Circulatory System - Biology Double Award
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Explain the composition of Red Blood Cells:
RBCs have no nucleus so more haemoglobin can be packed in to the cell.
Haemoglobin joins with O2 in the lungs forming oxyhaemoglobin.
They have a biconcave disk shape to increase the surface area to increase the speed of diffusion of oxygen into the cell
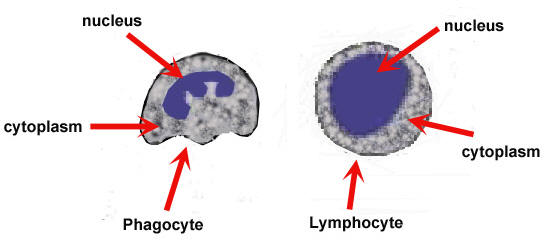
Explain the composition of White Blood Cells:
WBCs defend the body against pathogens which are organisms capable of causing disease
Phagocytes - Phagocytosis
Lymphocytes - Makes antibodies
Describe the composition of Platelets:
Fragments of cells involved in blood clotting and scab formation
At a wound site, they get trapped and rupture to release thromboplastin
Thromboplastin causes the conversion of soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin which forms the clot
Describe the composition of Plasma:
This is the liquid component of blood consisting mainly of water with dissolved substances such as:
Glucose, amnio acids, fatty acids, glycerol, hormones (insulin and ADH)
Waste products such as CO2 and urea and heat
Outline the functions of Blood:
To transport blood cells, platelets, nutrients, heat and waste products throughout the body. To collect and deliver O2 to the cells of the body
The blood also has a role in defense against disease whereby the WBCs destroy pathogenic bacteria and viruses
Blood clotting - Platelets contain thromboplastin which triggers the blood clotting mechanism
To transport hormones from glands to target organs
See Image For Practice - Answer = Cat
Cat
What is the heart made of?
Cardiac muscle
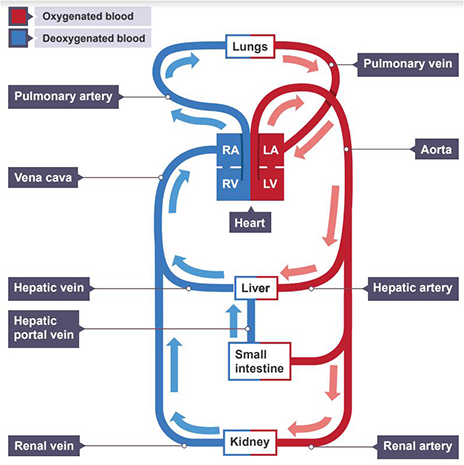
What is double circulation?
Blood passes through the heart twice on each journey through the body. Once to be pumped to the lungs to collect O2 and again pumped around the body.
What -
Separates the heart
Pushes oxygenated blood out
Pushes deoxygenated blood out
Pulls deoxygenated blood in
Pulls oxygenated blood in
Septum
Aorta
Pulmonary artery
Vena cava
Pulmonary vein
List the valves used in -
Oxygenated blood
Deoxygenated blood
Oxygenated blood -
Bicuspid valve - Separates the atrium from the ventricle
Semi-lunar valves - Separates the ventricle from the Aorta
Deoxygenated blood -
Tricuspid valve - Separates the atrium from the ventricle
Semi-lunar valves - Separates the ventricle from the Pulmonary artery
Why is the left ventricle wall thicker than the right ventricle wall?
It is thicker because the left side of the heart pumps blood all around the body whereas the right side only pumps blood to the lungs.
Explain the characteristics of Arteries:
Very high blood pressure (close to heart)
No valves
Circular cross-section
Thick elastic and muscular tissue - contains muscle to control pressure and elastic tissue for stretch and recoil
Small lumen size
Oxygenated except pulmonary
Explain characteristics of Vein:
Low blood pressure (far from heart)
Has valves (prevent backflow)
Oblong cross-section
Thin elastic and muscular tissue
Large lumen size to reduce friction
Deoxygenated (except pulmonary)
Explain characteristics of Capillary:
Low blood pressure - greater SA of capillary wall and therefore increased friction
No valves
Circular cross-section
No middle layer - inner wall is only a single layer of cells to allow for diffusion
Tiny lumen size
Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
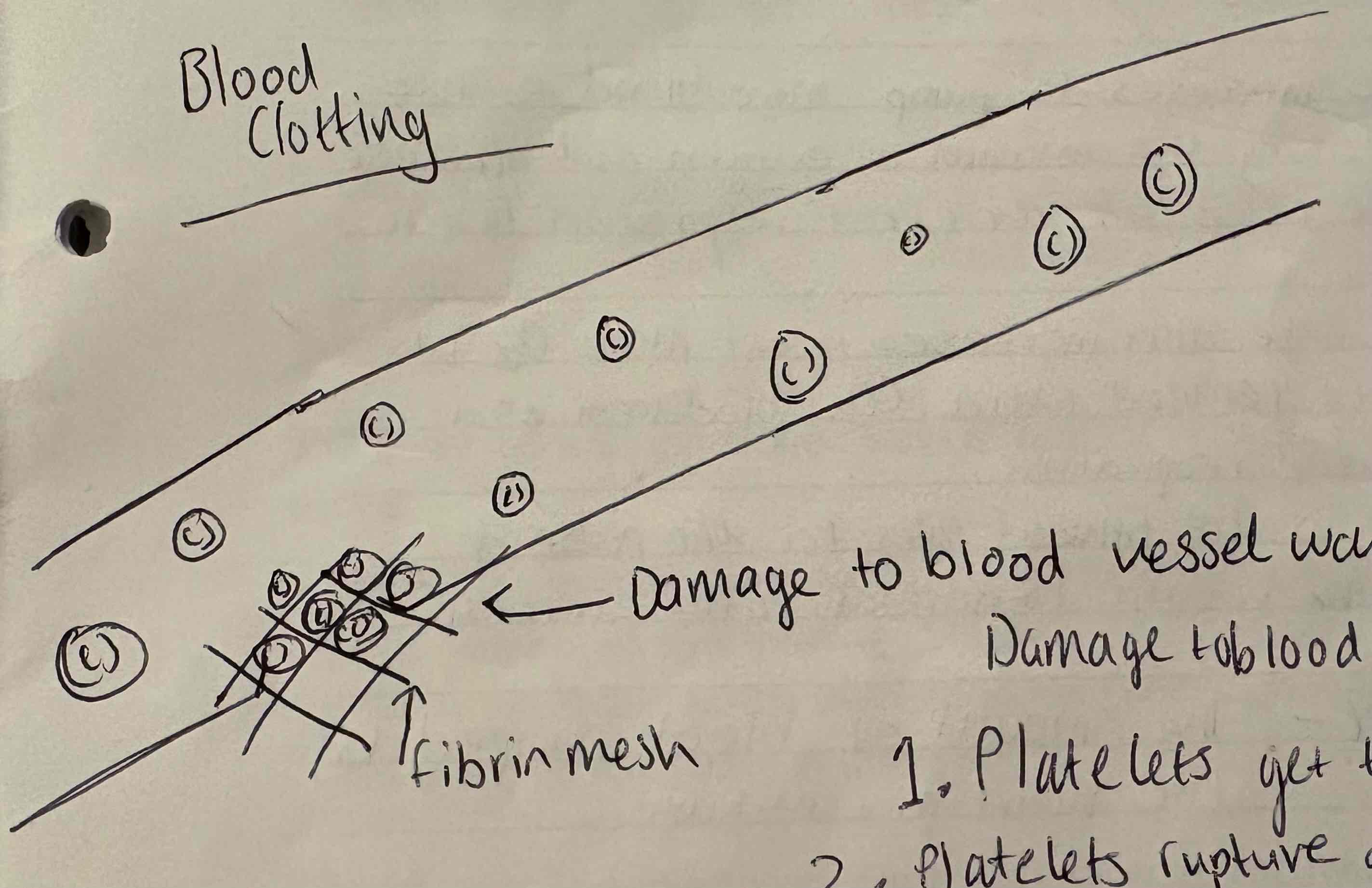
Explain the process of blood clotting:
Platelets get trapped in damaged fibres
Platelets rupture and released thromboplastin
Thromboplastin converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin
Fibrin forms a mesh which traps RBCs
This allows the RBCs to form a clot
Scab eventually forms and seals the wound
Explain the effect of exercise on pulse rate:
During exercise, heart rate and therefore pulse rate increases
During exercise, there is an increase in muscle contraction and this requires energy
Energy is released by respiration and respiration uses oxygen and glucose
So heart rate increases to pump more blood to the muscles, increasing the amount of oxygen and glucose delivered to the cells for the extra respiration that is occurring
The breathing rate also increases to get more O2 into the blood and to remove extra CO2 produced as a result of increased respiration
Recovery rate is the time it takes for the pulse or heart rate to return to normal after exercise
Cardiac Output - The amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute
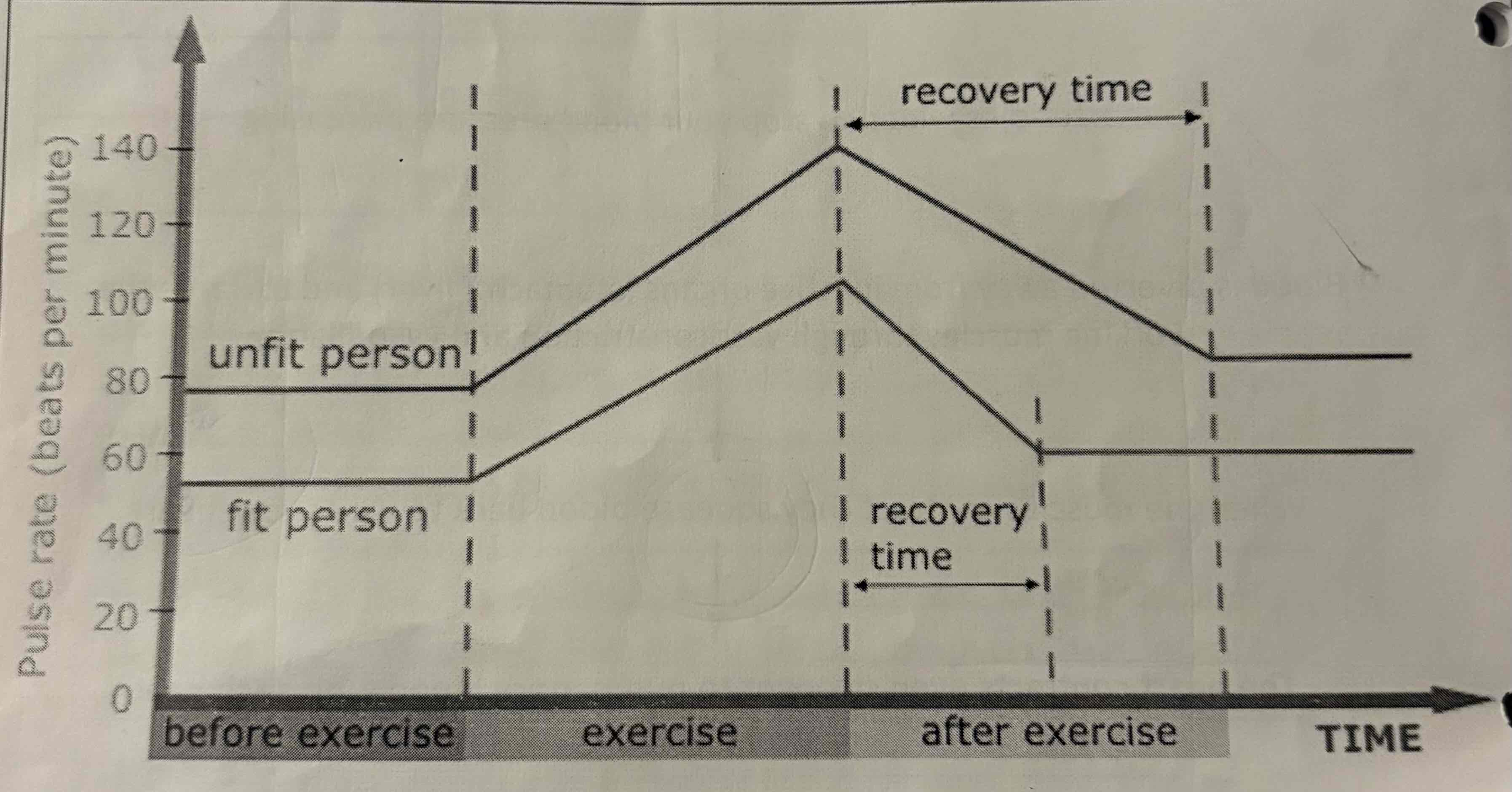
Explain the differences between these two people in the graph:
The unfit person has a higher resting heart rate
The rate at which the unfit persons heart rate goes up faster
It takes longer for the unfit person to recover
The unfit persons heart rate has a higher max