Robotics Quizzies 4 , 5 , and 6
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I WILL GET AN A ON MY ROBOTICS MIDTERM EXAM! I WILL PASS WITH A HIGH SCORE! EVERYTHING WILL BE OKAY!
Last updated 5:33 PM on 2/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
3 broad categories of robots are …
* stationary
* wheeled
* walking
* wheeled
* walking
2
New cards
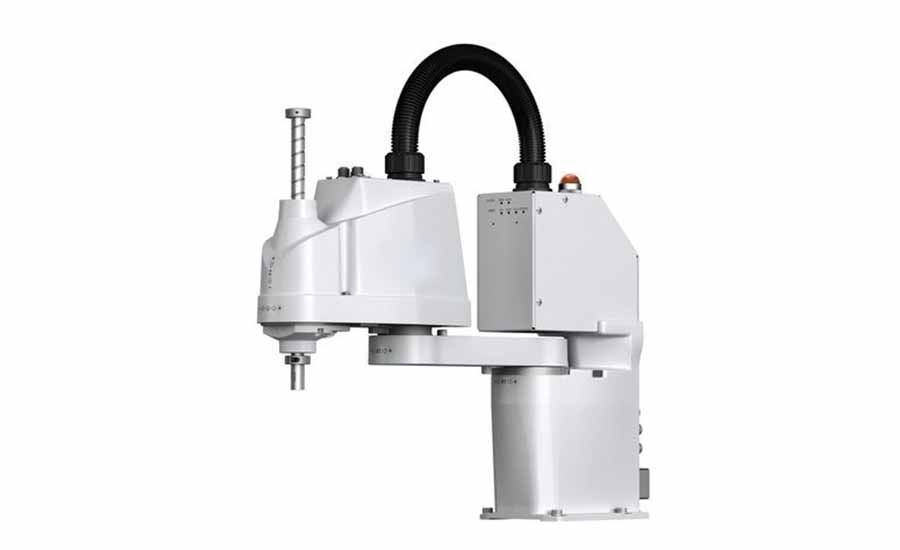

SCARA stand for …
Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm
3
New cards
What type of robot only has translational movement?
Cartesian
4
New cards
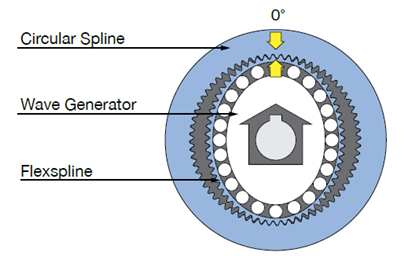
This is an example of a ____________ drive system.
harmonic
5
New cards

Name an **industrial** task, a robot end effector might handle. **Your answer should end in "ing"**
* material handling
* welding
* painting
* drilling
* deburring
* palletizing
* spraying
* picking
* placing
* assembling
* 3D printing
* engraving
* machining
* operating
* welding
* painting
* drilling
* deburring
* palletizing
* spraying
* picking
* placing
* assembling
* 3D printing
* engraving
* machining
* operating
6
New cards
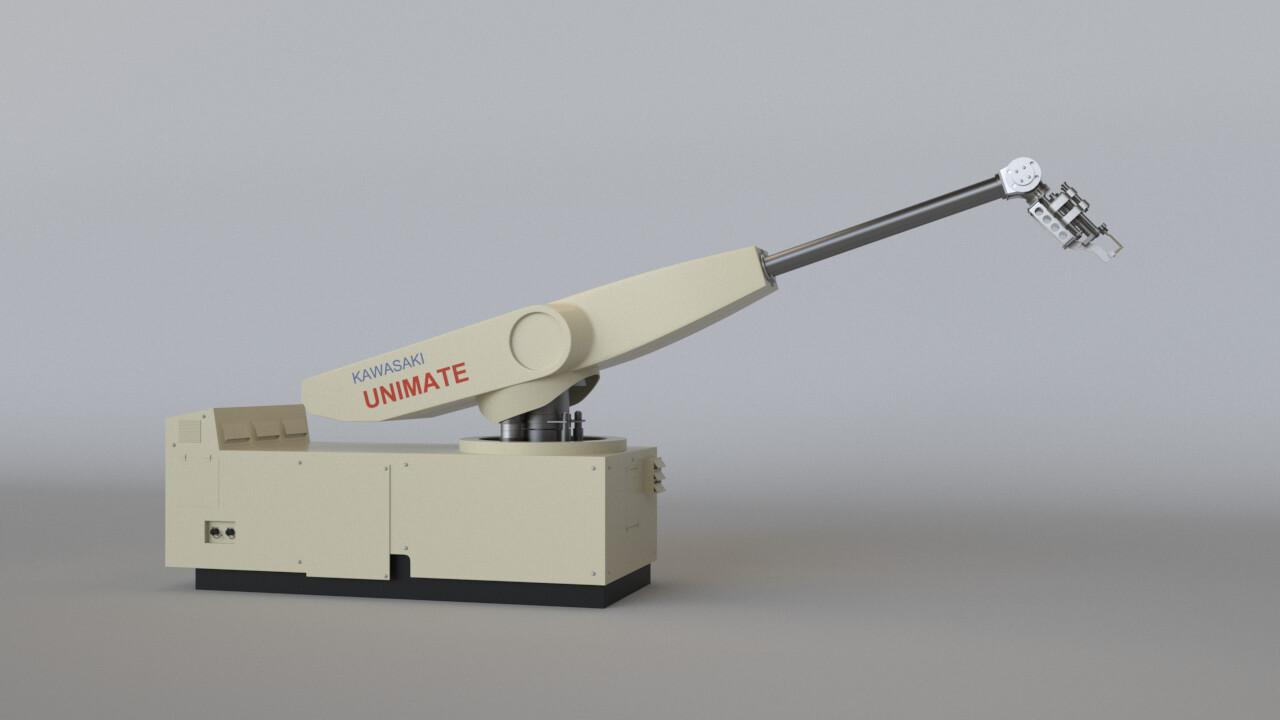

The Unimate is an example of __________ robot geometry.
polar
7
New cards

In RoboDK, what does this menu icon represent?
The online library
8
New cards
If you are having difficulty with a particular tool in RobotDK, the easiest way to get more information is to ....
press F1
9
New cards
Which coordinate system is at the base (AXIS 1) of an industrial robot?
world
10
New cards
What are 2 conditions that must be met in order to jog the Kuka robot arm?
* Robot must be in Teach Mode
* The enabling switch must be pressed
* The enabling switch must be pressed
11
New cards
Which 3 statements below accurately describes the WORLD coordinate system?
* The arm can move linear in, and rotate in X , Y , and Z
* By default, the world coordinate system is located in the base of the robot
* All 6 axes may move for the robot arm to attain a position in X , Y , or Z
* By default, the world coordinate system is located in the base of the robot
* All 6 axes may move for the robot arm to attain a position in X , Y , or Z
12
New cards
What are the 2 predetermined ***FEATURES*** on the Universal robot?
* Base
* Tool
* Tool
13
New cards

Which symbol represents the Tool Coordinate system?
d
14
New cards
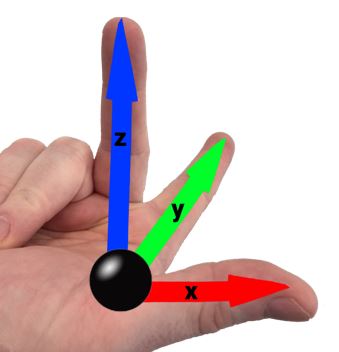
This is an example of …
the right hand rule
15
New cards
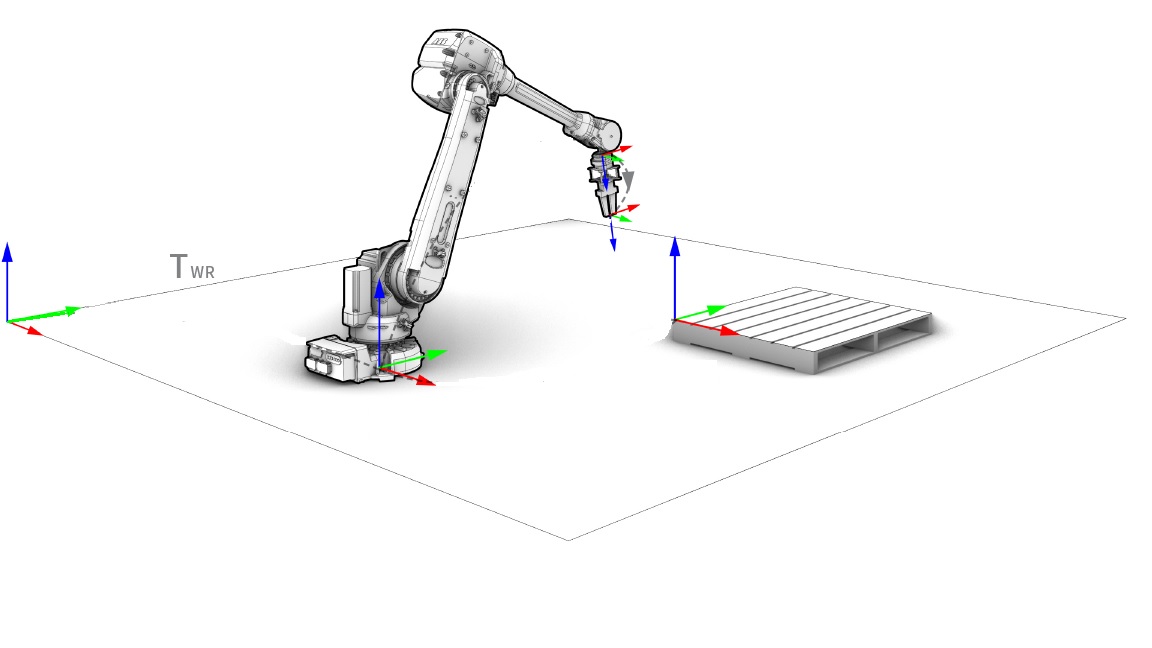
Which set of coordinates best describe where the pallet is located in respect to the base of the robot?
X = 100 , Y = 300 , Z = 10
16
New cards
3 places a robot could receive a **digital** input signal include:
* safety equipment (light curtain)
* a light sensor
* an external switch is on (1) or off (0).
* a light sensor
* an external switch is on (1) or off (0).
17
New cards
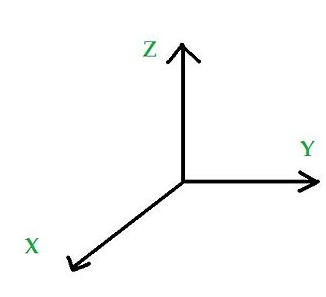
Match the axis rotation with its movement description.
* rotation about the X axis : roll
* rotation about the Y axis : pitch
* rotation about the Z axis : yaw
* swing
* rotation about the Y axis : pitch
* rotation about the Z axis : yaw
* swing
18
New cards
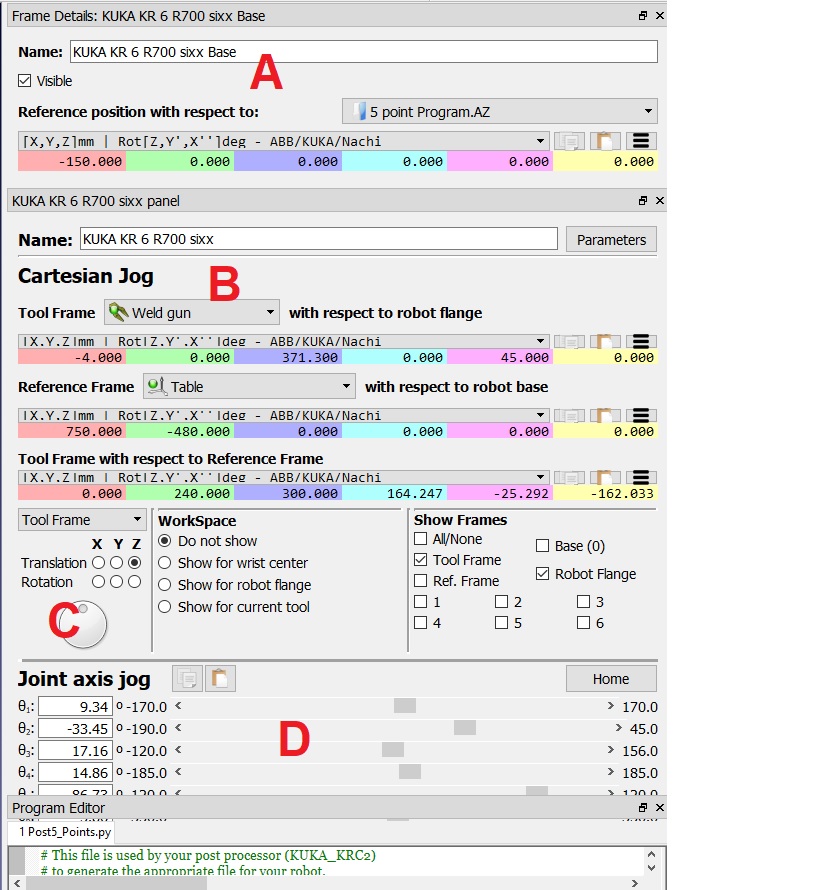
Where on the RoboDK screen would you jog the shoulder axis (Axis 2)?
D
19
New cards
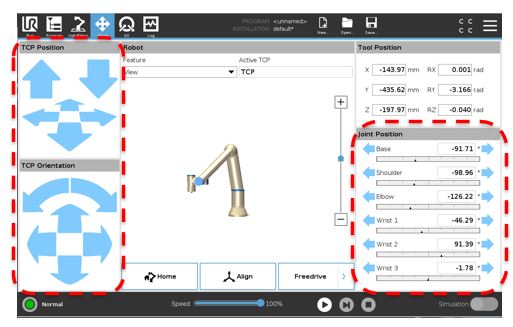
This screen shows where you would.....
jog the robot by axis
20
New cards
A tool (attached to the flange of a robot arm) coordinate system will always be based on the ____________.
TCP
21
New cards
On **the Kuka robot**, jogging the robot arm can only occur when in ____________ mode, when the ____________ _____________ is in the middle position.
* manual
* enabling switch
* enabling switch
22
New cards
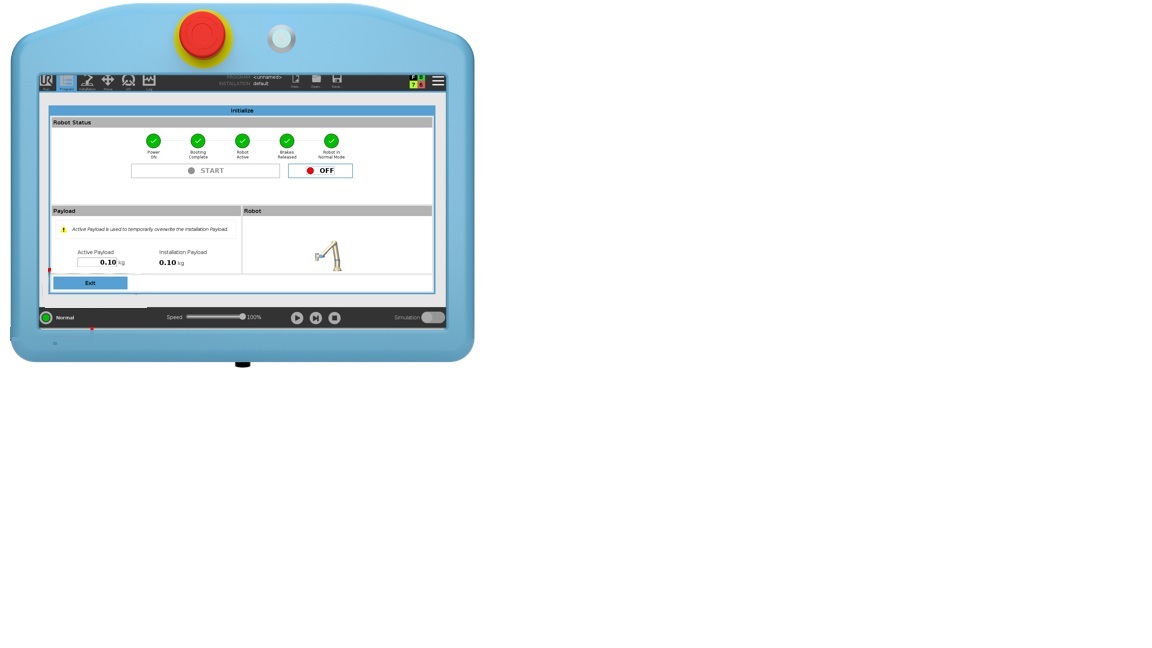
How many time do you have to press an ON or POWER ON button to activate the Universal Robot?
3
23
New cards
_______________ _________________ jogging allows the TCP to move along the X-Y-Z axes.
tool coordinate
24
New cards
**FEATURE** on a Universal Robots is equal to a ________________ on RoboDK.
FRAME
25
New cards
The _____________________________________is the point on the tool/end of arm system where weight is distributed evenly on each side (of the point).
center of gravity
26
New cards
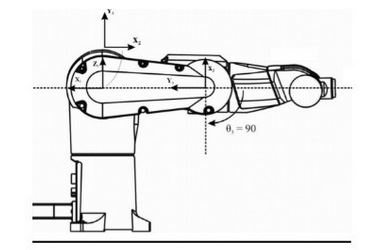
An irregular pose of an articulated arm robot, where joints are aligned, and cannot resolve the next position is called __________________.
singularity
27
New cards
Which 2 of these are **characteristics** of a MoveL and MoveC commands?
* The tool follows a defined path
* The path is predictable
* The path is predictable
28
New cards
Which would be the best time to use MoveJ?
Moving through an open space with no obstructions
29
New cards
RoboDK is an example of
Flexible Offline programming
30
New cards

This type of robot move has a constant TCP speed and “blends” the waypoints.
MoveP
31
New cards

On the UR robot, what are the units used for the Tool Speed?
mm/sec
32
New cards
What would be 2 reasons for using a WAIT or PAUSE command in a computer program?
* After a call for a gripper to open or close
* Waiting for an input signal from a sensor
* Waiting for an input signal from a sensor
33
New cards
What are 3 characteristics of LINKED waypoints?
* It is possible to re-use the same waypoint in the program
* They share their position
* Each linked waypoint can have unique speed and acceleration
* They share their position
* Each linked waypoint can have unique speed and acceleration
34
New cards

What are 2 differences between a MoveL ,and a MoveL with a blend?
* with a blend the robot and will not stop at the waypoint
* with a blend the robot will take a curved path around the waypoint
* with a blend the robot will take a curved path around the waypoint
35
New cards
What is a "Popup" used for in a program?
It will pause the program and wait for the operator to either stop the program or click "Continue".
36
New cards

Which motion produces a predictable robot path?
point to point motion commands with path control
37
New cards
If a change is made in a programming point or waypoint, you should always run the program _____________________.
at reduced velocity, to test its performance
38
New cards

The only way to resolve a "singularity" is to....
put the robot in joint jogging mode and jog the affected joint
39
New cards
For a MoveC you need 3 things.
* starting point
* via point
* end point
* via point
* end point
