Current, Voltage, and Resistance
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Electric Current
A flow of electric charge, it is measured in amperes (A)
Electric Current
Is a flow of charge.
Electric Current Formula
i = Δq / Δt
Electric Current
Is the flow of electrons.
Direct Current (DC)
Flow of electrons in one direction. car battery, flashlight batteries, photovoltaic (solar) cell.
Alternating Current (AC)
Flow of electrons back and forth along a path. Magnet electric generator.
Voltage
Is the pressure from an electrical circuit's power source that pushes charged electrons (current) through a conducting loop, enabling them to do work such as illuminating a light.
Voltage
Also called electromotive force, is a quantitative expression of the potential difference in charge between two points in an electrical field.
Voltage
Is equal to water pressure
Potential Difference (Voltage)
In a battery, a series of chemical reactions occur in which electrons are transferred from one terminal to another. There is a _____
Maximum Potential Difference
A power source can have is called the electromotive force or (EMF).
Electromotive Force (EMF)
The term isn't actually a force, simply the amount of energy per charge (J/C or V).
Resistance
Is the opposition that an electrical device has to the flow of electrical current.
Resistor
Is a device that has a particular resistance.
Electrical Resistance
Is a measure of how difficult it is for electricity (electrons) to flow through a material.
Ohms (Ω)
The units of resistance ____
Anmeter
Measures the current flowing through the bulb. It is connected in series with the bulb.
Voltmeter
Measures the potential difference (p.d.) across the lamp. It is connected in parallel with the lamp.
Electric Resistance
The ability of a material to slow or stop the flow of electric current.
Resistance
The property of the conductor due to which it opposes a flow of current through it is called resistance.
The SI unit of resistance is Ohm.
The resistance of a conductor depends on its length and area of cross section.
Resistivity
The resistivity of a conductor is the resistance of a conductor of unit length and unit area of cross section.
The SI unit of resistivity is Ohmmetre (m).
The resistivity of a conductor does not depend on its length and area of cross section.
Resistivity
For a conductor of length L and uniform cross-sectional area, A, its resistance R is proportional to L but inversely proportional to А.
R = pL / A
The resistance of a piece of material of length L and crosssectional area A is given by ___
R (R = pL / A)
Resistance
p (R = pL / A)
Resistivity (units are m).
L (R = pL / A)
Length of the path through the material
A (R = pL / A)
Cross sectional area of the material
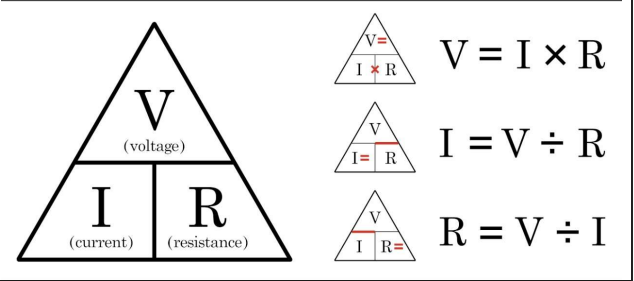
Ohm's Law
The current in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Ohm’s Law Formula
I = V / R
I (I = V / R)
Electric current (amps or A)
V (I = V / R)
Voltage (Volts or V)
R (I = V / R)
Resistance (Ohms or Ω)
Ohm’s Law Triangle