AP Human Geography Unit 7: Cities and Urbanization
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Urban Hierarchies
Megacity - over 10 million; 35 in world and growing
Megalopolis/Conurbation - several Metro areas linked (BOSNYWASH)
Metropolitan (Metro) Area - over 50,000 to millions
City - tens of thousands
Towns - a few thousand
Village - 100 or so
Hamlet - few dozen
Isolated dwelling - 1-10
Urban Hierarchies Population - Megacity
Over 10 million; 35 in world and growing
Urban Hierarchies Population - Megalopolis/Conurbation
Several Metro areas linked (BOSNYWASH)
100,001 - 1,000,000
Urban Hierarchies Population - Metropolitan (Metro) Area
Over 50,000 to millions
Urban Hierarchies Population - City
Tens of thousands
Urban Hierarchies Population - Towns
A few thousand
2,001 - 100,000
Urban Hierarchies Population - Village
100 or so
101 - 2,000
Urban Hierarchies Population - Hamlet
Few dozen
11 - 100
Urban Hierarchies Population - Isolated Dwelling
1-10
The Settlement Hierarchy
Population, size, and sphere of influence of settlement increases BUT number of settlements decreases
Settlement Patterns
Dispersed
Linear
Nucleated
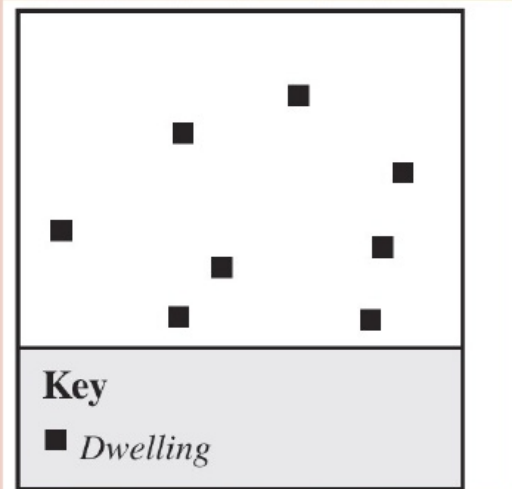
Settlement Patterns - Dispersed
Refers to the scattering of houses over a large area.
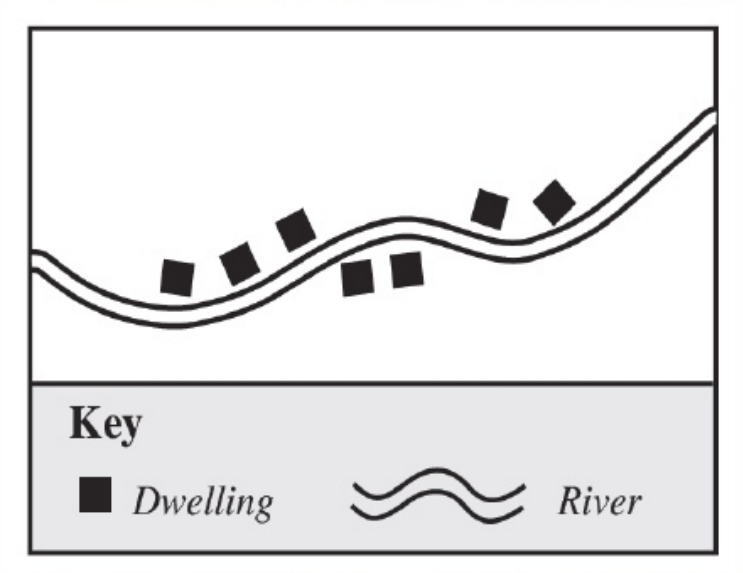
Settlement Patterns - Linear
Refers to the grouping of houses along a line.
Ex) River, roads, railway tracks, along the coast
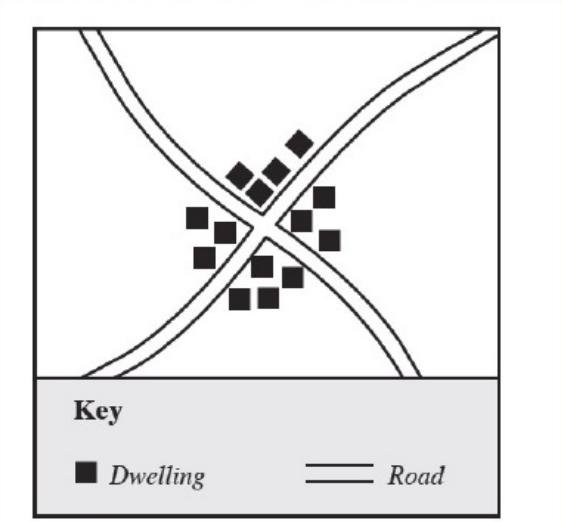
Settlement Patterns - Nucleated
Refers to the grouping of many houses around a centre called a nucleus.
Ex) Road intersections, focal points of an area, confluences of rivers
City: Main Function
To act as an economic hub or concentrator
Types of Cities
Emerging
Gateway
Entrepot
Types of Cities - Emerging
City growing in population, economic + political influence
Often in developing countries
Ex) Bangkok, Hanoi, Dubai
Types of Cities - Gateway
City connects one area or region to another
Ex) St. Louis (east to west USA), NYC (immigrants from Europe to USA)
Types of Cities - Entrepot
A major port city where goods are imported or exported
Ex) Shanghai, NYC, London, Longbeach California
What are the most influential cities?
New York, London, Tokyo
Examples of Alpha Cities
Shanghai, Singapore, LA, Mumbai
Examples of Beta Cities
Chicago, Berlin, Paris, Mexico City, Rio
Examples of Gamma Cities
Jakarta, Atlanta, Rome
Functional Zonation
The internal division of the city into certain regions (zones) for certain purposes (functions) “zoning laws”
Not random; cities are spatially organized to preform their functions as places of commerce, entertainment, production, or education
USA Zoning
Little national government involvement (local gov.)
Segregated zones (residential, commercial, industrial, historic) the norm
Preference for single-family residential zones (sub-divisions)
Large planning zones
Europe Zoning
Strong national government involvement
Mixed use development the norm
No strong preference for single-family residential zones
Smaller planning zones (blocks)
US City Characteristics
Poorer central area; suburbs wealthy
More car dependent
Less walkable
Cheaper energy; lower overall cost of living; lower unemployment
Government policies favor suburbs, lower taxes on cars and fuel
European City Characteristics
Richer central area; suburbs poorer
Better mass transit
More walkable; narrow streets
Less violent crime
Government policies favor less pollution, mixed zoning, higher taxes on fuel and cars
Fewer skyscrapers
Basic Industry
City forming industry
Non-basic Industry
City serving economic activities, from services to government to manufacturing
Evolution of American Cities
1) Wagon-Sail
2) Iron-Horse
3) Steel-Rail
4) Auto-Air
5) Computer-Internet
Wagon Sail
1st in the Evolution of American Cities
1790s-1830s
Ex) Boston, Charleston, Philadelphia
Iron Horse
2nd in the Evolution of American Cities
1830-1870
Ex) Chicago, St. Louis, San Francisco
Steel Rail
3rd in the Evolution of American Cities
1870-1920
Ex) Denver, LA, Dallas, Houston
Auto Air
4th in the Evolution of American Cities
1950-1980s
Ex) Phoenix, Vegas, Atlanta, Miami, Charlotte
Computer Internet
5th in the Evolution of American Cities
1990s-now
Ex) “new'“ urbanization and gentrification
Central Place Theory
Developed by Walter Christaller
Predicts how and where central places in the urban hierarchy will be functionally and spatially distributed.
Range
The maximum distance people will travel to purchase a product or service
Ex) Convenience —> Low range
Ex) Apple Store —> High range
Why? Scarcity
Threshold
The minimum number of customers needed for a product or business to succeed
Ex) Soda can —> High threshold (sell a lot)
Ex) Waterbed —> Low threshold (sell a few)
Why? How often do you need to buy it?
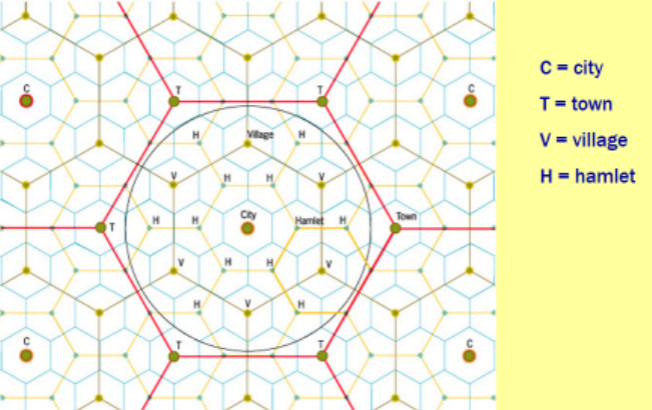
Hinterland
The area in which a product or business, or where any place had influence
Sometimes called the “market area'“
Often use Census Tracts (areas with about 3-8 thousand people) to locate business
Hexagonal Hinterlands
Gravity Model
The greater the influence of a city, the greater it’s impact on other cities/places around it
Larger cities pull people in from larger distances
NYC and London have more connections than NYC and Richmond
Rank Size Rule
The size of cities within a country will be in proportion to each other.
Ex) The 2nd largest city will be 1/2 the size of the largest city'; the 3rd largest should be 1/3 the size of the largest
Primate Cities
A dominant city with more than 2x the population of the next largest city
Ex) London, Paris, Mexico City
USA City Models
Concentric
Sector
Multiple Nuclei
Urban Realms
Galactic Periphery
USA City Models - Time Period: Concentric
1920
USA City Models - Time Period: Sector
1930s
USA City Models - Time Period: Multiple Nuclei
1940s/50s
USA City Models - Time Period: Urban Realms
1960s/70s
USA City Models - Time Period: Galactic Periphery
1960s/70s/80s
Concentric Zone Model Image
“Burgess Model”

Sector Model Image
“Hoyt’s”
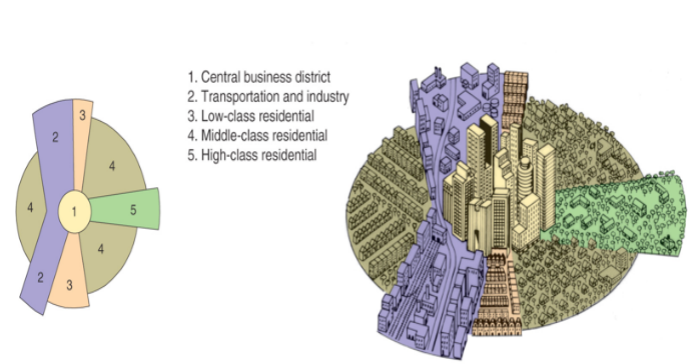
Multiple Nuclei Model
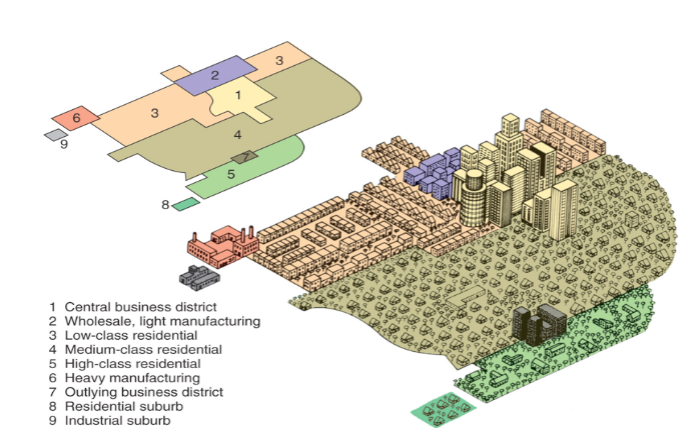
Urban Realms Model
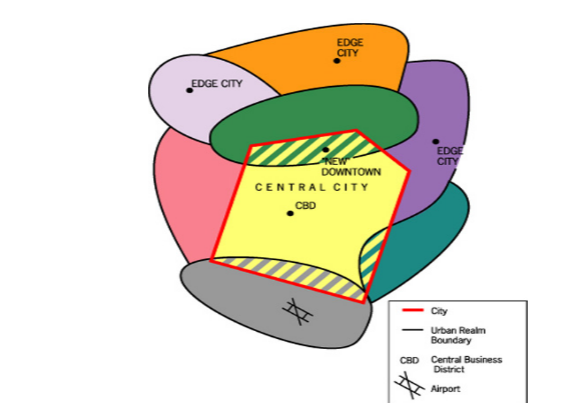
The Peripheral Model
Also known as the “Galactic”
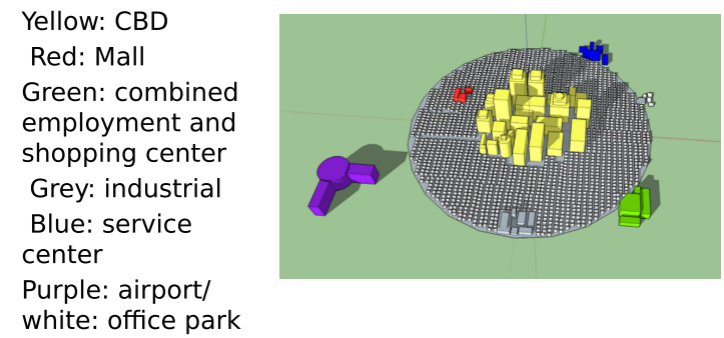
Global City Models
Latin American
African
Islamic
South East Asian
Latin American City Model
“The Griffin-Ford Model”
South East Asian Model
“The McGee Model”
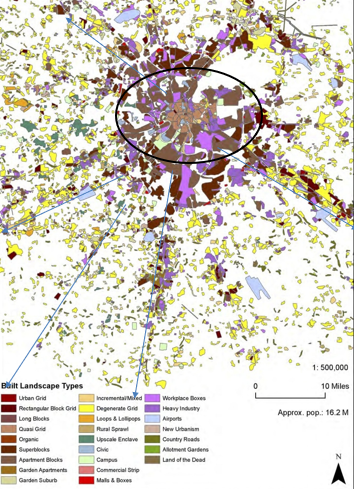
Global Urban Pattern: Moscow
Large core
Lots of large apartment blocks from USSR era
Lots of public transportation
Notice “spines” of development?
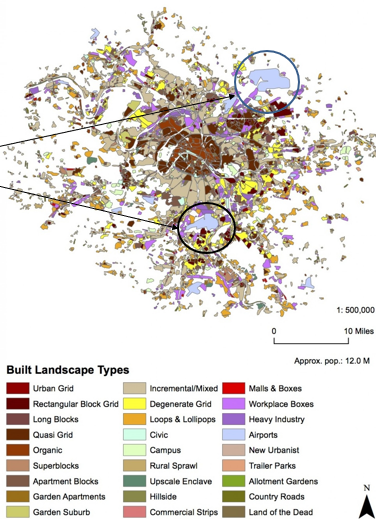
Global Urban Pattern: Paris
Very dense older urban core
Two large airports
Very walkable; car not as necessary
Poorer areas on periphery
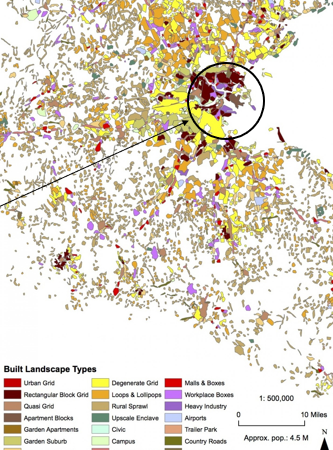
Global Urban Pattern: Boston
Older city core
Few “loops and lollipops'“ suburban subdivisions
Not as car dependent
Port centered
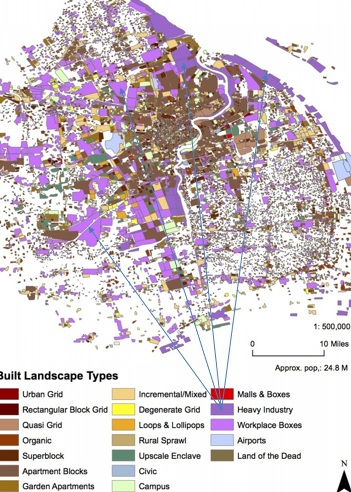
Global Urban Pattern: Shanghai
Massive industrial presence
Large dense core
Little impact from cars, yet…
Global Urban Pattern: Atlanta
LOTS of subdivisions (suburban sprawl)
Car dominated city
Lots office parks
Poorer area in core
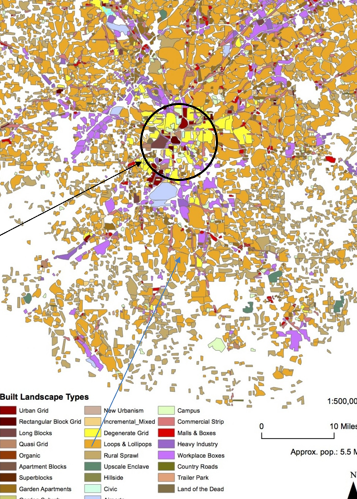
The Suburbs: America’s Dream?
Outside primary city
Car/commuter oriented
Larger homes/plots (high energy use)
Cheaper land
Higher % of families w kids
Can be very segregated
Redlining
A practice used to limit minorities of gaining loans and access to business and residential property near white neighborhoods
Began in 1930s
Outlawed in 1970s
White Flight
The movement of white urban residents to the suburbs, away from more ethnically and racially diverse areas.
Began in 1940/50s
Still happens today
Racial Steering
The practice in which real estate brokers guide prospective home buyers towards or away from certain neighborhoods based on their race.
Blockbusting
The practice in which real-estate brokers convinced white residents to sell their homes undervalue because of fears of minorities moving into the neighborhood.
New Trends in City Design
Walkup (Walkable Urban Place)
Walkable Neighborhood
Drivable Edge City
Drivable Sub-division
New Urbanism
A movement to redesign urban and suburban spaces.
What did New Urbanism Promote?
Walkability
Biking
Environment Sustainability
More energy efficiencies
Mixed use development
Mixed income development
Denser development
‘Older” style and “retro” architechture
“Urban Death Loop”
A negative feedback cycle where one negative development in a city leads to a chain of other negative consequences, potentially causing the city's economy and quality of life to decline. It happens when businesses close, people move out of a city, and in turn, tax revenue goes down.
Gentrification
The process in which wealthier people begin to move into poorer neighborhoods in older areas of the city.
What does Gentrification Cause?
Homes improved, new businesses open
Property values, rents, and taxes increase over time.
Poorer citizens are forced to move to other parts of the area or region; some become homeless