unit 1 ap psych
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Cognition
study of internal mental processes—all of the workings inside your brain, eg: perception, thinking, memory, attention, language
Executive functions (+ examples)
cognitive skills that are needed for self-control and managing behaviors, eg: self-control, working memory → to control emotions, maintain goals, follow directions
Framing
presentation of an issue
Anchoring bias
compare everything to the first piece of information you received
Gambler's fallacy
If event occurred more in the past, it is less likely to happen in the future (ie: land on heads twice = will land on tails)
Hindsight bias
in hindsight
cognitive bias
systematic error in thinking
negativity bias
dont like negative things (eg: 10% change of death)
loss aversion
fear loss more than gain
sunk cost fallacy
should continue investing into situation --> making it difficult to walk away
functional fixedness
see smth as one funtion (ie: box of pins)
what are three components of memory
encoding, storage, retrieval
why is our brains unlike a compuer infomration processing model
parallel processing
three types of retrival
a) recall (retrieve info not currently in ur conscious awareness b) recognition (heard of before) c) relearning (learning smth quickly again
how is working memory model diff from multistore memory model
newer understanding of STM & focus on active processing of incoming sensory info & info retrieved from LTM
sensory memory
immedient, brief recording
what are the three types of sensory memory
iconic, echoic, haptic
how many things can u hold in short term memory & for how long
7+-2, hold for 25 secs
what is explicit memory & two types
a) conscious, effortful recall includes 1) facts & general knowledge (semantic memory) 2) personally experienced events (episodic memory) eg: what u ate yesterday
Divergent thinking
Expand number of solutions available
Convergent thinking
Ability to determine best possible solution
Metacognition
awareness of thought processes & thinking patterns
Dunning-Kruger effect
cognitive bias - overestimate abilities
Heuristics
Simpler thinking strategies that you individually group tgt - oftentimes limiting your options in the process (Mental shortcutes, subject to bias)
Algorithms
Step by step produces that offer a solution
Assimilation
Assimilate new experience by interpreting them i terms of current understandings or schemas eg: learning math
Schemas
Concepts or mental molds into which individuals pour your experiences ie: the concept of love or dog
Representativeness heuristic (+example)
compare informtion of existing mental prototypes (linda is a bank teller/ linda is a bank teller and a feminist —> linda being a bank teller is more likely)
Availability heuristic
info that comes to ur mind first perceived as more impt (shark attack vs vending machine)
Belief perseverance
maintaining a belief despite new information that firmly contradicts it
Working memory
Holding temporary amount of information
Working memory model
Has a central executive, brain can process many things at once
what are the three components of working memory model
phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, central executive
what does phonoloigcal loop control & what does it compose of
1) hearing + speech (including voice in your head) 2) compose of phonological storage
multi-store memory model & its components
three unitary (separate) memory stores, and that information is transferred between these stores in a linear sequence (enviornmental input -> sensory memory -> STM -> LTM)
information processing model & what is it analogized to & why is it problematic
a) computer b) encoding -> storage -> retrival c) parallel processing
how do we create memories
1 stage: encoding (converted to form that can store in brain, more likely to encode details of what they pay attension to) 2 stage: retention (storage) - memory is preserved, sometimes incomplete or fades
permastore
LTM that developes after extensive learning or experience eg: foreign languages yrs ago/name of classmates (considered a semantic memory)
semantic
facts/general knowledge
episodic
personally experienced events eg: specific events (first day of school), personal facts (model of your first car), flashbulb memories (detailed snapshots of particularly personal/impt moments
what are explicit memories also known as
declarative
two types of memory processing
automatic & effortful
what are implicit memories also known as
nondeclaritive (w/o conscious recall, not things you need to say outloud)
autobiographical memory
type of episodic memory --> impt memory
how is autobiographical memory diff from flashbulb memory
flashbulb - refers to autobiographical memories that involve the CIRCUMSTANCES you learned of the event, highly detiled and exceptionally vivid snapshots, linked to emotional moements
four types of implicit memory
prospective (ability to rmb to do tasks in the future), space/time, procedural (motor/cognative skills), classical conditioning (reaction to docs' office)
two types of prospective memory
event based, time based
peak-end rule
people rmb emotionally significant events
recency bias
people rmb end of events
duration neglect
duration of smth doesnt matter, only intense moments
procedural memory
riding a bike/tying shoes etc.
prospective memory
rmbing dr. appt, paying bills - ability to rmb smth that is going to happen in the future
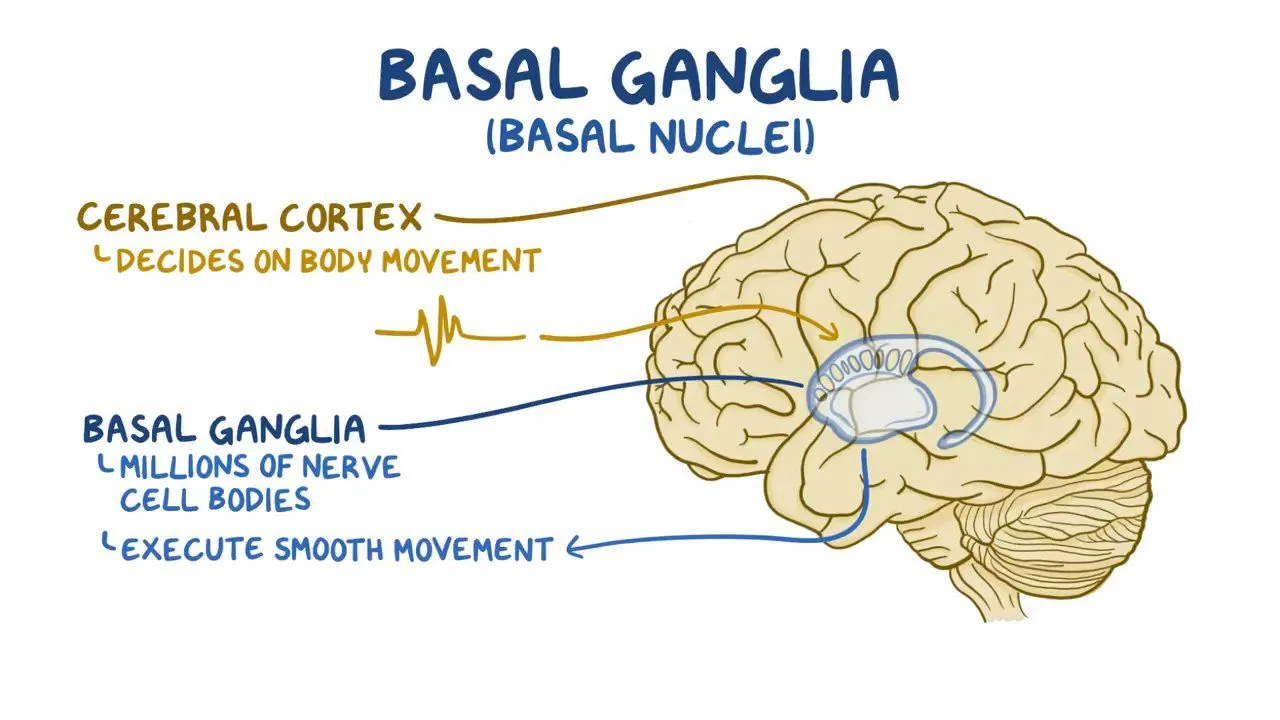
Basal ganglia
control conscious and movies, reeive signals from cortex
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
synaptic connections between neurons become stronger w frequent activation
cerebellum
rear of brainstem, process sensory info, balance, nonverbal learning, memory
frontal lobe
voluntary movement, expressive language, memory storage, thinking/emotions etc.
hippocampus
in charge of memory and learning (short & long term)
retrieval cue
stimulus that initiates remembering (eg: image, text, scent)
priming
one stimulus to activate memory for future encouters
Context-dependent memory
Things that are learning in class are better retrieved in places you learned them in
State-dependent memory
Ie: study when sleep = better able to retrieve when sleepy
Ie: do new thing when you drink alcohol
Mood-congruent memory
Depends on mood
Serial position effect
Rmb the first & last thing you learn
Recency effect
Last thing you see holds heavier weight (ie: end of show being bad ruins your perception of the entire show)
Primacy effect
Rmb first few info that you receive Ie: rmb first few serials of a number than later ones
Chunking
Grouping, ie: rmb phone # in 3 chunks
Mnemonics
Ways to memorize things
method of loci
mind palace method