Reflection/Refraction
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
When waves arrive at a boundary between two different materials what three things might happen:
1)The waves are absorbed by the material the wave is trying to cross into-this transfers energy to the materials energy stores
2)The Waves are transmitted-waves carry on travelling through new material often leading to refraction
4)Waves are reflected off surface of material
What do those three things depend on
-Depends on wavelength of wave and properties of materials involved
What does the law of reflection state?
The angle of incidence = The angle of reflection
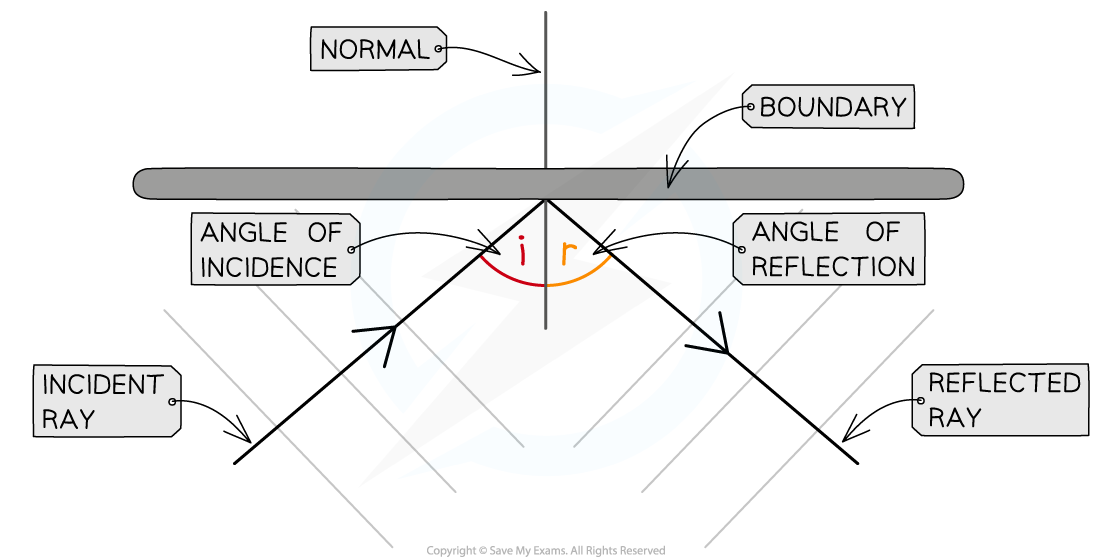
Explain each thing labeled
1)Get a reflected surface like a mirror
2)Draw a ray of light striking the surface of the mirror which is called the incident ray with a arrow showing the direction
2)Draw a dotted line at right angle of surface which is the normal which is a line that is perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence(point where the wave hits the boundary)
3)Measure angle between Incident Ray and normal which is called angle of incidence
4)Draw reflected ray with arrow going down
5)Measure angle between normal and reflected ray which is the angle of reflection
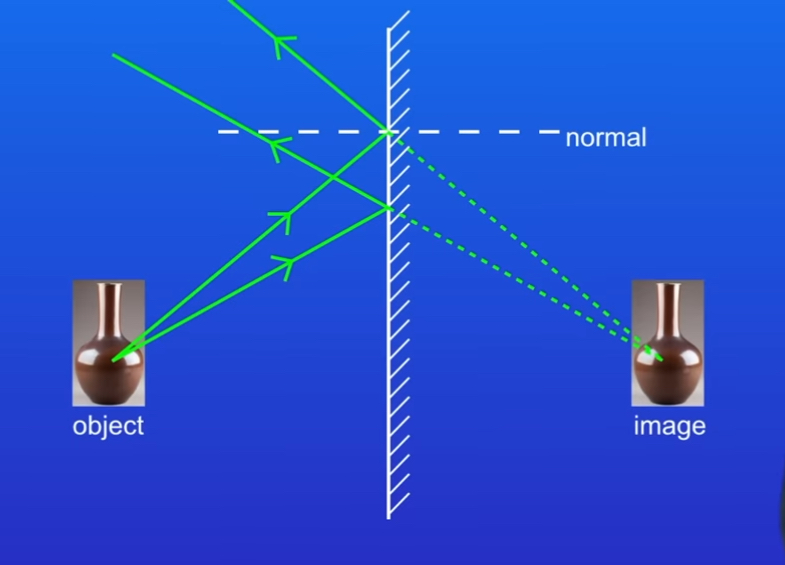
How do we use a ray diagram to work out where the image of an object will appear in a mirror
1)Draw an incident ray from object to the mirror
2)Draw a normal at right angle to surface of mirror and then draw the reflected ray(Remember to draw arrow showing direction of rays)
3)Now draw another incident ray from object reflecting off the mirror
4)Then extend the two reflected rays back into the mirror
5)Where these lines meet tells us the position of the image
How can waves change direction
When they change speed by moving from one medium to another
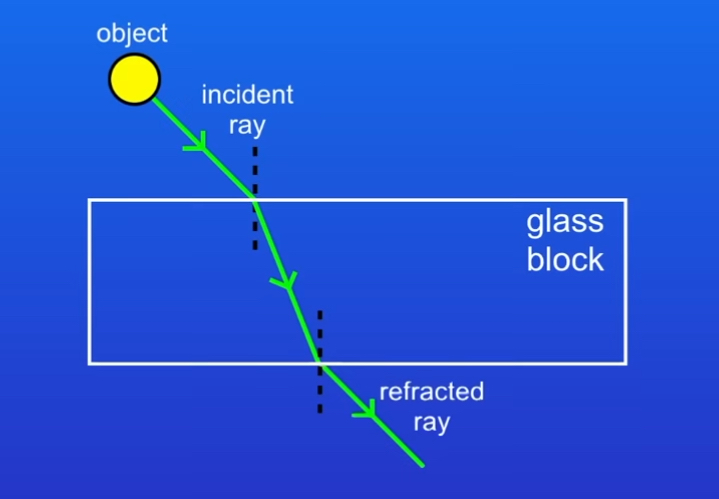
How do you construct a ray diagram
1)When light passes from air into glass, the velocity of light decreases(wave slows down) causing direction to change
2)Get a glass block and draw a normal at right angle of surface of glass
3)Draw an incident ray that meets the normal at the glass block. The angle between normal and incident ray is angle of incidence(If given this as angle using protractor)
4)Draw a refracted ray that bends towards the normal as wave is slowing down from less dense to more dense
5)When the wave pass from the glass block to the air its speed increases meaning the wave bends away from normal
6)This causes the image of object to appear to have shifted position
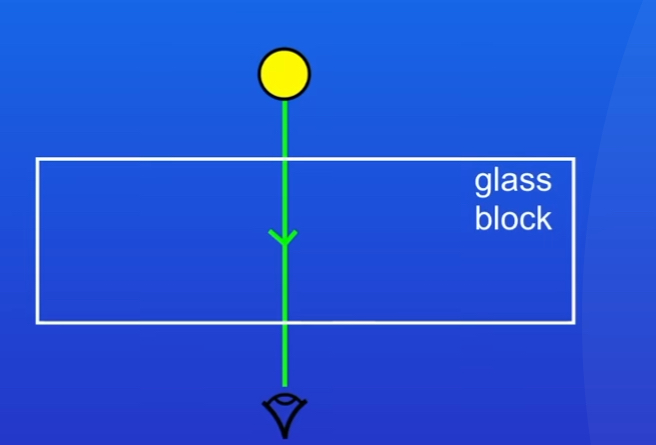
What happens if a wave enters or leaves the medium at right angles to the surface(along the normal) like image below
They do not change direction
What is the wavefront
An imaginary line that connects all the same points in a set of waves
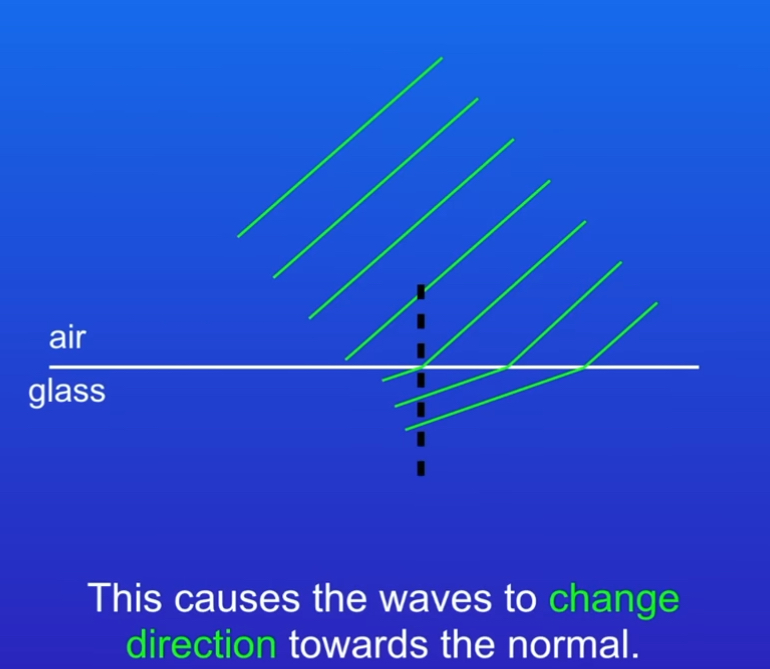
Describe this image
1st part of Wavefronts moving into glass slowing down which causes other parts to get closer together.
Causing waves to move towards the normal which is refraction

Describe this image
-Shows wavefronts approaching along the normal and slowing down at the same time. So waves don’t change direction