Ear examination
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What does the outer ear contain?
Pinna, external auditory meatus, lateral surface of tympanic membrane
What does the middle ear contain?
Medial surface of tympanic membrane, tympanic cavity, mastoid air cells and Eustachian tube
What is a diagram showing the diagram of the ear?
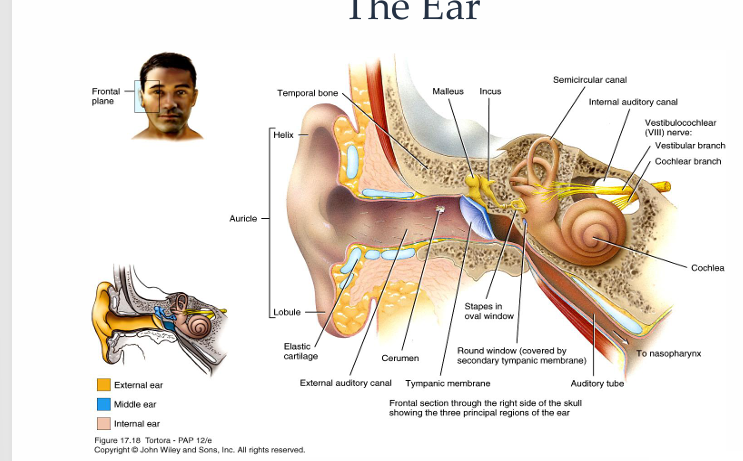
What is a diagram showing outer ear anatomy?

What is a diagram showing middle ear anatomy?

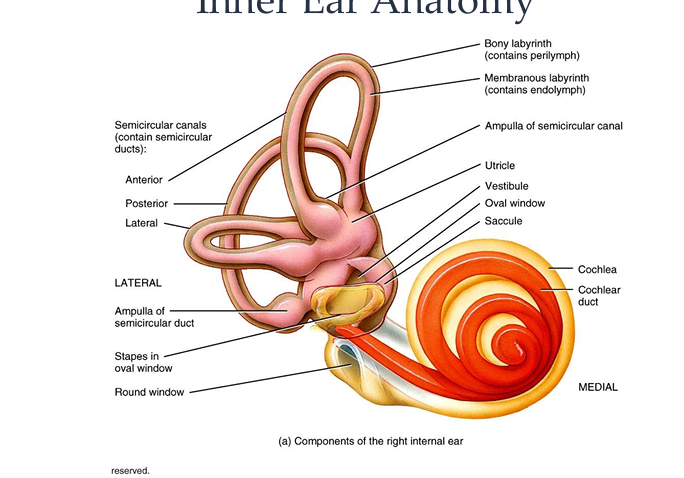
What is the inner ear anatomy of the ear?
What equipment is needed to perform an otoscopy?
Handheld otoscopes and specula
What should you check for otoscopes before completing an otoscopy?
Check the charge or battery
What 5 questions must be asked to take a history before an otoscopy?
Do you have any pain in your ears
Do your ears ever discharge or bleed
Have you had any recent infections in your ears
Have you ever had surgery/operations on your ears?
Do you have any perforations/holes in your ear drums that you know of?
What is the way to remember the history taking questions?
Pain, discharge and 3 “tions” - infections, operations, perforations
What are contraindications?
States or conditions of the ear which need to be taken into account before any other procedure is performed as they may affect the results or compromise the safety of the patients
What are some contraindications for ear procedures?
Occluding or excessive wax, blood, discharge, perforations, foreign bodies, abrasions and bruising, post-operative ears and pain
What are some contraindications to otoscopy itself?
Excessive pain and lack of consent
What safety tips should you remember before an otoscopy?
Skin in ear canal is very thin and delicate
Always consider patients comfort
Injuries can occur from otoscopy so be careful
What are the methods for preparing for an otosopy?
wash hands
instruct the patient clearly as to what the procedure involves and what will be happening to them
Obtain consent from the patient to perform this procedure
Take a brief relevant history e.g., recent pain, discharge, infections, past surgery, known perforations
What are the methods for carrying out an otoscopy?
choose the correct size of speculum according to the size and shape of the subjects ear canal
Hold the otoscope correctly and safely
Identify the main structures of the external ear around and behind the pinna before inserting the speculum
Using thumb and forefinger, pull pinna gently back and up to open and straighten the ear canal
Guide the speculum into the entrance of the ear canal without causing discomfort to the subject and remember to use fingers/knuckles to brace against the cheek
Only 1cm of the speculum should be inside the ear canal and do not rest against the walls
Observe tympanic membrane and identify main observable features and record findings
Dispose of using speculum appropriately
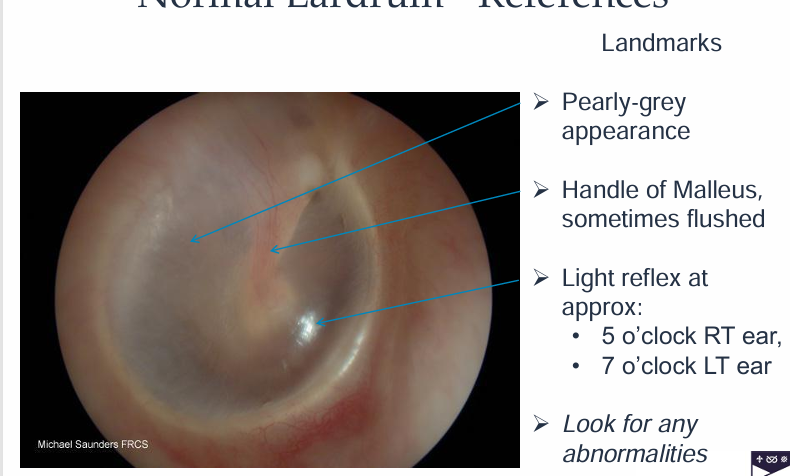
What is a diagram showing normal eardrums?
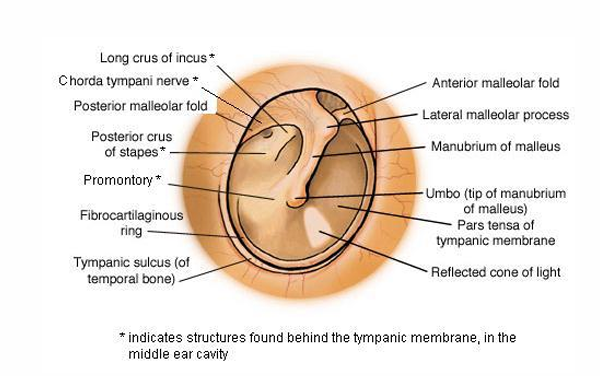
What is a diagram showing the tympanic membrane?
What are possible sights and conditions of ears?
Wax, foreign bodies - beads, cotton wool, infection and discharge, blood, swelling, boils, polyps, perforations, mastoid cavity, grommets
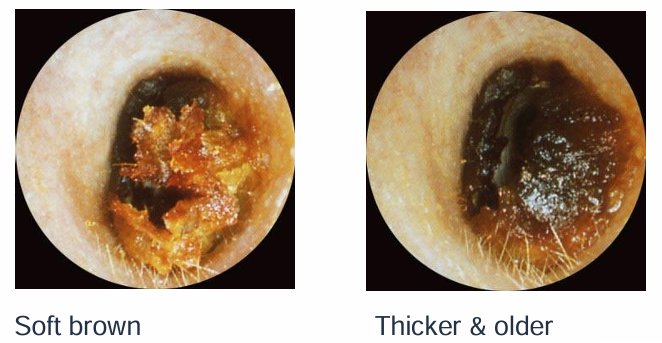
What are diagrams to show wax in the ear?
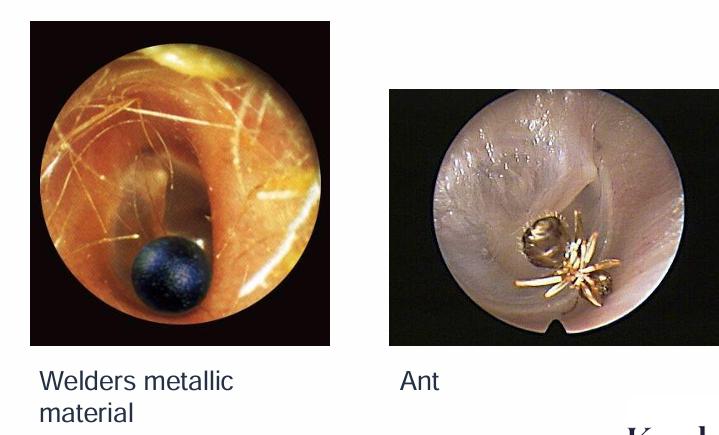
What are diagrams showing foreign bodies in the ear?
What does otitis externa affect?
Ear canal and eardrum
What is a diagram showing infections in the ear?

Where does otitis media occur?
Occurs behind the eardrum
What is a diagram showing otitis media in the ear?
Fluid - bubbles and lines - behind retracted semi-opaque ear drums
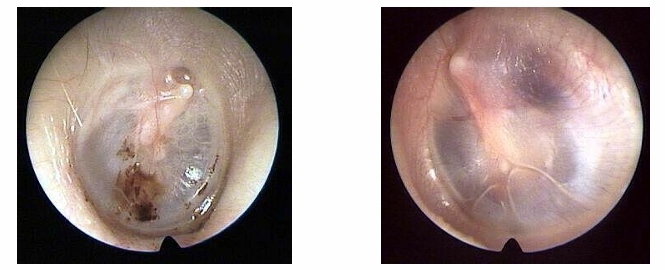
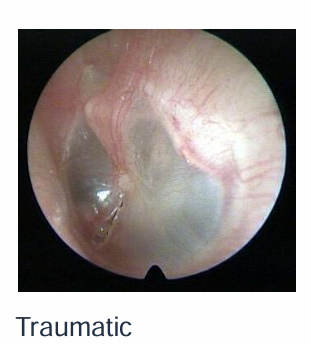
What is a diagram showing a traumatic ear perforation?
What is a diagram showing a sub-total ear perforation?

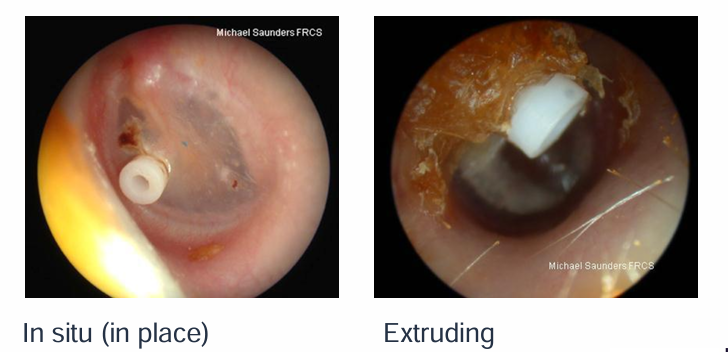
What is a diagram showing an in situ and extruding grommets?
What is a diagram to show the normal right tympanic membrane?
