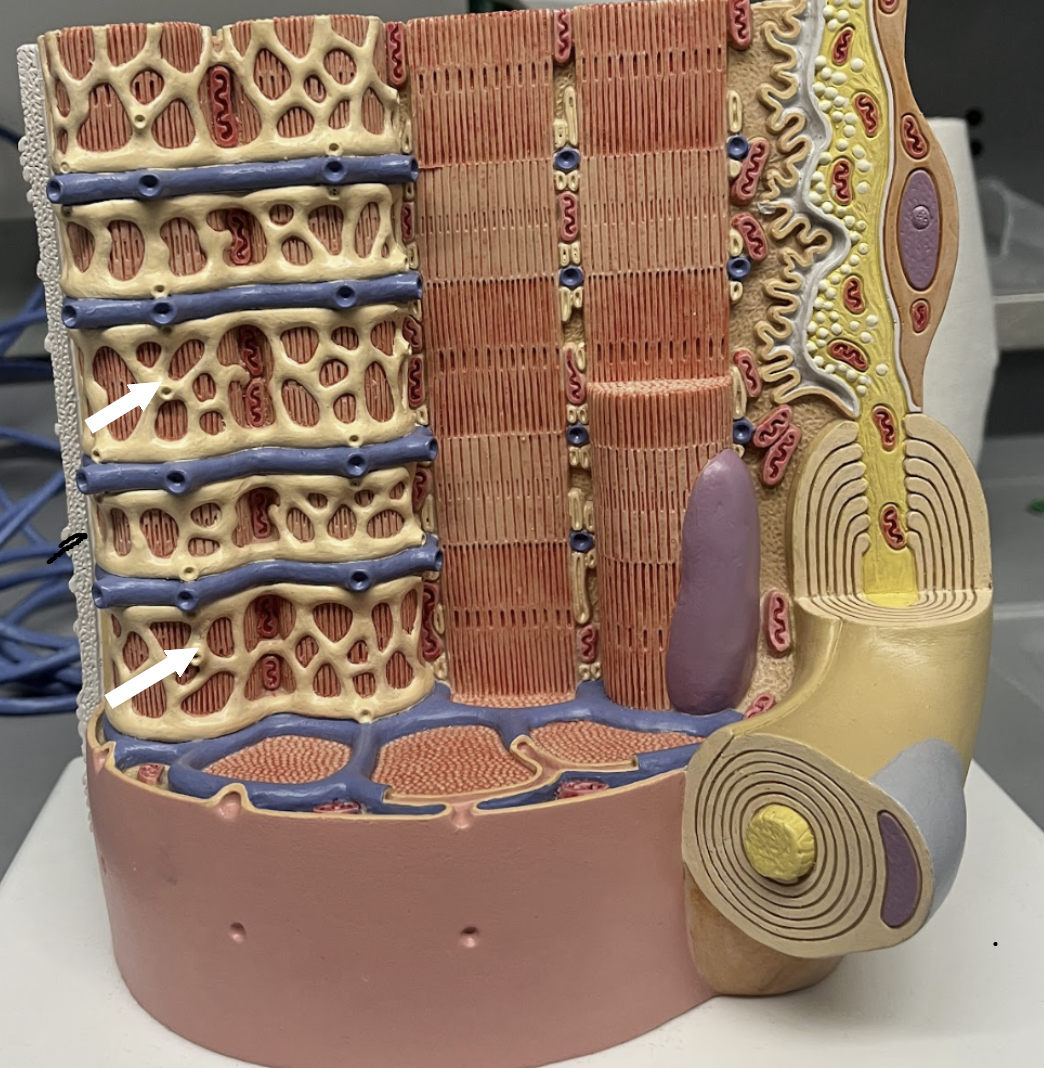
Myofibril
Myofilament, Myofibril, Muscle fiber, Fascicle, Muscle
organization of Skeletal Muscles smallest to largest?
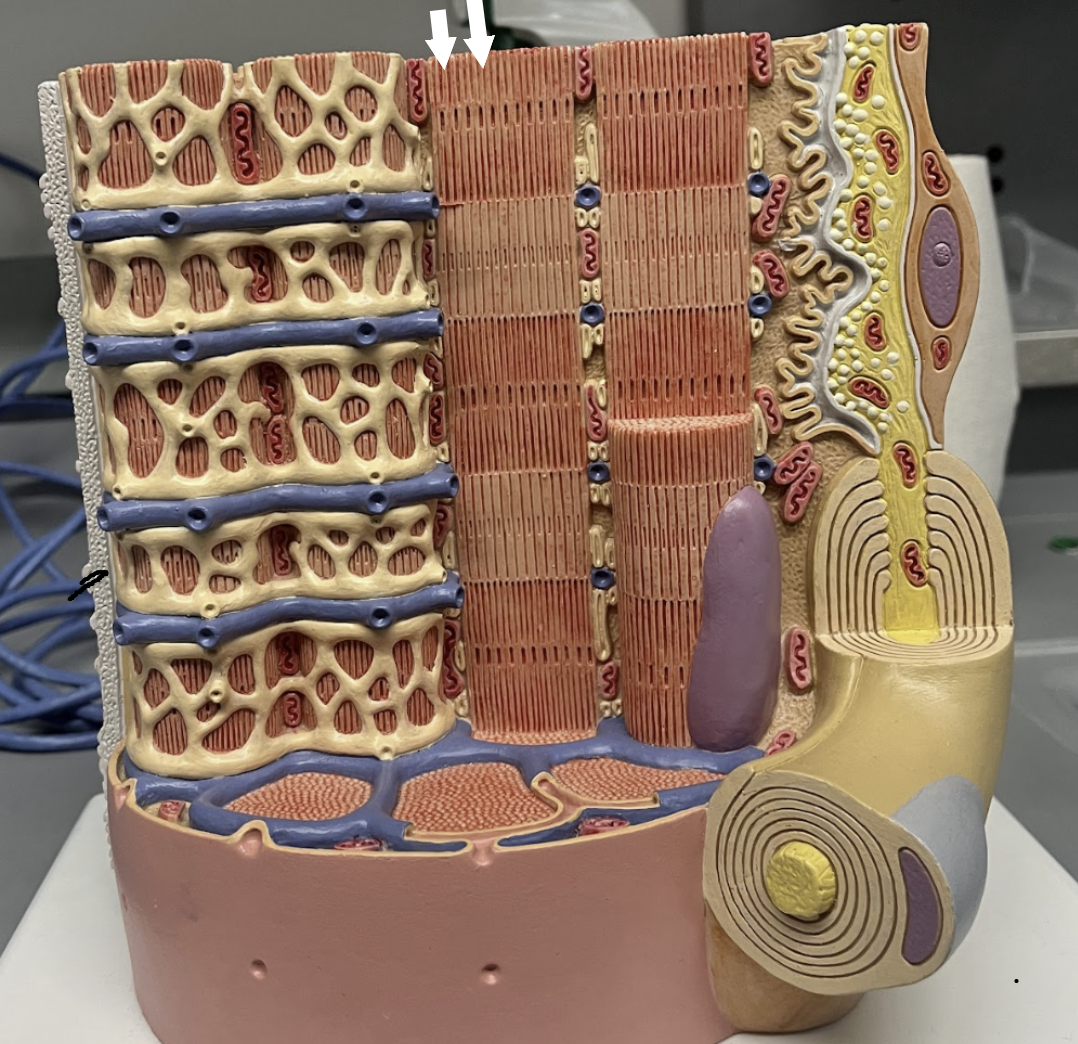
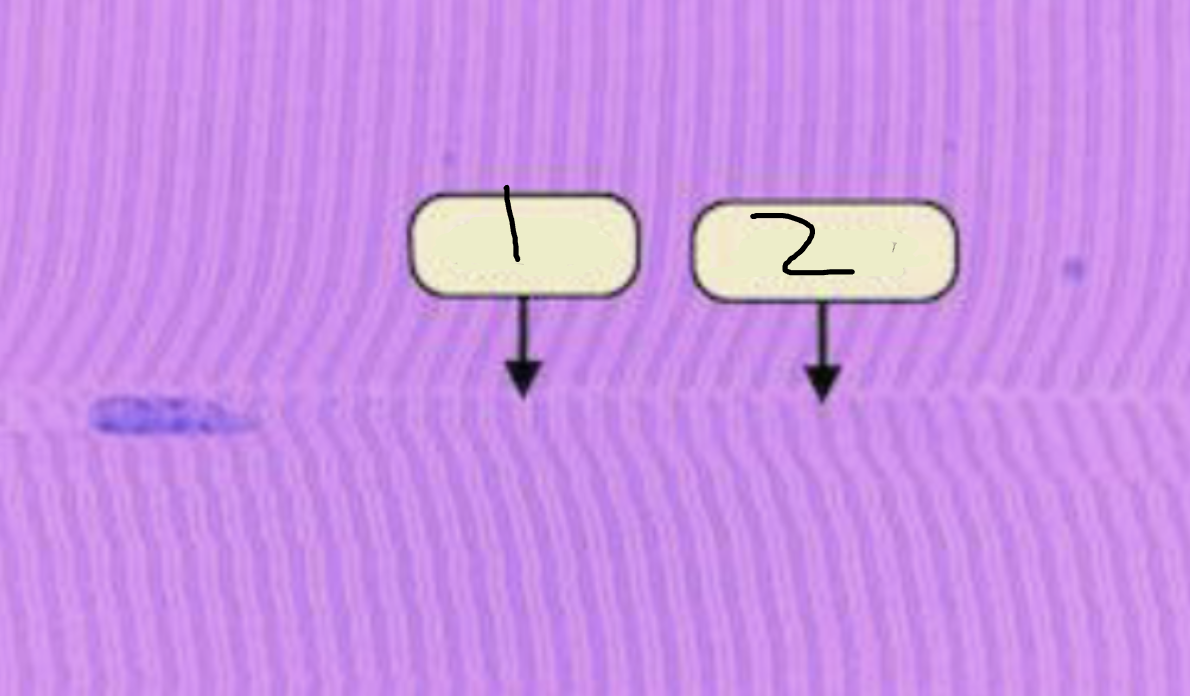
I band
1?
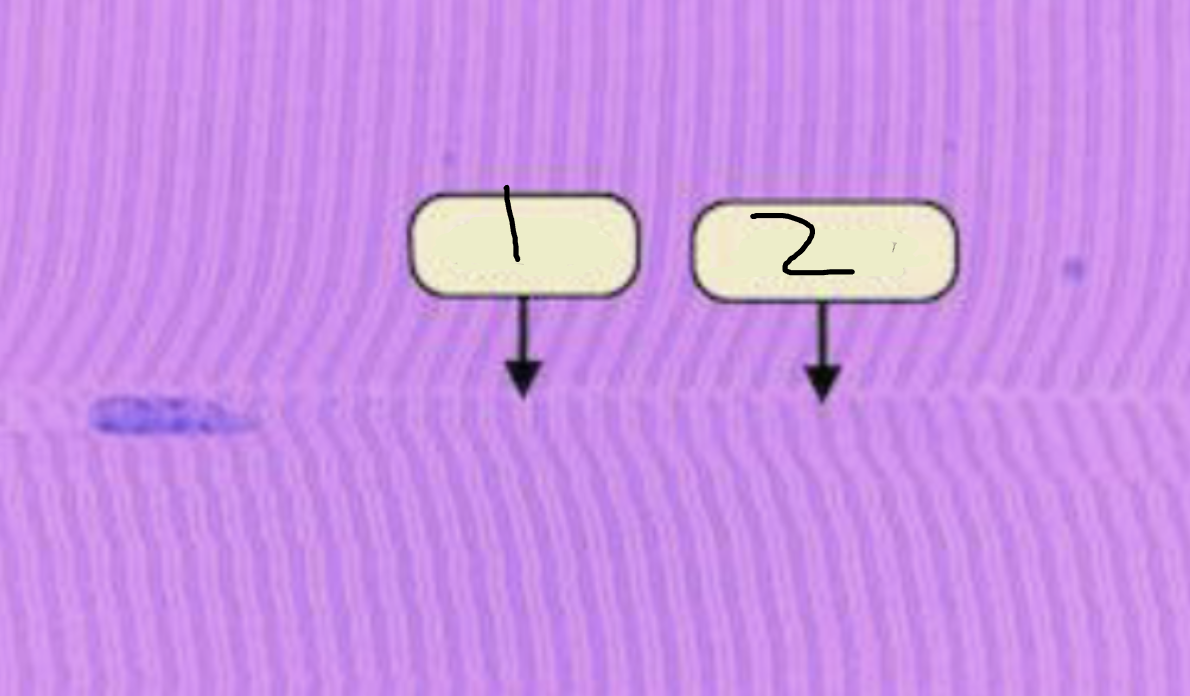
A-Band
2?
motor neuron
Entire image?
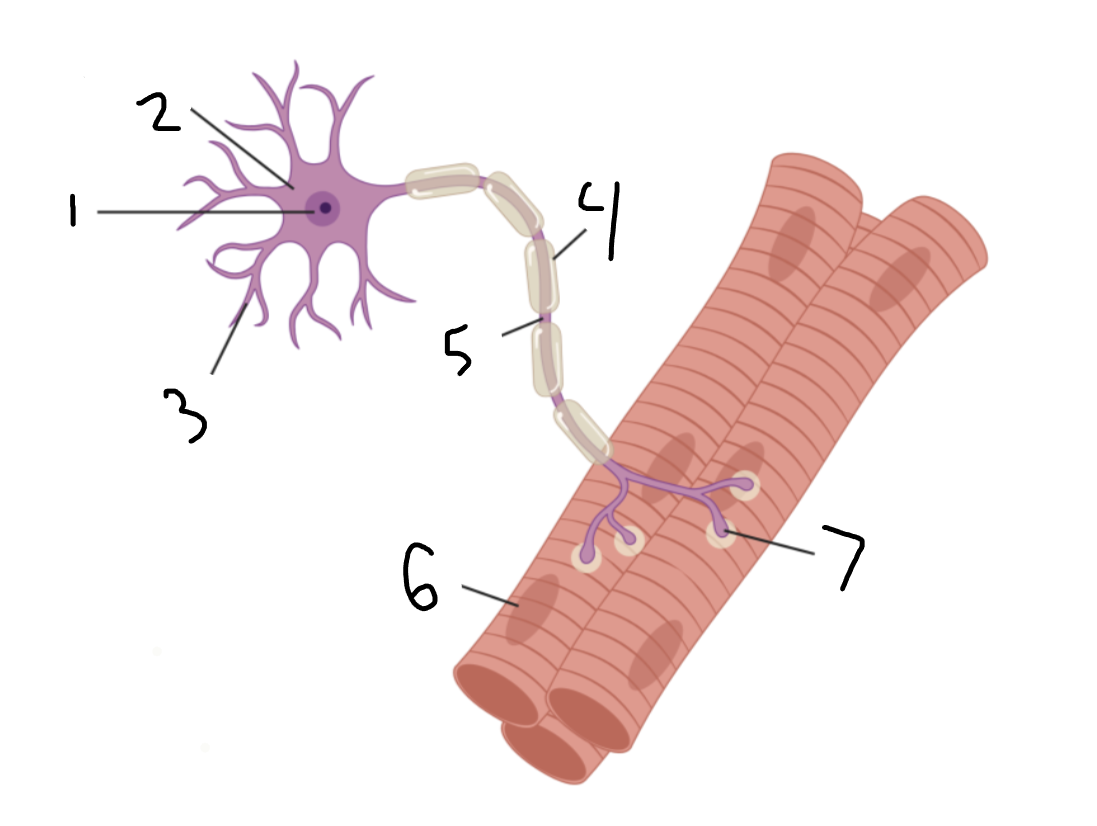
nucleus
1?
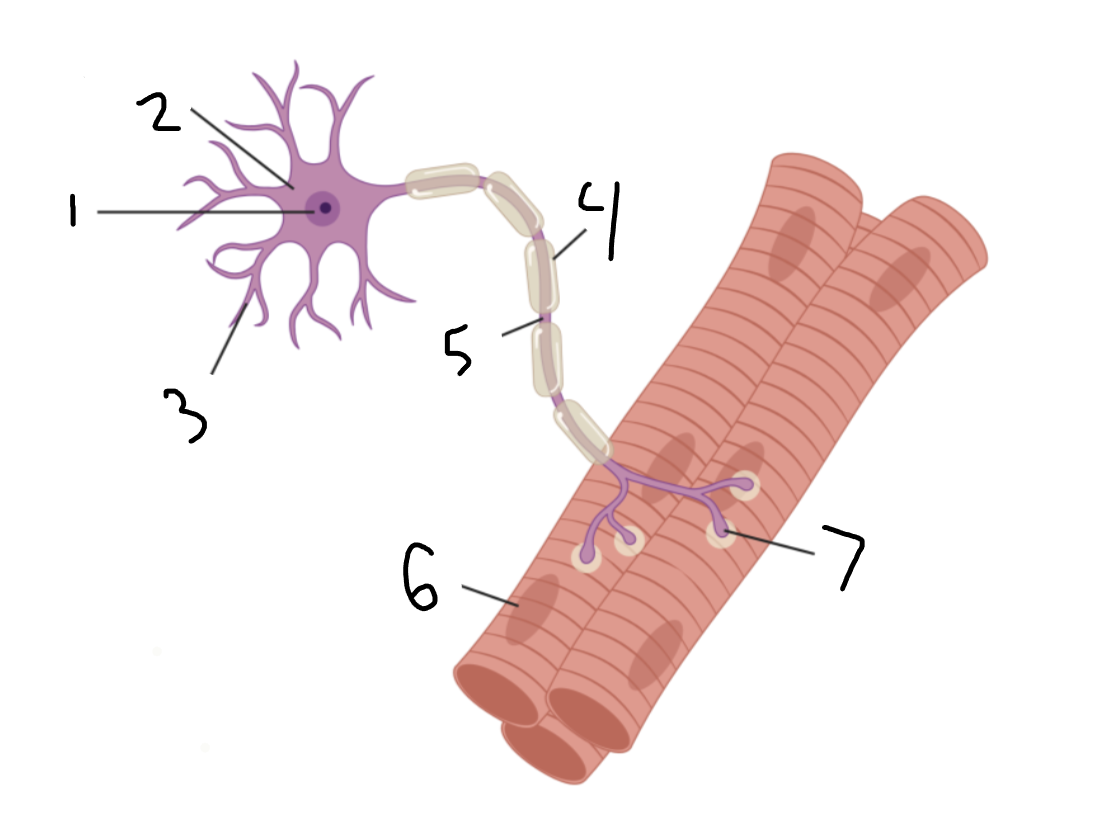
soma
2?
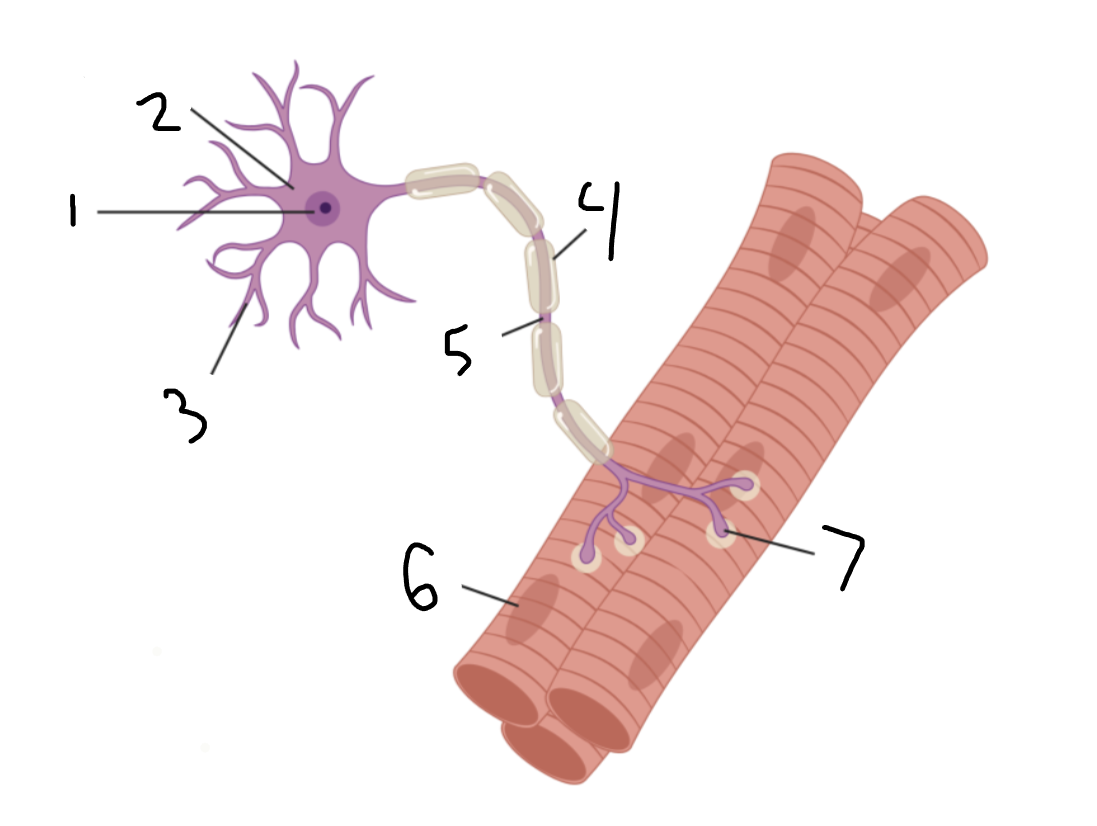
dendrites
3?

myelin sheath
4?
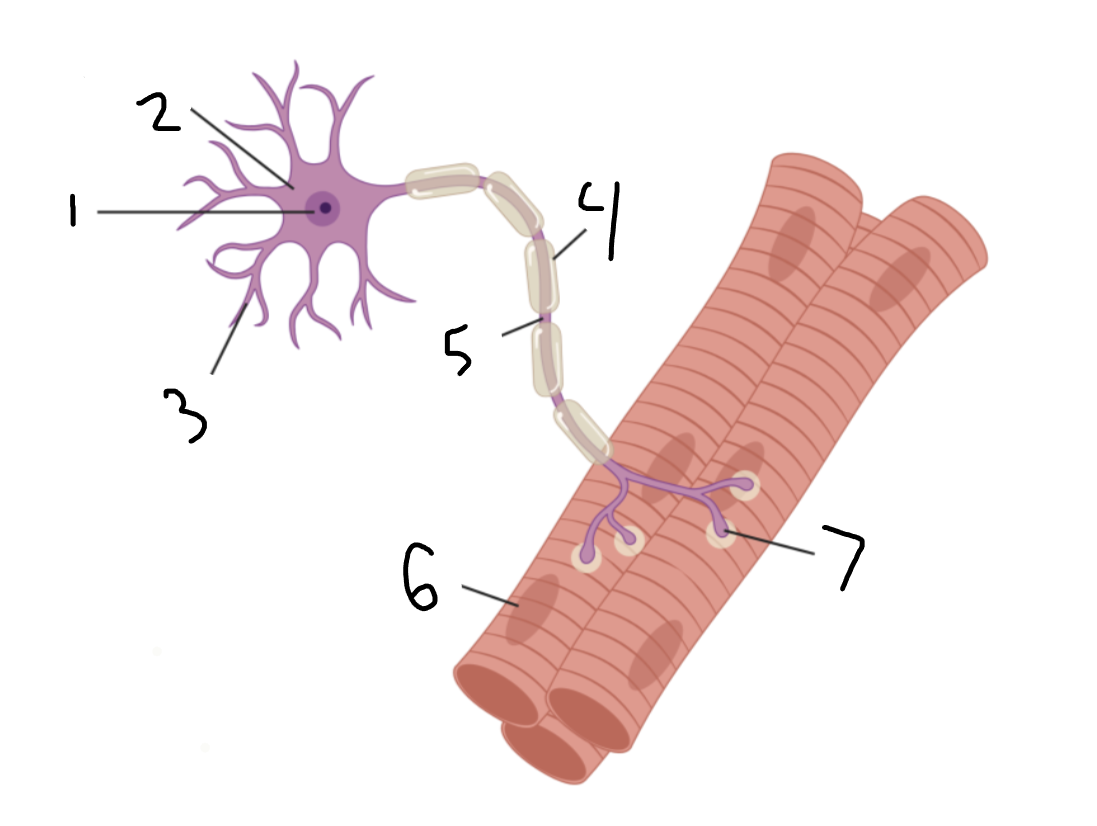
axon
5?
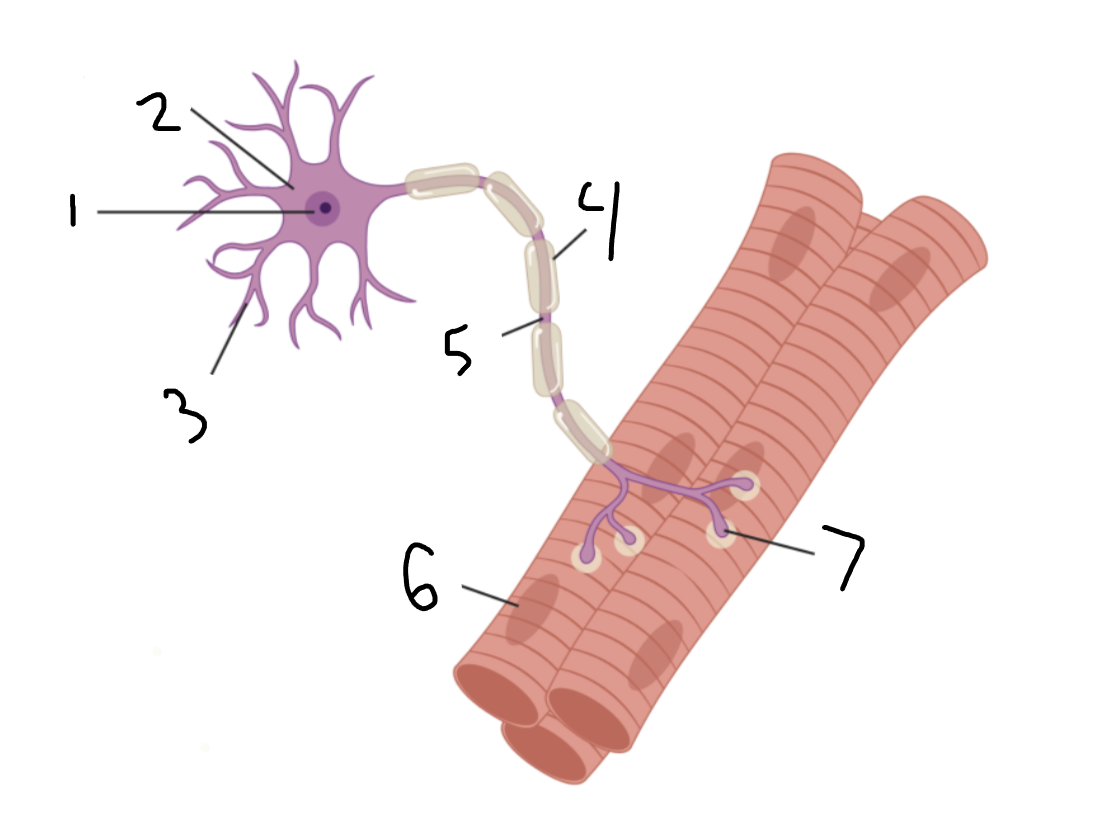
muscle fiber
6?
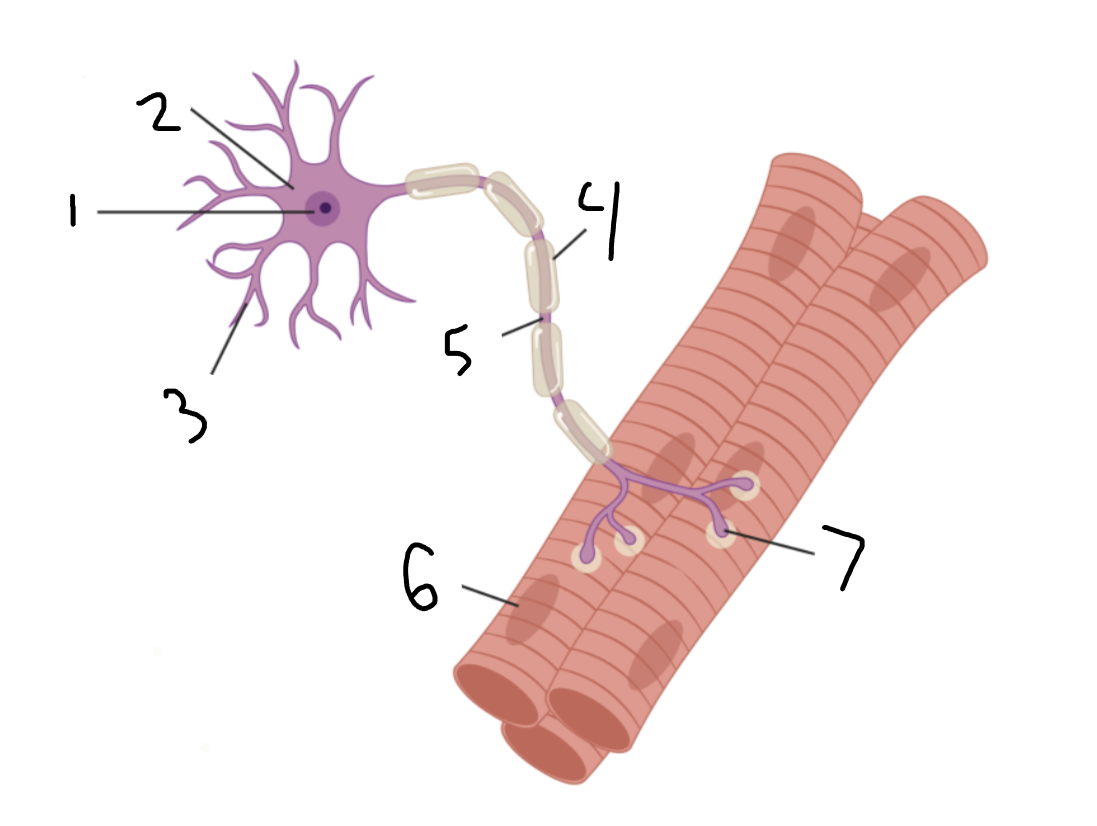
neuromuscular junction
7?
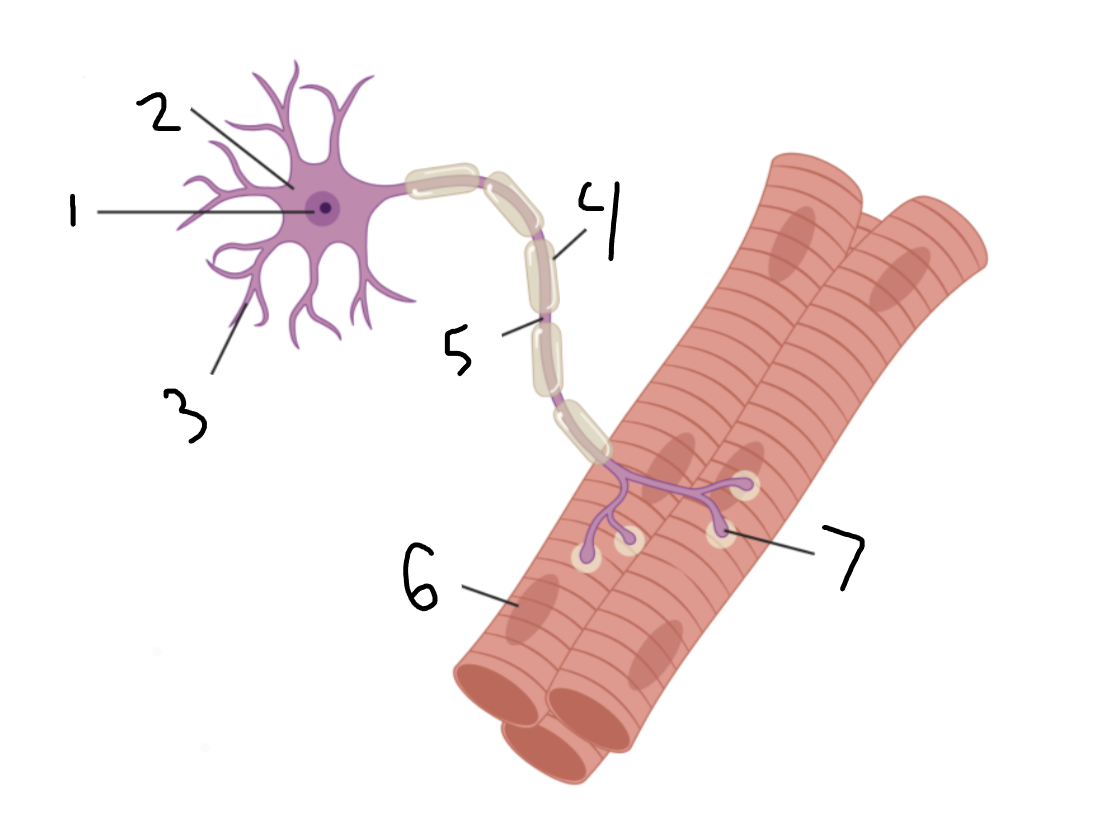
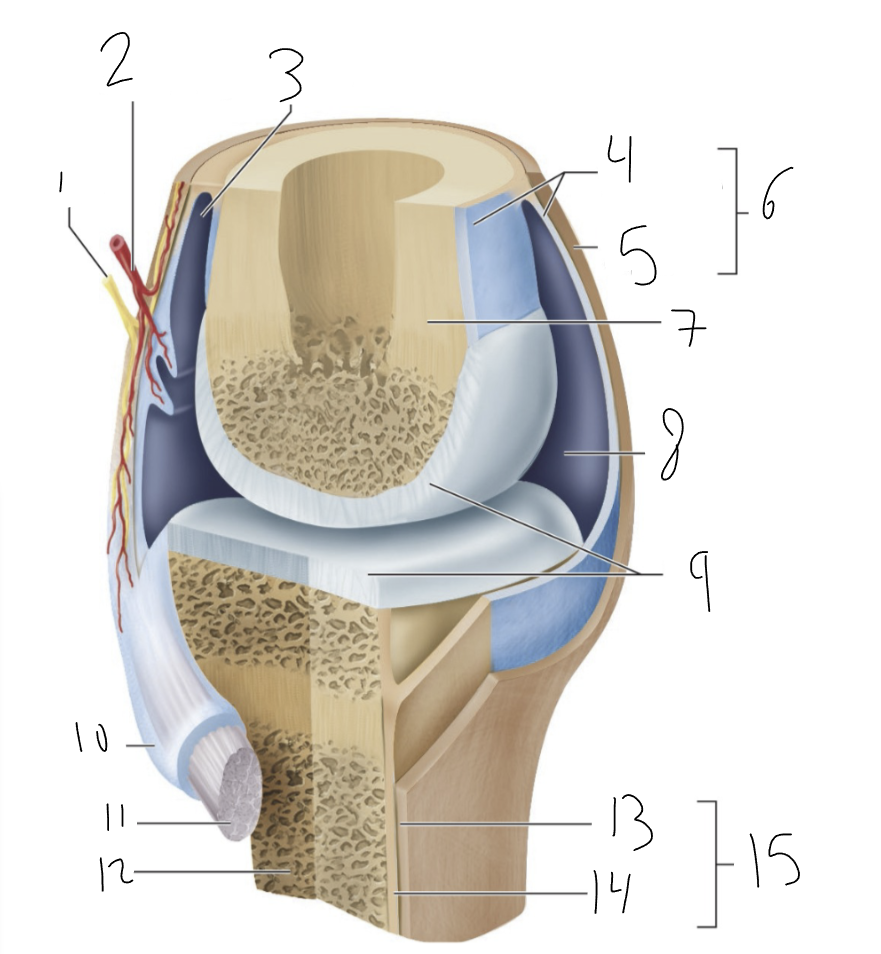
nerve
1?
blood vessel
2?
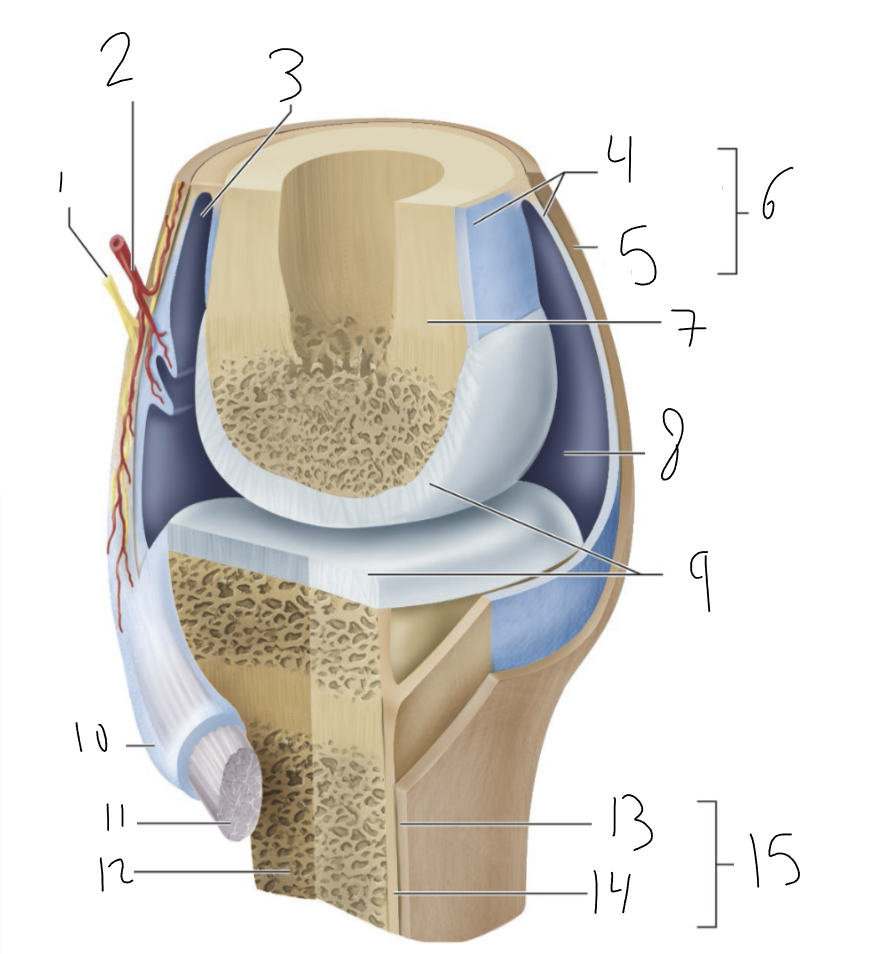
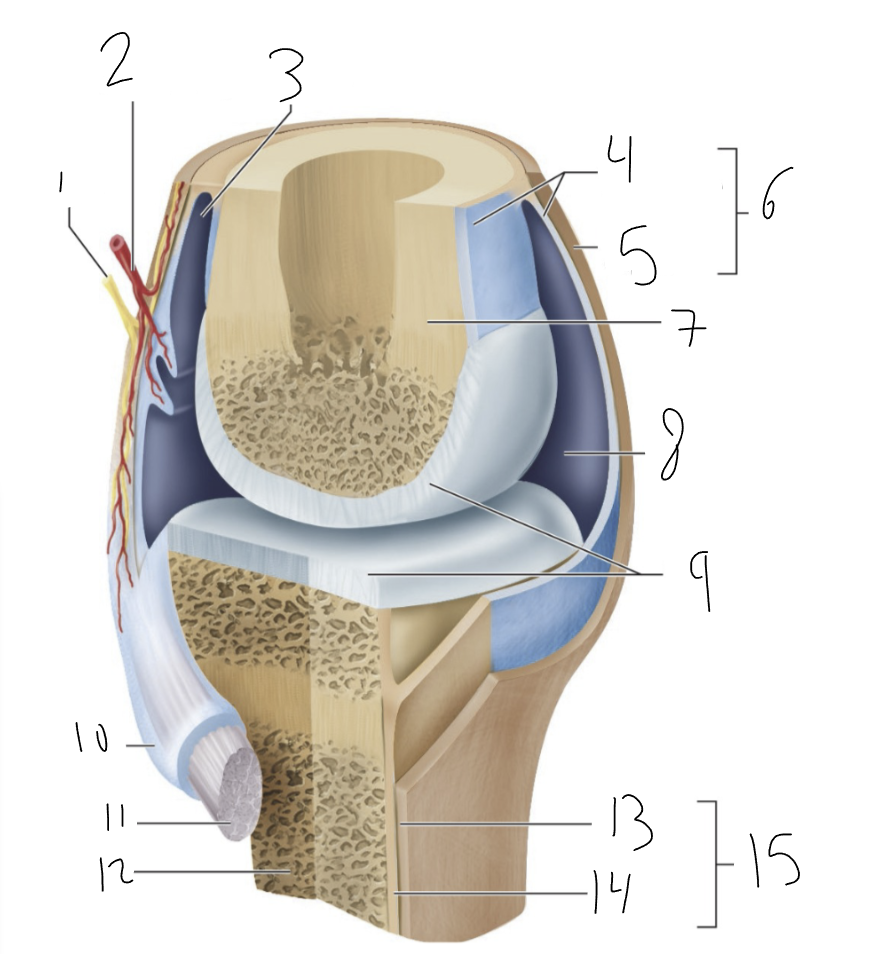
bursa
3?

synovial membrane
4?

fibrous capsule
5?
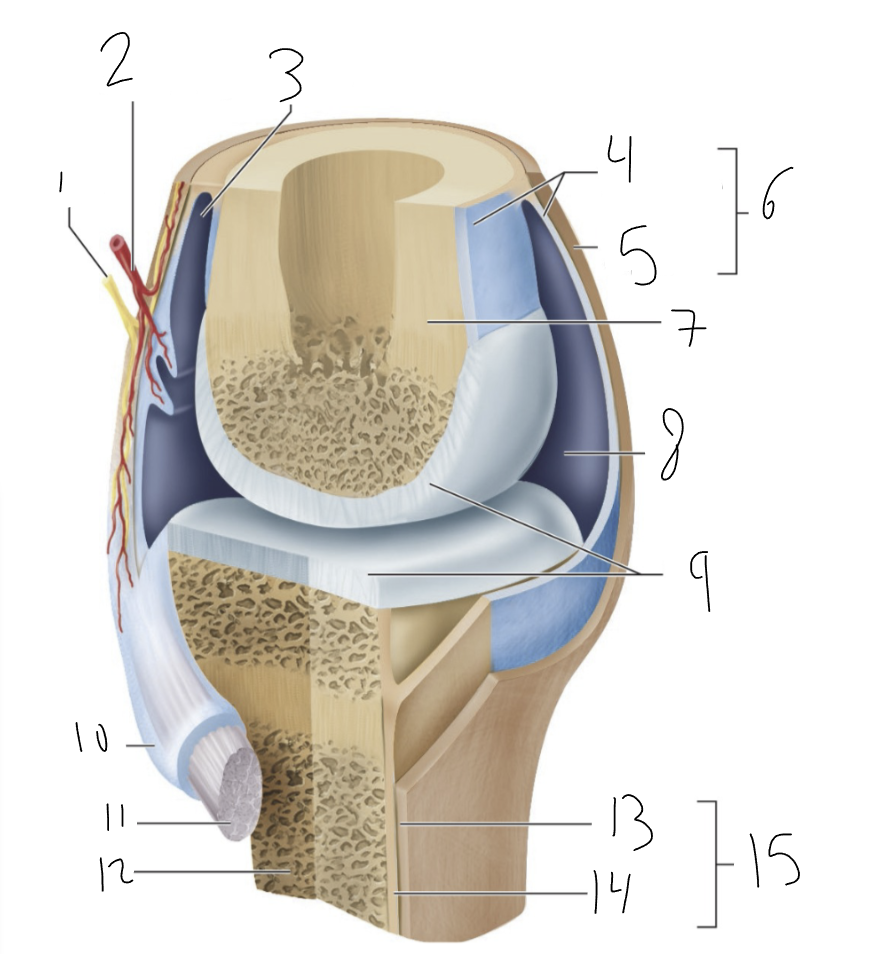
joint capsule
6?
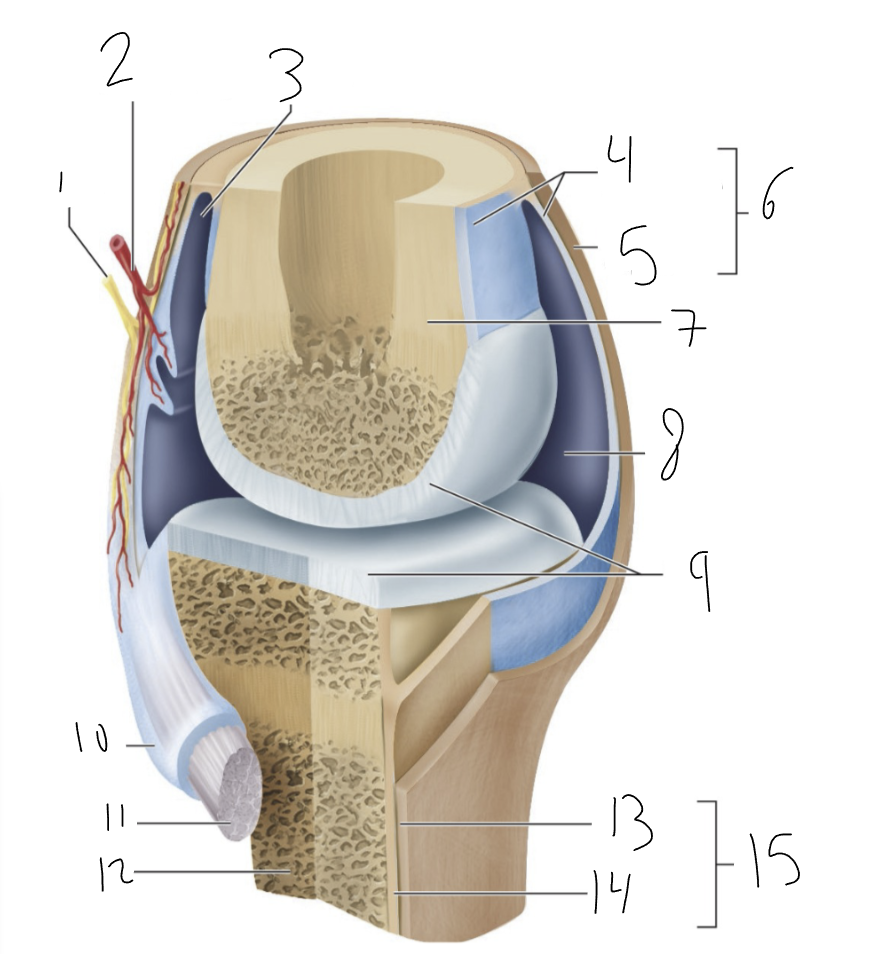
bone
7?

joint cavity
8?
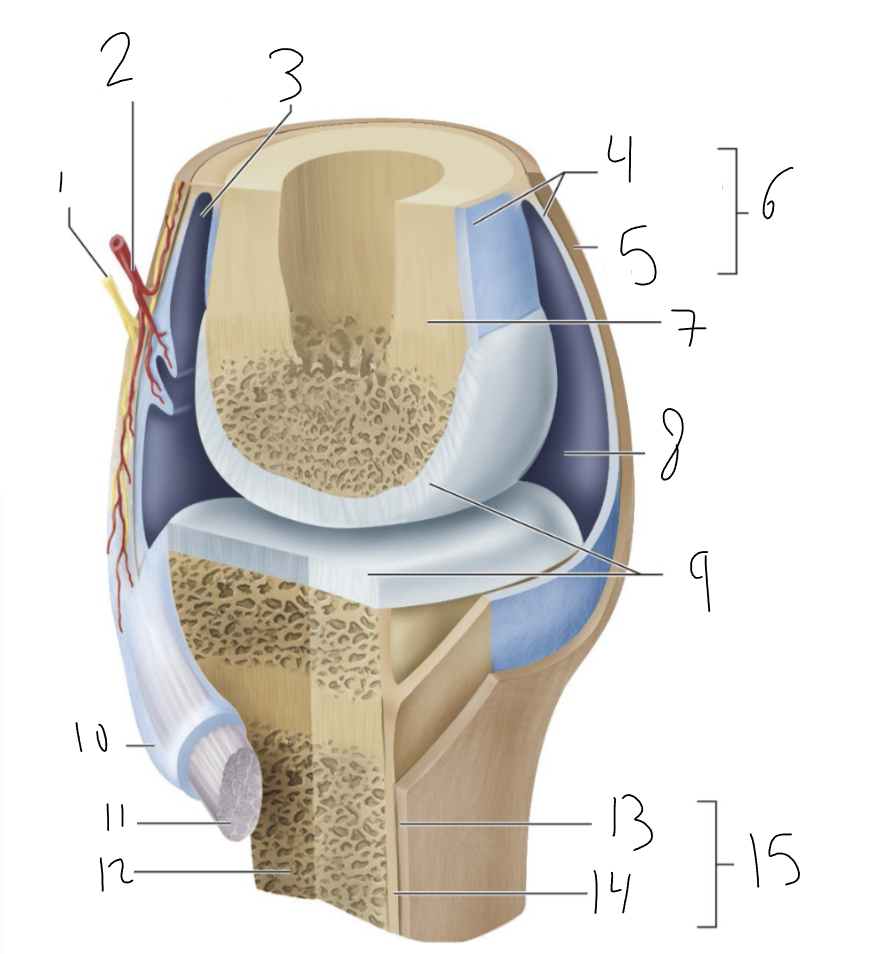
articular cartilage
9?
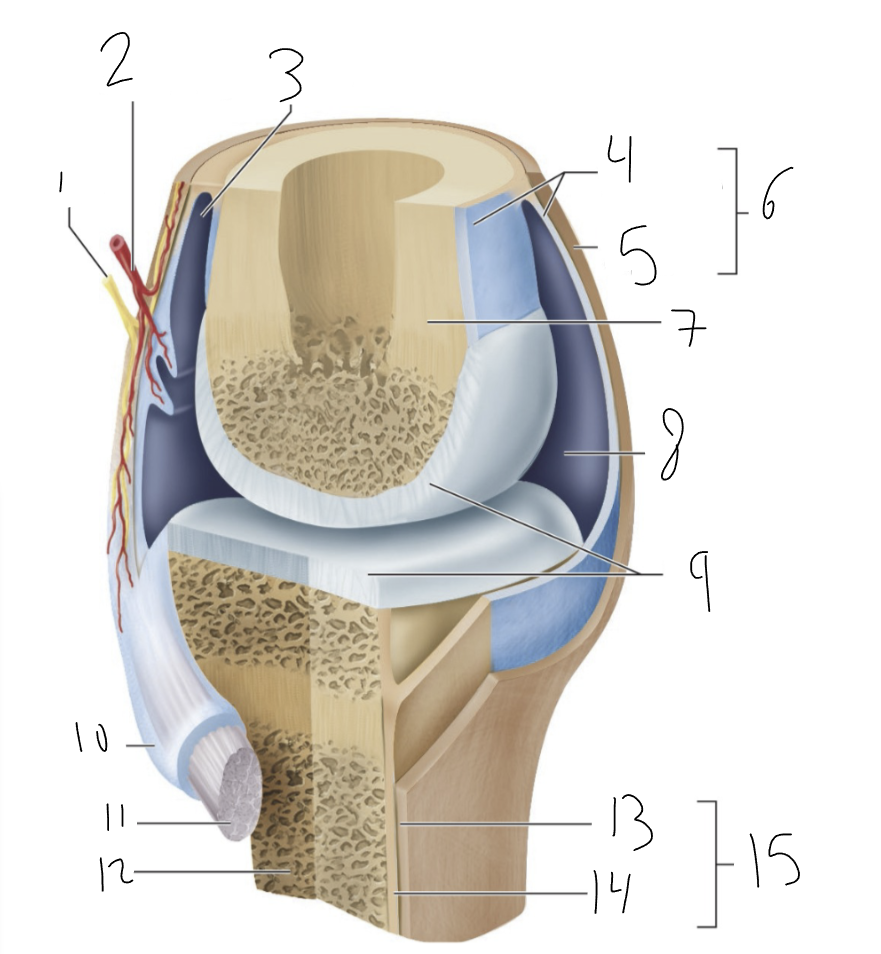
tendon sheath
10?
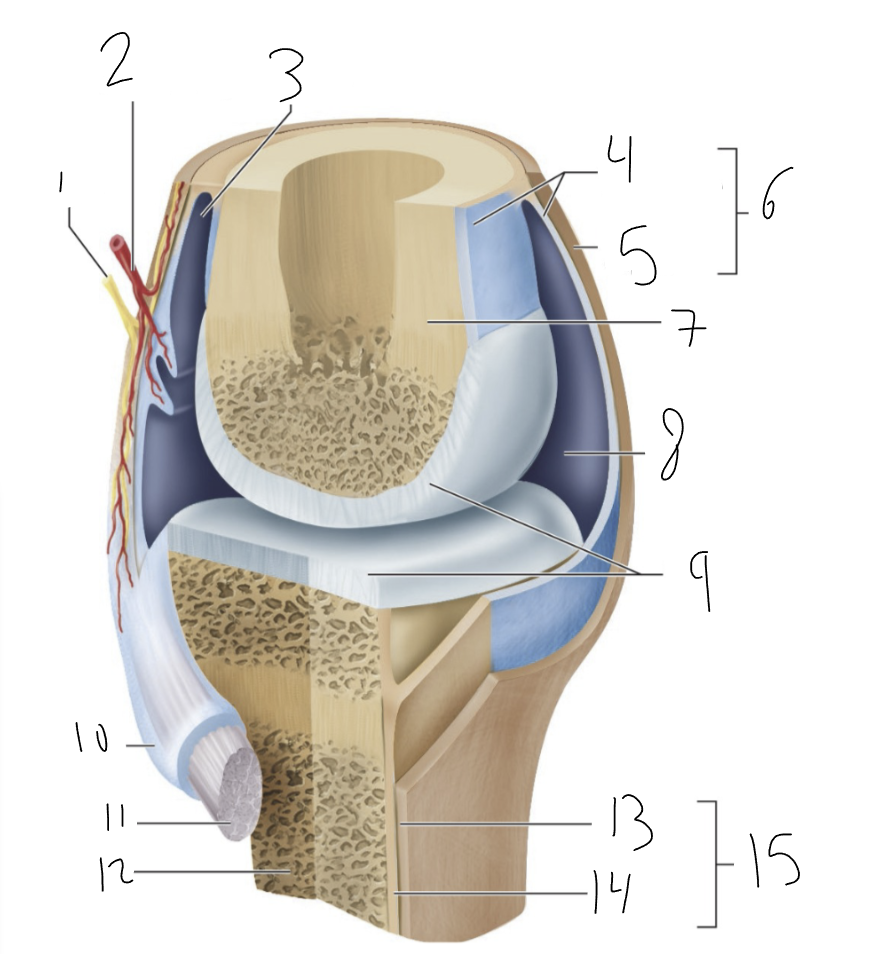
tendon
11?
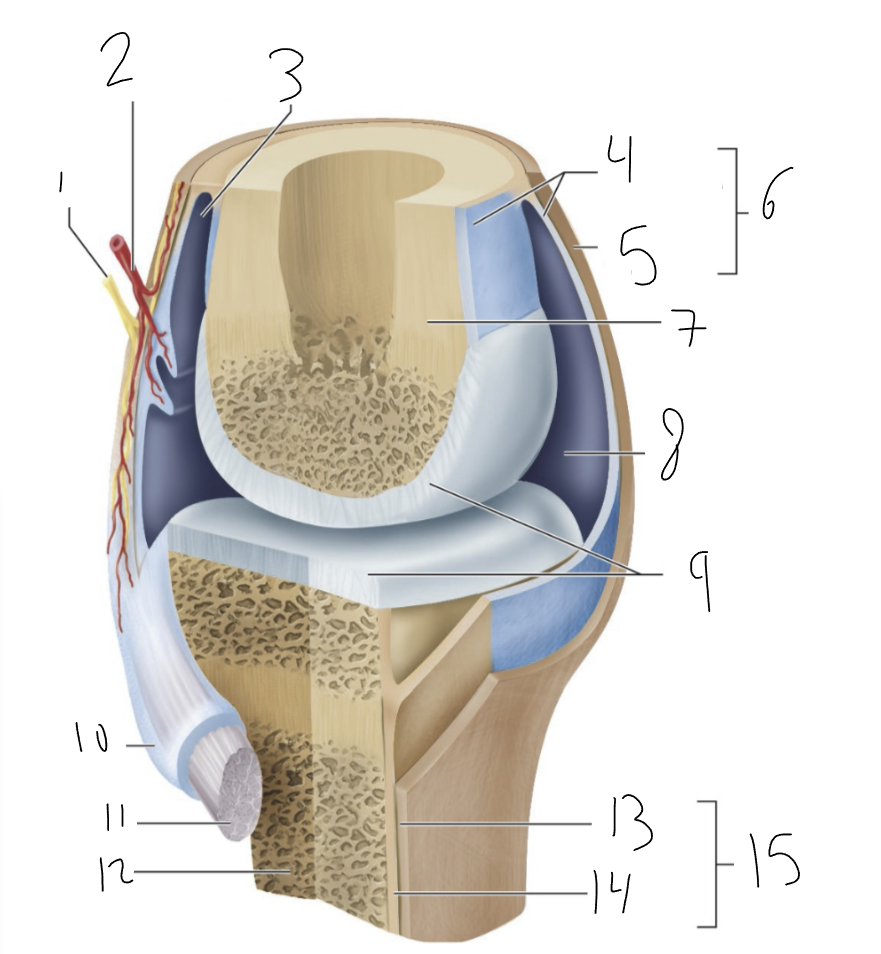
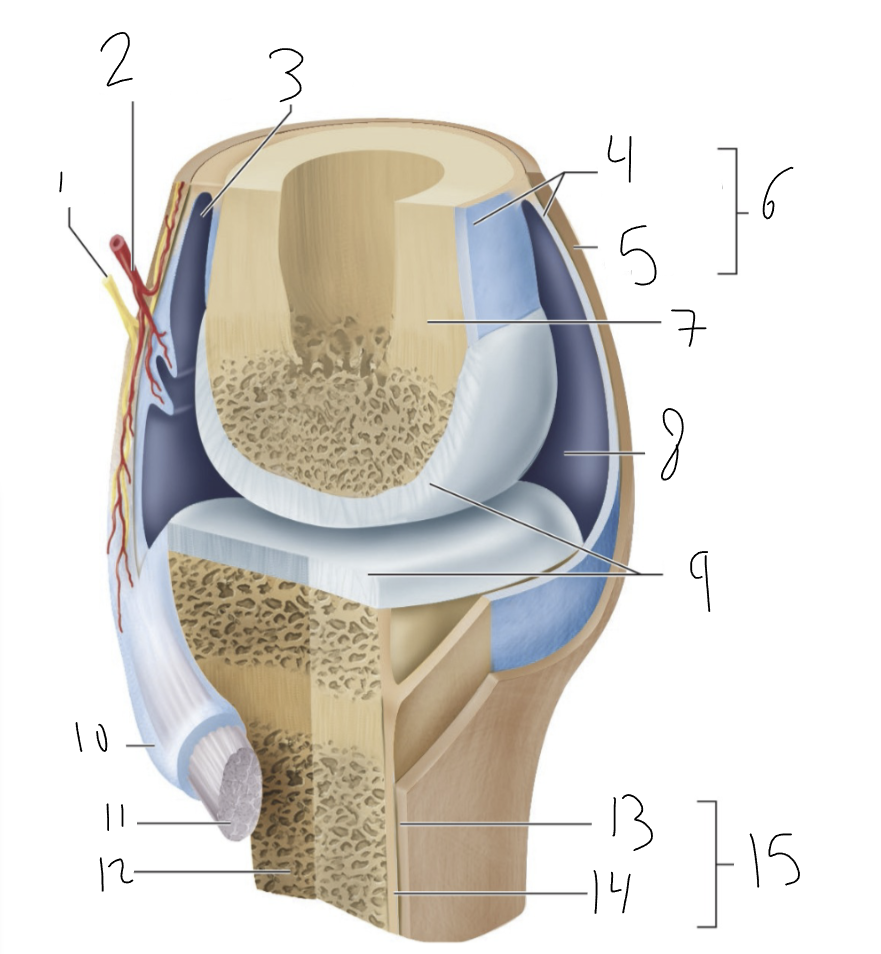
fibrous layer
13?
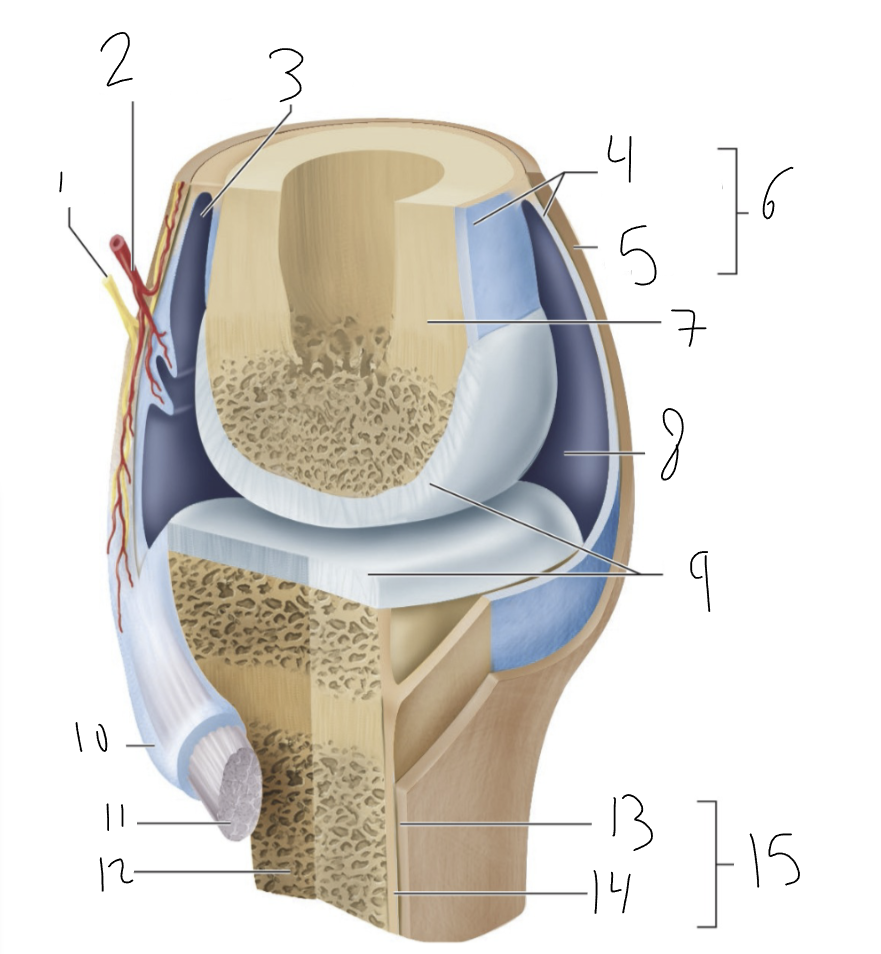
cellular layer
14?
periosteum
15?
synovial joint
type of joint found between bones that move freely
articular cartilage
provides smooth surface
joint cavity
encloses articular surfaces
fibrous capsule
dense irregular connective tissue, continuous with fibrous layer of the periosteum. Portions may thicken to form ligaments.
synovial membrane
membrane lines inside of joint capsule except at actual articulation of articular cartilages. Thin, delicate. Sometimes separated from fibrous capsule by areolar C.T. and fat, sometimes merged with fibrous
synovial fluid
complex mixture of polysaccharides, proteins, fat and cells. Hyaluronic acid- slipper
epithelial, connective, nervous, muscular
the four basic tissues?
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
3 types of muscular tissue
flexion
a movement that decreases the angle between two body parts
extension
extension a movement that increases the angle between two body parts, returning them to anatomical position
contractility
ability of a muscle to shorten with force
excitability
capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus (usually from nerves)
extensibility
muscle can be stretched beyond its normal resting length and still be able to contract
elasticity
ability of muscle to recoil to original resting length after stretched.
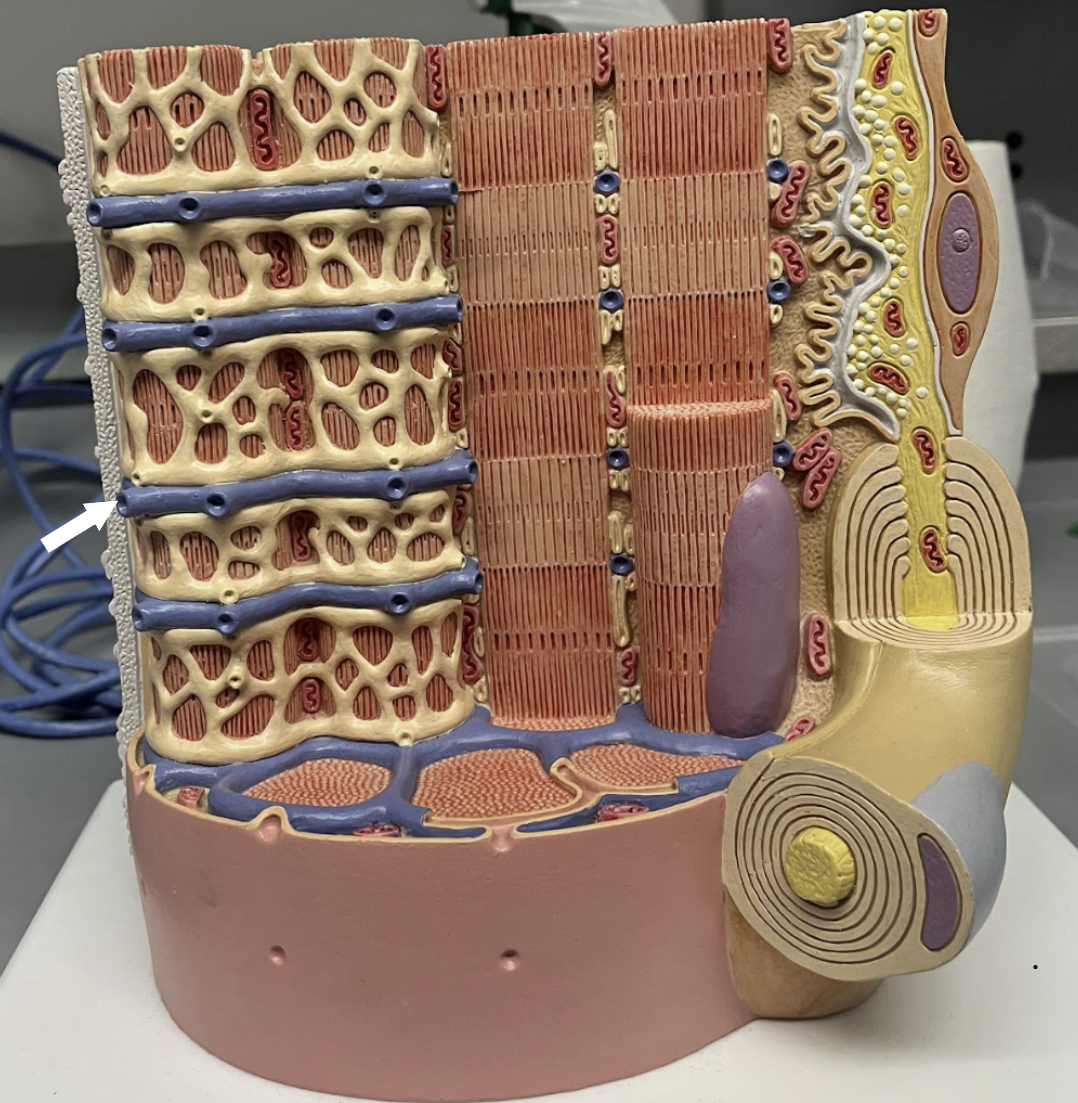
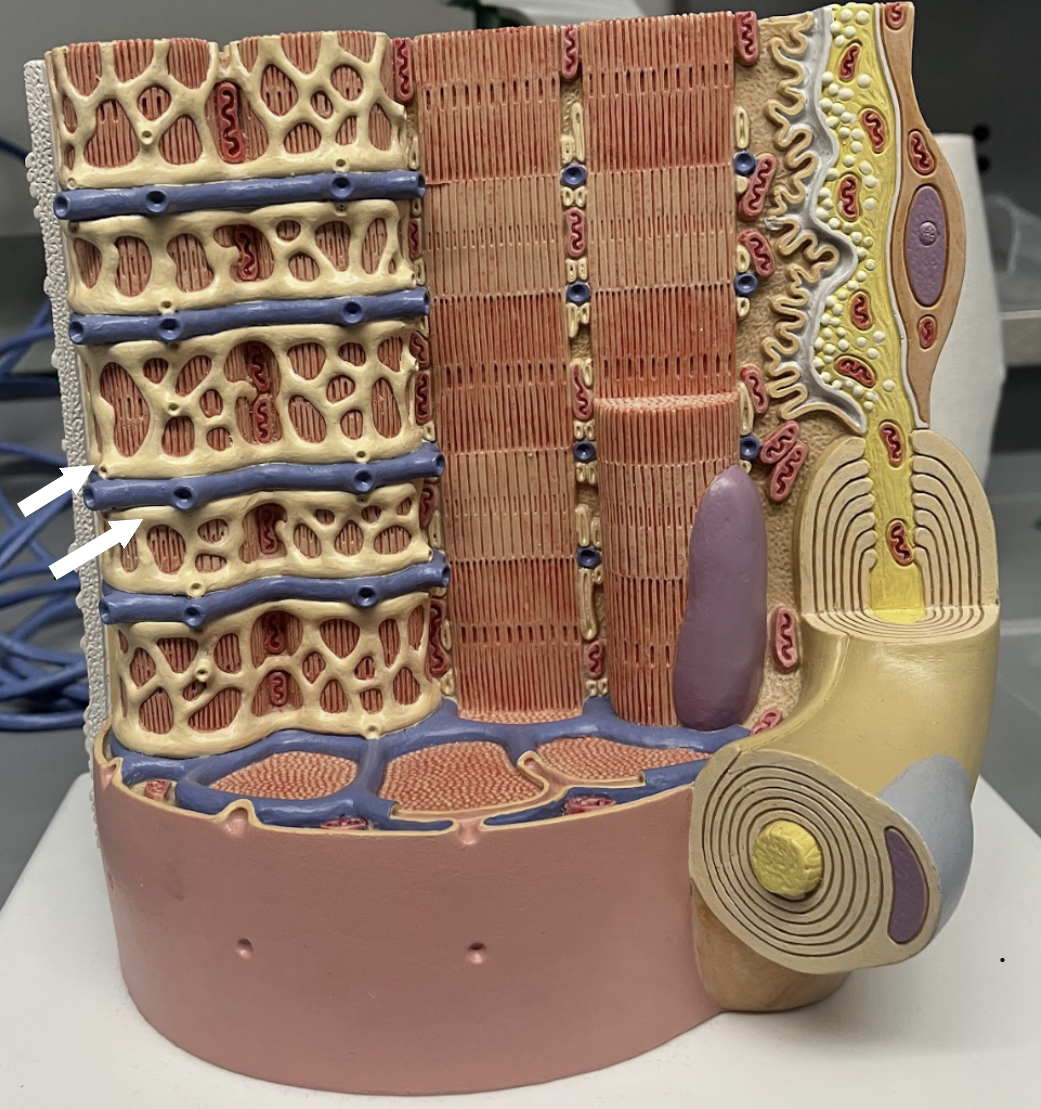
muscular fascia
muscle connective tissue layer that surrounds individual muscles
epimysium
muscle connective tissue layer that surrounds muscles
perimysium
muscle connective tissue layer that surrounds fascicles
endomysium
muscle connective tissue layer that surrounds muscle fibers
capillary
the smallest blood vessel in the body, forming networks between arterioles and venules
myoblasts
Embryonic muscle cells that serve as the building blocks for skeletal muscle fibers. proliferate, then fuse together to form multinucleated muscle fibers.
triad
the name for the sandwich of terminal cisterna and transverse tubules (t tubules)
sarcolemma
the plasma membrane of skeletal muscle fiber
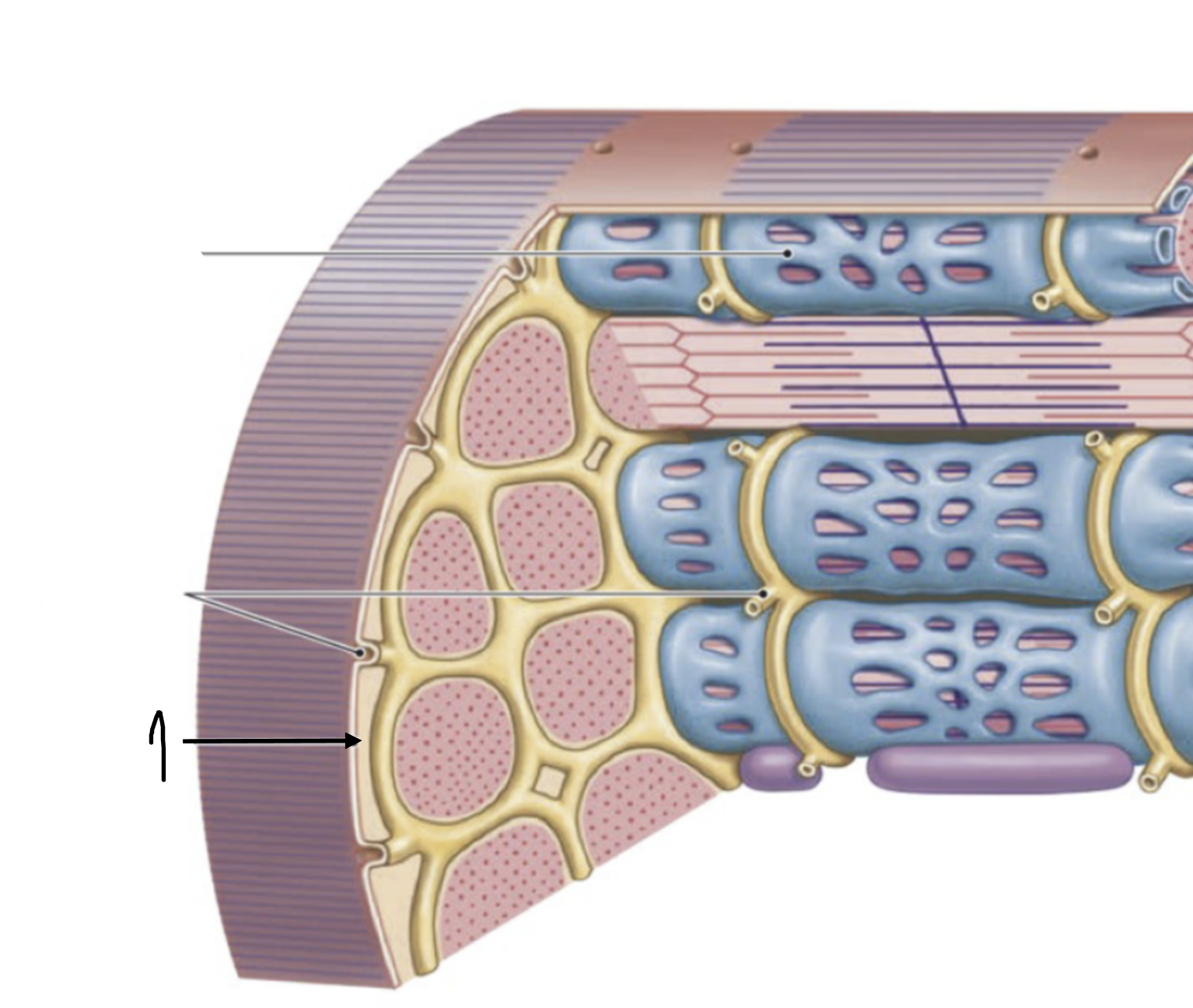
connective tissue, muscle fascicles, blood vessels, nerves
skeletal muscle is composed of…
muscle fibers
muscle fascicles is composed of individual….
sarcolemma, t-tubules, sarcoplasm, multiple nuclei
muscle fibers contain…
sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibril, mitochondria, glycogen granules
sarcoplasm consists of
glycogen granules
Small, dense clusters of stored glycogen found in the cytoplasm (sarcoplasm) of cells, especially in skeletal muscle fibers and hepatocytes (liver cells).
sacromere
myofibril is composed of…
troponin, actin, tropomyosin, myosin, titin, nebulin
sacromeres consist of ..
thin filaments
consist of actin, tropomyosin, and troponin.
thick filaments
consist of myosin
tropomyosin
A long, rope-like protein that covers the myosin-binding sites on actin when the muscle is relaxed.
troponin
A globular protein complex attached to tropomyosin. - Binds calcium ions (Ca²⁺) during stimulation, causing a shape change that moves tropomyosin off the binding sites.
titin
A giant elastic protein that anchors the thick filaments (myosin) to the Z disc in a sarcomere.
nebulin
A structural protein found in skeletal muscle, associated with thin filaments (actin). Helps align actin
myofilament
protein filament within a myofibril that plays a direct role in muscle contraction. consists of actin and myosin.
I band, H zone
which bands/zones shorten during contraction?
Motor neuron fires AP, Muscle fiber fires AP, AP travels into T-Tubule, Opens Ca2+ channels, causes sarcomeres to contract
Contraction Pathway?
Neuron AP, Volrage-gated Ca2+ channels open, Ca2+ triggers ACh vesicles to fuse with membrane, ACh released into synaptic cleft, ACh diffuses across cleft and bindsto ACh receptors, ACh receptor channels open (Na+ flows in and a little K+ out), end-plate potential (EPP) forms, if threshold met voltage-gated Na+ channels open, muscle ap generated
NMJ sequence?
troponin
Where on the sacromere does Ca2+ bind
contraction, SERCA pump, Ca2+ into SR, Ca2+ decreased in icf, Ca2+ detach from troponin, tropomyosin block actin:myosin binding, relaxation.
relaxation pathway?
stimulus, receptor, input, integrating center, output, target(s), tissue response(s), systemic response
general reflex pathway
deltoid muscle spindle stretch (shoulder abduction), muscle spindle in deltoid (intrafusal fibers), sensory neuron to spinal cord (afferent pathway), spinal cord, motor neuron to deltoid (efferent pathway), deltoid muscle fibers (extrafusal fibers), deltoid contraction, deltoi muscle spindle stretch decreased (shoulder stabilized)
specific reflex with one muscle
sudden load in hand, muscle spindle stretch in biceps brachii, sensory neuron to spinal cord, spinal cord, motor neuron to biceps brachii and brachialis, bicieps brachi and brachialis, elbow flexion to counteract load, muscle spindle feedback from both muscles stabilizing arm
specific reflex with two muscles