Intro to Money and Banking
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a financial Intermediary?
This the intermediate step for financial transactions to occur, an example of such would be a bank because banks allow borrowers and lenders to perform more transactions.
What is the first type of financial market ? (Order doesn’t actually matter)
The bond (or debt) market
What is the second type of financial market?(Order doesn’t actually matter)
The stock (or equity) market
What is the third type of financial market?(Order doesn’t actually matter)
The foreign exchange (or currency) market.
What is a security?
This is a claim on the issuer’s future income or assets.
What is an asset?
This is a financial claim or piece of property that is subject to ownership
What is a bond?
This is a debt security that promises to make periodic payments for a specified period of time. Bonds include coupon bonds, discount bonds, and perpetuities.
What is an interest rate?
This is the cost of borrowing or price paid for rental of funds. These include the prime rate, discount rate, federal funds rate, etc.
What is a stock?
Share of ownership in a corporation. They provide safer means of investment than direct ownership or partnership in a firm. This makes it easier for corporations to raise capital compared to sole proprietorships or partnerships.
What is the difference between a Bondholder and Stockholder?
Bondholders are entitled to a share of a company’s income stream and are paid before stockholders if a company is facing financial trouble. Stockholders are entitled to a share of the firm’s assets known as residual claimants.
What is a residual claimant?
Stockholders are entitled to a share of the firm’s assets known as this.
What is a currency exchange market?
Also known as a foreign exchange market, these are markets where exchange of currency takes place, typically in major commercial banks in global financial centers.
What is the exchange rate?
This is the value of one currency in terms of another.
What is purchasing power?
This is the ability of a currency to purchase domestic goods and services.
What are the three factors that the US banking system is decided by?
Federalism, a fear of centralized power and regulatory processes.
What is dual banking?
This is the idea that both the federal and state governments can charter banks.
How does the financial system work, visually?
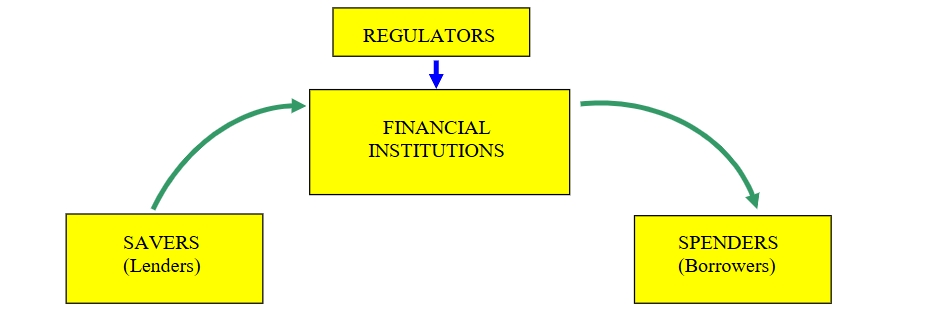
What are some examples of “mainstream” financial institutions?
Commercial Banks, Savings and loan associations, mutual saving banks, credit unions, insurance companies, financial companies, etc.
What are some examples of “fringe” financial institutions?
pawn shops, check-cashing outlets, payday loan centers, tax services, car dealers, etc. The type of institutions that serve the unbanked or marginalized groups. Profiting at the expense of these groups.