Eduqas Biology A Level Core Concepts - Transport Across Membranes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Define diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Define osmosis
Diffusion of water
What factors effect transport across membranes?
- Surface area
- Concentration gradient
- Thickness of exchange surface
- Temperature
- Size of molecules
- Lipid solubility
What is Fick's Law?
Rate of diffusion is proportional to (Surface Area x Concentration Gradient)/Thickness of exchange surface
What is simple diffusion?
The passive movement of molecules from high concentration to area of low concentration across a membrane
What is facilitated diffusion?
The passive movement of a particle across a cell membrane via a channel protein
What is active transport?
The movement of ions or molecules across a membrane using carrier proteins against a concentration gradient using ATP
What is endocytosis?
Bulk transport of substances into a cell
Phagocytosis
Transport of solid particles into a cell
Pinocytosis
Transport of liquids into a cell
What is exocytosis?
Bulk transport of substances out of a cell
What do Exocytosis and Endocytosis have in common?
Both of these transport larger molecules and require ATP
What kind of molecules pass through a cell membrane without transport proteins?
Smaller, lipid-soluble molecules, aka non-polar and uncharged
What kinds of molecules have to be transported across a cell membrane using transport proteins?
Large, water-soluble molecules (polar and charged)
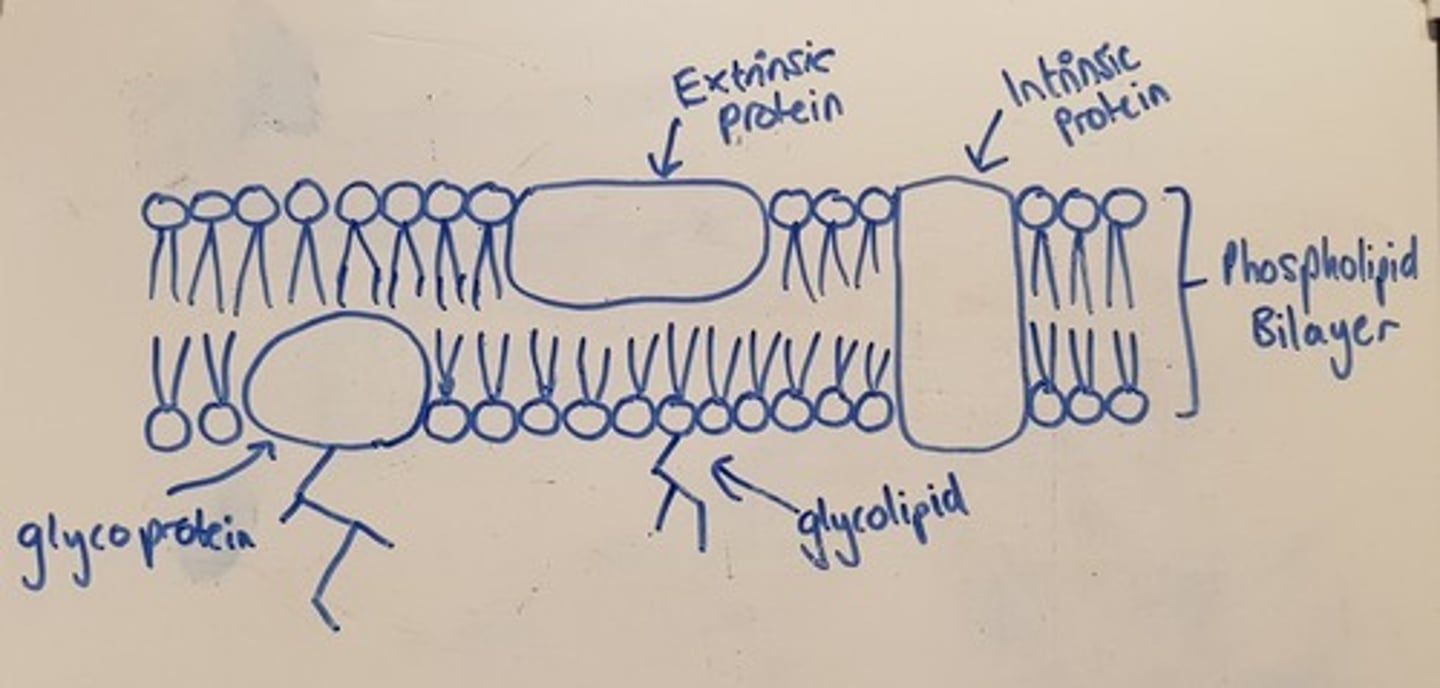
Draw a simple labelled diagram of a cell membrane. Include both an intrinsic and extrinsic protein, and both a glycoprotein and a glycolipid
How does glucose get into the cell?
facilitated diffusion or active transport
How do ions such as Sodium ions get into the cell?
facilitated diffusion or active transport
What is the name given to the transport protein that transports water across a membrane?
aquaporin
What are the 3 types of transport proteins?
channel proteins, carrier proteins, and ATP-powered pumps
What transport proteins are involved during facilitated diffusion?
channel proteins and carrier proteins
The rate of active transport is limited by...
the number and availability of carrier proteins
The rate of facilitated diffusion is limited by...
the number and availability of transport proteins
What transport proteins are involved during active transport?
carrier proteins
What is co-transport?
A type of facilitated diffusion that brings molecules and ions into cells together on the same transport protein molecule
What affect with the addition of cyanide have on the rate of active transport?
- Cyanide is a respiratory inhibitor, so will inhibit the production of ATP
- With no ATP available, active transport cannot take place
- The rate of active transport plummets to zero
Using your knowledge of the structure of the plasma membrane, explain how oxygen enters the cell
Oxygen enters via simple diffusion across the phospholipid bilayer (due to the fact it is non-polar and small)
Using your knowledge of the structure of the plasma membrane, explain how a phosphate ion enters the cell
Phosphate ions enters via facilitated diffusion or active transport through carrier and channel proteins
State one similarity between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion
Diffusion occurs down a concentration gradient
State one difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion only occurs at
specific points on the membrane, where there are proteins / facilitated diffusion involves the use of transport proteins
WHEREAS, simple diffusion occurs across the bilayer without the use of proteins
Where is the energy needed for active transport provided from?
ATP from the mitochondria
Which organelle is likely to be present in large numbers in a cell carrying out lots of active transport?
mitochondria
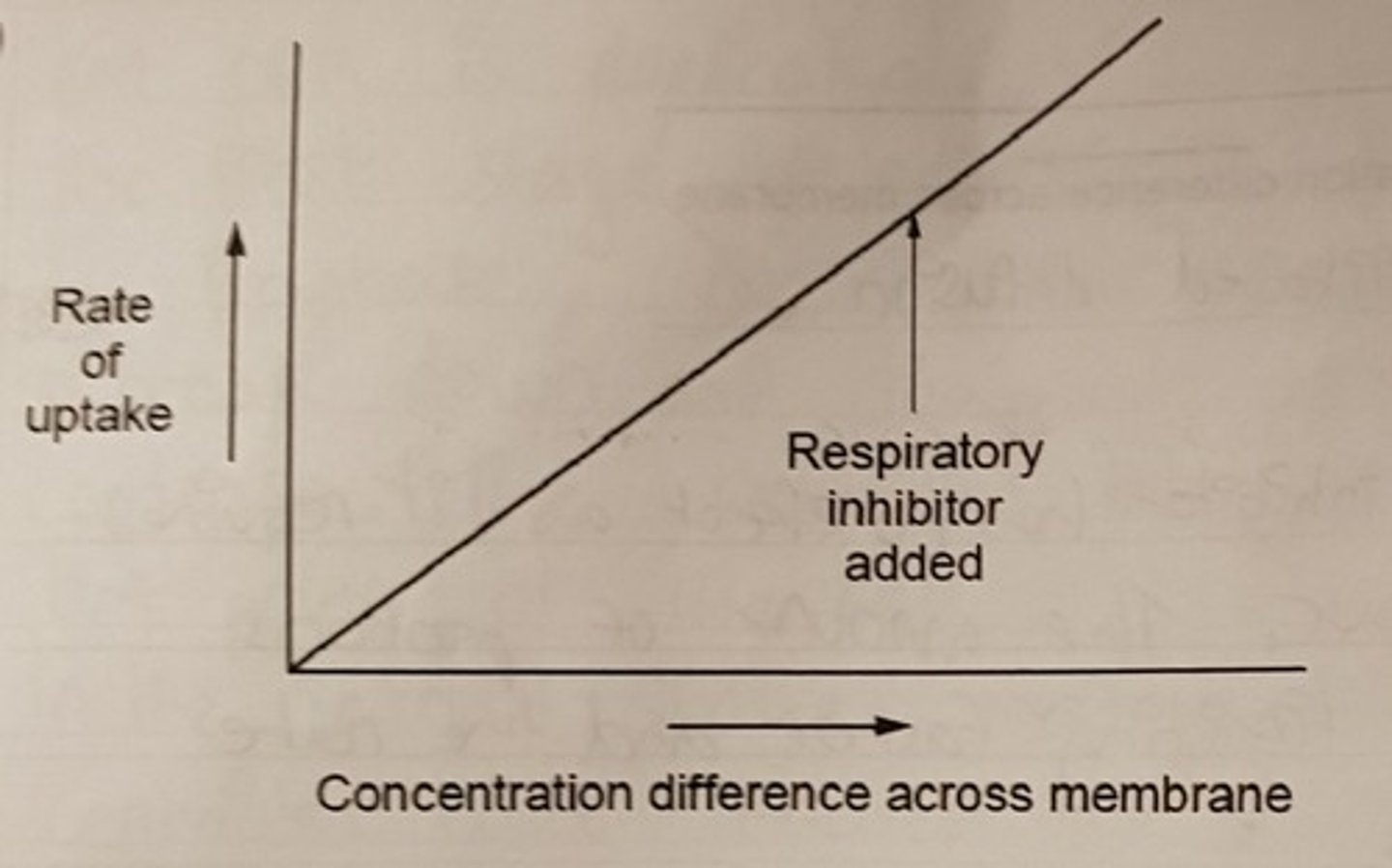
Draw a graph to show the rate of uptake against the concentration difference across a membrane, and the effect of the addition of a respiratory inhibitor for simple diffusion
Explain why the graph is this way
As the concentration increases, the rate increases. The addition of a respiratory inhibitor has no effect as simple diffusion is not dependant on ATP
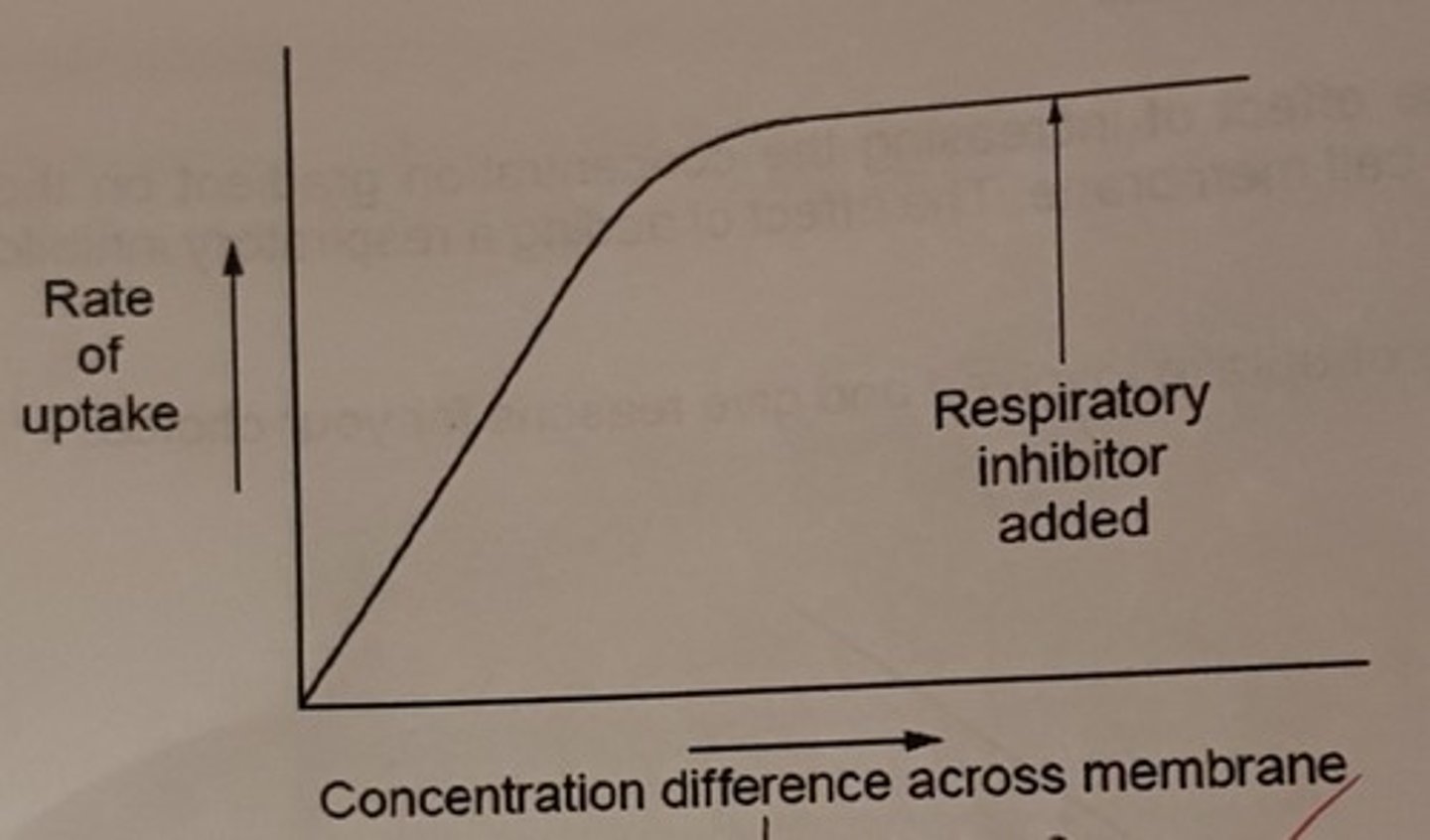
Draw a graph to show the rate of uptake against the concentration difference across a membrane, and the effect of the addition of a respiratory inhibitor for facilitated diffusion
Explain why the graph is this way
At low concentrations, as the concentration increases so does the rate. At high concentrations, the rate of uptake plateaus due to the limiting factor of transport protein availability coming into play. The addition of a respiratory inhibitor has no effect as facilitated diffusion is not dependant on ATP
Draw a graph to show the rate of uptake against the concentration difference across a membrane, and the effect of the addition of a respiratory inhibitor for active transport
Explain why the graph is this way
At low concentrations, as the concentration increases so does the rate. At high concentrations, the rate of uptake plateaus due to the limiting factor of carrier protein availability coming into play. The addition of a respiratory inhibitor causes the rate to plummet as active transport requires ATP in order to happen

Suggest two reasons why transport across the membrane is vital to the cell
- To maintain water potential
- To obtain nutrients
- To remove waste substances
State with an explanation how the solubility in lipid affects the rate of diffusion through a membrane
Lipid soluble substances can easily diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer. As the lipid solubility increases, the rate at which the substances diffuse increases
State with an explanation how the molecular size affects the rate of diffusion through a membrane
The larger a molecule is, the smaller the rate of diffusion. This is because larger molecules will have a greater difficulty passing through the plasma membrane