ZOOLOGY 101: Exam 1
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
covalent bond
electrons are shared between atoms
polar bond
electrons shared unequally
nonpolar bond
electrons shared equally
hydrogen bond
attraction of partial charges
hydrocarbon
chemical compound of only hydrogen and carbon atoms
functional group
certain atom groups that determine the chemical reaction of molecules
macromolecule
molecule with large number of atoms
monomer
a single molecule
dimer
two identical molecules linked together
polymer
molecular structure of large number bonded togeher
hydrolysis
breakdown of polymers (water in, monomer out)
dehydration synthesis
joining of monomers (water out, monomer in)
enzyme
speeds up chemical reactions
carbohydrate
a macromolecule that provides energy
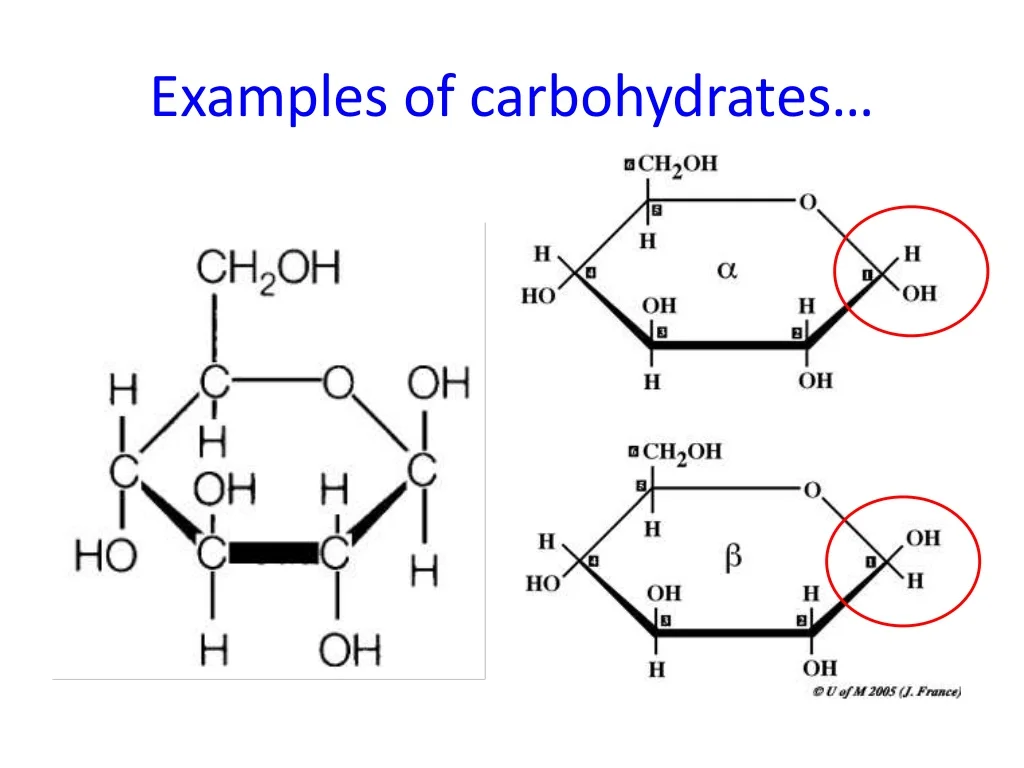
monosaccharide
single sugar (carbohydrate)
disaccharide
two simple sugars (carbohydrate)
oligosaccharide
3-10 simple sugars linked together (carbohydrate)
polysaccharide
10 + simple sugars linked together (carbohydrate)
cellulose
primary structural of plant cell walls
glycogen
energy storage of glucose in animals and humans
starch
energy storage molecule in plants
chitin
primary structural in fungi and exoskeletons
glucose
primary energy production and regulation of cell function
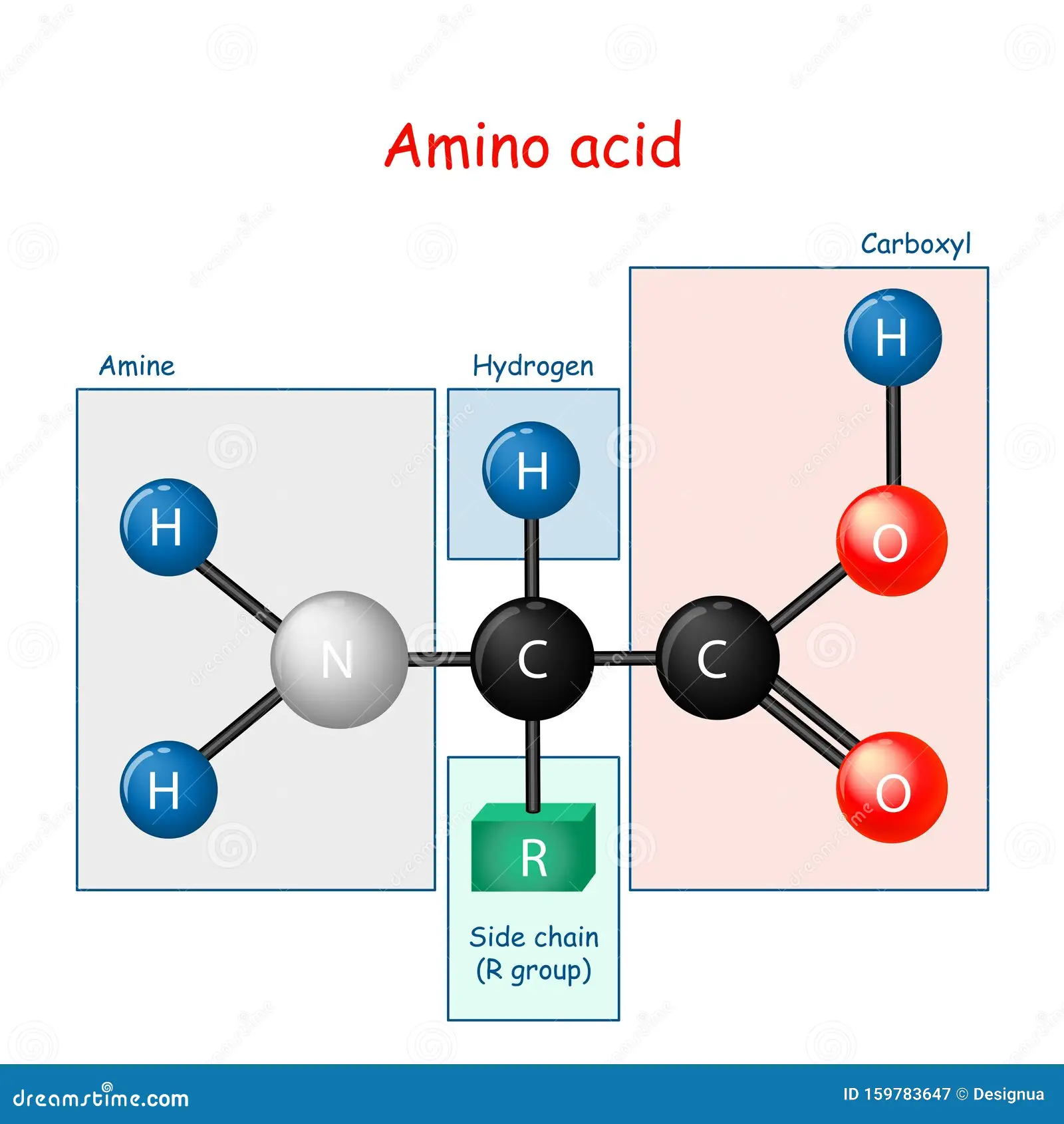
amino acid
simple organic compound: both a carboxyl & amino acid group
protein
complex macromolecules made up of multiple polypeptide chains
polypeptide
linear chain of amino acids linked together
peptide bond
covalent bond that links the amino acid group to the carboxyl group
hydrophobic
substances that hate water
hydrophilic
substances that love water
reactant
substance that participates in a chemical reaction
product
substance formed as a result of a chemical reaction
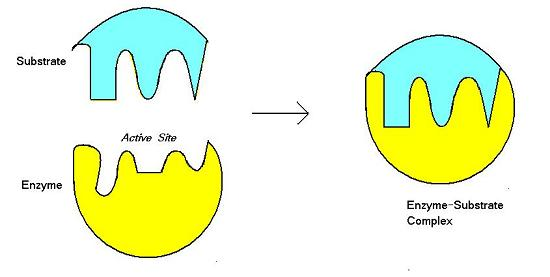
active site
specific part of an enzyme where the substrate binds and have chemical reaction
denaturation
alteration of the structure of a protein or nucleic acid
conformation
shape or structure of something
lipid
a complex macromolecule found in living organisms (fats)
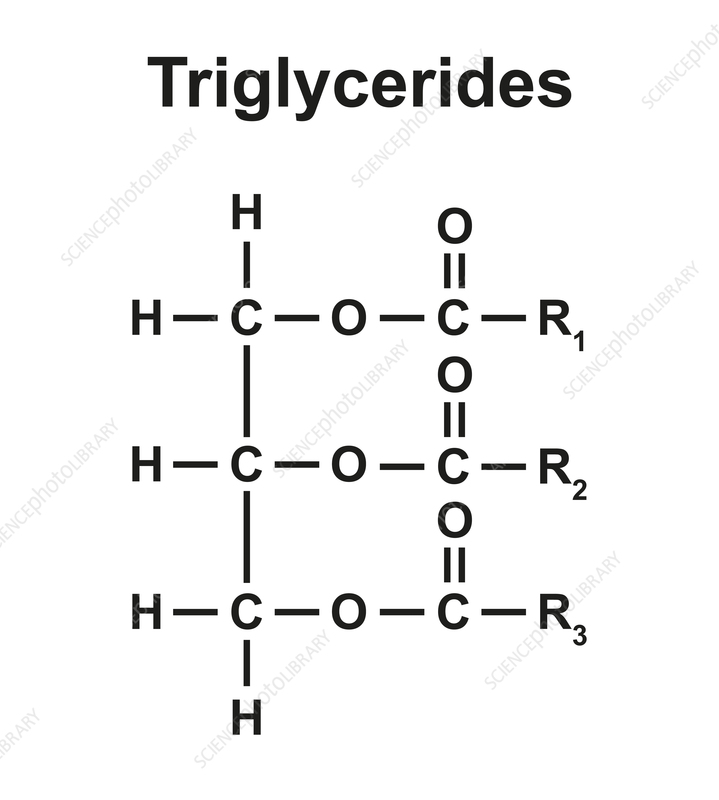
triglyceride
type of fat that stores energy in the body
phospholipid
type of fat molecule that contains phosphate group
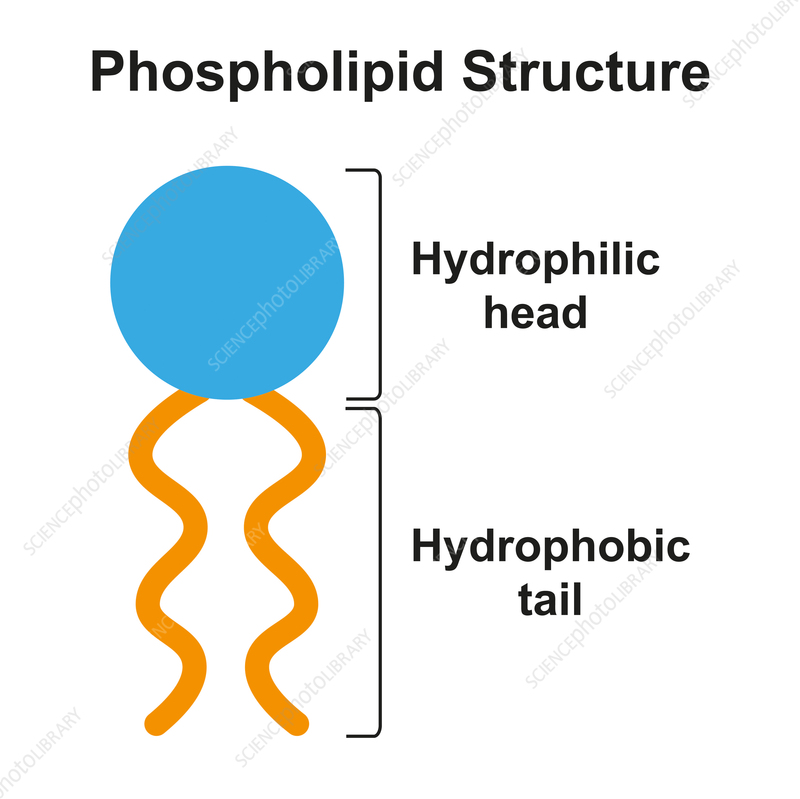
amphipathic
molecules that have both water loving and water hating parts
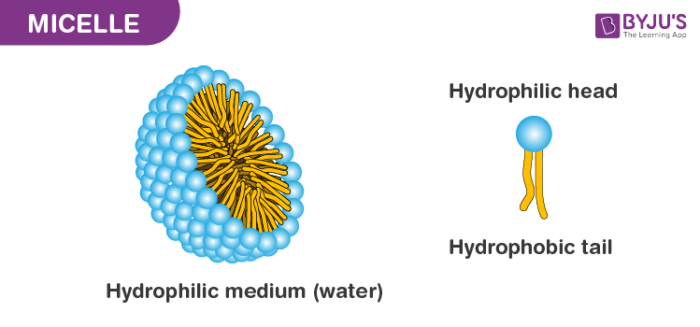
micelle
tiny, ball-like structure made up by sufactants
steroid
type of chemical compound in plants and animals
lipoprotein
proteins that carry fats through the bloodstream
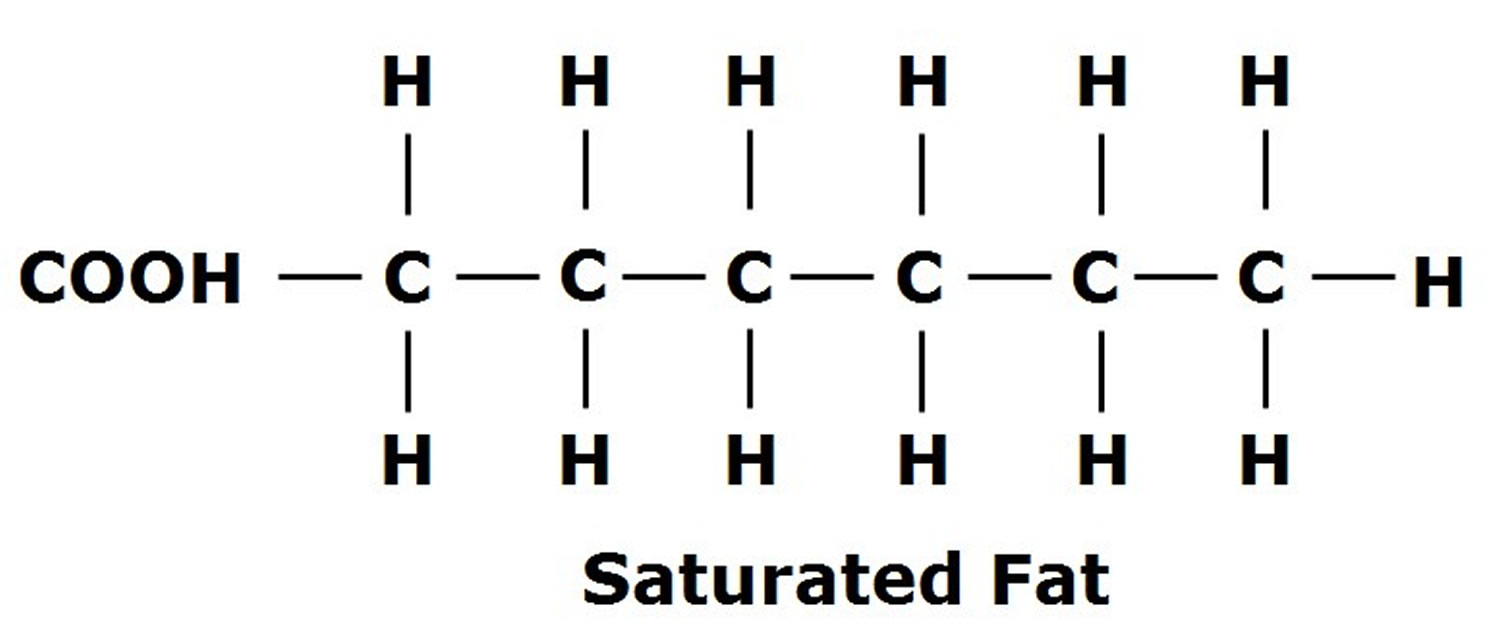
saturated fatty acid
fats with straight chain structure (no double bond)
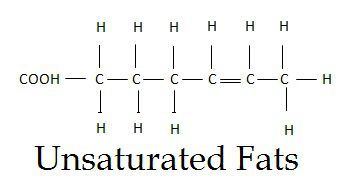
unsaturated fatty acid
fats with bent chain structure (one or double bonds)
prokaryote
single cell no nucleus organism
plasma membrane
thin, flexible layer that surrounds and protects the cell
cytosol
jelly-like liquid inside cells
ribosome
cytoplasmic structure composed of proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
chromosome
structures inside cells composed of DNA and proteins
DNA
special code that tells us how to grow and function
nucleoid region
area in a prokaryotic cell where genetic material is located
cell wall
strong, protective layer that surrounds plant cells
peptidoglycan
polymer that makes up the cell walls of bacteria
flagella
little motor that helps cells move around
decomposer
organisms that break down dead plants and animals
symbiosis
relationship between two different species at least one benefits
mutualism
relationship between two different species that both benefit (ex: bees and flowers)
microbiome
all the microorganisms that live on or in us
antibiotic
fight infections caused by bacteria
halophile
organisms that need salt to survive
thermophile
organisms that love hot places
methanogen
organisms that can live with no oxygen
sterol
subgroup of steroids maintaining cellular structure and function
transmembrane protein
cover the entire lipid bilayer of cell membranes
peripheral membrane
proteins that stick temporarily on the surface of the membrane
glycoprotein
type of molecule made of protein and carbohydrate
diffusion
passive movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration
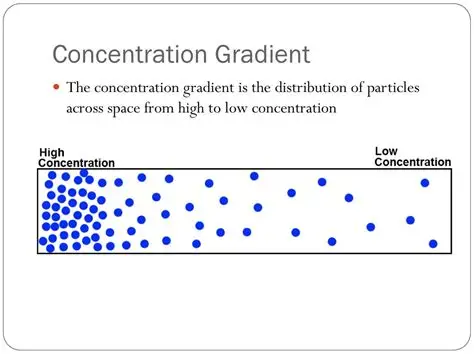
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance across a space
passive transport
movement of substances across cell membrane without use of ATP
active transport
movement of substances across cell membrane with use of ATP
facilitated difussion
assistance of certain transport proteins (passive transport mechanism)
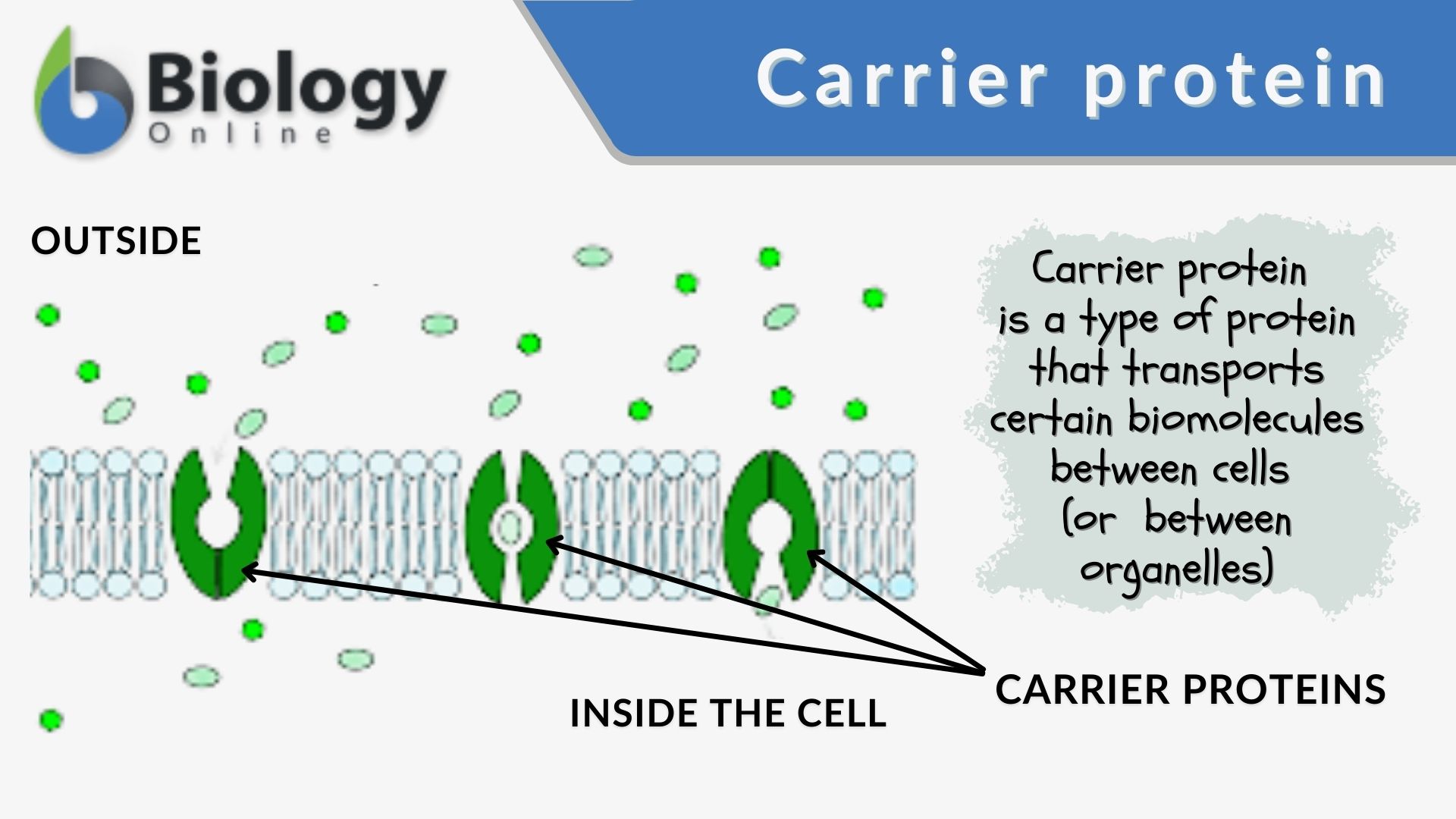
carrier protein
protein changes its shape to allow molecules to pass through
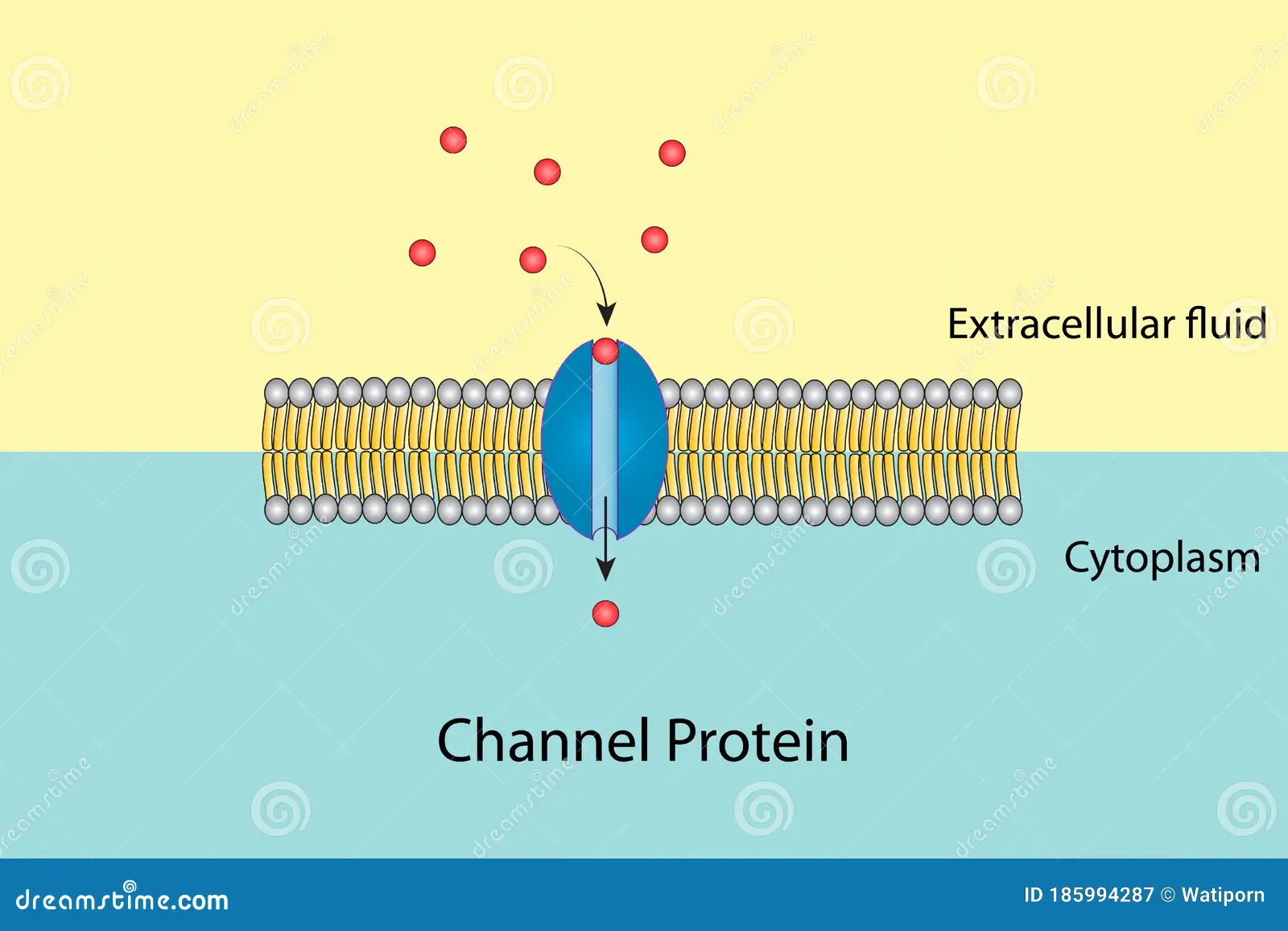
channel protein
proteins form small openings for molecules to diffuse through
osmosis
movement of water molecules through a permeable membrane from low to high solute concentration
aquaporin
specialized channel proteins to help with rapid transport of water molecules
hypotonic
higher concentration of water
hypertonic
lower concentration of water
isotonic
same concentration of water
ATP
primary energy carrier in all living cells
pump
actively transports ions and molecules across plasma membrane
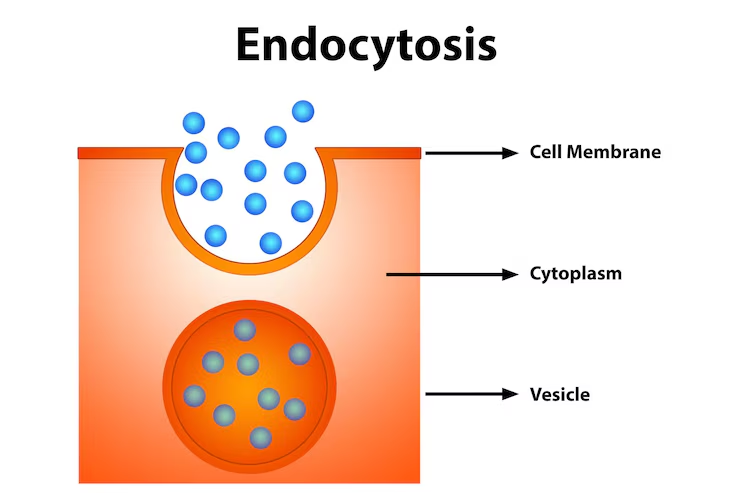
endocytosis
bring substance into cell
exocytosis
substance released from cell
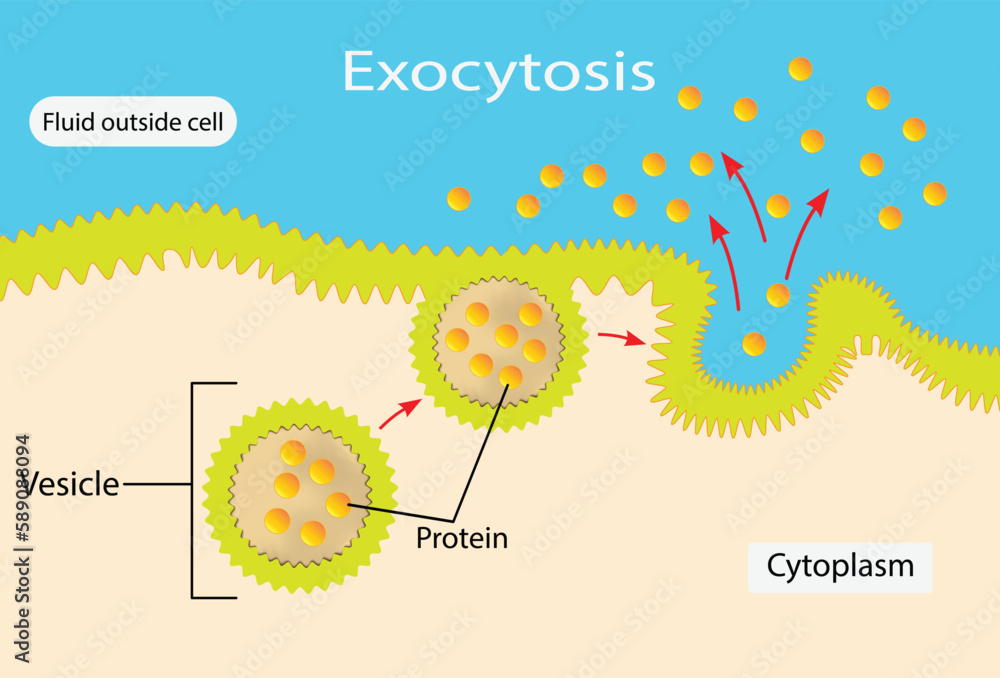
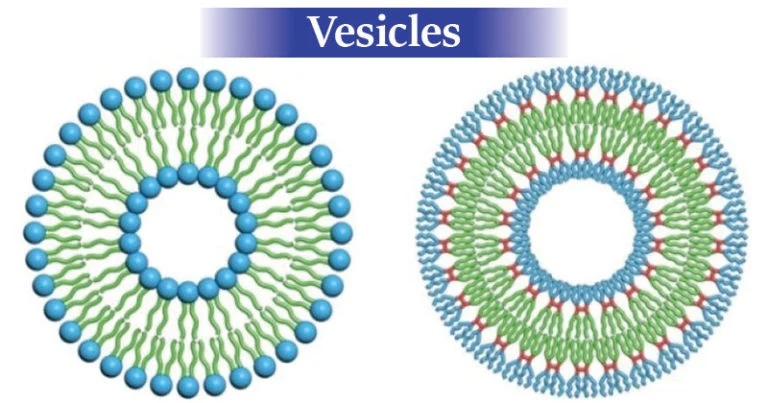
vesicle
membrane-bound sac
pinocytosis
“cell drinking” takes in fluid
phagocytosis
“cell eating” takes in food
receptor
membrane protein with binding site with specific shape for signal to bind
LDL
bad cholesterol
eukaryote
complex cells that contain nucleus
organelle
tiny part inside cell that has a special job
nucleus
control center of cell
nuclear pore
small opening to allow molecules in
nuclear lamina
dense network of protein filaments
nuclear envelope
double layer membrane surrounds the nucleus
nucleoplasm
jelly-like substance
nucleolus
small part that makes ribosomes
endomembrane system
keep the cell’s parts from mixing
endoplasmic reticulum
delivery system that make and move important proteins and fats
golgi apparatus
“post office” package and send materials to different parts of cells
glycoprotein
special protein that has carbohydrate attached
glycosylation
carbohydrate molecules are attached to proteins or lipids
lysosome
“garbage trucks” breaking down waste and keeping cell healthy